Pseudotuberculosis is also called Far Eastern scarlet fever and yersiniosis. These names, which are so different from each other, have explanations. Observing something unusual in the child’s behavior and well-being, paying attention to strange symptoms, adults take the kids to the doctor. Parents are often scared almost to the point of fainting when they hear the diagnosis of “pseudotuberculosis” from the doctor, because they associate it with the well-known infection caused by Koch’s bacillus.
In fact, the disease has nothing to do with tuberculosis: morphological changes reminiscent of tuberculosis were simply discovered in the organs, and this is where the name comes from. We will talk about the treatment of this pathology in this article.
Features of the pathology
The disease is also called pasteurellosis, Far Eastern scarlet-like fever, yersiniosis, and acute mesadenitis. The carriers are mainly rodents. Their excrement contaminates food in storage areas. The bacterium is found in soil, air, water, rhizomes, dairy products, livestock feed, and vegetables.
General information about pseudotuberculosis in children
origin of name
The concept of “pseudotuberculosis” was introduced by the German physician Ebert in 1885. He isolated the pathogen from various organs of rabbits. This disease began to be registered only in the middle of the 20th century, and before that it was believed that it was an animal pathology. Due to the similarity of manifestations with scarlet fever, the disease was initially called “Far Eastern scarlet-like fever.”
It is interesting to note that Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (the causative agent of pseudotuberculosis) belongs to the same genus Yersinia, along with the causative agents of plague and intestinal yersiniosis.
Frequency of occurrence
Pseudotuberculosis is widespread throughout the world. Until the middle of the last century, this diagnosis was made only through pathological examination. Outbreaks of this disease are rare, mainly isolated isolated cases of pseudotuberculosis are observed.
The disease is registered throughout the year, but the risk of its development and spread is slightly higher when the temperature reaches +2-+4 degrees, which is due to the basic properties of Yersinia.
The most vulnerable age for this disease is 3-6 years. In younger children, pseudotuberculosis is practically not detected, which is due to the characteristics of their diet.
Characteristics of the pathogen
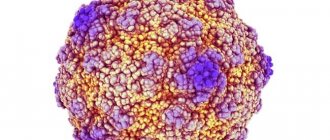
The causative agent of pseudotuberculosis is Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. It is a gram-negative bacterium that can adapt to various conditions. This is a very cunning microorganism. It is able to live in a warm-blooded host, in the external environment and actively reproduce at low temperatures.
Yersinia thrives on vegetables in the refrigerator or warehouse and even then actively reproduces. It grows well on both liquid and solid nutrient media. At the same time, the optimally comfortable temperature for this is room temperature, but at a temperature of +2-+4 degrees, the growth ability is preserved.
That is, Yersinia can live and reproduce both at room temperature and in the refrigerator. Moreover, low temperature can even enhance the activity of some of its enzymes.
Yersinia can withstand freezing, and dies in hot water only after 40 minutes-1 hour. She is only afraid of the effects of ultraviolet rays and chlorine-containing disinfectant solutions.
Thus, Yersinia is insidious, unpretentious and capable of living and reproducing in the external environment for a long time without a host.
Factors predisposing to the development of the disease
- The source of pseudotuberculosis in nature is wild and domestic animals. The carriers most often are rodents (mice, rats, voles), which live in vegetable stores, warehouses, and basements.
- Infection can also occur from domestic animals - rabbits, cats, guinea pigs, dogs.
- Infection and development of the disease is possible through direct contact with animals, during cutting of meat or its insufficient heat treatment.
- Unpasteurized milk can also be a source.
- A significant role in the occurrence of pseudotuberculosis is played by the consumption of vegetables and fruits contaminated with Yersinia in the soil or during storage.
- We should not forget that environmental factors can also be sources - water, soil, in which Yersinia not only live, but also actively reproduce.
Bacterial persistence
The optimal temperature for a stick is between twenty-two and twenty-eight degrees Celsius. The microorganism remains infectious at temperatures from one to four degrees, which prevail in our refrigeration units. The pathogen remains viable in the aquatic environment for up to eight months.
In an oil environment and bakery products, it retains its properties for a period of five months. In sugar crystals, the pathogen dies after twenty-one days, in dairy products - after 30 days. Enterobacteriaceae survive the longest, up to twelve months, in the soil layer.
Exposure to high temperature, ultraviolet radiation, and disinfectants: chlorinated ammonia, mercury chloride, water, and alcohol is destructive to the microbe.
Disease statistics
Infants do not become infected with this infection until they are six months old. Further, up to a year, the percentage of cases is still small. Children under adolescence are most often affected.
False tuberculosis is all-season, but worsens, as a rule, with the start of eating raw vegetables. Among thousands of children, up to five percent become infected with pseudotuberculosis. Every year, ten thousand Russians are diagnosed with this condition. A high level of economic development does not protect against periodic epidemics or local cases of disease.
Development mechanism
The pathogen penetrates the intestinal epithelium. The infection spreads to the regional lymph nodes, causing them to become inflamed. Bacteria and their poisons penetrate the bloodstream. Signs of pseudotuberculosis begin to appear. Next, the macrophage system is affected, pathogens accumulate in the tissues of the spleen and liver.
Organs become enlarged and their functioning is disrupted. Recovery occurs as a result of a cellular immune response. The allergic component plays a role in the development of infection. In patients who have recovered from the disease, the development of immunoglobulins against the pathogen is observed. If there is insufficient antigenic activation, this may occur only after repeated episodes, but relapses are rare.
Typical varieties
With abdominal pseudotuberculosis, the right lower abdomen constantly or periodically hurts, gives rise to fever, and the large and small intestines become inflamed. Can be confused with acute inflammation of the appendix.
Manifestations of arthralgic infection, which accounts for more than half of all infections, include inflammatory processes in the joints with hyperemia, swelling of nearby tissues, their dysfunction, and fever.
In the case of a mononucleosis-like form, the tonsils become inflamed, general intoxication of the body occurs, the liver and spleen become enlarged, and the lymph nodes are affected.
The icteric form of the disease is very common among children. Young patients experience pain under the ribs on the right, urine becomes dark and stool loses color, the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow, and the liver becomes enlarged. Tests reveal an excess of bile pigment, and enzyme hyperactivity is observed.
Coagulation may be disrupted and protein levels may drop. If inflammation is also observed in the pancreas, painful sensations in the abdomen from above will give lumbago to the dorsal region. Diarrhea and bouts of vomiting are added.
The scarlet fever-like variety of pathology is primarily diagnosed by rashes on the epidermis, similar to those that occur during scarlet fever.
The most serious disorders are present in septic pseudotuberculosis. But it is not typical for children. The patient's condition is aggravated by fever, intoxication, and various systemic dysfunctions.
There is irregular heartbeat, hypotension, and inflammation of the myocardium. Infringement of the intercostal nerve, spinal nerve roots, and cephalalgia are recorded. Sleep disappears, vomiting attacks occur. The extreme severity of the condition is expressed in the focus of inflammation in the brain and its membranes.
The combined form is characterized by a simultaneous combination of various disorders: dyspepsia, rashes, arthritis. They may be accompanied by persistent or intermittent fever.
Atypical presentation
With erased yersiniosis, the symptoms are superficial and unstable.
The latent subtype of pathology does not reveal itself clinically. Only immunological responses can be observed. The disease is detected by studying tissue samples from patients taken from infectious foci.
To the list of forms, some add acute inflammation of the appendix, mesenteric lymph nodes, Crohn's disease, secondary focal manifestations (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large and small intestines, erythema nodosa, triple inflammation of the joints, urethra, outer eye membrane). The most serious violations affect secondary foci of infection. It is impossible to become infected from a sick person.
Classification
Pseudotuberculosis can occur in various clinical forms with the development of isolated or mixed syndromes. Based on this principle, the following are distinguished:
Some authors supplement the classification of pseudotuberculosis with forms of acute appendicitis, mesenteric lymphadenitis, terminal ileitis and a secondary focal form (enterocolitis, erythema nodosum and Reiter's syndrome). In typical cases, pseudotuberculosis occurs with a partial or complete combination of symptoms of various clinical forms. The severity of pseudotuberculosis (mild, moderate and severe) is assessed by the severity of intoxication and changes in internal organs.
Symptoms of pseudotuberculosis
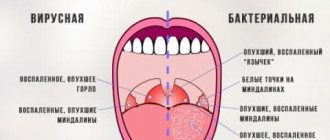
The latent phase of the disease varies between three days and three weeks, but is usually seven days. The first symptoms of pseudotuberculosis in children can easily be mistaken for the onset of an acute respiratory infection: red throat, snot, coughing attacks, hyperthermia up to forty degrees, a painful feeling of cold.
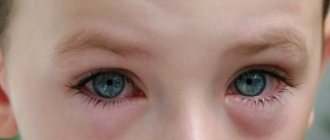
The whites of the eyes turn red, the vascular pattern of the sclera intensifies. Against the backdrop of a weakened body, the nose and lips may be covered with herpetic blisters. There is a loss of strength, lethargy, a headache, and you don’t feel like eating.
Ailments appear quickly. Hyperthermia is present for up to seven days. Occasionally there may be a sore throat and pain when swallowing.
Dermatological reactions
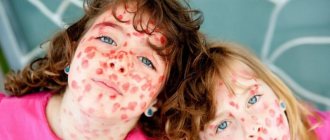
The epidermis on the face, neck, hands and feet turns red. After three to four days, the skin is covered with symmetrical rashes of different types: small dots, nodules, spots, bruises. They may be slightly itchy.
Localization of the rash: the bends of the arms, legs, groin area, sides of the body. On folded surfaces, near large articular joints, the rash is more intense. The epidermis can be of normal color, red, or yellowish. This symptom persists for up to a week.
Soon after this, the skin begins to dry out and peel off: finely on the face, body, in large pieces - on the base of the feet, palms. Spots may remain on the skin.
Intestinal disorders
A dense whitish coating appears on the tongue. It disappears after five days, the mucous membrane becomes crimson, the papillae become clearly defined. Painful sensations of various types, from dull to cutting, are localized in the abdomen on the lower right, in the epigastrium, around the navel, and on the right under the ribs.
I suffer from nausea, flatulence, vomiting, and diarrhea. There may be mucus or blood in the stool. Inflammation can affect the lymph nodes around the intestines or the appendix. There may be a need for surgical intervention.
Joint problems
The active development of pathology in half of the cases is accompanied by swelling and joint pain. The areas between the phalanges, knees, ankles, and wrist areas often suffer.
Cardiac and vascular failures
A relative disturbance of sinus rhythm is recorded, sometimes the heart begins to ache, beats too quickly, and noises are heard during ventricular contractions. Heart sounds are muffled, there are manifestations of hypotension, disturbances in the contraction of the middle muscular layer of the heart, conduction, etc.
Forecast
If the disease passes without complications, after a week the temperature returns to normal, the skin clears, and the functioning of internal systems is restored. On the fifteenth day, the disease usually subsides. In severe cases, recovery can take up to one and a half months, and in case of repeated infection and exacerbations - for three months.
Diagnostic tools
If there is a possibility that the child has pseudotuberculosis, an infectious disease specialist will take care of him. You may need examinations by specialized specialists in the field of dermatology, rheumatology, otolaryngology, gastroenterology, hepatology, cardiology, neurology, and surgery.
Treatment of pseudotuberculosis begins with collecting anamnesis and complaints, observing symptoms, and conducting tests. The presence of rashes, like scarlet fever, a prolonged feverish state, and waves of ailments in the gastrointestinal tract and joints help to suspect this particular pathology. The time of illness and the patient’s menu are taken into account.
Bacteriological and serological tests of blood, feces, sputum, urine, and mucosal samples from the surface of the pharynx can completely clarify the situation. Serological methods include reactions of agglutination, precipitation, complement fixation, passive hemagglutination, inhibition of passive hemagglutination, enzyme immunoassay, immunofluorescence assay, emergency polymerase chain reaction. Sometimes exploratory surgery is required.
It is important to exclude during diagnosis:
- scarlet fever;
- measles;
- systemic inflammation of the cardiac membranes;
- enteroviruses;
- blood poisoning;
- viral hepatitis;
- typhus-like pathologies.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of tuberculosis during the incubation period allows it to be cured within a few months. Timely and effective therapy determines the mild course of the disease and guarantees its favorable outcome.
Infants who do not go to kindergarten or school, where regular medical examinations are carried out, should have a blood test at least once a year (we recommend reading: is it possible to attend kindergarten without a Mantoux test?). Children whose pediatricians suspect tuberculosis are referred for consultation to a TB specialist. This doctor prescribes such preventive and diagnostic measures as:
- general and enzyme-linked immunosorbent blood tests, which detect inflammation in asymptomatic cases of the disease,
- Mantoux test,
- X-ray of the lungs in children under 15 years of age or fluorography for patients over 15 years of age, which is performed to visualize local changes in the photo,
- computed or magnetic resonance imaging,
- ELISA and PCR studies that determine the causative agent of the pathogenic inflammatory process.
Mantoux test
The Mantoux test is an injection of tuberculin under the skin. Tuberculin consists of pathogens that should cause an allergic reaction if there is an infection in the child’s body (we recommend reading: assessment of the Mantoux reaction in a child). Three days after the injection, the doctor visually determines its result:
- negative - the injection site has not changed in size (acceptable norm is an increase of 1 mm), redness and induration are not detected (more details in the article: negative Mantoux reaction in a child - what does this mean?),
- controversial - at the injection site there is an increase of 2-3 mm, slight redness or thickening,
- positive - the sample has grown to 5-7 mm.
Blood analysis
Asymptomatic tuberculosis requires confirmation of the diagnosis, so first the pediatrician prescribes a general blood test, which reveals inflammation. If the result is positive, doctors refer the patient for an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to determine the presence or absence of tuberculosis antibodies. The patient receives the results of both tests on the day they are performed. This method cannot be considered particularly informative, unlike X-rays and PCR (we recommend reading: how is PCR for tuberculosis done instead of Mantoux for children?).
PCR diagnostics
The polymerase chain reaction is guaranteed to give an accurate result, which makes it possible to identify the disease at any stage of development, including during the incubation period.
The results of the study are given to the patient in a few days. This diagnostic method identifies the causative agent of the disease in the baby’s blood, urine or sputum, allowing it to be destroyed as soon as possible through drug therapy.
Therapy
Treatment of pseudotuberculosis in children is carried out in a hospital setting. Until the condition improves and stabilizes, it is better to spend time in bed. The menu of a recovering baby should be balanced; the presence of intestinal disorders can make amendments to it.
The pathogenic bacillus is treated with antimicrobial agents for ten days. The course can be supplemented with third-generation cephalosporin antimicrobial agents. Sometimes a combination of two drugs may be needed.
Detoxification is carried out by injection into a vein of a ten percent colloidal solution of dextran, a protein blood fraction, and a ten percent dextrose solution. Therapy is supplemented with intestinal sorbents.
Joint problems are relieved with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
With nodular rash and multiple joint inflammations, it becomes necessary to take steroid hormones from the adrenal cortex for a week. Antiallergic measures involve the use of histamine synthesis blockers.
Immunity is supported and restored with the help of combined products containing highly active enzymes of plant and animal etiology. They have an immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory effect, reduce swelling, dissolve intravascular blood clots, and reduce pain.
In the treatment of pseudotuberculosis, drugs that stimulate the formation of antibodies and multivitamins are also used. They try to eliminate the symptoms of life-threatening syndromes.
The fact that the infection has subsided is indicated by an improvement in the general condition, the absence of traces of the rod and its toxins in bacteriological analyzes performed twice.
Treatment
The main danger of pseudotuberculosis in childhood lies in the possibility of rapid dehydration. With high fever and repeated vomiting and diarrhea, a state of dehydration can develop within a few hours. This is deadly for a child, especially a toddler.
If this is not possible, you should immediately call an ambulance; doctors will be able to provide the child with an intravenous infusion of saline and glucose to replenish the fluid deficiency.
In the stage of acute intoxication, the child should be given oral rehydration agents - Smecta, Regidron, Humana Electrolyte and others. From the first symptoms associated with fever, you need strict bed rest with monitoring of body temperature and taking antipyretics. Just in case, parents should be prepared to provide emergency assistance for febrile seizures, which can also develop in the acute period.
You cannot force feed a child. But if he himself asks for food, then you should give only dietary food, porridge, vegetable soup with croutons, jelly. Spicy and salty foods, smoked meats and marinades, as well as dairy products should be avoided.
Mild forms of pseudotuberculosis do not require the use of antibiotics. Recovery can be achieved by providing the child with all possible home care in the form of plenty of drink and pureed food; the immune system will do the rest itself when it has formed a sufficient number of the necessary antibodies to the invading enterobacteria.
They are most easily perceived by the child's body. In case of ineffectiveness or laboratory resistance of the bacteria to penicillin, the doctor recommends drugs of the tetracycline group of antimicrobial agents.
Enterobacteriaceae are very sensitive to aminoglycoside antibiotics, for example, Gentamicin and Neomycin. But it is better for parents to refuse such an appointment, if it suddenly happens. The fact is that these antibiotics are ototoxic for children; their use can cause the development of partial hearing loss or complete permanent deafness. After completing the course of treatment, hearing does not return.
The course of taking recommended antibiotics for pseudotuberculosis is from 7 to 14 days, depending on the type of disease and the characteristics of its course.
For joint pain, doctors often recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Ibuprofen. Anti-inflammatory ointments, such as Indomethacin, can be prescribed locally. Symptomatic treatment may include nasal drops with a vasoconstrictor effect for a runny nose, gargles and antiseptics for the throat for a sore throat, as well as antipyretics - Paracetamol and Ibuprofen. “Aspirin” and all products that contain acetylsalicylic acid are prohibited for children, as they can cause dangerous Reye’s syndrome.
To relieve gastrointestinal symptoms, enterosorbents are prescribed, for example, Smecta or Enterosgel. At the final stage of the disease, multivitamins may be prescribed. To relieve joint pain and pain in the lymph nodes, dry heat is indicated - a scarf or warm shawl. Compresses - oil or alcohol - are strictly prohibited.
Consequences
In most cases, recovery occurs without complications. But still, a person who has had pseudotuberculosis can pick up another infection. Or a silent chronic pathology may awaken in him.
The disease may not respond to treatment for several months. Half of sick children go through a stage of exacerbation of symptoms after the normalization of the condition. They may be overtaken by re-infection after healing between the tenth and twentieth days with a normal temperature. Skin symptoms do not return.
Typical complications of yersiniosis are:
- inflammation of the appendix;
- penetrating damage to the intestinal wall;
- intestinal blockage;
- glomerular nephritis, purulent pyelonephritis;
- myocardial inflammation;
- inflammation of the membranes and tissues in the brain;
- inflammation of the gallbladder, etc.
Some of the problems described are life-threatening, so being attentive and seeing a doctor at the slightest suspicion of an insidious disease can preserve health and save the life of your children.
Prevention
There is no vaccination against pseudotuberculosis, so prevention comes down to:
- rodent control;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- sanitary control over water supply.
Note! To avoid infection when eating fresh vegetables and fruits, the fruits must first be doused with boiling water.
Pseudotuberculosis is a dangerous disease that is sometimes difficult to diagnose due to unexpressed symptoms or symptoms similar to those of other diseases. At the same time, the disease can cause serious complications, including death. Therefore, if pseudotuberculosis is suspected, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment immediately.
Sovinskaya Elena, doctor, medical columnist
10, total, today
( 171 votes, average: 4.61 out of 5)
Escherichia coli: what it is and methods of treating the disease
Rotavirus vaccination: when to do it and how effective it is
Related Posts
Preventive action
In the event of an outbreak of pseudotuberculosis epidemic, the same measures are applied as if we were talking about any intestinal infections. There are no special preventive methods, such as vaccination.
It is important to control the spread of the main carriers of the disease - rodents. You should adhere to a competent and safe method of storing vegetables, fruits, and cereals. In public eating places, it is necessary to strictly control the sanitary conditions of food preparation, in particular, raw salads. In villages, water and soil analysis is mandatory.
By combining preventative measures and recording changes in well-being, you will reduce the likelihood of an unpleasant infection in your family to a minimum.
Causes
As a result of the studies, it was found that animals are carriers of the disease. We are talking about rodents, small and large livestock, poultry, rabbits, horses, cats, dogs. In addition, pigs can be sources of infection, while a sick person is not dangerous to others.
Important! Pseudotuberculosis is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. In other words, infection occurs through contact with food that has been in the soil, which has become a habitat for pathogens.
You can get pseudotuberculosis by consuming:
- unwashed vegetables, fruits;
- dairy, meat and fish products that have not undergone the necessary heat treatment;
- confectionery and bread if they were stored in dirty containers;
- juices, compotes, water;
- dried fruits.
People are susceptible to pseudotuberculosis everywhere. Moreover, it can occur at any time of the year, although outbreaks of the disease are most often recorded between February and March. At risk are children and adolescents under the age of 17 who live in cities and abuse food from street cafes and fast foods. From time to time, the disease is diagnosed in people who eat in enterprise canteens, children in kindergartens, schools, and pioneer camps.