At a young age, children experience many diseases, since the immune system is at the stage of formation. The body simply does not have time to fight infectious diseases, so sometimes complications occur. For example, from 3-7 years of age a child is susceptible to a disease such as adenoids. If the disease is not treated in time, the lymphoid tissue will increase in size, which in turn will lead to hearing loss, dizziness and difficulty breathing through the nose.
But what are adenoids? First of all, this is the nasopharyngeal tonsil, which is responsible for the immune system. When inflamed, the organs increase in size and block the nasal passages. The disease itself develops very slowly, but as the adenoids enlarge, changes occur in the body. The child begins to snore, sniffle, complain of headaches, discomfort in the nasopharynx, etc. Enlarged adenoids in a child are treated in several ways - conservative therapy or surgery (adenotomy). If the disease is grade 1 or 2, then it can be cured with medications and physical therapy.
Symptoms and causes of the disease
With a disease such as adenoids, symptoms may be as follows:
- the child has a stuffy nose all the time or periodically, but there is no discharge;
- at night or during the day the child breathes through his mouth;
- the baby snores, while he is holding his breath;
- the child's voice becomes nasal;
- The baby hears worse.
If your child has these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately. Often it's all about recurring acute respiratory viral infections. The adenoids react to an attack of the virus on the body by enlarging. The cells that multiply in them kill viruses. When the baby recovers, the adenoids return to their normal state. But if a child gets sick very often, then they simply do not have time to return to normal. That is why treatment of ARVI must be kept under strict control, for fear of relapses.
In domestic medicine, there are 3 degrees of adenoids:
- 1st degree - the tonsil covers 33 percent of the opening into the nasopharynx;
- 2nd degree - the tonsil covers 66 percent of the hole;
- Stage 3 – 99 percent of the hole is blocked.
If you do not want your baby to have to urgently remove the adenoids, keep the treatment of ARVI under control and pay maximum attention to hardening. Let us consider separately the degrees of adenoids in a child, treatment at different stages.
Symptoms (signs) of adenoiditis in children
The acute form of adenoiditis can begin with swelling or expansion of the lymphatic tissue, as well as a high temperature of up to 39. The tumor restricts or blocks the airways. This leads to difficulty breathing through the nose. As a rule, the acute course lasts about 5 days.
The main symptoms of adenoiditis in children:
- It is difficult to pronounce some letters of the alphabet, such as "M";
- nasal sound and feeling of nasal congestion;
- sore throat when talking;
- breathing through the mouth becomes more comfortable than through the nose;
- the presence of a runny nose with an abundance of thick, green discharge.
The chronic form is most often represented by diseases of the upper respiratory tract: runny nose, sore throat, sinusitis. Because of this, you have to breathe through your mouth, and sleep is accompanied by snoring or sniffling. Along with this, drowsiness, constant fatigue, apathy, poor appetite, and impaired attention appear.
Adenoids of the 1st degree
Most often, grade I adenoids are diagnosed in young children (from one and a half to five years). If parents carefully monitor the child’s development, then this disorder can be identified without much difficulty, and at a stage when treatment can still be conservative.
The first degree of development of adenoids in a child, which can be treated at home, manifests itself during night sleep. If during the day, when a person (most often a child) is in motion and in an upright position, breathing difficulties are practically unnoticeable, then at night the situation changes. Changing the position to horizontal and changing the speed of vital processes lead to difficulty breathing.
The main symptom of first-degree adenoids is difficulty breathing during night rest. Further development of the disease can lead to snoring and constant breathing through the mouth during sleep as well as wakefulness.
The physiological changes that appear during the first stage of adenoids are minor: the pharyngeal tonsil begins to grow and covers up to half of the nasal passages or vomer. These changes can be detected in several ways, of which computed tomography is considered the most informative. Endoscopic rhinoscopy and epipharyngoscopy are also equally popular. For the initial examination, a digital examination of the nasopharynx is used.
First-degree adenoids are a disease that should be treated by a doctor. Treatment of adenoids in a child of the first degree is simply necessary, because otherwise the disease progresses to the second degree. At this stage, conservative treatment methods are no longer effective and surgery is required.
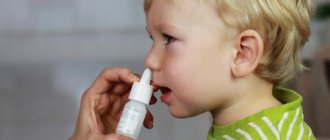
But how to treat adenoids? Treatment of first-degree adenoids is carried out comprehensively, with mandatory identification and treatment of the disease that caused the development of adenoids. The most effective is rinsing the nose with antiseptic drugs, as well as the use of decongestants and anti-inflammatory drugs. If necessary, and to alleviate the patient's condition, mucus suction and ozone therapy are used.
How to treat adenoids at home? Folk remedies, such as rinsing the nose with herbal decoctions, mineral and sea water, should only be used in consultation with a doctor. The fact is that such procedures can be fraught with infection in the middle ear, as well as psychological trauma for young children. After any rinsing, you must refrain from going outside for at least half an hour (in summer) or even for two hours (in winter) to prevent hypothermia of the sinuses and complications.
If first-degree adenoids are detected, treatment should be started immediately. The earlier treatment begins, the less likely there are serious consequences, especially for children - disturbances in the development of the immune, nervous, respiratory systems, and hearing organs.
Conservative treatment tactics
Treatment at home involves the use of medications and folk remedies in the fight against hypertrophied tonsils. Can adenoids be cured? Treatment tactics include:
washing the adenoids, which reduces the severity of the inflammatory reaction, tissue swelling and eliminates infectious microorganisms; inhalations with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs; breathing exercises, which allow you to restore breathing through the nose and ensure complete delivery of oxygen to the tissues; warming up, applications with clay.
Do not forget about proper nutrition, enriched with vitamin products, healthy sleep and strengthening the immune system.
Adenoids of the 2nd degree
We have reviewed the treatment features and symptoms of adenoids in children with the first degree of enlargement. But what is the second one? It is often not necessary to remove grade II adenoids in children. In general, surgery should be performed only in the most difficult situations. Adenotomy is performed not because the child is often sick (in any case, an infection is not something that can be cut off with a knife), but because conservative treatment does not help.
Adenoids of the 2nd degree today are treated without surgery, and very successfully. The nasopharyngeal tonsil is very important because it is the front line barrier to infection.
Symptoms and treatment for adenoids in children will vary depending on the extent. The fight against stage II adenoids begins with the treatment of a runny nose. Often, nasal congestion is not associated with an enlarged tonsil, but with inflammation that occurs in the area of the nasal passages due to swelling of the mucous membrane. The fact is that grade 2 adenoids in a child 3 years of age and older react violently to inflammatory processes, and when they subside, they decrease in size.
The child's nose should be washed twice a day with different means. Good remedies for treating adenoids in children without surgery are a solution of sea salt, tincture of eucalyptus and calendula, a decoction of oak bark, chamomile, sage and green tea. You should not get carried away with vasoconstrictor drops - they are unsafe for children. An overdose causes lethargy and drowsiness in children. There is a possibility of serious poisoning with damage to the nervous system. Therefore, it is so important to know how to treat adenoids in children in the nose correctly. It is necessary to pay a lot of attention to the general strengthening of the body.
If the doctor insists on surgery, you should agree with him. Don't delay surgery.
Conservative treatment tactics
Treatment at home involves the use of medications and folk remedies in the fight against hypertrophied tonsils.
Can adenoids be cured? Treatment tactics include: washing the adenoids, which reduces the severity of the inflammatory reaction, tissue swelling and eliminates infectious microorganisms; inhalations with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs; breathing exercises, which allow you to restore breathing through the nose and ensure complete delivery of oxygen to the tissues; warming up, applications with clay.
Do not forget about proper nutrition, enriched with vitamin products, healthy sleep and strengthening the immune system.
Adenoids of the 3rd degree
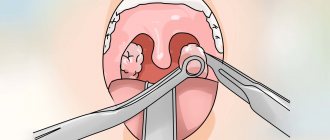
Adenoids are by no means a fatal disease. However, in some situations surgery is truly necessary. Adenoids of the 3rd degree are when virtually the entire nasopharynx is closed by the tonsil, and the child cannot breathe through the nose. In this case, it is better not to rely on folk remedies. Adenotomy (removal of the adenoids) falls into the category of simple and short operations. It lasts 15-20 minutes. The actual cutting process takes 2-3 minutes. A special ring-shaped knife is inserted into the nasopharynx. The adenoid tissue captured by it is cut off in one movement. After the operation, the child can easily lead his usual lifestyle after 7 days; in the first couple of days he needs to lie down more. The main thing is not to overheat the baby and not to feed him hot and hard foods, so as not to cause bleeding.
How do we treat grade 3 adenoids in children? At this stage, this is an undoubted pathology. At earlier stages, conservative methods may well help: antibiotics, herbs, homeopathy, cryotherapy, laser therapy.
Speaking about the treatment of grade III adenoids in children, it is worth paying attention to the fact that they, like the appendix, are not simply removed for prevention. The operation is performed not so that the child no longer gets sick, but because nasal breathing is difficult. In case of severe allergic diseases in children, treatment of adenoids with surgery is generally contraindicated.
Is surgery necessary?
The issue of surgery is decided after the child recovers. Not earlier than in a month. Factors such as the degree of adenoids and difficulty in nasal breathing are taken into account. How often does adenoiditis recur in a child?
The second and especially the third degree of proliferation of adenoid vegetations are an indication for surgical intervention.
If you haven’t found the answer to your question or don’t understand something, you can ask your question here
Acute and chronic adenoiditis is the most common disease of the upper respiratory tract, most often developing in children aged 3-8 years. It is during this period that the average child usually goes to kindergarten or school, often goes outside, and as a result, his immune system regularly encounters viruses and bacteria new to the body.
Represented by the adenoids, as well as the palatine, lingual and laryngeal tonsils, the “first line of defense” of the immune system does not always adequately respond to such an attack. The lymphoid tissue that makes up the adenoids cannot cope with neutralizing infections, becomes inflamed and grows. Over time, instead of fighting the infection, inflamed adenoids themselves become its source (in advanced cases, other organs, such as the ears, are affected, and the symptoms of adenoiditis are complemented by otitis media), and the inflamed, enlarged lymphoid tissue prevents full breathing.
The child has difficulty breathing through the nose, snoring during sleep, and a nasal voice. If you do not pay attention to alarming symptoms and do not start treatment of adenoiditis on time, children develop concomitant diseases - vasomotor rhinitis, bronchial asthma, sinusitis, bronchitis.
Cough, dizziness, sleep disturbances and even problems with the gastrointestinal tract in some cases are not independent symptoms, but consequences of untreated adenoiditis in a timely manner. Since with adenoiditis the immune organs of the nasopharynx cease to perform their direct functions, the baby easily catches a cold and is sick for a long time.
A mild form of the disease usually develops as a result of hypothermia, acute respiratory viral infection, seasonal weakening of the immune system and manifests itself in a slight increase (inflammation) of the pharyngeal tonsils: the child can remain active and does not complain of headache, fever and other symptoms characteristic of the inflammatory process. But you shouldn’t ignore the disease: if you do nothing, mild inflammation can become acute.
The symptoms of acute adenoiditis are very typical: breathing is impaired, the temperature rises, sleep becomes interrupted, children begin to complain of headaches and fatigue. The mucous membrane of the nasopharynx swells and secretes secretions that can flow through the nasal passages. A change in the color of the discharge from transparent to greenish-brown is a characteristic symptom of purulent adenoiditis.
In the chronic form of the disease, its symptoms are less pronounced, but consistently appear in the form of seasonal outbreaks (in autumn and winter) with the slightest hypothermia. The cause of the development of a chronic disease can be untreated acute adenoiditis, bronchial asthma, allergies (in particular, hay fever), general weakening of the immune system, vitamin deficiency or poor nutrition. It is important to start treatment on time to prevent complications from developing.
Treatment of adenoiditis, which occurs in an acute form with purulent discharge, in most cases involves taking antibiotics, and is therefore carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
The doctor will select the appropriate drug, taking into account the patient’s age, and describe in detail the antibiotic treatment regimen.
There is no need to be afraid of medications: modern antibiotics have a fairly gentle effect on the body, and with the correct dosage, the risk of side effects is minimal.
In addition to the main drug, the otolaryngologist may prescribe nasal drops, vitamin therapy and local procedures (for example, rinsing the nasopharynx with decoctions of medicinal herbs with pronounced antiseptic properties - St. John's wort, wormwood, chamomile, calendula, yarrow).
To ensure that unpleasant symptoms do not return and the treatment of acute adenoiditis in children is successful, do not get carried away with self-medication: folk remedies are good only as a supplement to a course of antibiotic therapy. Herbal remedies are prescribed especially carefully to children prone to allergic reactions.
Constant runny nose, nasal congestion, difficulty breathing and cough in chronic adenoiditis in children can only be eliminated with the help of complex treatment, including immunomodulation therapy, sanitation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa, and the use of antibacterial drugs. Often, ENT doctors recommend the most radical way to combat adenoiditis - surgery.
It should be understood that it is advisable to take such a step only in extreme cases: for example, an unambiguous indication for surgery is the enlargement of the adenoids to alarming sizes, at which they completely block the nasopharynx, the child stops breathing through the nose and has difficulty hearing.
In all other cases, it is worth switching to the prevention of exacerbations and conservative treatment, which in modern conditions gives good results and, unlike surgery, does not cause mental trauma to the baby.
It is strictly forbidden to remove adenoids:
- patients who have been diagnosed with bronchial asthma or an allergic reaction, since there is a high probability of their health deteriorating after surgery;
- within a month after any preventive vaccinations;
- with anomalies in the development of the soft or hard palate;
- for blood diseases;
- under 2 years of age;
- for acute infectious diseases of the respiratory tract.
Removal of the adenoids weakens the immune system, and often after the operation the child begins to get sick, as parents say, “everything in a row.” If conservative treatment turns out to be effective (completely eliminates or minimizes the manifestations of the disease), concentrate on prevention and wait a little - as a rule, from the age of 10-12 years, the adenoids return to normal and do not bother children at all.
Until then, it is necessary to provide them with protection from hypothermia (but without fanaticism, because moderate hardening is healthier than wrapping them up) and infections, conduct preventive courses of fortification, and monitor their diet and daily routine.
Parents need to know what to do when a child has difficulty breathing due to adenoiditis, and which doctor to contact for help: some simple procedures (nasal drops, taking pills) can be done at home, but sinus rinsing (especially for small children) should be done doctor in a clinic setting.
Did you like the article?
Share with your friends!
Adenoiditis
is an inflammation of the adenoids, lymphatic tissue that helps the body fight infection. Adenoids are located in the pharynx (throat) behind the nose. Along with the tonsils, they are the main protectors of your throat. The lymphatic system plays several roles to help protect you from infection. It contains white blood cells (lymphocytes) to destroy possible infections that threaten human health. Inflamed adenoids cannot perform their functions properly.
Since with age the human body begins to develop other methods of protection against harmful bacteria and viruses, the adenoids play a significant role in maintaining health. This is why adenoiditis most often occurs in children before adolescence.
Drugs for the treatment of adenoids
Classic drugs for the treatment of adenoids, which can be bought in every pharmacy, are the following: “Collargol” 1 - 3%, “Protargol” 1 - 2%, “Sofradex”, “Pinosol”, “Rinosept”, “Albucid”, as well as “ Dioxidin", diluted in half with saline solution.
If a 2 year old child has adenoids, treatment can be carried out using solutions. They are suitable for children and older. Wash solutions that can help with enlarged adenoids are a decoction of oak bark, St. John's wort, eucalyptus, horsetail infusion, St. John's wort infusion, sea salt, chamomile decoction, rotokan, elekasol, potassium permanganate, furatsilin.
Homeopathic medicines for the treatment of adenoids are now quite popular. Some of them are really helpful. They must be used according to the instructions and under the supervision of a homeopathic physician, especially if adenoids are being treated in a child 3 years of age or younger. Here are some of them: Lymphomyosot drops, Echinaceacompositum ampoules, Traumeel tablets.
In parallel, general treatment can be carried out. Sometimes doctors recommend taking an infusion of blackcurrant leaves internally. Antihistamines are effective: Pipolfen, Diazolin, Fenkarol, Suprastin. How to treat adenoids in a child 7 years old and younger? The doctor often prescribes taking multivitamins and microelements. Naturally, the more the baby eats fresh fruits and vegetables, the better. Antibiotics are prescribed in acute cases, which, by the way, usually develop against the background of acute respiratory infections.
Rinsing and inhalation for adenoids
For adenoids, nasal rinsing may be helpful. You can select several options from this list:
- Horsetail infusion.
- A decoction of oak bark, St. John's wort, eucalyptus.
- Sea salt.
- Green tea.
Treatment with celandine is recommended when the adenoids are enlarged by 2-3 times. After instilling celandine infusion, a burning sensation often appears.
Inhalations for adenoids are sometimes a good additional treatment. The following option is quite effective. Take 15 g of ivy budra per 200 ml of water. The herb is poured with cold water, the mixture is simmered over low heat for half an hour, and then filtered. You need to breathe over this decoction, gradually adding boiling water. Steam inhalations with eucalyptus, soda, calendula and Kalanchoe juice are effective. You can use them all separately or together, using half a teaspoon of each product per MentoClar-type inhaler. You need to breathe for 5-8 minutes (no more than 1-2 times a day). You can try inhalations with ready-made drugs, such as Bronchicum, Mentoclar, Cedovix. Be sure to read the included instructions.
Diagnostics
For adenoids, in addition to collecting anamnesis, the following examination methods are carried out:
- pharyngoscopy - examination of the pharyngeal tonsil by a doctor using a special mirror, with lifting of the soft palate with a medical spatula,
- anterior rhinoscopy – examination of the nasal passages after instillation of vasoconstrictors,
- posterior rhinoscopy - examination of the nasal passages using a special mirror through the oropharynx,
- X-ray of the nasopharynx – a lateral image taken with the patient’s mouth open,
- endoscopy of the nasopharynx - a study carried out using a thin tube with a flashlight and a camera (endoscope), the image is displayed on the monitor (babies are given anesthesia).
If the adenoids are inflamed, is treatment possible without surgery?
The question of conservative treatment or removal of adenoids in children should only be decided by a doctor. For this disease, treatment without surgery is possible. If the disease is not advanced, conservative methods will give a good effect. The most commonly used are homeopathic drugs (“Lymphomyosot”, “Job-baby”), antiseptics and astringents (liquid chlorophyll, colloidal silver, collargol), as well as physical procedures (cryo and laser). Of course, the adenoids will not return to normal size, but if you manage to keep adenoid hypertrophy to grade 2, then there will be no big problems. By puberty, adenoid tissue is likely to atrophy.
If adenoids are found in a child, treatment without surgery necessarily involves hardening. Swimming, walking, and sea air give a good effect. Hardening begins from the nasopharynx. It is necessary to instill hydrocarbonate mineral water without gas into the nasal passage. You should also gargle with it. This procedure must be done in the morning and in the evenings. Every 2 days the water temperature drops by 2 degrees. Finally, it should reach 4-5 degrees. Then you can start contrasting dousing of the feet: first warm water, then cold. After a month, you can safely move on to a contrast shower.
Physiotherapeutic methods:
- Ural Federal District. Can be used endonasally (inside the nose), up to 10 procedures.
- Helium is a neon laser. Also endonasally, up to 10 times.
- Electrophoresis with solutions of potassium iodide, diphenhydramine - endonasally.
- UHF on the nose area - up to 10 procedures.
Grade I adenoids can be treated without surgery.
Prevention
To prevent inflammation of the adenoids, it is necessary to introduce a number of general hygiene measures into the child’s family.
Organize the child's daily routine. Lack of sleep, overwork, lack of walks in the fresh air - all this negatively affects the immune system. Change your child's diet towards a more balanced diet. Eliminate allergenic foods, reduce the amount of carbohydrate foods. Carry out hardening procedures (cool shower, therapeutic exercises, sleep in the fresh air). Develop in your child the habit of hygienic procedures - rinsing the nose, gargling after eating.
The doctor may also prescribe vitamin-mineral complexes, immunomodulators and homeopathic remedies aimed at preventing ARVI.
Chronic inflammation of the adenoids is dangerous because this pathology impairs breathing. Lack of oxygen negatively affects the general condition of the body. In addition, inflamed adenoids serve as a reservoir for viral and bacterial pathogens. In most cases, the problem can be eliminated by conservative treatment.
The treatment won't be easy
If your child has adenoids, the treatment that almost every doctor will suggest is surgery. Meanwhile, this method is fraught with psychological trauma, as well as complications such as fusion of the soft palate with the wall of the pharynx, paralysis of the soft palate, stenosis of the nasal pharynx, scarring of the auditory tubes, and torticollis. In this case, the operation eliminates not the cause of the disease, but its consequence, that is, the increased volume of adenoid tissue. Remember that it is not just unnecessary tissue that is being removed, but a rather important immune organ! As a result, relapses often occur after surgery.
Perhaps, for a disease such as adenoids, conservative treatment is more effective? Unfortunately, this is not always the case. If you neglect the disease and allow it to progress to stage III, then surgery will remain the only option. You need to carefully prepare for it. The child will be in dire need of your moral support. In addition, a couple of weeks before the operation he should not take aspirin or drugs that contain it. Taking other medications must also be agreed with your doctor. Be sure to tell your doctor if your baby is allergic to certain medications or has an increased tendency to bleed.
The operation itself to remove adenoids is not as complicated as, for example, removing tonsils. A stay in the hospital is not required; after the bleeding stops, the child can be taken home, provided he remains in bed. Another thing is that children are terrified of such operations, and you, parents, will need to do your best to support and reassure the child. Explain that the operation is quick, that it will not hurt him, since the doctors will provide anesthesia.
Recovery after surgery
At first, the child should be fed soft foods: porridge, soup, jelly, etc. The first 24 hours are prohibited from consuming dairy products. Afterwards, yogurt, milk, and puddings are perfect for nutrition. Make sure your child drinks enough fluids to avoid dehydration. At first, the child will have to give up vigorous activity and spend more time in bed, preferably more sleep. You can return to kindergarten or school only when the child easily eats any food, does not need medication and sleeps peacefully throughout the night.
If adenoids do not go away, surgery is necessary
If conservative methods of treating adenoids in children do not help, then surgery remains the only option.
Indications for adenotomy are determined not by the size of the growths, but by the severity of the symptoms. Due to the anatomical characteristics of the body, each child has different options: sometimes grade III adenoids do not interfere with nasal breathing too much, and sometimes they cause serious hearing problems even in grade I.
The essence of adenotomy is to remove the enlarged tonsil. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia. In terms of duration, this operation is one of the shortest. It only takes a few minutes, and the cutting process itself takes a matter of seconds. But the simplicity of the operation in this case does not equate to its safety. There are complications after anesthesia, bleeding, and trauma to the palate. True, such troubles happen quite rarely.
If a child is diagnosed with adenoids, surgery is not urgent. You need to prepare for it, undergo a thorough examination, etc. It should not be done during a flu epidemic or after an acute infectious disease.
The recovery period is extremely fast. After the operation, the child can be taken home and put to bed. Bed rest is prescribed. It is recommended not to eat hot or hard foods for 1-2 days.
What is inflammation of the adenoids (adenoiditis)
Adenoids are formations consisting of lymphoid tissue. They are also called pharyngeal tonsils. These areas of the nasopharynx are involved in the production of immunoglobulins. Pharyngeal tonsils are formed during the fetal development of the child, but only after birth they begin to perform a barrier function. This is an essential element of the nasopharynx immune system.
Important! The adenoids receive maximum load between one and three years. At this time, the child’s social circle is expanding, his immune system is faced with a huge number of viruses and bacteria. In this regard, the adenoids begin to increase in size. They reach their largest size at about four to five years, then begin to gradually decrease. In an adult they are barely noticeable.
The adenoids may not cope with their task, as a result of which the child constantly suffers from respiratory diseases. This is also facilitated by the immaturity of the child’s immune system. Constant inflammatory processes in the body also suppress the immune system, creating a vicious circle.
Inflammation of the adenoids in children
As the nasopharyngeal mucosa begins to produce more and more viral-bacterial antigens, the adenoids expand. The diagnosis of adenoid hypertrophy is made when there is a pathological increase in adenoid tissue, affecting the condition of the nasopharynx and middle ear cavity. In this case, the adenoids impair breathing and become reservoirs of pathogenic bacteria. Staphylococci, pneumococci, and streptococci linger on their surface. All these microorganisms can cause respiratory diseases.
Acute and chronic form
Acute adenoiditis is an inflammatory process in the adenoids, which is associated with infection of the nasopharynx. This disease usually lasts no more than one month.
Chronic adenoiditis develops due to disruption of immune processes in the pharyngeal tonsils. Chronic inflammation of the adenoids is considered to be inflammation that lasts more than two months in a row and repeats several times during the year. There are no strict criteria separating acute and chronic forms of adenoiditis in modern science.
Adenoiditis prevents a child from leading a full life. A sick child experiences difficulty breathing through the nose, often coughs and blows his nose, acquires the habit of breathing through the mouth, and his speech becomes nasal.
Adenoid face
Important! In advanced cases, children develop an “adenoid face.” Its distinctive features are swelling of the face, circles under the eyes, a slightly open mouth, and a shortened upper lip. Regular inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils can lead to recurring otitis media. One of the most dangerous complications is hearing loss.