Gluten and gluten-containing products
Gluten is a protein of plant origin. It is found in the seeds of some cereal plants such as oats, rye, barley and wheat. The second name for gluten is gluten. It is included in about 80% of human daily food products, including products for infants.
The obvious presence of gluten can be found in bread, bakery products, porridges from the above-mentioned cereals, baked goods, semolina, pasta, and bran. Products with hidden gluten content include deli products, candies, ice cream, sauces, mayonnaise, dressings, chips, crab sticks and other products to which gluten is added as an auxiliary ingredient.
What is gluten
Gluten is a complex protein found in most cereals (wheat, rye, barley). The word “gluten” is more commonly known among the common people. The main purpose of gluten is to glue particles together.
Lately you've heard a lot about the dangers of gluten and newfangled gluten-free diets. Is gluten really that bad? No, gluten is not harmful for most ordinary people. The exception is 3% of the population who have developed intolerance to this protein.
It is a mistake to believe that gluten is only found in grains and products made from them.
Gluten significantly reduces the cost of some food products, so it can be found in coffee, sauces, processed meats, cookies and much more.
There is a trend towards an increase in the number of people who are allergic to gluten. Therefore, most manufacturers indicate on the packaging whether this protein is included or not.
Reasons for appearance
Why does a child become allergic to gluten? Scientists adhere to the immunological theory. Namely, when gluten enters the digestive tract, it breaks down into fraction proteins - glutelin and gliadin. The latter is perceived by the body as a foreign body. As a result, antibodies to gliadin and autoimmune antibodies to intestinal cells are produced in the blood. Its walls are damaged, irritated, and full functioning and absorption of nutrients stops. This is why a child is allergic to gluten, the symptoms of which are often considered manifestations of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The intestines become a place of accumulation of decay products, and this negatively affects the general condition of the body. In addition, in severe cases, disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine, cardiovascular systems and kidneys may be observed.
Allergy to cow protein
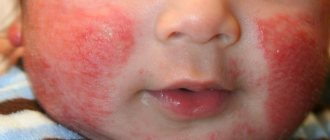
An allergy to cow protein (photo 2) in humans is caused not by a lack of enzymes for digestion, but by an atypical immune reaction to the ingestion of protein from cow's milk. The reaction to milk protein in a child is caused by enzymes contained directly in the milk itself. The peak incidence occurs in the first year of life. Protein allergies in adults persist throughout life, if they do not go away by the age of three in childhood.
An allergy to cow's milk protein appears mainly during the period of introduction of complementary foods, and also develops against the background of feeding with artificial formulas, rather than breast milk. The direct cause is various proteins; an allergy in a baby to milk protein can occur to one of 25 different types.
The most allergenic are casein and whey protein. Transferrin, lactoferrin, and microglobulin can cause rashes. Moreover, a child is allergic to cow protein, both fresh and boiled milk.
Symptoms of gluten allergy in a child
An allergic reaction to gluten most often occurs when parents begin introducing complementary foods to their baby. During this period, the child gets acquainted with new food in addition to mother's milk. In most cases, especially if the baby is not gaining weight well, the first complementary foods are cereal porridges that contain gluten. As a result, you may develop a gluten allergy. In a child, symptoms appear immediately or even after several weeks and months after the allergen enters the body, the so-called cumulative allergy. The reaction depends on the serving size, frequency of administration, immunity, and the state of the digestive system. The sooner parents detect symptoms and diagnose allergies, the easier it will be for the baby.
Allergy to gluten manifests itself in a wide variety of variations. A child's symptoms may include the following:
- swollen, bulging belly. Parents will think that the child is overeating, and the doctor may recognize this as a sign of rickets;
- poor weight gain and slower growth, particularly after the start of complementary feeding. If before the porridge the baby gained weight normally, then when the child becomes allergic to gluten, symptoms of weight loss and complex developmental delay are present;
- unstable, frequent, copious stools (5 times a day or more), mushy consistency with a bad odor, greasy, difficult to wash off, foamy, different colors, shiny due to fat.
These were typical symptoms of a gluten allergy in children. In addition to them, there are a number of others that depend on the presence of microelements, vitamins and nutrients in the body. Therefore, each child's reaction may be completely different. Minor symptoms include:
- moodiness, tearfulness, irritability, aggressiveness or, conversely, lethargy and fatigue;
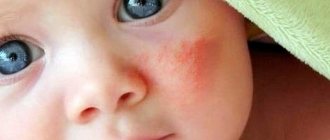
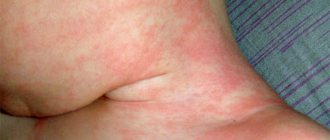
- unsatisfactory condition of the skin - peeling, dermatitis, bad hair - weak, dry. Skin rashes most often form on the elbows, knees, buttocks, and head;
- Bones often break, even with minor injuries. This is rare in healthy young children because their bones are very elastic;
- posture is disturbed;
- weak muscle tone;
- anemia;
- oral problems - gums bleed, enamel is destroyed, caries;
- outwardly the baby looks tired;
- sometimes a child is compared to a spider, because his tummy becomes bulging, and his arms and legs are thin and skinny, like the legs of a spider.
This is how a child’s gluten allergy can manifest itself. The symptoms, photos of which are given in the article, show that the reaction can be stunning.
Is it possible to cure the disease?
Gluten intolerance accompanies a person throughout his life. The situation with allergies is much more positive. If it appears in newborns, it may disappear after 3-5 years. Signs of a reaction are clear and parents should consult a doctor immediately.
Children are given a special diet. Avoid products that contain wheat, oats and other grain products.
Medications for allergic reactions to gluten
For infants, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor. Taking into account the age of the baby, medications are prescribed to eliminate allergic reactions:
- to eliminate the rash, use ointments with glucocorticosteroids (Lokoid Advantan) and creams with a moisturizing effect (Bepanten);
- itching and allergic rhinitis are eliminated with the help of antihistamines (Erius, Fenistil).
The drugs provide a temporary effect. You can get rid of allergies for a long time if you follow a gluten-free diet. Grain should be excluded from the diet of the baby and mother through breastfeeding.
Should mom follow a gluten-free diet?
All food products from the mother's digestive system pass into breast milk. Therefore, breastfeeding is a reason to follow a gluten-free diet. The allergic protein with mother's milk quickly enters the baby's digestive tract. The presence of the allergen damages the walls of the small intestine, and the first symptom of the reaction appears.
Principles of introducing complementary foods for infants
When breastfeeding, the first complementary foods are introduced to the baby at approximately 6 months. One new product is introduced once a week. Because a small organism can perceive new components differently. If at least 1 sign of allergy appears, then complementary feeding is suspended for a while. Wheat porridge and other cereals are introduced last. Mom should keep a food diary and write down all new foods in it. This way it is easier to determine the cause of an allergic reaction.
Watch this video on YouTube
Nutritional features of young children with allergies
At this age, it is difficult to stick to a diet, since children begin to go to kindergarten. At home, it is much easier to limit a child’s contact with an allergen. Such children cannot eat large quantities of foods. Despite this, their diet should be complete.
A child’s diet can include rice porridge, cottage cheese, omelettes, butter, fruits, vegetables, and meat (except beef). There are also cookies and breads without wheat flour or gluten.
List of prohibited foods with hidden gluten
If an infant suffers from allergies, then you need to choose foods for complementary feeding very carefully. Most of them contain hidden gluten. These include:
- canned fish and meat, semi-finished products;
- cereal containing molasses;
- sausages;
- baby puree;
- some medications;
- nutritional supplements;
- sweets, candies;
- ice cream.
For children with hypersensitivity to cereal allergens, it is recommended to order food from abroad. German and Italian manufacturers are considered to be of high quality.
How to diagnose allergies?
If you detect at least one of the symptoms in a child, you must urgently consult a doctor. Delay in this matter threatens the baby with a developmental delay and a deterioration in the condition of the body as a whole.
How to identify a gluten allergy in a child? To do this, allergy tests are carried out, and enzyme immunoassay of venous blood is done. As a result of the analysis, the amount of antibodies in the blood serum is determined - antigliadin, autoimmune antibodies to reticulin, tissue transglutaminase, endomysium. A healthy child has no antibodies to gluten in the blood serum or their amount is minimal. If the result is positive, then there is an allergy to gluten. Symptoms in infants may only appear after gluten-containing foods are introduced into their diet.
An increased number of eosinophils, immunoglobulins E, G in the blood most often indicates an allergic reaction. The doctor will make the final diagnosis based on the tests taken and existing symptoms. For a more accurate picture, it is advisable for the doctor to know what the child’s diet has been like recently. A good aid in making a diagnosis would be a food diary, in which parents note what the baby ate, in what quantity and from what period foods were introduced, and what the body’s reaction was to them.
Diagnostics
Gluten allergy is a dangerous condition, especially for a young child. If any of the above symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostic measures begin with examination of the baby and collection of anamnestic data
It is important to identify the cause-and-effect relationship between consumption of gluten-containing foods and symptoms. If the doctor suspects this particular disease, the following tests are prescribed:
- Blood test for antibodies to gluten. Venous blood is collected. In healthy people, the amount of antibodies will be minimal, and if there is an allergy, it increases sharply. The main indicator is the presence of immunoglobulin E (IgE) in the blood.
- A food diary is of great importance in diagnosing gluten intolerance. The child's mother should write down symptoms and sensations after each meal. It is necessary to carefully note in the diary exactly what foods the child ate. If there is a relationship between gluten-containing products and allergies, we can conclude that the child has an intolerance to this protein.
Confirmation of a gluten allergy is the absence of reactions when the child does not receive this protein. Diagnostic measures are simple and allow you to identify the problem in a short period of time.
Allergy prevention
To reduce the risk of developing a gluten allergy in a baby, it is necessary to introduce complementary foods in a timely manner (no earlier than six months) and breastfeed the baby for as long as possible. You should start feeding with gluten-free porridges - rice, buckwheat, corn and one-ingredient vegetable purees.
It is important to monitor the quality and composition of food for your baby. Try new products gradually and keep a diary of observations of the reaction.
A nursing woman can eat foods containing vegetable protein. It does not enter the baby's body through milk. In some cases, infants are fed or supplemented with formula milk almost from birth. They may also contain gluten, so the choice of mixture must be taken responsibly. Children with allergies are given a gluten-free formula.
Features of the treatment of gluten allergies in older children
If for very young children it is enough to organize a gluten-free diet at home, then parents of three-year-olds are faced with social and psychological problems. After all, most children at this age begin to attend kindergarten.
It is almost impossible to fully feed a child who is allergic to wheat and rye in a preschool institution. Such children are not allowed more than half of the products included in the menu. There is only one way out - we need to create specialized kindergartens for children with celiac disease and gluten allergies.
Here is a sample menu for children 1 - 3 years old who are allergic to gluten:
- breakfast: rice porridge / omelet with cheese / cocoa / butter;
- second breakfast: fruit juice;
- lunch: beetroot salad with apples / meat cabbage soup with vegetables / potato casserole with minced meat / dried fruit compote;
- afternoon snack: cottage cheese with fresh fruit, corn sticks;
- dinner: poached fish fillet with boiled potatoes / fresh vegetables / tea with milk;
- at night: kefir with sugar;
- All day gluten free bread. Gluten-free cookies and baked goods can be provided.
Parents of babies with gluten sensitivity face a huge number of problems, most of which are social and psychological. You need to constantly monitor your baby's nutrition.
As time passes, it will get easier. Children tend to outgrow food allergies. Only 10% of people have a severe allergy to gluten-like proteins that lasts a lifetime.
Treatment methods
Once a child has been diagnosed with a gluten allergy, the symptoms of which are similar to many other childhood diseases, treatment must begin immediately.
The first thing to do is switch to food products that do not contain plant protein. To do this, you need to know which foods contain gluten and which do not. Unfortunately, not everything sold on the domestic market is labeled for the presence of plant protein. On the packaging of foreign products that do not contain gluten, a crossed out spikelet is depicted. This makes it more convenient to purchase the right product if your child is allergic to gluten.
Treatment with medications that will help the child cope with allergy symptoms is prescribed by the doctor. Symptomatic therapy involves taking antihistamines, agents that adjust intestinal motility, enterosorbents, vitamins to boost immunity, gastrointestinal immunostimulants that help restore microflora, anti-inflammatory creams and ointments.
These measures eliminate the child’s gluten allergy. Symptoms that are treated in several stages can be tracked by repeat tests. Some medications contain gluten as an ingredient, so you need to be careful when choosing them.
Nutrition for a child with a gluten allergy
The main food for infants, including those with gluten allergies, up to about one year of age should be mother's milk or gluten-free infant formula. The introduced complementary foods should not contain vegetable proteins.
List of foods that can be consumed if you have an allergic reaction to gluten:
- natural dairy products, eggs;
- fresh, natural fish, meat, poultry, not marinated, without spices;
- natural, unprocessed legumes;
- rice, buckwheat, millet, corn, quinoa, amaranth, flour and products made from these grains;
- fruits vegetables;
- vegetable and butter;
- sweets - marmalade, marshmallows, chocolate, certain types of ice cream and candies;
- root vegetables, nuts;
- jelly, freshly squeezed juices, natural cocoa and tea;
- tapioca, teff, sorghum.
Diet for gluten intolerance
The main method of treating gluten sensitivity has been and remains a specialized diet for gluten intolerance in adults and children. Its main principles:
- Completely eliminating or minimizing all foods containing gluten from the diet.
- Drawing up a menu only from high-quality and minimally industrially processed food.
- According to various sources, the diet should be followed for at least 3 months, and preferably a year. During this period, the intestinal mucosa will be able to recover. There is also an increased likelihood that normal microflora will no longer be sensitive to this plant protein, so it can be gradually reintroduced into the diet.
What can you do if you are gluten intolerant?
The recommendations of nutritionists regarding the preparation of a diet for gluten intolerance during the period of intensive therapy include various food groups. Protein-rich foods on the table should include:
- lean meats without breading;
- river or sea fish;
- eggs;
- legumes and soybeans;
- nuts;
- fermented milk products and cheeses.
You can choose as a source of carbohydrates:
- potato;
- corn, rice, buckwheat, quinoa, amaranth, sorghum and flour based on them;
- any fruits and berries.
The diet should include:
- butter and vegetable oils;
- vegetables and herbs;
- mushrooms.
What not to do if you are gluten intolerant?
If a person is diagnosed with intolerance to plant protein - gluten, then it is important for him to exclude from the diet:
- cereals: barley, wheat and rye;
- bread and bakery products, cookies made from wheat or rye flour;
- pasta;
- semolina porridge;
- bulgur;
- wheat bran;
- pearl barley, barley and oatmeal (due to the nature of production) porridge.
In addition, on store shelves you can find a huge number of products with so-called “hidden” gluten, which contain wheat flour or modified starch. These include:
- sausages and sausages;
- ketchups and industrial sauces;
- kvass;
- beer;
- canned food;
- chips and crackers;
- candies, cakes, halva and marshmallows;
- freeze-dried coffee and tea with flavors;
- any meat and fish semi-finished products;
- powdered soups and bouillon cubes.
Menu for gluten intolerance
Many people at the beginning of treatment may feel that a gluten allergy is severely depleting their diet. However, nutritionists assure that with some skill you can create an extremely healthy and very tasty and healthy menu that is completely gluten-free. It might look like this:
- Breakfast can consist of gluten-free milk porridge (rice, for example), an omelet with cheese, cottage cheese with fruit, cheesecakes or pancakes made from gluten-free flour. All this can be seasoned with honey and a portion of fresh berries.
- For lunch you can eat meat or fish soups without pasta, potato or vegetable puree with baked or stewed meat. Be sure to include a salad of vegetables and herbs.
- For dinner you can cook potato pancakes, cottage cheese casserole or fish (meat) baked with vegetables.
- For snacks, you can eat a handful of nuts, low-fat yogurt, a sandwich with butter and cheese, or fruit.
What should you exclude from your diet?
All products that contain hidden or obvious gluten:
- barley, wheat, rye, oats. All products and products made from them. Pearl barley, semolina;
- canned food, marinades;
- sausages, sausages, semi-finished products, offal;
- some seasonings and spices, ketchup, mayonnaise, sauces, mustard;
- concentrated soups, bouillon cubes;
- oriental sweets;
- some nutritional supplements;
- confectionery products - cakes, pastries, cookies;
- yogurt, whole milk.
Are celiac disease and gluten allergy the same thing?
Celiac disease is a congenital and hereditary intolerance to gluten. With this disease, vegetable protein is absolutely not absorbed or digested by the intestines. Celiac disease remains for life, forcing the patient to constantly adhere to a strict diet. If the disease is not treated in time, it can provoke complications in the form of serious illnesses.
In case of allergies, the walls of the small intestine are irritated by plant protein, and it is partially absorbed by the intestinal villi. Gluten allergy disappears if it is diagnosed in time, treated and followed a diet.