Causes of food allergies
An allergic reaction is the response of the immune system to certain irritants. By food allergy we mean an excessive reaction of the body to foods or their individual components. Children under 1 year of age are more susceptible to such phenomena. The reason for this is the immaturity of their digestive and immune systems. When any rash appears, it is important to understand the cause so that you can respond appropriately and take appropriate action.
In infancy and childhood, a food reaction can occur due to:
- Genetic predisposition. If one of the parents suffers from allergic reactions, then the chance that it will be passed on to the child is reduced to 20-30%, but if both parents suffer, then the chance of passing this feature on to the child rises to 60%.
- Poor lifestyle and nutrition during pregnancy. It often happens that women during this period cannot give up smoking or drink alcohol, in which case the child after birth has an increased susceptibility to allergies.
- Overfeeding, incorrect selection of formulas, early transition from breastfeeding to artificial feeding can be reflected in the unpreparedness of the baby’s digestive system and, as a result, cause some kind of reaction.
- Hypersensitivity to the product or any specific component of it. Food allergies are especially common in children to: sweets, strawberries, citrus fruits, peanuts, chocolate, and dairy products.
- Weak immunity or problems with the gastrointestinal tract and intestinal dysfunction.
- Unfavorable environmental situation. Contamination of the drinking water you use for cooking and drinking.
This process occurs due to the fact that when food enters the body, the immune system mistakes it for a hostile element and begins to fight it, producing immunoglobulins, which perform a protective function. This phenomenon triggers allergic reactions in the body.
Symptoms
A pediatrician or allergist makes a diagnosis of “food allergy” if the child’s immune system is overly susceptible to certain food components. With increased sensitivity, immunoglobulin E enters into a chemical reaction with the allergen, which provokes the occurrence of external and internal manifestations of allergy.
Food allergies can be hidden or pronounced. A hidden type of food allergy can manifest itself in the form of a headache when consuming certain foods, and not necessarily allergenic ones. It can occur not only in food products, but also in smells.
The external symptoms of a pronounced allergic reaction are so specific that they are difficult to confuse with manifestations of another disease. They develop within a few hours or even minutes after eating and look like this:
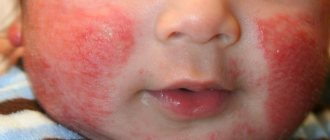
- redness of the skin, rash, single spots or spots merging into large plaques. Their characteristic feature is severe itching, which prevents the child from sleeping. The baby becomes lethargic and capricious;
Peeling on the cheeks of a child with food allergies
- swelling – appears in severe forms of allergies. Everything can swell: the face, lips, eyes, ears, hands and even genitals; swelling of the oropharynx is often encountered;
- nasal congestion and allergic rhinitis. In rare cases, if the diet is not followed for a long period of time, bronchial asthma may develop.
A pathological reaction can be observed not only in the oral cavity and on the skin. The digestive system is also capable of expressing its protest to the allergen in the form of:
- digestive disorders (diarrhea, constipation);
- flatulence, bloating, intestinal colic;
- nausea, vomiting;
- loss of appetite.
Allergic reactions at the level of the gastrointestinal tract are explained by the immaturity of the child’s body. They can cause diseases of the digestive system such as allergic enterocolitis, gastroenteritis, esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus).
Symptoms of food allergies in children
The reaction can be of varying intensity. It all depends on the sensitivity of the body and the amount of allergen that has entered. The most dangerous are instant reactions and those that are acute. For example, swelling of the throat and palate, or numbness of the tongue is an urgent reason for calling emergency services and hospitalization.
In addition, it is very important to understand how food allergies manifest in children. Since treatment will not work if you are diagnosed with an allergy to a cat or a dog instead of a reaction to some product. Therefore, let's try to find out what symptoms should alert you:
Skin allergic manifestations
It often manifests itself in the form of a skin rash of varying intensity, red spots, peeling, itching and swelling of the affected area. This type of reaction is the most common. You may notice a rash not only on the cheeks, but also on the neck, arms, legs and stomach.
Atopic (allergic) dermatitis
At the age of two years, it appears as a rash in the form of small blisters, which then merge into a single element, and after that a crust forms. Typically, the appearance of such a reaction can be noted on the arms, legs, and neck.
At the age of 1 to 2 years, food allergies in a child are accompanied by peeling and severe cracking of the skin. After the rash goes away, hyperpigmentation forms in that area.
Quincke's edema and urticaria
Hives refers to the appearance of large blisters and swelling on the skin as a reaction of the body to an allergen that has entered the body. Often such swellings can go to the throat and also cause nausea or vomiting.
The appearance of severe swelling on some part of the face or limbs indicates a disease - Quincke's edema. Its danger is that the swelling can spread to the throat and larynx area. As a result, breathing becomes difficult, and changes in the voice and a dry, barking cough may also occur.
Late response and assistance from medical personnel can result in death.
Strophulus
A childhood disease that most often accompanies children aged 1 to 4 years. Its manifestations are very similar to urticaria. Bubbles with liquid inside may appear on the bends of the arms and legs. They are very itchy, which leads to the baby scratching his body until there are bloody wounds.
When choosing the right treatment method, the disease often goes away in adulthood. However, if not treated at all, the disease can become more severe.
Causes
Allergic manifestations can appear both in the first months of a child’s life and much later. The causes of occurrence in infancy are:
- improper nutrition of a woman during pregnancy. The expectant mother should be attentive to her diet. To avoid allergies in a child, from the first days of life it is better to give up aggressive allergens: citrus fruits, strawberries, seafood, and in the last months of pregnancy - cow’s milk, replacing it with fermented milk products;
- earlier or incorrect introduction of artificial formulas or complementary foods into the child’s diet. This is due to the presence of cow's milk in most formulas, the protein of which often causes allergies in children. Regarding complementary feeding, premature consumption of unfamiliar food or a large amount of complementary foods at one feeding can also cause a pathological reaction;
- inattention to the nutrition of a nursing mother: consumption of foods that can cause allergies in the baby. Every mother knows what foods need to be excluded from her diet so that her baby does not have an allergic reaction.
Diagnostics
Only an allergist can accurately diagnose what the cause is. At the appointment, he examines the baby, studies his test results and draws up a complete clinical picture for himself.
Food allergies are the most difficult to differentiate, since a diagnosis can only be made by the body’s immediate reaction to the allergen. In the case of very young children, the allergen can be found and excluded through testing. The child is put on a strict diet, and then new foods are gradually introduced. To help diagnose the cause in older children: an immunological blood test and skin allergy tests.
The latter method is performed on children over 5 years of age. A small scratch is made on the skin of the forearm or back with a special instrument, and allergens are applied to it. After a while, the doctor observes the body’s reaction. The advantage of this method is that it is cheap, but it involves introducing an allergen into the body and, accordingly, no one can know what reaction it will cause.
The immunological blood test method is very similar to a regular blood test. Its essence lies in the fact that research is carried out with the taken material in a laboratory setting. The advantage of it is that, firstly, it is not worth tormenting the baby for so long, and secondly, it can be carried out in almost any health condition. And, thirdly, you can check not only the reaction to the main allergens, but also to everything you want. The only disadvantage of this method is its price, which is significantly higher than that of the two previous methods.
Treatment methods
The fight against food allergies is carried out in 3 directions:
- diet;
- taking antihistamines and, if necessary, hormonal drugs;
- treatment of concomitant diseases and complications.
Even the most miraculous medications will be powerless without eliminating the source of the allergy. Therefore, first of all, treatment consists of following a diet.
Breastfeeding is the best nutrition option for a child with allergies. But a nursing mother should be extremely careful about her diet and keep a food diary, writing down everything she eats during the day. If natural feeding is not possible, it is recommended to use mixtures with hydrolyzed protein to avoid an allergic reaction to cow's milk or soy. Introduce complementary foods carefully, in accordance with the recommendations of a pediatrician, observing the baby’s reaction.
If an allergic reaction occurs in an older child, highly allergenic foods are excluded from his diet:
- chocolate, honey,
- nuts,
- citrus,
- strawberry,
- cocoa, tomatoes, eggs,
- mushrooms, sea fish,
- Milk is replaced with fermented milk products, salt and sugar are limited.
- Cereals are soaked in cold water before cooking.
If the allergen is precisely known, it is completely removed from the diet. If this is not done, the pathological reaction will renew with each contact with it, which will lead to worsening and progression of the disease.
Properly selected drug therapy will help quickly stop the manifestations of an allergic reaction. Such drugs as Suprastin, Tavegil, Fenkarol, Loratadine are used.
But it should be remembered that antihistamines only mask the absence of symptoms. If you do not follow the diet, the allergy will return immediately after stopping the medications. To quickly “remove” the allergen from the body, any absorbent is used: activated carbon or Enterosgel.
Treatment of food allergies in children
The most important thing that parents should do in this situation is to show the baby to the doctor . Only after passing all the tests and diagnosing the problem will he prescribe complex therapy.
In the future, you will be advised to eliminate the allergen from your life, give medications prescribed by your doctor, and take measures that will help improve your baby’s immunity, namely, exercise, establish a diet and daily routine, proper nutrition, and natural vitamin supplementation. You should not self-medicate before consulting a doctor; this can cause irreparable damage to your baby’s health. Once you see improvements, you should not stop the course of treatment. You must complete it to the end.
Let's figure out what the essence of treatment is so that you are not afraid of this terrible word. So, after identifying the allergen, the doctor will prescribe a strict diet. It often happens that all the symptoms go away and the treatment ends. But in cases where it is more serious, the doctor prescribes complex therapy, which is aimed at: relief of symptoms, removal of allergens from the body and restoration of intestinal microflora. Depending on the age of the baby, he may be prescribed medication. To do this, use: enterosorbents, antihistamines, topical creams or ointments to relieve redness and inflammation, drugs that relieve respiratory symptoms.
Modern medicine also often resorts to treatment with homeopathic medicines. Their advantage is that they do not contain chemicals that have a harmful effect on the child’s body. However, treatment in this way requires a longer time.
Complications
The danger lies in its acute manifestations. Unqualified and untimely assistance to a child can lead to the most dire consequences.
The following manifestations are considered dangerous: bronchospasm, anaphylaxis, laryngeal edema. If measures are not taken to stop the attacks, the allergy can develop into atopic dermatitis or bronchial asthma.
Allergic reactions leave their significant imprint on the functioning of the child's immune system. It weakens significantly, which leads to more frequent colds and infectious diseases.
Features of food allergies in newborns
In the first months and even years, mother’s milk is very important for the child. It helps to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, develop strong immunity, and also establish a strong psychological connection between mother and baby.
Sometimes a child may have an allergy, although he has not eaten anything other than “mother”. In this case, you should understand that everything that you have eaten and everything that is in your stomach is also in the baby. During the first time of breastfeeding, it is important to stick to a simple diet, gradually expanding and replenishing your diet with more and more new dishes and products.
Indeed, there are foods that most often cause reactions in children: chocolate, citrus fruits, peanuts. However, you can structure your diet in such a way that it is as rich as possible and does not contain these products. For example, you can try replacing peanuts with seeds when breastfeeding. If you really want to eat something, then start with a small slice or piece, gradually increasing the portion.
If you see a reaction on your baby, then exclude this product and try it again after 3 weeks. Small restrictions on food will not cause you discomfort, but they will protect your baby from discomfort in the stomach, colic, bloating and will help him develop correctly and fully.
Life situations are different, and if you are not breastfeeding, then your doctor should help you choose a formula, taking into account the characteristics of your baby. Buying any mixture without consultation, relying on advertising, is very risky.
Prevention
To prevent the development of an allergic reaction in a child, you need to pay attention to the following facts:
- the need for natural feeding (of course, whenever possible);
- maintaining a hypoallergenic diet for a nursing mother;
- strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions when choosing artificial mixtures, the use of special gluten-free and dairy-free cereals, monocomponent fruit and vegetable purees;
- exclusion from children's diet of highly allergenic foods, as well as foods containing dyes and preservatives;
- maintaining a proper and healthy diet
Lifestyle of a child with food allergies
With proper and comprehensive treatment, the child’s recovery occurs quickly. However, you should be wary of foods that cause a reaction, do not use them in cooking at all, or, in extreme cases, add a little at a time.
Remember that if you are allergic to peanuts, you should also limit your consumption of similar products, such as hazelnuts and cashews.
When a reaction occurs, you should not rely on your experience and the knowledge of your friends; immediately go to the doctor and follow all the rules prescribed by him. Of course, you have the right to resort to traditional medicine methods, but it is better to do this when the danger to the baby’s health has passed.
After complete recovery, start improving his immunity: proper nutrition, adherence to a daily routine and regular exercise will help not only strengthen your baby’s immunity, but will also be an excellent preventive measure against allergies.
Video about food allergies in children
I suggest you watch a short video in which an allergist explains what most often causes food allergies in young children. You will also be able to hear some recommendations that will help you cope with this disease.
Once born, the baby finds himself in a completely new and unknown world. First of all, his parents surround him with care, affection and love. The best thing a young mother can give her baby is breast milk. However, sometimes, due to imperfections in the functioning of the immune system, the baby’s body does not accept this or that product that comes to him with mother’s milk or during complementary feeding.
Now share with us in the comments on the site, did your baby suffer from any allergies and how did you deal with it?
Treatment
3.1 Conservative treatment
Etiological treatment with exclusion of causally significant foods from the diet.
For mild PA and a limited number of causally significant proteins, monotherapy with an elimination diet with monitoring of indicators of the child’s physical development.
Diet therapy for PA:
- Stage 1 – diagnostic
- Stage 2 – therapeutic elimination diet
- Stage 3 - expansion of the diet.
Children with an allergy to CMP are prescribed specialized formulas containing highly hydrolyzed milk protein or amino acids.
Mixtures and products based on unmodified (non-hydrolyzed) milk proteins - goat, sheep, camel and other types are not recommended for children with an allergy to CMP.
Drinks - "milk" made from soy, rice, almond, coconut or chestnut are not suitable for the needs of infants.
(Antihistamines)
Due to severe side effects, first generation antihistamines
- chloropyramine,
- mebhydrolin,
- clemastine
There are no registered second generation antihistamines before 6 months of age, but a short course of dimetindene , 3–10 drops 3 times a day, is possible.
In PA, second-generation antihistamines are used to relieve non-life-threatening manifestations:
- Desloratadine 1 time/day from 1-5 years old syrup 1.25 mg (2.5 ml), from 6-11 years old syrup 2.5 mg (5 ml), from 12 years old - 5 mg tablet or 10 ml syrup;
- Loratadine 1 time/day after 2 years, less than 30 kg weight 5 mg, more than 30 kg - 10 mg;
- Levocetirizine 2-6 years old drops 2.5 mg/day, from 6 years old - 5 mg/day;
- Rupatadine fumarate 1 time/day from 12 years old 10 mg;
- Fexofenadine 1 time/day 6–12 years 30 mg, over 12 years — 120–180 mg;
- Cetirizine 6 - 12 months. 2.5 mg 1 time / day, 1-6 years 2.5 mg 2 times / day or 5 mg 1 time, from 6 years - 10 mg once or 5 mg 2 times a day.
Mild sedation may occur in some children.
Long-term prophylactic use is not recommended.
Severe and life-threatening manifestations of PA are treated with the administration of epinephrine .
For concomitant bronchial asthma, the inhaled short-acting β2-agonist salbutamol must be used.
It is recommended to carry out external therapy differentiated, taking into account pathological changes in the skin.
Mast cell membrane stabilizers are not recommended for the preventive treatment of food allergies.
Specific immunotherapy is not recommended in routine practice due to the high risk of anaphylaxis.
3.2 Surgical treatment
Not required