IVF is carried out in several stages, which are usually called the IVF protocol. When a woman “enters the protocol” or “starts the protocol,” this means that she has begun taking medications to later obtain eggs and prepare the endometrium for embryo transfer.
With long IVF protocols, special preparation of the ovaries can be started, that is, suppression of their function with hormonal contraceptives, less often with other medications, so that during hyperstimulation, the growth of a larger number of follicles begins simultaneously.
Stimulation of ovulation - obtaining follicle growth
If the goal of conventional ovarian stimulation is to obtain 1-2 mature eggs, then for IVF you need much more of them, because almost 75% of the material obtained will be defective.
Ideally, for successful IVF, it is necessary that at least 8–10 follicles mature in each ovary. The older the woman, the more difficult it is to get a good ovarian response to stimulation. Ovaries damaged due to surgical interventions also react poorly to stimulation. This stage of IVF is accompanied by the use of different types of medications.
Assessment of ovarian reserve allows you to select the necessary protocol with an individual approach. For a long period of time, assessment of ovarian reserve before IVF was carried out by two methods: counting antral follicles (size 2–10 mm) and determining the level of AMH.
In women suffering from PCOS, the ultrasound picture of the ovaries and AMH levels are significantly different. New diagnostic criteria for PCOS suggest the presence of more than 24 follicles of this size in each ovary, and AMH should be significantly elevated. However, this picture does not reflect the presence of a good ovarian reserve. In addition, the greater the cycle disruption (long anovulatory cycles), the more follicles can be observed on ultrasound and the higher the AMH, even compared to those women who have periodic ovulations due to PCOS.
A relationship was also found between the number of antral follicles, AMH and a woman’s weight, LH level, and the duration of the menstrual cycle.
What is ovarian reserve?
If you have ever been to an appointment with a fertility specialist, you have probably heard this phrase, in an optimistic intonation: “well, your ovarian reserve is quite promising” or with a negative connotation: “the ovarian reserve is rather low”...
Ovarian reserve or functional ovarian reserve is the name given to the estimated number of eggs in a woman’s ovaries that can eventually lead to pregnancy.
This potential is laid in the ovaries of a girl in the womb; after her birth, about 400,000 cells remain in the ovaries. In the future, a sad fate awaits us, unlike the male reproductive reserve, which is periodically renewed throughout life, our female reserve is only spent during life, without the possibility of restoration. Every month we lose at least 20 cells, regardless of lifestyle, presence or absence of pregnancies, use of contraceptives, etc.
Thus, with age, the number of cells capable of giving birth to pregnancy normally decreases in all women.
In addition, throughout life, the ovaries are negatively affected by many factors that reduce the quality of these cells (inflammatory reactions, neoplasms, exposure to various toxic substances, etc.). Surgical interventions on the ovaries (removal of ovarian cysts, resection of the ovaries, etc.) can prematurely reduce the follicular reserve to 0 in young women.
Egg retrieval
Retrieving follicles containing eggs (10–18) is an invasive procedure with a risk of damage to the pelvic organs, including the ovaries. In this case, mature follicles, that is, ovarian tissue, are sucked out. In the past, follicle retrieval may have been done through laparoscopy. This procedure is now performed through the posterior vaginal fornix.
A comparative analysis of a Swedish study was recently published, which included almost 40,000 women undergoing IVF during 2007-2014. The average age of the women was 34 years, 6.5% had given birth to children earlier using IVF, and 48.6% had IVF with ICSI. The average number of oocytes obtained for the procedure was 9.
The live birth rate was 30.3%, and the average number of fresh oocytes (without embryo freezing) was 11. The live birth rate increased to 45.8% when 20 eggs were retrieved at a time.
After comparing these and other important study indicators, scientists came to the conclusion that the optimal number of oocytes for IVF is 18 without a high risk of developing OHSS.
The birth of live children after embryo collection and freezing did not depend on the number of eggs obtained using a single aspiration. Thus, an important factor is the IVF method - the operation is performed with fresh or frozen embryos.
How to behave during stimulation
IVF stimulation is an important period during which a woman experiences a whole range of emotions: from joyful hope to deep despair from fear that nothing will work out. At this important time, the support of loved ones, a stable psychological state, many hours of quiet walks in the fresh air and a healthy diet are very important. Dieting for weight loss and excessive exercise should remain a thing of the past, and an optimistic attitude should become the present and future.
However, a diet is still needed, but not a “weight loss” diet, but a special one. It is important to consume a lot of protein (lean meat, cottage cheese, eggs) and foods with plant fiber, that is, vegetables and fruits. At the same time, use less animal fats and more vegetable fats. Protein foods are needed to prevent ovarian hyperstimulation. And fiber and vegetable fats will promote comfortable digestion, which is very important at this stage. But if you have gastritis or other gastrointestinal problems, coordinate your diet with a gastroenterologist. Most likely, he will advise replacing raw vegetables with boiled ones, and raw fruits with baked ones.
A few more important principles:
- Avoid infectious and cold diseases to prevent excessive stress on the immune system: it has a more important mission ahead of it.
- Avoid coffee and caffeine-containing drinks: they can interfere with hormonal levels and interfere with conception.
- Avoid hot baths and do not go to the sauna.
- Give up cigarettes, passive smoking and alcohol in any doses.
- Avoid taking any medications other than those prescribed by your fertility specialist. All other medications (for example, if you have chronic diseases that require medication) - only as a last resort and in agreement with a reproductologist.
Preparing the endometrium for embryo transfer
It is performed simultaneously during ovarian hyperstimulation or separately before transferring previously frozen embryos. This stage of IVF is also accompanied by the use of a number of medications. In the past, hysteroscopic artificial preparation of the endometrium (scratching) was performed, but it turned out that this technique does not improve the outcome of IVF, and may also lead to a deterioration in the quality of the endometrium. They don't do this now.
Transfer of embryos into the uterine cavity
It is considered an invasive procedure, although compared to other interventions it is a short-term procedure and therefore easily tolerated. Not so long ago, several embryos were transferred into the uterine cavity, which worsened the outcome of IVF, so most reproductive specialists began to transfer one embryo at a time, which improved the results. But debate about the optimal number of embryos to transfer is still ongoing.
Old methods of progesterone support after embryo transfer
Maintenance therapy in the recent past has been quite aggressive despite the fact that the first IVFs were carried out for a long period of time without any hormonal support.
Since follicles are harvested during IVF, the development of corpora lutea is not observed. But the maturation of too many follicles and luteinization of those that were not taken for IVF leads to too high levels of steroid hormones, in particular progesterone, which automatically suppresses the production of luteinizing hormone by the pituitary gland. This, on the one hand, leads to premature luteinization of the follicles, on the other hand, it suppresses the production of progesterone.
However, in the 1990s, women after IVF began to be given oil solutions of progesterone for up to 16 weeks. These were painful injections, and they required women to patiently go to medical institutions to receive hormones, sometimes twice a day. Tablet forms of progesterone turned out to be completely ineffective.
When there was a greater understanding of the role of progesterone in the corpus luteum, maintenance therapy began to be used for no more than 8 weeks, switching to vaginal forms of progesterone administration. The combination of injections with vaginal forms of progesterone has been used very rarely.
Then hormonal therapy was recommended until a stable increase in hCG, which was observed in the 5th week of pregnancy, or an embryo with a heartbeat appeared on ultrasound, which could be seen in the 6th week.
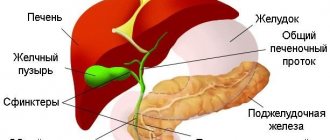
Follicle puncture during IVF
In vitro fertilization is a program of assisted reproductive technology that is carried out outside the woman’s body, but then pregnancy develops in her body under the strict control of reproductive specialists, which allows a married couple to acquire true family happiness. Just a few decades ago, no one could even imagine that fertilization was possible outside the female body. Nowadays, this is a fairly widely used procedure that allows many men and women to feel the meaning of true happiness.
The entire IVF procedure takes place in several stages: stimulation of superovulation, transvaginal superovulation, embryo transfer and maintenance of the luteal phase. A woman is often interested in how follicle puncture is performed, why is it dangerous and what are its consequences?
Let’s figure out a little about how follicles are collected during IVF, since a successful puncture affects a positive outcome and increases the chances of fertilization and pregnancy. To do this, a woman must contact an in vitro fertilization clinic at a certain time, since this procedure is carried out when the follicle matures to a certain size after preliminary preparatory materials. After emptying the bladder and after bowel preparation, the woman is taken to the operating room, where, under anesthesia, the follicles are punctured under ultrasound control transvaginally using a specific pump to obtain follicular fluid.
How many follicles are taken during IVF during puncture? According to standard IVF programs, it is necessary to take about 10-20 follicles, since embryos obtained by puncture may stop in their development. Therefore, to obtain such a number of follicles, the first step in fertilization is the doctor prescribes stimulation of superovulation.
Then, on a strictly individual basis, the reproductologist determines the day of the cycle to perform a puncture of the woman’s follicular apparatus with strict control over the cycle. To do this, he calculates the exact time from the first injection of human chorionic gonadotropin to the time of puncture, which should not exceed 1.5 days, which increases the likelihood of ovulation and then it will be impossible to remove eggs from the abdominal cavity. Therefore, there is no need to be late for the procedure and strictly arrive at the clinic at the appointed time with your husband to donate sperm.
In many cases, a woman is interested in how to prepare for a puncture? To do this, 5 days before the puncture, you must completely give up intimate relationships, give up alcohol, salty and spicy foods, as well as visit the bathhouse, sauna and take a hot bath. On the eve of the puncture, dinner should be light and you should not drink liquids 12 hours before the procedure. On the day of the procedure, do not drink, do not eat or brush your teeth, do not use makeup or nail polish, and also strictly take medications to stimulate ovulation and come to the clinic on time for the procedure.
After the puncture, rest is indicated on the first day, since the load reduces the chances of a favorable outcome of fertilization, a light diet, as well as strict intake of all medications according to the fertilization program, it is necessary to refuse to drive a car and equipment that requires strict attention, to avoid unnecessary emotional stress, sexual contacts, visits to baths and saunas.
The size of the follicles for puncture during IVF should be 18-22 mm, but there are cases when the follicle. Even if they have not grown 10 - 22 mm, they give positive results and there is an egg in them. Therefore, the size of the follicle does not always indicate the presence of an egg. Sometimes large follicles for IVF may not contain an egg, but small follicles do.
Empty follicles during IVF or empty follicle syndrome is when a mature egg is missing from a follicle for no reason. It occurs quite often, up to 7% of cases. Very often this happens when the technique for obtaining follicular fluid is violated, the IVF protocol is not properly maintained, chromosomal abnormalities, PCOS, obesity, endometriosis, premature aging of the ovaries, adhesions and severe stress. Empty follicles can be false or true. With true empty follicles on the day of puncture, the level of B-hCG in the blood is sufficient, but with false follicles its level is low, which is associated with the administration of hCG or with its insufficient bioavailability and is diagnosed very rarely. Diagnosis of empty follicles is carried out 36 hours after the first administration of gonadotropin by determining the level of B-hCG in the blood and if its level is below 10 units per ml, this indicates empty follicles. But don’t get upset right away; you need to introduce gonadotropin from a different batch.
Eco. Empty follicles do not indicate that pregnancy is impossible. First of all, it is necessary to replace the dose and drugs in the protocol, increase the time between punctures to activate ovulation, and also wash the ovaries. Often, the eco program uses GnRH agonists for egg maturation. In almost half of women with empty follicles, SPF is associated with late administration of gonadotropin.
If only one follicle in the ovary matures during IVF, then this significantly reduces the chances of fertilization, which indicates a weak response to hyperstimulation of ovulation. But here the quality of the eggs matters, since sometimes pregnancy occurs with one egg. Therefore, before starting an IVF program, a woman needs to evaluate her ovarian reserve, when the number of 10mm follicles is assessed on the 2nd day and, depending on their number, it is judged. If there are five of them, this indicates a weak reaction to hyperstimulation, up to seven indicates that it is necessary to change the dose of the drug, from 8 to 12 follicles indicate a satisfactory result, the presence of 13-20 follicles increases the risk of developing hyperstimulation syndrome.
Why do follicles grow poorly when stimulated?
All reproductive doctors know the norm for follicle enlargement during stimulation, and deviations from it indicate slow growth, which is determined by folliculometry. If a woman has a weak response to stimulation, this may be due to genetic abnormalities leading to ovarian depletion, chronic anovulation, endometriosis, or previous surgical interventions on the pelvic organs.
Follicular cyst and eco. Why does it occur and how does it affect the environment? It is known that if ovulation does not occur and the follicle does not burst, then it begins to persist and develop into a cyst. In most cases, such cysts resolve on their own within several cycles, but in some cases the cyst does not resolve and continues to grow, which increases the risk of its rupture or torsion of its pedicle, which requires urgent surgical treatment. With a follicular cyst, the issue of IVF is decided individually, since in some cases the hormonal background contributes to the resorption of the cyst, and in some cases, stimulation of ovulation leads to its enlargement or the appearance of new cysts, its degeneration into a malignant one or rupture of the capsule, which increases the likelihood of complications. Therefore, the decision on whether to carry out an IVF protocol depends on the ovarian reserve, and if it is low, then stimulation is carried out under strict ultrasound control.
Multifollicular ovaries and eco
Multifollicular ovaries are not a diagnosis, this is a conclusion from ultrasound doctors, and among gynecologists it is called polycystic ovary syndrome, PCOS or Stein-Leventhal syndrome. The classic syndrome is characterized by: polycystic ovaries, hyperandrogenism and infertility, which is the main reason for which women consult a doctor.
Using an ultrasound, the doctor diagnoses MFN if the volume of the ovary exceeds 10 cm3 with the presence of follicles of more than 12 pieces with a volume of up to 10 mm, while there are no follicles larger than 10 mm, which indicates the absence of ovulation, and do not increase on other days of the cycle.
Pregnancy with MFI is impossible only in the absence of ovulation, which is associated with changes in the hormonal levels of the body and leads to the formation of a large number of defective follicles. If such ovaries are accompanied by anovulatory cycles, then pregnancy is completely excluded.
IVF for multifollicular ovaries is indicated for women who are planning to become pregnant, through ovarian stimulation and folliculometry to determine the exact time of ovulation.
Stimulation of ovulation during mfya is a rather complex and painstaking task, since this pathology is not always corrected by selecting a drug, so sometimes it is necessary to stimulate ovulation several times by selecting the dose and stimulation schedule. This all increases the risk of developing ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome or ovarian depletion. Therefore, stimulation of ovulation in polycystic disease is carried out only when the weight of an obese woman is normalized and all metabolic processes in the body are stabilized.
To carry out IVF with MFN, according to health recommendations, it is necessary to check the patency of the fallopian tubes by laparoscopy, which allows for interventions on the ovary by dissecting the dense tunica albuginea, drilling - destruction of the androgen-producing stroma, as well as an ovarian biopsy and exclude other genital pathologies. This procedure increases the chances of restoring ovulation and improves the prognosis of an adequate response to the use of ovulation inducers. If a woman refuses such a procedure or there are technical reasons for its implementation, then the patency of the tubes is checked by hysterosalpingography or ultrasound hysterosalpingoscopy. If the patency of the fallopian tubes is impaired, then the issue of laparoscopy or IVF is decided. According to the health order, in vitro fertilization is carried out if pregnancy does not occur within a year of regular sexual activity without the use of contraceptive methods after laparoscopic surgery or after ineffective methods of ovulation stimulation. But if a woman is over 35 years old, then this period is reduced to half a year.
register-eco.ru
What does progesterone support look like after IVF today?
Modern IVF protocols, almost without exception, include 15 days of hormonal support with vaginal forms of progesterone. As soon as implantation begins, the fertilized egg begins to produce its own progesterone.
The function of the corpus luteum of the ovary gradually fades from the 4th–5th week of pregnancy (2–3 weeks after embryo transfer) and ceases to function by the 7th–8th week. During this period, the so-called luteo-placental shift in progesterone production occurs, when the chorion/trophoblast of the fetal egg takes over the production of progesterone completely, becoming independent of maternal progesterone. A healthy embryo does not need additional progesterone, especially since it will not use it.
Progesterone support after IVF (and most often if IVF was performed in the same cycle as stimulation) improves IVF outcome. Longer use of progesterone when a progressing pregnancy is confirmed has no benefit or advantage. The combination of different forms of progesterone and an overdose of the hormone are not recommended after using reproductive technologies.
Progesterone withdrawal regimens do not exist and never have existed. A gradual reduction in the dose of progesterone is an invention of doctors, based on their lack of knowledge about the role of progesterone in the progress of pregnancy.
Other medications (tablet estrogen, hCG, GhRH agonists, heparin, aspirin, vitamin D, other vitamins, various dietary supplements) are not used as maintenance therapy after IVF in modern reproductive medicine, as they have a placebo effect.
Superovulation stimulation protocols
Reproduction specialists have several types of protocols in their arsenal that are used to stimulate the ovaries. The protocol is prescribed by the attending physician based on the identified pathological abnormalities in the woman’s reproductive health, her age, sensitivity to drugs, tendency to allergies and other individual characteristics.
We have already mentioned that all protocols that result in superovulation are based on complete or partial blocking of natural hormonal levels. First of all, we are talking about the temporary “destruction” of natural luteinizing (LH) and follicle-stimulating (FSH) hormone. Their replacement is carried out using synthesized analogue hormones, the dosage of which is selected individually.
In order to monitor the effectiveness of the drugs used, ultrasound examinations are carried out regularly. According to established standards, during ovarian stimulation the endometrium should grow by 1 mm, and the follicle by 2 mm daily. If ultrasound diagnostics record indicators significantly lower, methods of ovarian stimulation can be reviewed on an individual basis, starting from changing the dosage of the drug and ending with its change.
Each protocol pursues very specific goals, regulated by the amount of hormonal agents consumed. Thus, IVF with minimal stimulation aims to collect the maximum number of oocytes in order to subject them to cryopreservation. The fact is that such a treatment regimen copes well with increased follicular growth, but inhibits the growth of the endometrium. Therefore, direct embryo transfer is carried out in other cycles that are favorable for these purposes.
Read more about different IVF protocols.