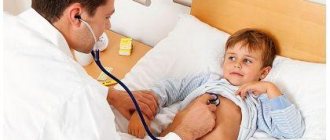
Vomiting is a reflex sudden emptying of the stomach, which triggers the vomiting center of the medulla oblongata. The nature of the vomit can help determine the cause of the vomiting itself.
Immediately before the process of vomiting, the child experiences deep, rapid breathing, increased salivation and nausea.
The gag reflex is reproduced due to the lowering of the diaphragm and closing of the glottis. The cause of vomiting may lie in various types of infections, neuralgic pathologies, and operations.
The processes of regurgitation and vomiting are different from each other. During regurgitation, the diaphragm and abdominal muscles do not tense; the process occurs without any effort due to the stomach being full of food and air.
Vomiting is dangerous because the child’s body is unable to protect the respiratory tract from food expelled from the stomach.
It is necessary to immediately call a doctor if the vomit contains blood or brown impurities. Frequent vomiting leads to dehydration; to avoid fainting and fever, you should call a doctor.
Vomiting of mucus is caused by various diseases of the central nervous system, food poisoning, as well as surgical pathologies. Vomiting occurs with appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, gastritis.
Vomiting can also be caused by increased intracranial pressure, inflammation in the brain, or damage to the inner ear. These reasons will be indicated by frequent fainting, sharp deterioration of vision, tachycardia and severe pain in the head.
1 Under no circumstances should you leave your child alone.
2 Place the child on his side or keep him upright to prevent choking on vomit.
3 After each vomiting process, it is necessary to wash the sick child and rinse his mouth.
4 Until the cause of vomiting is determined, it is forbidden to give any food or medications.
What is vomiting, what symptoms can it be accompanied by?
Vomiting is caused by a reflex and begins when the vomiting center in the brain is irritated - when impulses arrive from the liver, kidneys, olfactory organs, etc. he gets excited. First, the child feels nauseous, and then the stomach immediately empties through the mouth.
The release of its contents is a specific protective reaction for the body. This way it is cleansed of harmful substances produced by itself or coming from outside. Before the onset of vomiting, the baby experiences the following symptoms:
- cold sweat;
- pale skin color;
- uneven breathing;
- increased salivation;
- semi-fainting state.
What should parents not do?
Some common cough remedies may do more harm than good.
For example, for rubbing it is better to choose products that do not have a strong odor.
Ointments and rubs containing menthol, camphor and other strong-smelling ingredients should be used with caution.
They can irritate the already inflamed mucous membrane and cause new coughing attacks.
For dry coughs, mustard plasters are contraindicated. For bronchitis and tracheitis, they are used to increase blood flow to the respiratory organs. This speeds up the discharge of sputum. But with tracheitis, this remedy will only worsen the patient’s condition.
Firstly, there is a risk of knocking over the pan and getting burned by boiling water.
In addition, under the influence of hot steam, blood vessels dilate and swelling of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract increases.
Because of this, the outflow of fluid from the paranasal sinuses is disrupted and complications may arise.
Sometimes, to treat cough, parents use nebulizers and compressor inhalers designed to treat severe forms of bronchial asthma.
Only a few bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory drugs for asthmatics, a few antibiotics and the drug Ambroxol are registered for nebulizer use. Other drugs cannot be poured into the inhaler chamber.
A severe cough that causes your baby to vomit is not a reason to panic. This is a signal that parents should identify the cause of the cough and begin treatment as soon as possible. When planning treatment, you should choose effective, proven methods and not experiment with the child’s health.
Causes of vomiting in children
No fever or diarrhea
Frequent vomiting with a small amount of bile is observed with gastritis, but there are other causes of vomiting without diarrhea while maintaining a normal temperature:
- gallbladder dysfunction;
- reflex response to irritation of the digestive tract;
- release of food due to nervousness (more often observed in children over 6 years of age);
- damage to the nervous system;
- mucus accumulated in the nasopharynx during a runny nose;
- overeating (the risk of vomiting increases with active games that begin immediately after finishing a meal);
- eating too fatty foods;
- disorders of the pancreas.
Vomiting in a child 2 years of age or older that does not get better may be a sign of an object being swallowed and stuck in the esophagus. The baby complains of difficulty swallowing saliva and pain.
Vomiting and diarrhea without fever
When a child has diarrhea, he vomits, but there is no increase in the readings on the thermometer, this indicates that the body's defense system is working - it is trying to remove toxins. These are the symptoms:
- poisoning;
- dysentery, rotavirus, other intestinal infection;
- allergies;
- gluten or lactose intolerance.
Severe vomiting in a child and diarrhea, pain concentrated in the navel area are signs of appendicitis. There is no temperature at the beginning of the development of inflammation - it will rise only a few hours after the end of the attack.
The disease most often affects schoolchildren, but there are cases of it being diagnosed in one-year-old children.
Vomiting may be accompanied by an imbalance of intestinal microflora. After eating, the baby begins to experience colic, frequent vomiting and diarrhea up to 10–15 times a day. Food is poorly digested and weakness appears.
Causes
Vomiting mucus is possible when:
- Acute inflammation of the gastric mucosa, caused by poisoning with chemical compounds or taking medications.
- Viral respiratory tract infection.
- Surgical diseases of the abdominal cavity, such as intestinal obstruction, acute cholecystitis or appendicitis.
- Food poisoning.
- Brain damage, for example, due to meningitis, tumors, epilepsy and other pathologies.
- Stress caused by worries, strong emotions and nervous overload.
- Entry of a foreign body into the esophagus.
In infants, vomiting, which produces mucus, is a harmless symptom. The gag reflex can be caused by overeating, and mucus enters the secreted masses from the bronchi and nasopharynx.
First aid for a child who is vomiting
If a child is sick due to overeating, allergies, or fatty foods, you need to wait a couple of hours, monitoring his condition. Next time, infants should be given less milk, and older children should be given light food.
If the baby vomits, you need to:
- invite him to rinse his mouth with water or wipe his lips with a wet cloth;
- lay the child down and raise the head to prevent fluid or mucus from flowing into the trachea;
- Give boiled water to drink – 2 tsp for babies up to one year old. at intervals of 5 minutes, from 1 year old - 3 tsp, from 3 years - 4 tsp.
To restore the water balance, you can prepare a solution from Oralit, Gastrolit or Regidron. The child is fed 1–3 tsp. liquids every 10 minutes. If the baby vomits in his sleep and only once, he should be calmed down and placed on his side. A sleeping child can also be given liquid by dropping it with a pipette, 1-2 drops per cheek.
If the child feels well after a single vomiting, it is not necessary to call a doctor. If it is caused by poisoning, you need to perform gastric lavage. To do this, use a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate or water with salt dissolved in it (proportions - 2 tsp salt per 2 liters of liquid). The child should drink about 2 glasses, after which he should vomit.
If your baby is constantly vomiting, you should not put him down. The ideal position is semi-horizontal with the head turned to one side. If you are vomiting all day long, which is accompanied by diarrhea, pain, pale skin and lethargy, you should urgently call a doctor.
Treatment of cough before vomiting
Vomiting and coughing in a child without fever is usually caused by tracheitis and pharyngitis. For these diseases, it is necessary, first of all, to humidify the air in the room where the patient is. If you don’t have a special device, you can hang wet sheets to do wet cleaning. Drops of moisture dilute sputum and facilitate its easy evacuation.
To do this, close the door and open the hot water tap. When the air becomes humid, hold your baby and sit for 20 minutes.
If you have a wet cough, you need to stimulate the discharge of mucus by drinking plenty of water - apple juice, warm chicken broth. Avoid citrus drinks. They irritate the inflamed epithelium of the oropharynx. Drinking fluids also softens dry coughs.
Inhalations
Helps eliminate dry and wet cough inhalation. Advantages of the method:
- medications and solutions act directly on the epithelium of the respiratory tube, which reduces the risk of allergies;
- sputum thins;
- spasm of the laryngeal muscles is relieved;
- mucus removal is accelerated.
Five-minute inhalations can be carried out from a kettle with mineral water or saline solution. Infusions of herbs such as chamomile, eucalyptus, St. John's wort, and sage are suitable for warm, moist inhalations. Adding baking soda to the solution relieves dry and irritated throat. The old method is also used - inhaling steam over jacket potatoes.
Essential oils of eucalyptus, rose hips, and peach are used. Add 15 drops of oil to 100 ml of hot water. The composition is placed in a kettle. The child breathes steam through a paper funnel inserted into the spout of the kettle.
For bronchitis, it is convenient to use an inhaler into which the medicine is poured. In the nebulizer, it is converted into fine particles that penetrate the alveoli. Effectively eliminates bronchospasm Berotec, Atrovent, Berodual. If your child vomits from coughing during the procedure, calm him down and clean up soiled items.
Inhalations are not performed for children under 3 years of age to avoid bronchospasm.
Compresses
Sometimes compresses are used to treat dry cough. The most famous method is an application of grated boiled potatoes with the addition of sunflower oil. A gauze pad with the applied composition is applied to the back and chest, leaving the heart area free.
Diagnostic methods
Frequent vomiting in a child requires going to the hospital. Before this, parents should inspect the vomit for the presence of unusual impurities, odors, etc. – this will be needed to make a diagnosis. The following studies will help determine the cause of poor health:
- blood and urine tests;
- allergy tests;
- bacteriological examination of vomit and feces;
- ultrasound examination of the peritoneum and brain;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy for suspected gastrointestinal diseases;
- X-ray with contrast.
How can it be dangerous?
Symptoms of severe coughing leading to vomiting are dangerous because the disease may not have been noticed immediately.
That is, this is already a lingering cough, an advanced disease . Sometimes this is how parents can “miss” bronchitis or, as already mentioned, pneumonia.
Finally, such a cough irritates the esophageal mucosa, causes suffering to the child, and can cause eating disorders. Therefore, you need to react in a timely manner: relieve the attack, identify the cause, and begin adequate comprehensive treatment.
Any therapy must be prescribed by a doctor . Do not diagnose your child yourself, do not give him medications without consulting your doctor. Remember the ideal regime and conditions for the patient, plenty of fluids and humidified air.
Recipe for a natural cough remedy for a child in this video:
Source: pediatrio.ru
What is forbidden to do if a child is vomiting?
Providing first aid can harm the baby, so it is worth remembering that when vomiting it is strictly prohibited:
- rinse the stomach when the child is unconscious;
- select and buy enzymes, antibiotics, antiemetics, painkillers without a doctor’s recommendation;
- use antiseptics for gastric lavage.
If the child feels well, you still need to go to the doctor for a second appointment. He will examine the baby and interview the parents to make sure that the little patient is on the mend.
Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist, graduated from Samara State Medical University with a degree in Pediatrics. Read more »
Traditional methods of treating cough
If a child coughs and vomits, traditional methods help:
- Black radish with honey works well against colds. To prepare the potion, cut out the middle of the vegetable, into which 1 tbsp is poured. l. honey After steeping overnight, the drink is drained and used without dilution.
- A decoction of figs in a glass of milk is used for dry cough due to viral infections.
- Warm milk with mineral water from Essentuki or Borjomi removes toxins and softens the throat.
- Squeezed juice from fresh cabbage acts as an expectorant.
- Carrot juice mixed with sugar syrup fights against dry cough. Children take 1 tsp. 5 times a day.
- A decoction of viburnum helps relieve a painful dry cough. A glass of berries is poured into 1 liter of water and boiled for 10 minutes. After cooling to 60 degrees, add 3 tbsp. l. honey Children are given a quarter glass three times a day.
Should I call a doctor?
In most cases, if you are vomiting mucus, you should seek medical attention because this symptom may indicate the development of a serious illness and lead to dehydration. In addition, there is always the possibility of stomach contents getting into the baby’s respiratory tract, which is also dangerous for the child (especially for the infant).
Be sure to call a doctor in the following situations:
- Vomiting with mucus is combined with other symptoms of the disease - fever, pain, lethargy, drowsiness, loose stools and others.
- In addition to mucus, blood appeared in the vomit.
- You suspect that a large object has entered the child's esophagus.
- Before vomiting, the child took medication or ate poisoned food.
- Vomiting mucus appeared after hitting the head or falling.
- The child began to become dehydrated.
Vomiting mucus
Sudden emptying of the stomach is commonly called vomiting. The gag reflex is triggered by the vomiting center located in the medulla oblongata. At an early age, children often feel sick. The nature of the vomit can determine the cause of this condition.
Vomiting mucus in a child
Before vomiting, the child begins to breathe deeply and quickly, his salivation increases and nausea appears.
The diaphragm lowers, the glottis closes, the stomach contracts and vomiting occurs. Vomiting can occur due to infection, central nervous system pathology, surgery, and so on.
Regurgitation and vomiting are not the same thing. The baby burps effortlessly, the diaphragm and abdominal muscles do not tense. This process occurs due to the fact that the stomach is full of air or food.
The danger of vomiting lies in the fact that the imperfect child’s body cannot protect the respiratory tract from vomit. Often what is expelled from the stomach ends up in the respiratory tract.
An ambulance should be called if there is blood or something brown in the vomit. Vomiting can lead to dehydration, especially if it occurs every two hours. A doctor is needed if this condition is accompanied by lethargy, high fever or loss of consciousness.
What needs to be done before the ambulance arrives?
Firstly, under no circumstances should you leave your child alone. Secondly, in order to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract, you must either lay the child on his side or hold him upright. Thirdly, after each act of vomiting, you need to wash the child and rinse his mouth. Fourthly, until the cause of this condition is found, the patient should not be given food or medicine.
Vomiting mucus in a child may be due to surgical pathology, food poisoning, or central nervous system diseases.
Surgical diseases of the abdominal cavity are often accompanied by vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation. With appendicitis, cholecystitis, gastritis, intestinal obstruction and other diseases, vomiting often occurs.