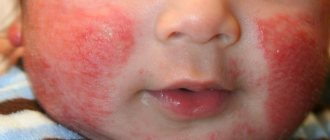
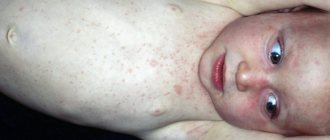
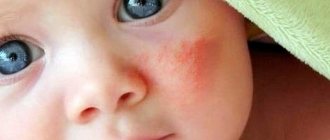
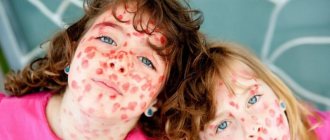
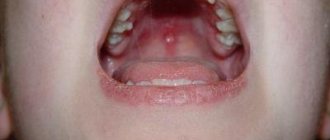
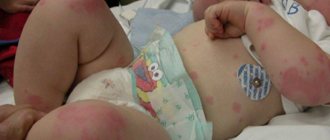
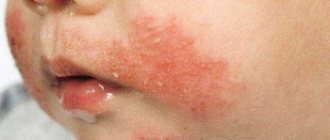
Allergy to the sun (solar urticaria) occurs in children at any age. Photodermatitis is increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight. For characteristic rashes to appear, just walking in direct ultraviolet rays is enough. Solar urticaria affects children with fair skin, red hair and freckles. Diseases of the endocrine system, kidneys, and liver contribute to the development of photodermatitis. The illness may go away in one day, or it may drag on for a long time.
Causes
Photodermatitis can appear after half an hour in the sun or after artificial sunbathing, taken in the treatment of certain diseases. Ultraviolet radiation is not the root cause of allergies, but provokes them.
Causes of sun allergies in children:
- Rare diseases - pellagra, Gunther's disease;
- Creams containing essential oils of citrus fruits, dill, St. John's wort, and brown tree bark reduce the resistance of skin cells to light;
- The use of sunscreens with para-aminobenzoic acid in children leads to severe allergies;
- Hygienic lipsticks with eosin are the strongest allergen;
- Antiseptics cause skin irritation in hot weather;
- Food products containing dyes, preservatives and flavors;
- Paints used for drawings on the body containing cadmium sulfate;
- Household chemicals – gels, shampoos, foams, washing powder, conditioners;
- Medicines taken during hot periods;
- Chlorinated water;
- Plant pollen.
Children with weak immunity, milky white and sensitive skin are most susceptible to allergic reactions. If a child cannot tolerate chocolate and nuts, then there is a high chance of developing a rash.
Kinds
With the onset of summer days, the time spent under ultraviolet rays increases. The desire to tan causes the appearance of allergic marks on the skin in the form of burns. They can appear in a few minutes or hours, depending on the intensity of the sun's rays and skin type.
Sometimes intolerance also occurs in a healthy person with a strong immune system who does not have a tendency to allergic reactions.
Inattention to safety rules leads to skin problems, most often in young children and people suffering from chronic diseases.
Types of solar allergies:
- Phototoxic allergies occur when taking medications containing photosensitizers under the influence of the sun. The appearance of intolerance can be judged by the symptoms: blisters, hives, swelling of the skin. Cosmetic procedures (peeling, tattooing), making the skin sensitive to external influences, can cause the appearance of photodermatosis.
- Phototraumatic allergies develop after prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Skin reactions (burns) will appear more quickly after exposure to direct sun at lunchtime, when the radiation is especially intense. You can observe such an example on the beach, when in completely healthy people, instead of the desired tan, the skin acquires a crimson color. It goes away on its own as soon as a person stops being exposed to solar radiation.
- A photoallergic reaction occurs in a child whose body does not perceive ultraviolet radiation, reacting to it as if it were a toxin. Pigmentation is disrupted, a rash appears, and the skin thickens. The temperature rises, disorientation is possible, including loss of consciousness. Characteristic is the development of urticaria and eczema, which look like a papular rash of various sizes and shapes.
Such an allergy requires constant monitoring, tracking time spent in the sun, and protecting the skin, especially in the summer.
Depending on the body’s contact with allergens, there are two types of allergies:
- Exogenous or external.
- Endogenous or internal.
Exogenous photodermatosis develops under the influence of ultraviolet radiation when certain components come into contact with the skin. Allergens include substances that, under the influence of the sun, as a result of chemical reactions, will cause the appearance of symptoms:
- Cosmetics (deodorants, lipstick).
- Perfumery.
- Sunscreen preparations containing benzophenone or para-aminobenzoic acids.
- Essential oils (citrus, sandalwood).
- Household chemicals.
- Care and hygiene items.
Stopping interaction with these substances reduces the severity of allergy symptoms until they disappear completely.
Endogenous photodermatitis is associated with metabolic disorders. The causes of allergies are hypovitaminosis, weakened immunity, melanin metabolism, pathologies of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, Prurigo's disease, and infectious diseases.
Allergies occur as a result of consuming the following things:
- Medicinal anti-inflammatory tablets, antibiotics, antidepressants.
- Hormonal medications containing estrogen.
- Traditional medicine, herbal preparations.
- Food products (citrus fruits, chocolate, honey).
- Pollen, when ingested during respiration.
In this case, the symptoms of photodermatitis also disappear after the allergens are eliminated from the body.
Based on its origin, photodermatosis is divided into acquired and congenital.
Acquired sun allergy occurs due to:
- Melanin deficiency.
- Immune failure.
- Accumulation of porphyrin in skin cells.
Allergies can be caused by the abuse of solariums, visiting countries in a different climate zone, different from the zone of permanent residence, abuse of alcohol, drugs, and medications.
Congenital photodermatitis is explained by heredity (true porphyria or Gunther's disease, xeroderma pigmentosum and others). This type of allergy is rare.
Classification
Based on the type of exposure to ultraviolet radiation, the following reactions are distinguished:
- Photoallergic – itching, burning, the appearance of rashes of varying sizes. Child's skin does not tolerate ultraviolet radiation.
- Phototoxic - rash, itching, swelling of mucous membranes, weakness, drowsiness. Allergens are provoking substances containing photosensitizers.
- Phototraumatic – burns that occur during prolonged exposure to the sun on any exposed areas of the body. The situation can be prevented by using protective creams. You also need to remember that it is not advisable to sunbathe between 11 a.m. and 4 p.m.
Allergies are considered to flourish in late spring and summer; in cold weather they subside.
Signs
The symptoms of sun allergy are difficult to miss, although the main signs may appear only after 12 hours.
Allergic rashes appear on open areas of the body: on the face, chest, arms. Not only the skin reacts, but the whole body.
Distinctive signs of allergies:
- Dizziness, loss of consciousness;
- Hyperthermia;
- Headache;
- Skin rash, blisters, redness, peeling, itching, burning;
- Swelling not only in the child’s eyes, but also in the nasal mucosa of the larynx;
- Puffiness;
- Digestive disorder;
- Sleep disturbance;
- General weakness.
Photodermatitis can occur in three stages:
- In mild cases, redness and peeling of the skin are observed;
- In more severe cases, serous accumulations appear inside the formed blisters and painful sensations during friction;
- In the third stage, blisters appear that burst, forming itchy sores.
If there is any doubt about the skin rash, it is recommended to have a scraping done at the clinic.
Chromophores are substances found in human skin that protect it from exposure to ultraviolet radiation. The concentration of this substance in the body increases with age. Photodermatitis can be outgrown, and allergy symptoms will become less pronounced or go away altogether.
In children under three years of age, prolonged exposure to the sun has a more pronounced allergic reaction. In no case and under any circumstances should an infant be left exposed to direct ultraviolet rays. An allergy to the sun in a child under one year old poses the greatest danger. The child refuses to eat and drink, which leads to dehydration and requires hospitalization.
Diagnostics
When a rash appears in a baby, it is advisable to show it to a doctor, since an inexperienced mother will not always be able to distinguish an allergy from a neonatal rash, or a viral infection from a fungal one. It is better to call a doctor at home, because with infectious diseases the baby is contagious. For which rash should you immediately call a pediatrician:
- With a small red rash, with a watery rash, accompanied by a rise in temperature, runny nose, and general weakness of the child.
- For a rash with purulent heads.
- For any type of rash, if it is extensive and covers more than 2% of the child’s skin.
- For any rash, the appearance of which preceded or occurred immediately after vomiting or diarrhea.
You can go to the clinic yourself if:
- a minor rash that does not in any way affect the baby’s general well-being (body temperature is normal or slightly above normal, there are no pustules, diarrhea, or nausea);
- single rash in the hair area, on the face.
You can treat yourself without a doctor only for diaper rash and prickly heat; you can also do it yourself in the case of neonatal hormonal rash, which looks like acne. The location of the rash is also of great importance. So, a rash on the stomach, back, lower back and inner thighs is always a reason to call a local pediatrician at home.
A rash on the neck, in the skin folds and on the back of the head is not such an alarming symptom, but consulting a specialist will not hurt in this case either. A rash on the butt and face is a reason to reconsider the diet of a nursing mother, and also make sure that hygiene is adequate.
Methods for diagnosing rashes in children are extensive. They include general and extensive tests of blood, urine, feces, scrapings of the epidermis for the presence of parasites, fungi, content analysis and the presence and type of bacteria, viruses, serological diagnostics.
Doctors who will help find the cause and prescribe adequate treatment:
- pediatrician;
- dermatologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- allergist.
First aid
It is not always possible for parents to see a doctor at the first symptoms of an allergy, or the wait for specialists is delayed. It is necessary to remain calm and take immediate assistance measures:
- Take the child out of the sun to a dark place;
- Give an antihistamine, the dosage should be appropriate for the age;
- Drink more liquids - plain non-carbonated mineral water with lemon;
- Moisten the affected areas of the skin with chamomile solution or green tea;
- Measure body temperature and give antipyretic if necessary.
Only a doctor should prescribe antiallergic drugs. You can find out about a single dosage by calling an ambulance.
How to treat sun allergies?
Treatment for solar urticaria depends on the severity of symptoms.
Staying out of the sun may relieve symptoms for mild allergy cases. The doctor may also prescribe oral antihistamines to soothe the rash or over-the-counter creams such as aloe vera or calamine lotion.
If the reaction is more severe, then other treatments are used - corticosteroids, hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), Montelukast (Singulair), which is usually used to treat asthma.
The British Association of Dermatologists suggests trying other treatments, including: cyclosporine (Sandimmune), the immunosuppressant omalizumab (Xolair), photopheresis, intravenous immunoglobulin.
Treatment
It is recommended to treat allergies in children using traditional methods. When using traditional recipes, a child may have an unexpected reaction to herbs. However, if the skin rashes are isolated and you already have experience with the successful use of the plants used, compresses made from them will be very useful.
Drugs
Drug treatment for allergies involves taking antihistamines. For children they are produced in the form of drops. Taking such medications has a time limit of no more than 5 days.
The most common:
- Zyrtec;
- Zodak;
- Loratadine;
- Fenistil;
- Suprastinex.
Local ointments, gels, creams will help get rid of skin rashes and pain:
- Fenistil;
- La Cree;
- Advantan;
- Desitin;
- Wundehill;
- Gestan.
Enterosorbents will not be superfluous; they remove allergens from the body:
- Activated carbon;
- Smecta;
- Polysorb.
They are taken for 3-5 days.
During allergies, it is recommended to take vitamins A, B, E, C. Their deficiency can be compensated for with food or purchased in the form of tablets at the pharmacy.
Folk remedies
The first assistants to traditional methods of treating allergies are considered to be herbs and vegetables. Effective home recipes:
- Chamomile is used as a tincture, which improves the general condition of the body, and also as a compress to relieve inflammation;
- Nettle infusion relieves redness, itching and burning of the skin;
- Aloe compress restores the epidermis, cut it and apply it to the affected areas twice a day;
- Apply a mixture of potato and cucumber to the areas of inflammation;
- Use juice from squeezed cabbage and potatoes to wipe the rash;
- While bathing, add infusions of chamomile, string or valerian to the water.
All traditional methods are good in combination with drug treatment. Do not use unfamiliar traditional medicine. Children are not objects for experimentation.
Read more about reaction to ultraviolet light
All mothers know that the sun's rays are beneficial, because under their influence vitamin D is produced, which is not synthesized by the body itself. Therefore, walks during daylight hours must be included in the daily routine.
But the “clear and warmly warming” sun is not always safe. After being outside or on the beach, your child may experience skin irritation in the form of pimples, blisters and red spots. It is very important at this moment to contact a pediatrician who will rule out other types of allergies: food, medications and personal hygiene products.
After examining a small patient, sometimes the doctor diagnoses photodermatitis or photodermatosis, that is, increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight. This disease can worsen and cause dangerous consequences for infants and older children. That is why it is important to promptly diagnose a skin reaction to ultraviolet radiation.
Prevention
It is possible to prevent allergic dermatitis in children by following preventive measures:
- Strengthening immunity;
- Plenty of fluids during hot periods, preference should be given to plain water;
- Do not overload the child’s stomach on a hot day, take healthy food;
- Before going outside, do not eat sweets, carrot juice, sweet peppers, figs, parsley;
- Do not overheat the child by wearing synthetic clothing;
- Clothes should cover the shoulders and stomach, and do not go outside without a light, wide-brimmed headdress;
- Wear things made of linen or cotton, white or red;
- Do not stay in the open rays of the sun for a long time, especially during dangerous hours;
- Apply a safe protective cream.
By following preventive measures, allergies will not cause a spoiled holiday.
Allergy to the sun is an unpleasant phenomenon, but with the right approach you can forget about this problem. If the first signs of sun allergy occur, you should consult an allergist. Frequent allergic reactions may be a sign of more serious illnesses.
How is sun allergy different from heat rash?
Heat rash occurs when pores become clogged and sweat accumulates under clothing or blankets. This can happen without exposure to sunlight - for example, in hot, humid weather on any part of the body that sweats, especially in the folds of the skin.
Areas most at risk for heat rash:
- under the breast;
- in the groin;
- in the armpits;
- between the inner thighs.
Solar urticaria, on the other hand, only occurs as a result of exposure to sunlight.
Heat rash usually goes away on its own after a few days, while sun rash usually lasts only a few hours.