Kinds
Allergic rashes in children affect not only the skin, but also damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes and nose. Particularly dangerous is a generalized allergic reaction that affects the respiratory tract, cardiovascular and endocrine systems, often leading to anaphylactic shock and death.
The types of allergic rashes in children by origin come down to two main options: caused by poor diet or contact with an allergen.
Food
Rash due to food allergies in children is most often caused by foods introduced in the form of complementary foods, artificial formula, and breast milk due to poor nutrition of the mother. An allergic rash in a one-year-old child is associated with errors in diet and drug therapy prescribed for various reasons.
With food allergies, the rash in a child does not have a clear localization, is usually widespread and appears in the form of spots. Parents note an increase in skin manifestations after feeding.
Non-food
A non-food type of allergic rash in an infant occurs quickly after local exposure to an irritant, since the immune defense mechanisms are not fully formed, and the skin is delicate and extremely vulnerable.
If the allergen is identified in time and contact with it is eliminated, the pathology is only local in nature and can be easily eliminated. It is often provoked by the use of low-quality diapers, creams, and powders. Non-food allergies in a child usually present as a rash on the legs. Small red spots are also often located on the buttocks.
What it looks like on the skin: types, localization
Any allergy is a signal of a disorder of the immune system . If the body's sensitivity is increased, negative reactions appear upon contact even with factors that are harmless to most people - animal fur, plant pollen, food, medicine, cold air.
A rash in children can be located on different parts of the body and manifest differently depending on the type of allergen:
- pustule - a small cavity with purulent contents inside;
- plaque - a flattened formation that rises above the skin;
- papule - a protruding tubercle with a diameter of up to 5 mm without a cavity inside, which can be palpated;
- spot - a discolored area that does not protrude above the skin and cannot be felt during palpation;
- vesicle - a cavity with a diameter of up to 5 mm with liquid inside;
- bubble - a vesicle measuring 5 mm or more.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you about a child’s rash:
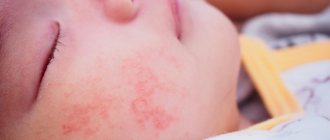
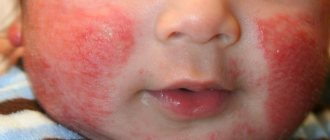
A rash with food allergies in children most often appears on the cheeks, in the area around the mouth, contact dermatitis - in the place where the skin comes into contact with the allergen.
And hay fever (pollen allergy) can manifest itself not as individual rashes, but as general swelling and redness of the face.
Visual photographs
Allergic rash in children on the back:
In the arms of a child:
On the legs and body of a child, photo of allergies:
Childhood eczema
This type is characterized by the presence of an exudative component - liquid is released from small blood vessels, which fills the rash.
In infants, it most often occurs in the form of exudative diathesis, one of the manifestations of which is itchy nodules that appear with a certain frequency.
May be accompanied by peeling, diaper rash, and induration. The manifestations are identical to the rashes in adults, but in children the tendency to merge and exudative symptoms are more pronounced.
Hives
Skin disease, also called urticaria, refers to dermatitis, which is based on an allergic reaction.
This type of dermatitis got its name because the rash resembles nettle burns. Flat, slightly raised, light pink to red-orange blisters appear quickly and are very itchy.
Occurs in acute or chronic forms. The duration of the acute variety of urticaria ranges from several days to 1–2 weeks, and the chronic form can last for months or even years, sometimes manifesting itself, sometimes dying down.
The cause is most often medications or some type of food.
Allergies and rashes in a child can occur to antibiotics, gamma globulins, serums, and X-ray contrast agents. Quite rare, but even parasites that live inside the body can cause urticaria to appear on the skin.
You can learn how to properly instill Otipax in a child from this article.
You will find reviews from parents about the use of the drug Glycine for children in this material.
Instructions for using Arbidol syrup for children are discussed in detail in our publication.
Cold allergy
This type of rash is called cold urticaria . They appear in the form of red spots or nettle fever in response to cooling of the whole body or some part of it. The rash that appears is itchy and may be accompanied by swelling.
Multiple formations increase in size, merge with each other over time, turn pale when pressed, and cause a burning sensation and itching.
Atopic dermatitis
This is a chronic dermatitis of an allergic nature, which has a seasonal dependence. In winter there are usually exacerbations, and in summer it is time for remission.
The rash may be lichen-like or exudative (fluid-filled).
They are usually located in the elbows, knees, armpits, on the face, neck, scalp under the hair, in the groin area, under the earlobes.
Sometimes with atopic dermatitis, keratinized papules appear on the elbows, lateral surfaces of the forearms, and shoulders.
Causes
The appearance of an allergic rash in a baby is due to the following reasons:
- illnesses of a woman during pregnancy;
- complications during childbirth, perinatal pathology;
- the presence of allergic diseases in the father or mother;
- taking antibiotics, antiviral and vitamin preparations and other medications by a nursing woman;
- maternal malnutrition;
- artificial feeding;
- drug therapy prescribed to the baby due to illness;
- low-quality children's clothing made from synthetic fabrics;
- bad ecology;
- bites of blood-sucking insects;
- prolonged exposure to fresh air during the flowering period of various plants (birch, quinoa, wormwood, poplar);
- frequent hypothermia;
- excessive insolation during summer;
- long stay in a dusty room;
- close contact with pets (fur, saliva, fluff).
An allergic rash in children under one year of age can be caused by immunodeficiency, disruptions in the enzymatic activity of the stomach or intestines, or the presence of parasites.
A mild allergic rash in a newborn on the face and chest is often explained by the removal of mother’s hormones obtained in utero. Manifestations of exanthema disappear without medical intervention.
Allergies in children: features and causes
Just a couple of centuries ago, the world did not even know what an allergy was, but today every third child suffers from it. At the same time, the symptoms of the disease often pass “under the guise” of completely different diseases, which can lead down the wrong path of treatment. So how not to confuse childhood diseases and identify their real cause?
How does it arise
All allergic reactions can develop in at least 4 ways, but in this article we will talk about the first and most common of them - the IgE-dependent way.
The characteristics of a child’s body, especially in the 1st year of life, normally protect the child from the development of allergies. The immune system is designed in such a way as to “introduce” the baby to the abundance of surrounding antigens, without causing pathological conditions.
In some cases, this mechanism fails, which may be due to:
- heredity (one parent “with allergies” - 30% risk of pathology in the child, both parents - 60% risk);
- violation of the barrier function of mucous membranes;
- innate characteristics of immunity.
In this case, at the first “meeting” with an allergen, the body only “remembers the unpleasant object” (begins the synthesis of IgE antibodies to the allergen), and the second time it “attacks” it.
The protection mechanism is implemented due to biologically active substances released by cells “on command” of IgE antibodies, and manifests itself:
- expansion of capillaries and increase in their permeability = redness and swelling (to accelerate the entry of immune cells into the lesion),
- irritation of nerve endings and spasmodic contraction of the “target” muscles = itching, coughing, sneezing (as a way to mechanically “get rid” of the allergen),
- increased mucus production = runny nose (to facilitate binding and removal of the “irritating” object).
Interestingly, allergies and acute respiratory viral infections have similar “points of application”. This causes the similarity of symptoms, as well as the tendency of allergy sufferers to acute respiratory diseases.
Symptoms and causes
Conventionally, allergic diseases can be divided into respiratory (inhaled antigens) and food. Symptoms of the former range from a slight runny nose to severe suffocation, while the latter have skin and “digestive” manifestations.
A “respiratory” allergy in a child can manifest itself not only with classic symptoms, but also simply with a “constantly stuffy nose,” and the cause may be:
1.mites (house dust, feather duster, flour mite and others)
This allergy appears upon contact with dust (household dust, books) and carpets, and most often occurs in a certain room.
2.down and feathers of birds
The reaction can be associated with both live birds (parrots, canaries and others) and with bedding (pillows and blankets), in which down and feathers are used as filler. In the second case, the allergy most often manifests itself during sleep and immediately after waking up (nasal congestion or cough that goes away during the day)
3.dander and epithelium of animals (cats, dogs, hamsters, guinea pigs, horses, etc.).
At the same time, wool (hairs) itself is safe in the context of allergies. The reaction is caused by skin elements that accumulate on the fur.
4. “domestic” molds
They live in warm, damp and poorly ventilated places in the room: seams between tiles in the bathroom and the space under the wallpaper of “damp” walls. Symptoms are often severe and only subside with prolonged stay outside the “allergenic” room.
5.trees and grass
Allergies are seasonal and appear during the flowering period of the plant: late spring, summer or early autumn.
Skin symptoms, in mild cases, consist of an itchy rash that goes away when the allergen is eliminated. And more severe reactions are accompanied by the development of dermatitis, which is characterized by a chronic course and is difficult to treat.
Thus, bowel irregularities, abdominal pain, as well as nausea and loss of appetite in a child may well be signs of an allergy and require a comprehensive examination.
Among the most “significant” food allergens in children are:
1. cow's milk proteins : β-lactoglobulin, a-lactalbumin, bovine serum albumin, and casein.
Depending on the reaction to certain proteins, dairy products should be excluded partially or completely.
2.chicken egg whites : ovomucoid, ovalbumin, lysozyme.
3.nuts;
4.cereal proteins, especially gliadin (gluten) of wheat and rye, barley and oats;
5.fish and seafood;
6.cocoa, citrus fruits and soy.
Diagnostics
It is often not possible to distinguish allergies from similar diseases by eye. “Experimentally” confirming the allergenic nature of symptoms can only be done by eliminating the “suspected” allergen. And in cases where there is none, laboratory tests can help in diagnosis.
The first stage of diagnosis serves to confirm the allergic nature of the disease and is based on:
1.1 General blood test with leukocyte formula, where eosinophils serve as a marker of allergy.
1.2. A blood test for immunoglobulin E, total and eosinophilic cationic protein, which increases tens and hundreds of times during allergies.
1.3. Microscopic examination of nasal secretions (nasal swab), also aimed at identifying eosinophils.
After establishing allergy as the main diagnosis, you can move on to determining the subgroup or the allergen itself.
The first option is used in case of doubt regarding the source of the allergy, and prefabricated panels are used to narrow the “search circle”. They contain several representatives of an allergy group at once, and the result is given in one number.
These may be allergen panels
- herbs,
- trees,
- animals,
- ticks,
- mold fungi,
- meat,
- dairy,
- citrus
- and many others.
If you receive increased results in any of the panels, you can proceed to the third stage of diagnosis - identifying the allergen itself. To do this, use a blood test for IgE to individual allergens (for example, a specific mold or a representative of citrus fruits).
Symptoms
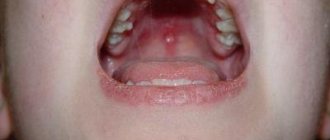
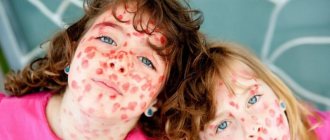
An allergic rash on a child’s body is usually represented by the following elements:
- pink or red spots of various sizes, often prone to merging;
- vesicles, sometimes with hyperemic edging;
- pustules, or small pustules that form when scratching and when a secondary infection occurs.
An allergic rash on the body of a baby is accompanied by swelling of the subcutaneous tissue, thickening of the skin, weeping or dryness. The child is worried about burning and itching. After the severity of the process decreases, skin cracks and peeling appear, crusts form on the cheeks, and faint pigmentation is possible.
In advanced cases, for all types of allergic rashes in children, a violation of the general condition is typical:
- anxiety, causeless crying;
- decreased appetite, regurgitation;
- constant lacrimation, conjunctivitis;
- sleep disturbance due to itchy skin;
- difficulty breathing, coughing.
If a breastfeeding woman consumes allergenic foods, urticaria appears within 3-24 hours. Characterized by unstable stools, in which constipation alternates with diarrhea, often mixed with greens and mucus. Food allergies affect the skin of the face, neck, and forearms. Sometimes it is possible for a child to develop an allergic rash on his stomach. In severe cases, life-threatening Quincke's edema develops.
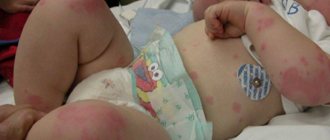
A rash in an infant with an allergy caused by external factors is initially localized at the point of contact - in the elbows, armpits, popliteal fossae, and on the inner thighs. The soles become red and swollen, and blisters appear on them, the contents of which tend to suppurate. Elements of an allergic rash are often found on a child’s bottom.
If measures are not taken in time, allergic rashes on the legs of children can spread to other parts of the body.
The severity of clinical manifestations depends on the characteristics of the body - contact with the same allergic factor can result in a quickly passing rash or anaphylactic shock, often resulting in death.
First aid
The most dangerous allergic reaction is an allergy to medications. Red, swollen spots and itching appear on the skin. Then weakness, dizziness appears, the skin turns pale and breathing becomes difficult. Following the appearance of spots on the skin, swelling of the larynx, nose, lips, face and airways occurs.
Drug allergies can cause angioedema, as well as Lyell's syndrome, so you must immediately call an ambulance and provide first aid.
Actions for severe allergic symptoms:
- sit the child in an upright position to facilitate breathing;
- If an antihistamine is available, give it to the child. If he cannot swallow the tablet on his own, he must crush it and put it in his mouth, followed by a small amount of water;
- calm yourself and your child;
- in case of loss of consciousness, constantly monitor the pupils, breathing and pulse;
- in the absence of breathing and pulse, it is necessary to carry out artificial respiration and indirect cardiac massage until breathing is restored and the pulse resumes.
Which doctor treats an allergic rash in a child?
Treatment of an allergic rash in an infant should begin at its first appearance.
Parents should call their local pediatrician. After interviewing and examining the baby, he will give directions for tests and consultations with specialized specialists - an infectious disease specialist, a dermatologist, an allergist. Allergic skin rashes in children, accompanied by pastiness of the face and neck, wheezing, severe anxiety and other signs of Quincke's edema, require an immediate call to the ambulance.
Forms of manifestation and symptoms
Allergic skin rashes in children are one of the forms of allergic reactions.
Main skin manifestations:
- Hives. It is characterized by the sudden appearance of red spots, occasionally with slightly protruding blisters, with pronounced itching. The cause of urticaria is the ingestion of one of the allergens into the body or onto the skin.
Hives are one of the causes of allergic skin rashes in children.
- Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into regular contact with an allergen.
- Atopic dermatitis. It is formed due to a hereditary tendency to allergies. It is characterized by clearly defined contours of the skin reaction. Initially, the rash appears in one area of the body, but later it may appear in other places. The most common locations for the rash are the cheeks, upper and lower extremities, chest, back and abdomen.
- Eczema. It is characterized by the appearance of swelling, redness, fluid-filled blisters on the skin, and the formation of crusts in places where the blisters break out. Accompanied by painful itching and burning.
- Neurodermatitis. The initial sign is the appearance of severe itching, then redness of the skin occurs with dryness and peeling, and a rash in the form of small blisters appears. The most common places where neurodermatitis is localized are the knees and elbows, neck, and face. The main reasons: exposure to allergens on the skin, but also occurs as a manifestation of food allergies.
- Quincke's edema is a dangerous allergic reaction characterized by swelling of the skin and mucous membranes, pain, burning and itching. The main sites of localization are the face, larynx and genitals.
- Lyell's syndrome is one of the most dangerous skin diseases of toxicodermic nature in children. It is characterized by very rapid development. After 2-3 days from the moment of onset, the condition becomes extremely dangerous, and death is possible. After the temperature rises to 39° C and above, abundant and numerous rashes appear throughout the skin in the form of red spots with slight swelling, which subsequently grow and merge, forming large lesions. Within 24 hours, blisters of various sizes with an easily torn surface appear on the affected areas. In addition to pain, when you touch the skin, the outer layers of the skin begin to peel off, and erosions form in these places. Over a short period of time, the entire skin becomes red. The disease is accompanied by severe pain even with a light touch. With Lyell's syndrome, severe dehydration occurs with its characteristic general manifestations in the form of severe thirst, headache, loss of orientation and drowsiness. In addition to bleeding of the mucous membranes of most organs, disturbances in the functioning of almost all organ systems of the child are observed. The main causes of the development of the disease are infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and taking medications.
Diagnostics
The appearance of a rash on the body if an allergy is suspected in a child implies the following diagnostic measures:
- survey of parents - the course of pregnancy, the mother’s taste preferences, living conditions;
- complete blood count (eosinophilia);
- immunogram (increased immunoglobulin E);
- Analysis of urine;
- Checking stool for worm eggs.
To accurately identify the cause of an allergic rash, tests are carried out with the subcutaneous injection of common allergens. But usually they are used after reaching the age of 5-6 years.
Treatment
It is important to identify the allergen and completely eliminate its contact with the baby. Then the doctor will prescribe an individual treatment regimen in accordance with the symptoms and condition of the little patient.
When treating allergic skin rashes in children, the following pharmacological groups of medications are usually used:
- desensitizing drugs - relieve allergic manifestations - Claritin, Zyrtec, Tavegil;
- sorbents - Polysorb, Enterosgel, Smecta;
- probiotics that normalize intestinal microflora - Linex, Bifidumbacterin;
- hormonal agents - Prednisolone, Dexamethasone;
- immunomodulators - Viferon;
- antibiotics - for the treatment of pyoderma - Cefazolin.
Medicines are prescribed in the acute phase of allergies; they neutralize toxins, relieve swelling, itching, inflammation, preventing anaphylactic shock.
Drugs administered orally must be ground and mixed with milk or formula. Before use, you must carefully study the instructions.
Treatment of allergic rashes in children includes the use of local remedies. Hormonal ointments, gels and creams containing corticosteroids (Advantan, Fluorocort) are used. They help quickly relieve exacerbations and prevent the progression of the disease. Due to unwanted side effects, they are prescribed in short courses and under medical supervision.
Non-hormonal topical agents are used to reduce itching, inflammation and pain. They can be used for a long time, as they have no serious contraindications and rarely cause complications. The moisturizing and wound-healing effect of these drugs is also important. The most popular creams are Bepanten, Elidel, Lanolin, Desitin.
Allergic rashes in newborns, accompanied by redness, swelling, itching, are well relieved by La-Cri cream. It also heals scratch marks.
It is important for parents to know how to behave if a sudden allergy appears:
- calm the baby;
- stop exposure to the allergen - bathe, change clothes, ventilate the room;
- if you have a food allergy, induce vomiting, give a sorbent (Enterosgel, activated carbon);
- drink warm water to remove toxins.
Pathology is also treated with traditional medicine. They use decoctions of oak bark, chamomile, calendula, plantain, and string. They relieve allergic swelling and skin itching when added to the baby’s bath. An infusion of nettle leaves can be used to wipe diaper rash and rashes on the legs. Manifestations of allergies are reduced by cooling compresses using weak soda or saline solutions.
How to treat: basic principles and schemes
The main goal of therapy is to identify the allergen and eliminate it. As long as the child is exposed to the irritant that causes these spots, treatment will be ineffective.
Therapy begins with a visit to the doctor. Self-diagnosis is not allowed - if the rash is due to an infectious disease and not an allergy, you can waste time and lead to complications.
The doctor will identify the nature of the rash and prescribe measures to identify the allergen. In mild cases, it is enough to eliminate the factor causing irritation, and the baby’s skin becomes clear.
Additionally prescribed:
- sorbents - remove toxins and allergic components (activated carbon, Lactofiltrum, Polysorb);
- cool compresses or anti-itch lotions for relief (calamine);
- sedatives - to eliminate increased excitability (valerian tablets, lemon balm decoction, motherwort);
- antiallergic ointments - for cases accompanied by severe rashes (Advantan, Fenistil-gel);
- herbal decoctions - to relieve irritation, swelling, itching (baths with sage, string, chamomile).
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you about allergy medications:
If drug treatment is necessary, antihistamines are used and are considered the first line of therapy.
In difficult cases, it is necessary to supplement with anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants - the last line. They are used in difficult cases due to potentially severe side effects.
If you don’t know whether Acipol can be given to a one-month-old baby, we recommend reading our publication.
Reviews of the use of the drug Miramistin for children are in this material.
Instructions for use and price of the drug Faringosept for children are in this article.
Prevention
Allergies in a child can be prevented with proper care:
- use clothes made from natural fabrics, excluding wool, as it irritates the skin;
- dress according to the weather, avoiding overheating;
- change diapers on time;
- use hypoallergenic detergents;
- exclude contact with pets;
- carry out regular wet cleaning;
- use gels, shampoos, emulsions, creams with natural composition that do not contain hormonal agents or dyes;
- bathe in cool water.
It is advisable to feed newborns with breast milk, as this helps improve immune defense. In this case, it is necessary to exclude citrus fruits, chocolate, coffee, caviar, canned food, nuts, and honey from the mother’s diet. If the baby receives formula, it must be of high quality and hypoallergenic. It is important to control the conditions and shelf life of food products and avoid overfeeding.
To avoid allergy rashes in children, it is important to follow all the pediatrician’s recommendations and not rush into introducing complementary foods and expanding the range of foods. If you have a history of even minimal allergic manifestations, you cannot use non-adapted formulas, milk porridges, and do not introduce cottage cheese for up to 9 months.
An allergy rash in children is a serious sign. If measures are not taken in time, the pathology can lead to anaphylactic shock or provoke the further formation of bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, and dermatitis.
Author: Olga Shchepina, doctor, especially for Dermatologiya.pro