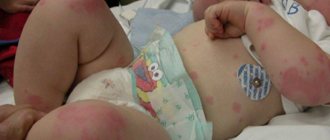
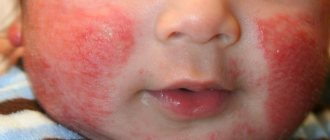
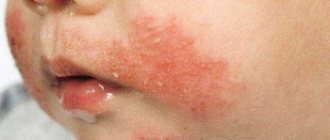
Sore throat in childhood is considered a serious infectious disease. Follicular tonsillitis is especially common in children, one of the manifestations of which is enlargement of the tonsils and the formation of follicles with purulent contents on their surface.
This disease is a consequence of the negative influence of a bacterial infection caused by staphylococci, streptococci or pneumococci. Particularly favorable conditions for the development of pathogenic bacteria are created against the background of a child’s reduced immunity or hypothermia.
Quite often, the parents of the baby are carriers of staphylococcal bacillus. Without being sick themselves, they infect children through everyday life, as a result of which sore throats constantly recur, becoming chronic. In such a situation, it is important to promptly identify the carrier of the infection (a throat swab is a mandatory test) and carry out antibacterial therapy.
Factors predisposing to the development of the disease include:
- Unbalanced poor nutrition;
- Impaired nasal breathing;
- Avitaminosis;
- Prolonged exposure to polluted or dry air.
Features of the development of follicular tonsillitis
Follicular tonsillitis (another name is tonsillitis) is a disease of purulent etiology, mainly affecting the tonsils. It leads to inflammation of the lymphoid tissue and accumulation of pus in the follicles. Usually changes are observed in the palatine tonsils.
Features of the follicular form of tonsillitis:
- it always manifests itself in an acute form. The disease progresses very quickly, lasts up to 2 weeks and ends after appropriate therapy;
- the clinical course of the disease in children is more complex than in adults;
- the peak incidence occurs in autumn and winter;
- The incubation (latent) period in children lasts up to three days. Usually the first manifestations become noticeable the next day after infection.
The further course of the disease depends on the correctly selected drug.
It is important to know! Purulent tonsillitis can occur as a result of other infectious pathologies, such as diphtheria, agranulocytosis, scarlet fever, and mononucleosis.
Parents fundamentally need to understand that the amygdala itself is formed in six months, not earlier. Before this, babies have no tonsils at all, but only a small proportion of lymphatic tissue. This means that follicular tonsillitis cannot develop at all in a child under 6 months of age. From 6 months to 1 year, the disease is extremely rare, but after 3 years, children already go to kindergarten and have a lot of contact with other children, as a result of which infection occurs more often.
Types of diseases in children and their etiology
There are several types of tonsillitis, differing in the depth of inflammation of the tonsils:
- Lacunar angina follicular.
- Catarrhal tonsillitis (pharyngitis).
- Ulcerative-membranous.
It is also classified into types:
- Primary tonsillitis is characterized by tissue damage to the pharyngeal ring and general intoxication.
- Secondary tonsillitis - as a rule, occurs against the background of such acute infectious diseases as diphtheria, scarlet fever, infectious mononucleosis in children, as well as with some blood diseases - leukemia, agranulocytosis, etc.
- Specific sore throat - spirochete, fungal infections.
Depending on the type of pathogen, sore throat is classified into types:
- Viral (herpetic, enteroviral, adenoviral).
- Bacterial (diphtheria, streptococcal).
- Fungal.
In all cases, the main symptom of tonsillitis in children is high body temperature, refusal to eat and drink, severe sore throat, while the child is capricious, often has a headache and often vomits.
The inflammatory process in sore throat usually affects the vocal cords, which is one of the common signs of the disease.
On physical examination - redness of the pharynx, tonsils, swelling of the arch. Removal of plaque in a number of sore throats (diphtheria, candidiasis) is accompanied by a bleeding, eroded surface. Also, in children with sore throat, the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes enlarge and become very painful.
This disease lasts no more than 10 days, and the success of its treatment depends on correct, timely diagnosis.
Since it is impossible to determine the type of sore throat on your own, you should immediately contact a pediatrician when the first signs appear. The doctor determines what type of sore throat the child has and prescribes antibiotics to treat the disease.
What causes follicular tonsillitis in children?
Bacterial infection plays a major role in the development of purulent tonsillitis. In approximately 90% of cases, these are streptococci (especially hemolytic ones), and staphylococci and some other microorganisms are rare.
Viruses can also cause follicular tonsillitis in children. They are especially easy to become infected with in kindergarten or school. Sore throat is transmitted by airborne droplets, through various objects, contact with sick people, dirty food and water.
In some cases, inflammation is caused by an endogenous infection, when microorganisms that are normally present in a person’s tonsils are activated. This is necessarily facilitated by the deterioration of the body’s immune defense. However, exogenous infection is more common.
Interesting to know! Infectious disease specialists have long noticed that inflammation of the tonsils often occurs as a result of acute respiratory viral infections, which leads to a decrease in the local immunity of the tonsils and subsequent invasion of microbes.
Indirect factors contributing to the occurrence of follicular tonsillitis in a child include:
- general hypothermia;
- eating cold food and drinks;
- poor environmental conditions;
- malnutrition;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- lack of vitamins.
Accordingly, in order to reduce the risk of disease, it is necessary to remove the listed factors.
Symptoms of a sore throat in a child
Sore throat in 2-year-old children has symptoms similar to many colds:
- Body aches and weakness;
- Redness of the palate;
- Temperature 38-39°C;
- White or gray coating on the tongue;
- Significant enlargement of lymph nodes.
Distinctive signs of tonsillitis in a two-year-old child in comparison with other ENT diseases:
- The appearance of ulcers on the tonsils and tonsils. In its advanced form, pus accumulates in the pharynx and palate;
- Strong headache;
- Swallowing solid food is accompanied by acute painful sensations;
- Absence of a runny nose, if the sore throat does not occur in combination with other diseases.
With angina, the main criterion determining the occurrence of the disease is the child’s sensations. Such a sore throat, lasting no more than 5-7 days, is not typical for other ENT diseases, while the disease without proper treatment can last for a month with constant deterioration.
Symptoms and manifestations of the disease
The severity of follicular tonsillitis is higher than with simple catarrhal inflammation.
First of all, the patient experiences:
- progressive sore throat;
- body temperature, which rises to 39-40o C;
- severe weakness and malaise, loss of appetite, as well as headache and chills.
A common occurrence with this disease is inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck and ear pain. Sore throat without fever is not a typical case, which indicates inhibition of the immune system.
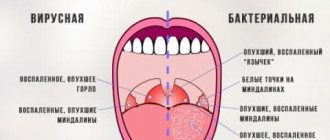
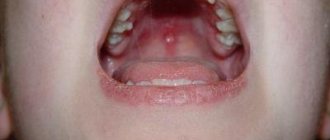
The distinctive symptoms of follicular tonsillitis in children can be detected when examining the oral cavity. Hyperemia and swelling of the tonsils, as well as adjacent areas of the soft palate and palatine arches, will be visible to the naked eye. Small white bubbles are visible through the mucous membrane of the tonsils - these are purulent follicles. Such points are clearly separated from each other. If the follicles begin to merge and form islands, then the sore throat takes on a lacunar form.
Important! Typically, the transition to lacunar tonsillitis occurs when appropriate therapeutic measures are not implemented. In childhood, such complications occur more often than in adults. There is nothing critical in this transition, but lacunar tonsillitis often causes an even greater deterioration in the child’s condition, so urgent measures must be taken to treat it.
In some situations, symptoms of follicular tonsillitis in children may include vomiting and dizziness. The child may even lose consciousness. Severely swollen tonsils can completely close the pharyngeal ring, making it impossible to eat any food or even inhale air. This condition requires urgent medical attention!
Causes
Infection is a key factor in the development of sore throat.
The main infectious agents that provoke follicular tonsillitis:
- Streptococcus. This is the main microorganism that causes this disease, both in adult patients and in children. Up to 80% of cases of the disease are caused by it, and the most common strain of the pathogen is group A streptococcus (hemolytic). Much less common pathogens are group C and G streptococci.
- Other bacteria. Staphylococcus, pneumococcus, spirochetes, and Haemophilus influenzae can also cause a sore throat, which at the initial stage resembles a follicular one. However, due to the peculiarities of the course of the disease caused by atypical flora, angina transforms into other types, for example, Simanovsky-Vincent angina, caused by a combination of a spirochete and a spindle-shaped rod.
- Viruses. In children under 5 years of age, one of the common etiological factors of acute tonsillitis is adenovirus. Less commonly, herpes simplex viruses, Epstein-Barr viruses, and cytomegalovirus act as pathogens.
- Other microorganisms. In 1% of cases, the cause of the disease is either fungi or chlamydia with mycoplasmas.
Considering the fact that most pathogens can normally be detected in healthy people, provoking factors are necessary for the occurrence of sore throat.
These include:
- hypothermia;
- violation of nasal breathing;
- hereditary predisposition;
- consumption of supercooled foods and drinks that cause local hypothermia of the tonsils;
- chronic infections: pharyngitis, sinusitis.
The combination of several such factors increases the risk of getting sick by 5-7 times.
The weakening of the body's defenses leads to the fact that streptococci penetrate into the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils, where they actively multiply. Phagocytes cannot cope with them, and pathogenic microorganisms produce huge amounts of toxins. It is the influence of toxins that causes the systemic manifestations of angina.
Diagnosis of the disease
The symptoms of follicular tonsillitis in children are similar to some other inflammatory diseases. An inexperienced person can easily confuse it with chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or herpangina. Therefore, it is advisable to diagnose the disease with the help of a specialist. He will be able to make a diagnosis after a simple examination of the throat.
If, in the opinion of the doctor, it is necessary to determine the causative agent of the disease, and then prescribe effective antibiotics, then a quick test for streptococcal or staphylococcal infection should be performed, or a smear should be taken for bacterial culture. Additionally, the child will have a blood test.
Symptoms
In children, the most pronounced symptoms of such inflammation of the tonsils, which should serve as a signal to seek help from a specialist, are:
- increase in body temperature to 39-40 degrees;
- general malaise of the body: weakness, drowsiness, lack of appetite, sweating, headache, aching joints;
- painful sensations in the throat, which are especially noticeable when swallowing, and can radiate to the ear;
- enlargement and pain (manifested by pressure) of the cervical and maxillary lymph nodes;
- redness and enlargement of the palatine tonsils, as well as visible inflammation of the palatine arches;
- the presence of small yellowish-white bubbles on the tonsils;
- disorder of the gastrointestinal tract.
Follicular tonsillitis in children: treatment
If bacterial follicular tonsillitis has been diagnosed in a child, the first thing to do is prescribe antibiotics. What drug do doctors usually choose? First of all, these are penicillin antibiotics: Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, less often Ampicillin, Oxacillin, etc. If necessary, penicillin antibiotics can be replaced with cephalosporins (Zinnat) or macrolides (Sumamed).
The prescription of the drug should be based on bacteriological analysis. Unjustified prescription of antibiotics leads to the formation of resistant bacteria, which complicates subsequent therapy for other infectious diseases.
The main task of antibiotics for follicular angina in children is the total eradication of pathological microflora from the body to prevent relapse and complications. The duration of the course of taking antibacterial agents is usually 7-10 days, provided that an adequate dose is selected.
Interesting to know! Dr. Komarovsky tells a lot of useful information about the treatment of follicular tonsillitis in children.
The pharmacological effectiveness of the selected medication is assessed within 48 hours from the start of use. If the drug is suitable, the patient’s condition will improve. Otherwise, you need to change the drug.
If the cause of the disease is a virus, then treatment of follicular tonsillitis in children will include only symptomatic medications. A prerequisite for a successful outcome of angina is compliance with bed rest, as well as nutritional correction.
If the choice of medicine was correct, then the situation will develop as follows:
- during the first two days after starting antibiotic treatment, the child’s health improves, the temperature decreases slightly, and appetite returns;
- on days 3-4, the follicles begin to ulcerate, leaving behind erosions that heal within a couple of days. After this, the inflammation decreases, the temperature returns to normal, and the child begins to swallow regular food;
- after 10-12 days, complete recovery occurs.
Interesting! Sore throat ceases to be contagious 1-2 days after taking the first dose of antibiotic. During this period, almost no bacteria remains in the tonsils, but the symptoms persist until the damaged throat tissue is restored.
Diagnosis of sore throat
Clinical examination
- Finding out the reason for the patient’s request and complaints, that is, all the information about the disease. It is the first step to making a correct diagnosis. It is necessary to find out how long ago the first symptoms began, any treatment was undertaken, if any, what the effect was and other information that the doctor needs. When visiting a doctor, the patient must answer all questions - frankly, without hesitation.
- External examination and palpation of the neck, parotid and occipital areas.
- Pharyngoscopy - examination of the oral cavity and pharynx using a medical spatula. An examination of the mucous membrane is carried out by a general practitioner, pediatrician or ENT doctor.
- Mucous membrane of the soft palate
- Conditions of the cavity walls
- Gum
- The mucous membrane of the palatine tonsils.
, pharyngoscopy is a key method in determining the stage of angina and its form.
Laboratory diagnostics: Smear from the throat and nasal cavity of hemolytic streptococcus About the diagnosis of throat diseases in children
Additional treatments
To alleviate the child’s condition, a wide range of symptomatic medications can be used in the form of:
- antipyretic substances (tablets or children's syrup with Paracetamol or Ibuprofen). An antipyretic should be given when the temperature rises above 38 °C. They not only eliminate fever, but also have an anti-inflammatory and mild analgesic effect. Please note that in pediatrics, the use of aspirin is contraindicated because it causes Reye's syndrome;
- painkillers and antiseptic sprays for the throat (from 2 years old - Orasept or Ingaflu, from 3 years old - Ingalipt N, from 5 years old - Cameflu, from 6 years old - Angilex). Follicular tonsillitis in children cannot be cured with such remedies; they only alleviate the symptoms in the throat;
- lollipops and lozenges. They essentially have the same effect as sprays, so you need to choose one product or combine them to find the right one for your child. In the pharmacy you can find the following throat lozenges: “Rinza Lorsept” or “Olesan” (from 5 years), “Lisobakt” (from 3 years), “Neo-Angin” (from 6 years);
- gargling solution. Follicular tonsillitis is accompanied by the accumulation of pus in the follicles. It is advised to periodically remove it by gargling (preferably at least 5 times a day). To irrigate the throat with follicular sore throat, it is permissible to use saline or antiseptic solutions, such as Angilex, Lorolik, Chlorophyllipt, Miramistin, Furacilin. They can treat follicular tonsillitis in children 4-5 years of age and older. For the younger group, the solution should be diluted with water.
All aerosols, tablets and throat solutions are allowed no earlier than 2 years, and mainly from 3-4 years. How to fight follicular tonsillitis in a child aged 2 and 3 years? You can try lubricating your throat with the same antiseptics using a bandage wrapped around your finger. There are also appropriate homeopathic remedies for children, for example, Tonsilotren tablets are indicated from 1 year. In general, parents have to rely on antibiotics and the child’s own immunity.
Interesting to know! The temperature with follicular sore throat is usually not completely reduced with the help of antipyretics. It will begin to decline only after starting antibiotic therapy.
Toxins released by bacteria cause allergic reactions, so desensitizing agents (Cetrin or Diazolin tablets) must certainly be included in the drug therapy regimen. To treat intoxication syndrome with follicular tonsillitis in children, Komarovsky advises drinking plenty of fluids.
Follicular tonsillitis in a child can be treated surgically, but tonsillitis is removed strictly according to generally accepted indications. Tonsillectomy is performed if a child is diagnosed with acute tonsillitis more than 6 times a year, as well as if complications develop. In this case, removing the source of infection will be the best choice, although many parents think that such an operation will lead to a deterioration of immunity.
Treatment of catarrhal tonsillitis
A child with catarrhal sore throat has a temperature of 39C, he becomes lethargic, apathetic, and feels sharp pain while swallowing. The soreness of the lymph nodes and the inflammatory process in this type of disease are not intense.
This type of sore throat most often occurs after influenza or ARVI.
The main condition for the treatment of catarrhal sore throat in children is plenty of warm drinks, frequent treatment and gargling with various sprays and bed rest.
If an antibiotic is prescribed during treatment, this form of tonsillitis usually goes away within 10 days.
Treatment of lacunar and follicular tonsillitis
These forms of the disease are quite severe in children, as they are often accompanied by very high temperatures (above 40°C) and fever .
A distinctive feature of this type of sore throat is the presence of yellow pustules (up to 3 mm), and with lacunar - a yellow-white purulent coating, which is located in the lacunae located between the lobes of the tonsils.
Medicines for the treatment of these types of sore throat are identical. The main thing is to choose exactly the antibiotic that will help you accurately and quickly deal with the causative agent of the disease.
The best option is an examination (bacterial culture), which will accurately determine the sensitivity of bacteria to a specific drug.
If a child aged 1-3 years has tonsillitis, it is recommended to carry out treatment under the supervision of a pediatrician in a hospital setting. An older child can undergo treatment on an outpatient basis, but only under conditions of isolation, since purulent tonsillitis is a contagious disease.
What medications treat tonsillitis in children?
If a child has a sore throat for more than 3 days, develops a fever, and refuses water, this condition should alert parents.
It is imperative to call the attending physician, and he will decide what to give the child at home, so as not to hospitalize him.
Since it is quite difficult to cure this serious disease on your own, the treatment regimen for children should be based on professional treatment.
The medicine is selected for each child individually , and since the sensitivity of streptococci is quite high to penicillin, as a rule, doctors prescribe an antibiotic of this group for a course of 7-10 days. Also quite often prescribed is a systemic antimicrobial drug, Pancef.
Local treatment of the disease involves frequent gargling with the use of special antiseptics (hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin solution, chamomile and calendula infusion).
If a child under the age of 2 years often has a sore throat, then this condition requires medical attention. Children may have a fever of up to 40°C, breathing becomes difficult, and the throat becomes covered with a grayish film. In this case, the attending physician may recommend surgery involving removal of the tonsils.
What contributes to proper therapy
With intense movement, the baby's temperature rises, and the treatment process becomes more difficult. The occurrence of hyperthermia in children two years of age is treated with antipyretics.
Children under 3 years of age are recommended to use such drugs in the form of suppositories.
Before treating a child's sore throat, you should make sure that he consumes plenty of liquid. This could be still mineral water, tea, fruit drinks or compote.
It is not recommended to drink heated milk, as it causes a gag reflex. It is also undesirable to use honey as an antiseptic; it can irritate an already sore throat. The child gargles every 3 hours, since he cannot do it on his own.
To cure tonsillitis, the attending physician prescribes both antiviral, antipyretic and antibacterial drugs, as well as drugs with a strong antihistamine effect. These drugs will help reduce any complications and have an effective anti-inflammatory effect.
Medicines prescribed by the doctor should be given to the child strictly as prescribed. After complete disappearance of all symptoms of angina, therapy is stopped.
With tonsillitis, the child’s mobility should be limited; in order to avoid any complications, he should be kept in bed.
When does a child need to be hospitalized?
There are several reasons for hospitalizing a child:
- Suppuration of the tonsils or ulcers from bursting ulcers;
- Chronic sore throat, recurring more than 4 times a year;
- Severe swelling of the tonsils, which prevents the child from eating, breathing or sleeping normally;
- Prevention of complications after a sore throat.
If any complications arise, specialists may decide to remove the tonsils.
Follicular tonsillitis in children: treatment at home with folk remedies
A substitute for pharmaceutical preparations for gargling are the following folk remedies:
- a solution of soda with the addition of salt and iodine (200 ml of water, 1 tsp of salt and soda, a few drops of iodine);
- solution with propolis tincture (200 ml of water and a few drops of tincture);
- manganese solution (200 ml of water and manganese on the tip of a knife);
- eucalyptus tincture (15 drops, 200 ml water).
If the child does not have a fever, give him warm milk with honey at night. This will soften your throat and reduce inflammation. Cinnamon tea is also beneficial as it has anti-inflammatory properties. It is also recommended to chew a piece of propolis for inflammation.
Note! Treatment of follicular tonsillitis at home is unacceptable if the disease develops in an infant. Children under one year old are strongly recommended to be sent to the hospital so that they are always under the supervision of doctors.
Treatment
Conservative
Antibacterial therapy for follicular sore throat is mandatory
An integrated approach to the disease will allow you to achieve good results. The following groups of drugs are mandatory for follicular angina:
- Antibiotics. They can be used in the form of a suspension for internal use or as a solution for injection. Such drugs as Cefamezin, Ampicillin, Sumamed, Flemoxin Solutab are widely used for angina.
- Local anti-inflammatory sprays (Chlorophyllipt, Orasept, Bioparox, Furacilin, Lugol). The use of aerosols is contraindicated in children under 5 years of age to avoid the development of laryngospasm.
- Immunostimulating agents (Amiksin, Anaferon, Immunal).
- Antipyretic drugs in the form of a suspension or rectal suppositories (Panadol, Paracetamol, Nurofen).
- Vitamins. As a rule, drugs from this group are prescribed in the form of an injection solution for severe tonsillitis. In other cases, a nutritious diet is sufficient.
Medicines for angina can only be prescribed by a doctor. The specialist, in accordance with the patient’s complaints and individual characteristics, will determine what scheme of therapy should be followed.
Physiotherapeutic methods such as:
- inhalations with drugs (immunostimulating and antibacterial solutions);
- electrophoresis of tonsils;
- UHF (ultra high frequency therapy);
- UFO (ultraviolet ray therapy).
If complex therapy is carried out correctly, it is possible to completely overcome follicular tonsillitis in 7–10 days.
Surgical
If a child is diagnosed with “follicular tonsillitis” more than four times a year, and each time the illness is quite severe, a specialist will consider removing the tonsils. The most suitable age for surgical intervention is considered to be 5–7 years of age. Such children tolerate the postoperative period more easily.
There are several methods for removing tonsils. The most popular method is to excise tissue using special scissors. The surgical intervention is performed under local anesthesia and, as a rule, does not lead to complications. Removing tonsils (tonsils) is a simple operation. The patient may remain in the hospital for 24 hours.
ethnoscience
The most effective traditional medicine recipes used in the treatment of follicular tonsillitis include:
- Gargling with a decoction of chamomile or sage. Ready-made sachets of medicinal herbs can be purchased at the pharmacy. Chamomile or sage is poured with 200 ml of boiling water. Rinsing is carried out after the infusion has cooled to room temperature. When treating children under 3 years of age, you can use a spray bottle.
- Semi-alcohol compresses. For preschool children, alcohol is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:4. A gauze bandage is moistened in the prepared solution and applied to the neck closer to the tonsil area for 2 hours. This method allows you to relieve swelling.
- Cabbage. A fresh vegetable leaf must be applied to the baby’s throat and bronchi. With this recipe it is possible to relieve swelling and pain.
- Inhalations with propolis. This method is suitable for children over 8 years old, but children can get burned. Add a tablespoon of propolis infusion to a liter of boiling water (can be purchased at a pharmacy). The patient bends over the container with the solution and covers himself with a blanket. You need to breathe the steam for 15 minutes.
Folk remedies in the photo
The use of any folk recipes should be discussed with your doctor.
General recommendations for caring for a sick child
We must not forget that sore throat is a contagious disease. Therefore, it is necessary to provide separate dishes and linen for the child. Bed rest is a mandatory element in the treatment of follicular tonsillitis. Any physical activity can lead to complications.
There is no special diet that allows you to quickly overcome the disease. All you need is to eat well, eat foods rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements. If the child refuses to eat for the first few days, you should not force him. But drinking plenty of fluids is a must. Preference should be given to fruit drinks and compotes at room temperature. You should not give your child hot tea to drink.
After recovery, you should adhere to a gentle regimen for a month. Overwork or hypothermia often leads to re-infection.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=RIoKJ_pdP-8
Consequences and complications of the disease
Complications of follicular tonsillitis in children are usually of a local nature, for example, it can be an abscess or purulent lymphadenitis. Such pathologies require immediate surgical intervention.
But even worse, a streptococcal infection without antibiotic treatment can cause harm to the entire human body. The waste products of these bacteria enter the bloodstream and have a toxic effect on one or another organ. If you do not give the patient an antibiotic in time, dangerous consequences may occur, for example, rheumatic fever, impaired functioning of the kidneys and heart (sinus tachycardia, bacterial endocarditis).
Timely use of antibiotics helps prevent the consequences of follicular tonsillitis in children. Also, you cannot interrupt treatment halfway through the course.
Symptoms and signs of follicular tonsillitis
The onset of clinical manifestations in follicular angina is usually acute and is characterized by a rapid increase in the symptoms of intoxication syndrome. Thus, the temperature with follicular tonsillitis, as a rule, is long-lasting and hectic in nature. Before the start of empirical drug therapy, elevated temperature in follicular tonsillitis is not controlled by taking standard antipyretic drugs.
Follicular tonsillitis without fever belongs to the category of an atypical course of the disease and indicates persistent inhibition of the function of the human immune system.
Follicular tonsillitis at the beginning of the clinical picture is characterized by the appearance of catarrhal symptoms in the form of dry mouth, sore throat, dry cough and progressive pain in the throat. By the end of the first day from the onset of the disease, a person experiences swelling of the tonsils, limited hyperemia of the arches and small pustules on the surface of the follicles.
Follicular tonsillitis in almost 99% of cases occurs with a pronounced intoxication syndrome, manifested by general weakness, chills, headaches, loss of appetite and even dyspeptic disorders. In the adult population, intoxication syndrome is also accompanied by constipation and severe myalgia. The negative impact of toxins is manifested in impaired cardiac activity, manifested by sinus tachycardia. The clinical symptom pathognomonic for follicular tonsillitis is severe sore throat, aggravated by swallowing both solid and liquid food, radiating to the parotid region and accompanied by regional lymphadenitis.
Characteristic laboratory markers of the acute period of follicular angina are the detection in the patient’s hemogram of an increased concentration of leukocytes above 9 g/l with a shift in the leukocyte formula in the form of an increase in band leukocytes, eosinophilia, and increased ESR.
Separately, mention should be made of the features of the clinical course of secondary follicular tonsillitis that occurs against the background of mononucleosis. A characteristic feature is the undulating course of the clinical picture and a pronounced reaction from the regional lymphatic collectors, affecting various groups of lymph nodes. Unlike the classic version, follicular tonsillitis in mononucleosis is accompanied by hepatosplenomegaly and the appearance of pronounced lymphocytosis and a high concentration of mononuclear leukocytes in the blood test. To establish a reliable diagnosis in this situation, the fundamental step is to conduct an immunological and serological blood test. Antibiotics for follicular tonsillitis of a secondary nature are not only not used, but are also absolutely contraindicated.
Prevention of follicular tonsillitis in children
To prevent follicular tonsillitis in children, it is recommended to strengthen the body’s protective functions and follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle: regularly walk outdoors, engage in physical activity, eat more vegetables and fruits. If necessary, you can take a course of vitamins or a mineral complex.
In addition, it is important not to overcool the child and avoid drinks that are too cold if he is prone to tonsillitis. To prevent infection, you need to teach your child to wash their hands with soap and avoid contact with sick people.
These tips will help prevent many ENT diseases!
Ensuring proper patient care
In a medical institution, a child hospitalized with follicular tonsillitis is provided with professional care by nurses. When treating an illness at home, it is necessary to create the proper conditions for a speedy recovery.
Here are some basic recommendations for home care for a child with angina:
- Providing bed rest.
- Frequent ventilation of the children's room.
- Maintaining a certain temperature and humidity.
- A ban on active and noisy games and street walks.
- Drink plenty and often, warm.
- The use of fruit drinks and decoctions of medicinal berries and herbs: with oregano, chamomile, rose hips, etc.
- Gentle nutrition, preferably ground. Complete exclusion of spicy, smoked, pickled, hot dishes, carbonated and sweet drinks.
- Keeping your feet and neck warm at all times.
Compliance with these simple recommendations in combination with medication and auxiliary treatment will help a sick child significantly improve his condition in 7-10 days, smooth out the symptoms of an infectious disease and set himself up for a further full recovery.
Lacunar tonsillitis: treatment with antibiotics
What medications most effectively treat this form of acute tonsillitis? The whole insidiousness of lacunar angina lies in the fact that, unlike the previous, follicular one, where minor purulent formations appear, this type of angina is diagnosed when the elements of the nasopharynx are completely filled with pus. Since the main pathogen is beta-hemolytic streptococcus, which causes a characteristic rash on the tonsils and tongue, the disease is also called scarlet fever. Such signs of infectious inflammation occur in children; the disease is contagious and transmitted by airborne droplets.
Symptoms of lacunar tonsillitis in children:
- High body temperature, reaching 39.5-40.5º C. Moreover, the younger the child, the stronger the reaction and the higher the temperature.
- Lethargy, general weakness, tearfulness, lack of appetite.
- Complaints of pain during swallowing.
- Sore throat and feeling of the presence of a foreign object.
- Lymph nodes have a very pronounced painful condition.
- Diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal (stomach) pain, indigestion.
A characteristic and specific sign is purulent plaque on the baby’s tonsils. In the first stages, the focus of inflammation has a yellowish-pale coating on the walls.
Competent diagnosis with timely consultation with a doctor is the key to qualified treatment and recovery of the child. So, lacunar tonsillitis, what antibiotics are used to treat the disease? First of all, among medicinal pharmacological agents, antibacterial drugs with a wide spectrum of action are isolated during treatment. The dosage and course of treatment is determined by the doctor, based on the severity of the inflammatory process and the age criteria of the young patient. In the absence of an allergic reaction, it is effective to treat sore throat with antibiotics. It is up to the attending physician to decide which methods of influencing streptococci and staphylococci. In medical practice, penicillin groups, macrolides, antipyretics and antihistamines, as well as probiotics are traditionally used.