All children are different, but the table will help determine obvious anomalies in the development of the child Normal weight and height of children from 0 to 17 years old, accepted by pediatricians and leading pediatric specialists.
When a long-awaited baby appears, every mother dreams of her child growing up healthy and happy. Using statistical data from tables of weight and height of children , you can understand whether development is normal or whether there are deviations.
Statistical data on height and weight standards are quite approximate, because the stage and pace of development for each child is unique.
Many factors influence a person’s physical development:
- living environment,
- heredity,
- nutrition,
- bone mass
- structure.
Based on the fact that statistical data was obtained through many studies and observations, it is worth considering tables created no later than ten years ago. It is also worth remembering the influence of a person’s genotype on height and weight, i.e. country of residence and climate.
What affects a child’s height and weight:
- hereditary factors: usually a child inherits growth parameters from one of the parents;
- a well-designed diet: if there is a lack of vitamins and essential substances, height and weight parameters can be seriously reduced; Smoking in childhood, as well as abuse of carbonated drinks and harmful carbohydrates, can retard growth.
- participation in certain sports: for example, height can increase significantly in basketball players, tennis players, volleyball players, and decrease in wrestlers, gymnasts, ballet dancers, weightlifters; Weight loss can occur in long-distance runners.
- health status: in children suffering from chronic pathologies, height and weight parameters are usually far from normal;
- psychological problems: tension between the child and parents, lack of sleep, problematic relationships with peers, etc.
Baby's height at birth
- The growth of a newborn at a gestational age of 38-40 weeks, as an important anthropometric indicator, can range from 46 to 56 cm. It depends on the blood flow of the placenta, the nutrition of the expectant mother, heredity, as well as the sex of the child
- When assessing the condition of a newborn, short stature is not always a sign of poor development or prematurity of the fetus. For example, if the child’s parents are short, then the newborn may also be small
- In addition, normal indicators also fluctuate for multiple pregnancies, in which children are born shorter and weigh less. However, each case is assessed individually by pediatricians based on general anthropometric indications and the physical condition of the newborn.
- The ratio calculated using the weight/height formula (Quetelet index) is important. For full-term babies, the normal value is 60-70
In the first year of life, given the active development of the baby, height is extremely important for assessing health and nutritional balance. It is believed that the norm is an increase in height of about 25 cm per year. Here is an approximate table of height growth in the first year of a child’s life:
Height and weight gain in the first year of life
In the first six months of a baby’s life, its weight is calculated using the formula: weight of the newborn + 800 * number of months. So, if at birth the child’s weight was 3200 g, then at 4 months the weight should be no less than 3200 + 800 * 4 = 6400 g.
After 6 months the formula becomes more complicated. Now we add 400g for each month from 6 to 12 months. So, take the same data for an 8 month old child: 3200+800*6+400*2 = 8800 - the average weight of the child.
Important: Height and weight are important indicators of a child’s development, and if you have any doubts about your baby’s growth, share them with your pediatrician.
Norms of height and weight of a newborn
Centile table of height and weight of a child up to one year
| Age | Girls | Boys | ||
| Weight, kg | Height, cm | Weight, kg | Height, kg | |
| Newborns | 3,33 ± 0,44 | 49,50 ± 1,63 | 3,53 ± 0,45 | 50,43 ± 1,89 |
| 1 month | 4,15 ± 0,54 | 53,51 ± 2,13 | 4,32 ± 0,64 | 54,53 ± 2,32 |
| 2 months | 5,01 ± 0,56 | 56,95 ± 2,18 | 5,29 ± 0,76 | 57,71 ± 2,48 |
| 3 months | 6,07 ± 0,58 | 60,25 ± 2,09 | 6,26 ± 0,72 | 61,30 ± 2,41 |
| 4 months | 6,55 ± 0,79 | 62,15 ± 2,49 | 6,87 ± 0,74 | 63,79 ± 2,68 |
| 5 months | 7,38 ± 0,96 | 63,98 ± 2,49 | 7,82 ± 0,80 | 66,92 ± 1,99 |
| 6 months | 7,97 ± 0,92 | 66,60 ± 2,44 | 8,77 ± 0,78 | 67,95 ± 2,21 |
| 7 months | 8,25 ± 0,95 | 67,44 ± 2,64 | 8,92 ± 1,11 | 69,56 ± 2,61 |
| 8 months | 8,35 ± 1,10 | 69,84 ± 2,07 | 9,46 ± 0,98 | 71,17 ± 2,24 |
| 9 months | 9,28 ± 1,01 | 70,69 ± 2,21 | 9,89 ± 1,18 | 72,84 ± 2,71 |
| 10 months | 9,52 ± 1,35 | 72,11 ± 2,86 | 10,35 ± 1,12 | 73,91 ± 2,65 |
| 11 months | 9,80 ± 0,80 | 73,60 ± 2,73 | 10,47 ± 0,98 | 74,90 ± 2,55 |
| 12 months | 10,04 ± 1,16 | 74,78 ± 2,54 | 10,66 ± 1,21 | 75,78 ± 2,79 |
Periods of intense growth in children: growth spurts
In the first year of a newborn’s life, approximately 5 so-called growth spurts are observed:
- 1-3 weeks
- 6-8 weeks
- 3 months
- 6 months
- 9 months
During growth, your baby may become whiny and will likely have a significantly increased appetite and require more time and food to satisfy his desires. If you are breastfeeding your baby, you may feel like you are not getting enough milk. The main thing is not to worry and continue feeding. Your body will do everything for you.
- It is worth noting that in infants growth spurts do not last long - on average 2-3 days. In addition to increased appetite, you may notice increased anxiety during these periods, the emergence of new skills
- Sometimes a growth spurt may be indicated by sudden sleep disturbances - the child wakes up more often or does not sleep at all, or, on the contrary, may fall asleep unusually soundly and for a long time
Growth spurts in children under one year old
After a year, the child gains weight and grows more steadily. The next noticeable growth spurt occurs at approximately 6-7 years.
- You need to understand that at this age extremely important changes occur in the child’s body, among which the first place is the formation of the musculoskeletal system and strengthening of the skeleton
- Pay attention to the child’s posture; this is the time when problems with the spine can develop. The average height increase is about 8-10cm per year
Important: During the period of 6-7 years, it is difficult for a child to maintain one position for a long time or to remain motionless.
The next major growth spurt occurs during adolescent puberty. In this case, it is impossible to guess at what age it will happen. In girls, puberty occurs at 10-12 years of age, but in boys it is usually 1-3 years later. Growth per year can reach 8-10 cm, sometimes more.
- A growth spurt is accompanied by hormonal changes in the child’s body, and secondary sexual characteristics appear
- Moreover, the child’s body often negatively experiences rapid growth and weight gain.
- A teenager may begin to experience seizures, headaches, and dental problems.
- Hormonal changes affect the child’s behavior: he may become whiny or aggressive, get tired quickly
During this period, it is important for you to ensure that your child receives all the necessary substances and vitamins. Please note that during a growth spurt, fluid requirements may increase by up to 20-30%.
Growth spurts in children
Centile table of height and weight of a child by year up to the age of 18
| Age | Girls | Boys | ||
| Weight, kg | Height, cm | Weight, kg | Height, kg | |
| 1 year 3 months | 10,52 ± 1,27 | 76,97 ± 3,00 | 11,40 ± 1,30 | 79,45 ± 3,56 |
| 1 year 6 months | 11,40 ± 1,12 | 80,80 ± 2,98 | 11,80 ± 1,18 | 81,73 ± 3,34 |
| 1 year 9 months | 12,27 ± 1,37 | 83,75 ± 3,57 | 12,67 ± 1,41 | 84,51 ± 2,85 |
| 2 years | 12,63 ± 1,76 | 86,13 ± 3,87 | 13,04 ± 1,23 | 88,27 ± 3,70 |
| 2 years 6 months | 13,93 ± 1,60 | 91,20 ± 4,28 | 13,96 ± 1,27 | 81,85 ± 3,78 |
| 3 years | 14,85 ± 1,53 | 97,27 ± 3,78 | 14,95 ± 1,68 | 95,72 ± 3,68 |
| 4 years | 16,02 ± 2,30 | 100,56 ± 5,76 | 17,14 ± 2,18 | 102,44 ± 4,74 |
| 5 years | 18,48 ± 2,44 | 109,00 ± 4,72 | 19,70 ± 3,02 | 110,40 ± 5,14 |
| 6 years | 21,34 ± 3,14 | 115,70 ± 4,32 | 21,9 ± 3,20 | 115,98 ± 5,51 |
| 7 years | 24,66 ± 4,08 | 123,60 ± 5,50 | 24,92 ± 4,44 | 123,88 ± 5,40 |
| 8 years | 27,48 ± 4,92 | 129,00 ± 5,48 | 27,86 ± 4,72 | 129,74 ± 5,70 |
| 9 years | 31,02 ± 5,92 | 136,96 ± 6,10 | 30,60 ± 5,86 | 134,64 ± 6,12 |
| 10 years | 34,32 ± 6,40 | 140,30 ± 6,30 | 33,76 ± 5,26 | 140,33 ± 5,60 |
| 11 years | 37,40 ± 7,06 | 144,58 ± 7,08 | 35,44 ± 6,64 | 143,38 ± 5,72 |
| 12 years | 44,05 ± 7,48 | 152,81 ± 7,01 | 41,25 ± 7,40 | 150,05 ± 6,40 |
| 13 years | 48,70 ± 9,16 | 156,85 ± 6,20 | 45,85 ± 8,26 | 156,65 ± 8,00 |
| 14 years | 51,32 ± 7,30 | 160,86 ± 6,36 | 51,18 ± 7,34 | 162,62 ± 7,34 |
| 15 years | 56,65 ± 9,85 | 161,80 ± 7,40 | 56,50 ± 13,50 | 168,10 ± 9,50 |
| 16 years | 58,00 ± 9,60 | 162,70 ± 7,50 | 62,40 ± 14,10 | 172,60 ± 9,40 |
| 17 years | 58,60 ± 9,40 | 163,10 ± 7,30 | 67,35 ± 12,75 | 176,30 ± 9,70 |
From 11 to 18 years old
At 11-18 years of age, the intensity of the set of physical indicators changes. Parents need to understand why a teenager is extremely unstable emotionally. Physiological differences or sexual dimorphism are manifested by external signs, structural features of the body, and the functional capabilities of individual body systems. All these changes have an impact on the minor. Girls begin to develop earlier; at the age of 12-14 years, their indicators are higher than those of boys. However, by the age of 15-16, boys surpass girls in physical development.
Adolescence for boys is characterized by active growth of the tubular bones of the skeleton. This manifests itself in the stretching of the limbs, although the torso lags a little behind in this race. Because of this, one often gets the impression that the teenager is awkward and disproportionate. The chest remains narrow, the muscles are weak for such a size, which leads to stooping and the inability to hold the back straight for a long time.
Muscle mass increases more slowly than bone mass. It is thoroughly established at the age of majority. The weight increases slowly, but unevenly: the norm for boys ranges from 2.4 to 5.3 kg over 12 months, for girls - from 2 to 5 kilograms. After the age of 15, girls' body weight increases more than their height. This process is associated with an increase in muscles, subcutaneous fat, and the development of skeletal bones. This is the period when motor reactions and coordination of movements become more accurate, spatial and muscle sensations develop.
Features of puberty
The sharp jump in physical indicators is explained by hormonal activity. Puberty differs between girls and boys. At this time, it is important to control the body weight of a teenager - prevention will protect not only from many serious diseases, but also emotional outbursts that manifest themselves during puberty in minors. However, dieting is prohibited. Proper nutrition skills need to be instilled from birth. To normalize height, it is necessary to take vitamins.
Puberty in boys goes through several stages and lasts several years. It is characterized by the onset of hormonal maturation of the gonads and reaches its peak in adolescence (13-18 years). At the age of 18-19 the time of puberty begins. In parallel with these changes, muscle mass increases and the whole body grows. The figure becomes masculine: the shoulders expand in comparison with the pelvic bones.
Puberty in a girl is manifested by the active “play” of hormones called estrogens. They force the body to grow quickly: hair appears in the groin, armpits, and breasts enlarge. Girls who mature too early should be under special adult supervision. Puberty in girls lasts approximately 7-8 years.
Physiological features characteristic of a teenager during puberty:
- the contour and proportions of the head change;
- the skeleton is finally formed;
- boys have hyperplasia of the muscles and shoulder girdle;
- in girls there is hyperplasia of adipose tissue and the ilium;
- boys experience dizziness and fainting;
- girls become capricious, touchy, and hot-tempered.
Height and weight chart for girls
Girls' weight (in kilograms) according to WHO:
| Age, years | Short | Below the average | Average | Above average | Tall | Overpriced (more than specified) |
| 11 | 25-28 | 27-30 | 30-39 | 39-44 | 44-55 | 55 |
| 12 | 27-32 | 31-36 | 36-45 | 45-52 | 52-63 | 63 |
| 13 | 32-38 | 38-43 | 43-52 | 52-59 | 59-69 | 69 |
| 14 | 37-44 | 43-48 | 48-58 | 58-64 | 64-72 | 72 |
| 15 | 42-47 | 46-50 | 50-60 | 60-66 | 66-75 | 75 |
| 16 | 45-48 | 48-52 | 51-61 | 61-67 | 67-75 | 75 |
| 17-18 | 46-49 | 53-59 | 59-62 | 62-68 | 68-76 | 76 |
Girls' height (in centimeters) according to WHO:
| Age, years | Low | Below the average | Average | Above average | Tall | Overpriced (more than specified) |
| 11 | 132-136 | 136-140 | 140-149 | 149-153 | 153-157 | 157 |
| 12 | 137-142 | 142-146 | 146-154 | 154-159 | 159-163 | 163 |
| 13 | 143-148 | 148-152 | 152-160 | 160-167 | 164-168 | 168 |
| 14 | 148-152 | 152-155 | 155-163 | 163-167 | 167-171 | 171 |
| 15 | 151-154 | 154-157 | 157-166 | 166-169 | 169-173 | 173 |
| 16 | 148-152 | 155-158 | 158-167 | 167-170 | 170-174 | 174 |
| 17-18 | 152-156 | 156-158 | 158-167 | 167-170 | 170-174 | 174 |
Height and weight chart for boys
Boys' weight (in kilograms) according to WHO:
| Age, years | Short | Below the average | Average | Above average | High | Overpriced (more than specified) |
| 11 | 26-28 | 28-31 | 31-40 | 40-44 | 45-51 | 51 |
| 12 | 28-30 | 30-34 | 34-45 | 45-50 | 50-58 | 59 |
| 13 | 30-33 | 33-38 | 48-50 | 50-56 | 57-66 | 66 |
| 14 | 34-38 | 38-42 | 43-57 | 56-63 | 63-73 | 73 |
| 15 | 38-43 | 43-48 | 48-63 | 63-70 | 70-80 | 80 |
| 16 | 44-48 | 48-54 | 54-69 | 67-76 | 66-84 | 85 |
| 17-18 | 49-54 | 54-59 | 60-74 | 74-80 | 80-87 | 88 |
Height of boys (in centimeters) according to WHO:
| Age, years | Short | Below the average | Average | Above average | High | Overpriced (more than specified) |
| 11 | 131-134 | 134-138 | 138-148 | 148-153 | 153-156 | 156 |
| 12 | 136-140 | 140-143 | 143-154 | 154-159 | 159-163 | 163 |
| 13 | 142-145 | 145-150 | 150-160 | 160-166 | 166-170 | 170 |
| 14 | 148-152 | 152-156 | 156-167 | 167-172 | 172-176 | 176 |
| 15 | 154-158 | 158-162 | 162-173 | 173-177 | 177-181 | 181 |
| 16 | 159-163 | 163-167 | 167-178 | 178-182 | 182-186 | 186 |
| 17-18 | 163-166 | 166-171 | 171-181 | 181-186 | 186-188 | 186 |
Why may there be minor deviations from the table in weight or height?
If you notice insignificant differences from the table values, do not worry. Minor deviations may occur for the following reasons:
- The WHO tables calculate the so-called reference weight and height of a child, that is, they do not take into account many real life factors, including the parameters of a child born prematurely (there are separate tables for such babies).
- The increase in a child’s weight and height over the years is purely individual. In addition, it is necessary to take into account that in the first 12 months development does not occur evenly, but spasmodically. Also keep in mind that in the first months of life, every new food product that you offer your baby always requires adaptation of the body, so during this period the child’s weight may decrease.
How to calculate a child's height based on the parents' height: formula
Naturally, it is impossible to determine exactly how tall the baby will be, but it is still possible to make an assumption based on the hereditary factor. I suggest you familiarize yourself with the most popular formulas for calculating the height of boys and girls.
| Folk | Formula by Dr. J. Hawker from the Mayo Clinic | Formula of G. Gorbunov | Formula of V. Karkus | Narodnaya 2 | |
| Girls | (mother’s height + father’s height) * 0.51 - 7.5 | (mother’s height + father’s height): 2 – 6.4 | (mother’s height + father’s height - 12.5): 2 ± 8 | (mother's height + father's height * 0.923): 2 | height at 1 year + 95cm |
| Boys | (mother’s height + father’s height) * 0.54 - 4.5 | (mother’s height + father’s height): 2 + 6.4 | (mother's height + father's height + 12.5): 2 ± 8 | (mother's height * 1.08 + father's height): 2 | height at 1 year + 100cm |
Any of the above formulas helps determine the ideal weight of a child, referring to the genetic factor. You can also use an online height calculator to calculate.
Child growth formula based on parents' height
Reasons for significant deviations in weight and height from norms
If the child’s height and weight by year significantly from the parameters presented in the table, it is necessary to contact a specialist - a pediatrician or pediatric endocrinologist.
Causes of pathologies of height and weight:
- Late puberty: when a delay in height and weight in a particular child occurs later than in his peers.
- Hereditary factor: stunted growth can be observed from an early age if the child’s family has short relatives.
- The child was born prematurely.
- The baby suffered from intrauterine injuries or received them after birth.
- Genetic abnormalities: usually present with a range of symptoms. Stunted growth, as well as non-standard weight indicators, are precisely such manifestations.
- Chronic pathologies of various systems and organs: heart and blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, bronchi and lungs, anemia.
- Acute lack of vitamins and essential nutrients.
- Use of certain pharmacological drugs.
- Deficiency of growth hormone, which regulates growth dynamics after the child is two years old.
- Thyroid hormone deficiency. It is usually a congenital endocrine pathology and slows down not only the growth, but also the intellectual development of the child.
- Insulin deficiency due to type 1 diabetes.
- Increased production of glucocorticoid hormones due to Cushing's syndrome.
- Vitamin D deficiency, as a result of which the skeletal bones are deformed and symptoms of rickets occur, including growth and weight retardation.
Here are the indicators of the ratio of height and weight of a child at different periods of age from 1 to 3 years. Particular attention must be paid to the RATIO of height and weight, which should be (in the table) in the same centile (in the same column of the table).
Height and weight calculator
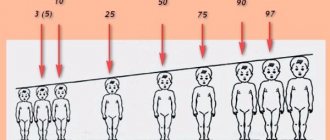
Anthropometric (centile) tables
The tables for height, weight and head circumference show ranges by group. The middle “blue” column shows the average for a given age. The “green” columns on the right and left show indicators within the normal range, which are slightly below or above the average. The “yellow” and “red” columns show indicators below or above normal that require special attention from parents and doctors.
- The average height of the child should be within the green and blue values (25-75 centiles). This height corresponds to the average height of children of this age.
- Growth, the value of which is between the yellow and green values (10-25 centiles) is also normal, but indicates a tendency for the child to be stunted.
- Growth, the value of which is between the blue and yellow values (75-90 centiles) is also normal, but indicates a tendency for the child to be ahead in growth.
- Growth, the value of which is between the red and yellow values - low (3-10th centile), or high (90-97th centile), which can be due to both the characteristics of the child and a disease with hormonal imbalance (usually endocrinological or hereditary ). In such cases, you should bring this to the attention of your pediatrician or family doctor, who, if necessary, will refer you to the appropriate specialist. Be sure to monitor the further growth, weight, and general condition of such a child.
- Growth that is beyond the red line (less than the 3rd or more than the 97th centile) indicates a pathology in the child’s growth. Such children must be consulted by appropriate specialists, primarily an endocrinologist, who will recommend further examination and prescribe appropriate treatment. Remember that diseases accompanied by impaired growth lead in the future to various disorders of physical and mental health.
Height of boys from 1 year to 3 years (cm)
| Age | Index | ||||||
| very low | short | below the average | average | above average | high | very tall | |
| 12 months | 71,2-72,3 | 72,3-74,0 | 74,0-77,3 | 77,3-79,7 | 79,7-81,7 | >81,7 | |
| 15 months | 74,8-75,9 | 75,9-77,1 | 77,1-81,0 | 81,0-83,0 | 83,0-85,3 | >85,3 | |
| 18 months | 76,9-78,4 | 78,4-79,8 | 79,8-83,9 | 83,9-85,9 | 85,9-89,4 | >89,4 | |
| 21 months | 79,3-80,3 | 80,3-82,3 | 82,3-86,5 | 86,5-88,3 | 88,3-91,2 | >91,2 | |
| 24 months | 81,3-83,0 | 83,0-84,5 | 84,5-89,0 | 89,0-90,8 | 90,8-94,0 | >94,0 | |
| 27 months | 83,0-84,9 | 84,9-86,1 | 86,1-91,3 | 91,3-93,9 | 93,9-96,8 | >96,8 | |
| 30 months | 84,5-87,0 | 87,0-89,0 | 89,0-93,7 | 93,7-95,5 | 95,5-99,0 | >99,0 | |
| 33 months | 86,3-88,8 | 88,8-91,3 | 91,3-96,0 | 96,0-98,1 | 98,1-101,2 | >101,2 | |
| 3 years | 88,0-90,0 | 90,0-92,3 | 92,3-99,8 | 99,8-102,0 | 102,0-104,5 | >104,5 | |
Weight of boys from 1 year to 3 years (kg)
| Age | Index | ||||||
| very low | short | below the average | average | above average | high | very tall | |
| 12 months | 8,5-8,9 | 8,9-9,4 | 9,4-10,9 | 10,9-11,6 | 11,6-12,1 | >12,1 | |
| 15 months | 9,2-9,6 | 9,6-10,1 | 10,1-11,7 | 11,7-12,4 | 12,4-13,0 | >13,0 | |
| 18 months | 9,7-10,2 | 10,2-10,7 | 10,7-12,4 | 12,4-13,0 | 13,0-13,7 | >13,7 | |
| 21 months | 10,2-10,6 | 10,6-11,2 | 11,2-12,9 | 12,9-13,6 | 13,6-14,3 | >14,3 | |
| 24 months | 10,6-11,0 | 11,0-11,7 | 11,7-13,5 | 13,5-14,2 | 14,2-15,0 | >15,0 | |
| 27 months | 11,0-11,5 | 11,5-12,2 | 12,2-14,1 | 14,1-14,8 | 14,8-15,6 | >15,6 | |
| 30 months | 11,4-11,9 | 11,9-12,6 | 12,6-14,6 | 14,6-15,4 | 15,4-16,1 | >16,1 | |
| 33 months | 11,6-12,3 | 12,3-13,1 | 13,1-15,2 | 15,2-16,0 | 16,0-16,8 | >16,8 | |
| 3 years | 12,1-12,8 | 12,8-13,8 | 13,8-16,0 | 16,0-16,9 | 16,9-17,7 | >17,7 | |
Boys' head circumference, (cm)
| Age | Index | ||||||
| very low | short | below the average | average | above average | high | very tall | |
| 12 months | 44,6-45,3 | 45,3-46,2 | 46,2-49,1 | 49,1-49,8 | 49,8-50,7 | >50,7 | |
| 15 months | 45,3-46,0 | 46,0-46,7 | 46,7-49,5 | 49,5-50,3 | 50,3-51,3 | >51,3 | |
| 18 months | 46,0-46,6 | 46,6-47,3 | 47,3-49,9 | 49,9-50,7 | 50,7-51,6 | >51,6 | |
| 21 months | 46,5-47,2 | 47,2-47,7 | 47,7-50,3 | 50,3-51,0 | 51,0-52,0 | >52,0 | |
| 24 months | 47,0-47,6 | 47,6-48,1 | 48,1-50,5 | 50,5-51,3 | 51,3-52,3 | >52,3 | |
| 27 months | 47,3-47,9 | 47,9-48,5 | 48,5-50,8 | 50,8-51,7 | 51,7-52,7 | >52,7 | |
| 30 months | 47,5-48,2 | 48,2-48,8 | 48,8-51,1 | 51,1-52,0 | 52,0-53,0 | >53,0 | |
| 33 months | 47,8-48,4 | 48,4-49,2 | 49,2-51,3 | 51,3-52,3 | 52,3-53,3 | >53,3 | |
| 3 years | 48,0-48,6 | 48,6-49,5 | 49,5-51,5 | 51,5-52,6 | 52,6-53,5 | >53,5 | |
Height of girls from 1 year to 3 years (cm)
| Age | Index | ||||||
| very low | short | below the average | average | above average | high | very tall | |
| 12 months | 70,1-71,4 | 71,4-72,8 | 72,8-75,8 | 75,8-78,0 | 78,0-79,6 | >79,6 | |
| 15 months | 72,9-74,5 | 74,5-76,0 | 76,0-79,1 | 79,1-81,5 | 81,5-83,4 | >83,4 | |
| 18 months | 75,8-77,1 | 77,1-78,9 | 78,9-82,1 | 82,1-84,5 | 84,5-86,8 | >86,8 | |
| 21 months | 78,0-79,5 | 79,5-81,2 | 81,2-84,5 | 84,5-87,5 | 87,5-89,5 | >89,5 | |
| 24 months | 80,1-81,7 | 81,7-83,3 | 83,3-87,5 | 87,5-90,1 | 90,1-92,5 | >92,5 | |
| 27 months | 82,0-83,5 | 83,5-85,4 | 85,4-90,1 | 90,1-92,4 | 92,4-95,0 | >95,0 | |
| 30 months | 83,8-85,7 | 85,7-87,7 | 87,7-92,3 | 92,3-95,0 | 95,0-97,3 | >97,3 | |
| 33 months | 85,8-87,6 | 87,6-89,8 | 89,8-94,8 | 94,8-97,0 | 97,0-99,7 | >99,7 | |
| 3 years | 89,0-90,8 | 90,8-93,0 | 93,0-98,1 | 98,1-100,7 | 100,7-103,1 | >103,1 | |
Weight of girls from 1 year to 3 years (kg)
| Age | Index | ||||||
| very low | short | below the average | average | above average | high | very tall | |
| 12 months | 8,0-8,5 | 8,5-9,0 | 9,0-10,2 | 10,2-10,8 | 10,8-11,3 | >11,3 | |
| 15 months | 8,6-9,2 | 9,2-9,7 | 9,7-10,9 | 10,9-11,5 | 11,5-12,1 | >12,1 | |
| 18 months | 9,0-9,8 | 9,8-10,3 | 10,3-11,5 | 11,5-12,2 | 12,2-12,8 | >12,8 | |
| 21 months | 9,7-10,3 | 10,3-10,6 | 10,6-12,2 | 12,2-12,8 | 12,8-13,4 | >13,4 | |
| 2 years | 10,2-10,8 | 10,8-11,3 | 11,3-12,8 | 12,8-13,5 | 13,5-14,1 | >14,1 | |
| 27 months | 10,6-11,2 | 11,2-11,7 | 11,7-13,3 | 13,3-14,2 | 14,2-14,8 | >14,8 | |
| 30 months | 11,0-11,6 | 11,6-12,3 | 12,3-13,9 | 13,9-14,8 | 14,8-15,5 | >15,5 | |
| 33 months | 11,5-12,1 | 12,1-12,7 | 12,7-14,5 | 14,5-15,4 | 15,4-16,3 | >16,3 | |
| 3 years | 11,7-12,5 | 12,5-13,3 | 13,3-15,5 | 15,5-16,5 | 16,5-17,6 | >17,6 | |
Head circumference of girls, (cm)
| Age | Index | ||||||
| very low | short | below the average | average | above average | high | very tall | |
| 12 months | 43,5-44,2 | 44,2-45,0 | 45,0-48,2 | 48,2-49,2 | 49,2-50,1 | >50,1 | |
| 15 months | 44,2-45,1 | 45,1-45,9 | 45,9-48,7 | 48,7-49,6 | 49,6-50,5 | >50,5 | |
| 18 months | 44,9-45,7 | 45,7-46,4 | 46,4-49,0 | 49,0-49,9 | 49,9-50,9 | >50,9 | |
| 21 months | 45,4-46,1 | 46,1-46,9 | 46,9-49,4 | 49,4-50,2 | 50,2-51,2 | >51,2 | |
| 24 months | 46,0-46,6 | 46,6-47,3 | 47,3-49,7 | 49,7-50,5 | 50,5-51,5 | >51,5 | |
| 27 months | 46,5-47,0 | 47,0-47,8 | 47,8-50,0 | 50,0-50,7 | 50,7-51,8 | >51,8 | |
| 30 months | 47,0-47,5 | 47,5-48,0 | 48,0-50,4 | 50,4-51,0 | 51,0-52,0 | >52,0 | |
| 33 months | 47,3-47,9 | 47,9-48,4 | 48,4-50,6 | 50,6-51,4 | 51,4-52,4 | >52,4 | |
| 3 years | 47,6-48,1 | 48,1-48,6 | 48,6-51,0 | 51,0-51,7 | 51,7-52,7 | >52,7 | |