Measurement of head and chest circumference should be carried out during a routine visit to specialists. It is important to evaluate the shape of these body parts. The data will help assess the state of the child’s development and take the necessary measures in a timely manner.
Very important indicators of child development are anthropometric data of head and chest circumference. Immediately after birth, these parameters are measured. It is important to examine the child’s skeletal system. When examining the head, its shape and size are assessed.
The shape of the chest can also be different and indicate the state of health. Subsequently, the local pediatrician will correlate new indicators with them. Any deviations from the norm are regarded as serious pathological changes in the development of the body. In this case, the doctor prescribes a consultation with other specialists in order not to miss the progression of the disease and to begin appropriate treatment.
How to use norm tables to assess the physical development of children under one year old and preschoolers?
Features of the compilation of WHO tables released in 2006:
- Initially, monitoring was carried out in different countries and clinics around the world . Based on such global studies, numerical indicators of the normal development of each child were derived, regardless of place of residence.
- The fundamental difference between the new system of assessing physical development and the outdated one is such an important indicator as breastfeeding. This is the type of food that is considered normal for babies. Previous “reference” figures were overestimated because they were focused on formula-fed infants. The new WHO standards are applicable in any region, regardless of race and national characteristics of medicine in a particular country.
- For five years, scientists and doctors, nutritionists and immunologists, nutritionists and children's rights advocates conducted research , and the resulting graphs and tables became a breakthrough in the children's healthcare system.
How to use WHO tables to assess child development?
WHO tables (used by Russian doctors) are divided into columns. Each contains numerical indicators that determine how much the child’s development is in the generally accepted norm. To assess whether a child is developing correctly, you need to find in the WHO table in the first column a value corresponding to the child’s age or close to it, and then in the same row in other columns find an indicator close to the value of the body parameter measured in the child.
- Indicators in the middle column and in adjacent columns with values above and below average are considered normal . If the parents' measurements are identical to those in the middle columns, there is nothing to worry about.
- The indicators of the child’s physical development that are in the outer columns of the table with low/very low/high/very high values should alert parents and encourage them to contact a pediatrician.
How to use the domestic centile table to assess chest circumference in children?
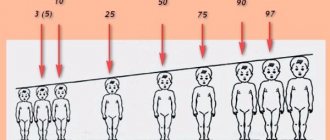
The centile graph-table is easy to use and understandable to ordinary average parents. Since centiles (or otherwise percentages) are indicated in average values, there is no need to panic if the child’s data is within the middle two columns. Below we will consider a method for assessing a child’s development using a centile table with chest circumference standards.
- To determine whether a child is developing normally based on the size of the chest, in the leftmost column of the table, find the age corresponding to the age of the baby. If the baby is 3 months and 6 days old, then we are looking for the norm for a three-month-old baby. If the baby’s real age is 3 months and 20 days, then we look for the corresponding indicators in the “4 months” line.
- The top line is graduated by centiles (percentages) - 3, 10, 25, 75, 90, 97. Having measured the chest circumference, check the data obtained with the average normal indicator in the corresponding line.
- If the baby's chest circumference falls between the 25th and 75th centiles, then this is great and there is no reason to worry.
- If the child's chest circumference corresponds to the value in the column 10 or 90, then this indicates a possible emerging imbalance in development.
- If the child’s chest circumference corresponds to the values in the column with the 3rd or 97th centile, then this is a reason to consult a pediatrician or neurologist.
An important factor is the consistency of the indicators of all tables with each other. For example, in a small, slender child, even an indicator of the 3rd centile can only indicate his asthenic build, and not the development of pathologies in the body. Be sure to check whether your height corresponds to your age, your weight to your height, or your head and chest measurements to your age.
Chest circumference table for girls from 0 to 17 years old
| Age | Very low | Short | Below the average | Average | Above average | High | Very tall |
| Newborn | 31,0 | 32,0 | 32,8 | 34,0 | 35,2 | 36,0 | 37,0 |
| 1 month | 33,0 | 34,0 | 34,9 | 35,9 | 37,1 | 38,1 | 39,0 |
| 2 months | 34,6 | 35,6 | 36,6 | 37,7 | 38,8 | 39,9 | 40,9 |
| 3 months | 36,3 | 37,3 | 38,3 | 39,4 | 40,5 | 41,4 | 42,8 |
| 4 months | 38,0 | 38,9 | 39,8 | 40,9 | 42,1 | 43,0 | 43,3 |
| 5 months | 39,5 | 40,3 | 41,2 | 42,3 | 43,5 | 44,5 | 45,7 |
| 6 months | 40,7 | 41,6 | 42,4 | 43,5 | 44,7 | 45,8 | 47,1 |
| 7 months | 41,8 | 42,7 | 43,6 | 44,6 | 45,8 | 47,2 | 48,5 |
| 8 months | 42,8 | 43,7 | 44,6 | 45,7 | 46,9 | 48,3 | 49,8 |
| 9 months | 43,6 | 44,5 | 45,5 | 46,6 | 47,8 | 49,3 | 50,9 |
| 10 months | 44,3 | 45,2 | 46,2 | 47,2 | 48,6 | 50,1 | 51,7 |
| 11 months | 45,0 | 45,8 | 46,8 | 47,8 | 49,3 | 50,8 | 52,3 |
| 1 year | 45,5 | 46,3 | 47,2 | 48,3 | 49,9 | 51,4 | 52,8 |
| 1 year 3 months | 46,4 | 47,3 | 48,0 | 49,3 | 50,8 | 52,3 | 53,9 |
| 1 year 6 months | 47,1 | 47,8 | 48,7 | 49,9 | 51,3 | 52,9 | 54,5 |
| 1 year 9 months | 47,5 | 48,2 | 49,1 | 50,4 | 51,9 | 53,5 | 55,0 |
| 2 years | 47,8 | 48,5 | 49,5 | 50,2 | 52,5 | 54,0 | 55,6 |
| 2 years 3 months | 47,9 | 48,8 | 49,8 | 51,3 | 53,0 | 54,5 | 56,2 |
| 2 years 6 months | 48,0 | 49,0 | 50,0 | 51,5 | 53,3 | 54,9 | 56,8 |
| 2 years 9 months | 48,1 | 49,0 | 50,0 | 51,8 | 53,6 | 55,5 | 57,2 |
| 3 years | 48,2 | 49,1 | 50,3 | 51,8 | 53,9 | 56,0 | 57,6 |
| 3.5 years | 48,6 | 49,7 | 50,9 | 52,5 | 54,3 | 56,2 | 57,8 |
| 4 years | 49,2 | 50,4 | 51,6 | 53,2 | 55,1 | 56,9 | 58,6 |
| 4.5 years | 49,6 | 51,0 | 52,3 | 54,0 | 55,8 | 57,8 | 59,7 |
| 5 years | 50,4 | 51,6 | 53,0 | 54,8 | 56,8 | 58,8 | 61,0 |
| 5.5 years | 50,8 | 52,4 | 53,8 | 55,7 | 57,8 | 60,0 | 62,2 |
| b years | 51,5 | 53,0 | 54,7 | 56,6 | 58,8 | 61,2 | 63,6 |
| 6.5 years | 52,3 | 53,8 | 55,5 | 57,5 | 59,8 | 62,4 | 64,7 |
| 7 years | 53,2 | 54,6 | 56,4 | 58,4 | 61,0 | 63,8 | 66,5 |
| 8 years | 54,7 | 56,3 | 58,2 | 60,8 | 64,2 | 67,6 | 70,5 |
| 9 years | 56,3 | 58,0 | 60,0 | 63,4 | 67,7 | 71,4 | 75,1 |
| 10 years | 58,0 | 60,0 | 62,0 | 66,0 | 71,3 | 75,5 | 78,8 |
| 11 years | 59,7 | 62,2 | 64,4 | 68,7 | 74,5 | 78,6 | 82,4 |
| 12 years | 61,9 | 64,5 | 67,1 | 71,6 | 77,6 | 81,9 | 86,0 |
| 13 years | 643 | 66,8 | 69,9 | 74,6 | 80,8 | 85,0 | 88,6 |
| 14 years | 67,0 | 69,8 | 73,0 | 77,8 | 83,6 | 87,6 | 90,9 |
| 15 years | 70,0 | 72,9 | 76,3 | 80,4 | 85,6 | 89,4 | 92,6 |
| 16 years | 73,0 | 75,8 | 78,8 | 82,6 | 87,1 | 90,6 | 93,9 |
| 17 years | 75,4 | 78,0 | 80,6 | 83,8 | 88,0 | 91,0 | 94,5 |
Boys' head circumferences are shown in centimeters.
These tables are indicative in nature for determining the chest circumference of a child of average height. Parameters between the segments “below average” and “above average” are considered indicators characterizing the normal circumference of the child’s chest
See also:
Child's head circumference
How to correctly measure a child's chest circumference
WHO tables: norms of weight, height, head circumference for boys and girls up to one year
Using the tables below, you can check how the head size, weight and height of babies should normally change in the first year of their life. The rates for boys and girls are different. To use the tables, you must first sequentially measure the circumference of the head, chest, height of the baby with a centimeter tape, and also weigh the child. All received data is recorded and the baby’s development is assessed using tables.
How to correctly measure the head circumference, chest circumference, height, weight of a child? It is not at all difficult to make correct measurements to assess the physical development of a baby. The main thing is to take into account several nuances:
- A measuring tape should be purchased specifically for these purposes; if necessary, it should be taken to a doctor’s appointment so that there are no significant discrepancies in the readings.
- When taking monthly measurements of a baby's skull, try to ensure that the measuring tape goes over the most convex areas of the head. This includes the eyebrows, the area above the ears and the back of the head.
- Measure height with the help of other family members who will help the baby lie calmly while taking measurements.
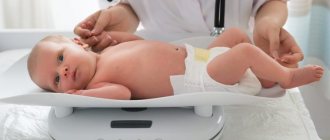
- A child’s weight can be monitored both at home and at an appointment at a children’s clinic, where special scales are available.
- Chest circumference in infants is measured in a horizontal lying position. It is advisable that the measuring tape be located at the level of the nipples in front, in the back in the area of the shoulder blades and through the armpit on the side. If possible, record the indicators on inhalation and exhalation.
In infants, it is worth paying attention to the chest and head circumference parameters in relation to each other. According to doctors working for the international organization WHO, the following changes in anthropometric data are considered normal for infants:
- The first 30 days of life - the circumference of the skull is greater than the circumference of the sternum by a couple of centimeters.
- Closer to the 90-day mark of life, the infant's head and chest circumference are equalized in terms of indicators.
- Closer to the 180th day of life, the chest circumference should be larger than the head circumference.
Height, weight, and chest and head circumferences undergo the greatest changes during the first year of life in both boys and girls. Do not forget that newborns have “fontanelles” that completely disappear only by the age of one and a half years. This affects the size of the baby's skull.
V Algorithm for performing a simple medical service.
Preparation for the procedure:
- Explain to your mother the meaning of the manipulation and obtain informed consent.
- Wash your hands hygienically and dry.
Weighing:
- Balance the scales.
- Wipe the scales with disinfectant. solution.
- Turn on the electronic scale system (up to 90 kg).
Performing the procedure:
- Place a clean diaper folded several times on the scale; weigh it (notice the weight on the display).
- Press the “0”, then “T” buttons so that the weight of the diaper on the display shows a (-) sign.
- Place the baby in a diaper.
- Note the child's weight on the display.
- Remove the baby, put him in the crib or give him to the mother.
End of the procedure:
- Record the result (remember to subtract the weight of the diaper) in your medical documentation.
- Remove the diaper from the table, treat the changing table with disinfectant. solution.
What might a deviation from WHO standards indicate?
Naturally, in this case, only maximum deviations are considered, the numerical indicators of which are indicated in the outer columns of the tables.
Baby's weight is too high or too low
Weight is very important for newborns, and weight gain should occur continuously during the first year of life.
The problem of dystrophy and obesity forces the World Health Organization to closely monitor this indicator, which led to its inclusion in generally accepted standards.
- A weight greater than the permissible norm should prompt parents to change the frequency of feeding the baby.
- Underweight is a reason to consult a pediatrician for advice and review the child’s diet and nutritional regimen.
Head circumference more/less than normal
Anthropometric indicators equal to the outer columns, in this case, may indicate such serious diseases as hydrocephalus, microcephaly, rickets, and intracranial hypertension.
- With hypertension , the baby's head grows too quickly, as excess fluid accumulated inside the skull puts pressure on it. This diagnosis can be confirmed by a neurologist and an ophthalmologist who will examine the fundus and vessels inside the eye sockets. In the case of hypertension, the “fontanel” will not grow together for a long time, and all the joints in the skull will be mobile or simply soft.
- Rickets changes the very shape of the skull, but is accompanied by additional painful and unpleasant symptoms.
- Craniostenosis is considered a defect in the development of the skull bones . The essence of the disease is premature fusion of sutures and their ossification. The child's brain will grow, but the skull will not expand, which will lead to excessive pressure on the walls.
- Microcephaly - this diagnosis is made if the brain does not increase in size. A lack of brain mass by more than 25 percent (of the accepted norm) leads to early closure of the “fontanel.”
Too big/small height
This indicator is important, but it is influenced by many factors. First of all, it's genetics. In general, babies with tall parents gain height quickly, but it is likely that a short great-grandmother or other distant relative may appear in the child’s genes. In this case, it is important that the development of this indicator be in harmonious combination with the others.
Deviations from average indicators do not always indicate diseases or pathologies. Weight gain or growth in many infants occurs in spurts. So what is missing in one month can be more than compensated for in the next. Therefore, it is important to record indicators constantly, without omissions. In most cases, this will help restore the emotional balance of the parents themselves, especially if the baby is the first in the family.
Possible deviations
The normal head size for a newborn baby ranges from 35 to 37 cm. If deviations from these values exceed 1-1.5 cm, this may indicate serious problems or injury received by the child during childbirth.
Birth injury
Most often, a baby receives a birth injury for the following reasons:
- violation of the behavior technique during childbirth on the part of the mother (for example, when a woman tries to sit during the pushing period);
- malposition;
- discrepancy between the size of the woman’s pelvis and the child’s head circumference.
Birth injuries most often do not pose a life-threatening threat, and their consequences completely disappear when the child is 10-12 months old.
But in some cases, the results can be very sad, so women need to attend all routine examinations with a gynecologist to monitor the baby’s position.
We should not forget about correct behavior at the time of labor - sometimes it is the mother’s actions that lead to tragic abnormalities in the newborn’s cerebral circulation.
Hydrocephalus
This pathology is an accumulation of fluid in the brain space, which puts pressure on the brain and prevents it from growing and developing.
If detected early, hydrocephalus and its consequences can be successfully treated, but in advanced cases, the disease can lead to the death of the child.
Hydrocephalus can be suspected based on the following signs:
- head circumference exceeds the norm by 3-4 cm;
- the fontanelles and frontal bone are enlarged;
- the bones forming the skull diverge slightly;
- a venous pattern appears on the head.
Children with hydrocephalus are restless and often cry. This is due to the fact that the fluid puts pressure on the brain, which causes severe headaches in the child. If such a baby is shown to a pediatric neurologist, other neurological problems can be detected.
Microcephaly
True microcephaly (small brain) is extremely rare. It is impossible to make this diagnosis based solely on the size of the head, since this parameter can be influenced by various factors, including hereditary ones.
If microcephaly is suspected, the baby must undergo an ultrasound scan of the brain. Only after the study can we talk about pathologies.
Hemangioma
This is a benign brain tumor that looks like a birthmark. As a rule, hemangioma appears in the first 7-10 days of a newborn’s life. With timely treatment, the pathology does not pose a threat to life, but the child will require constant monitoring. In addition to the characteristic spot, with this type of tumor there will be an excess of the head circumference above normal values.
What deviations are considered dangerous?
Medical care, including diagnostic measures and a full examination, is required for the baby in cases where the head circumference exceeds (or, conversely, falls short of) the norm by 3-4 cm.
Such indicators almost always indicate severe pathologies for which the child should be placed under the supervision of specialists.
Deviations in brain development are one of the most serious pathologies encountered in pediatric practice.
It is possible to get by with minimal consequences only in cases where the child begins to receive the necessary treatment in a timely manner, so it is important to monitor how the little head grows every month until the child reaches one year of age.
Child's chest
In addition to the volume of the chest, the doctor will definitely look at its shape. Normally it should be conical. The ribs should be at right angles to the spine. During the second half of life, the baby's breast size becomes larger, which is noticeable when measured during an examination by a pediatrician.
How to measure the chest correctly and accurately?
Measuring the sternum circumference of a baby under one year old is not difficult at all. In young children it is measured in a lying position, in older children - standing. At the time of taking measurements, the baby should be calm, arms relaxed, located along the body. The edge of the measuring tape should be placed on the left side of the armpit. From the side of the back it is carried out at an angle of both shoulder blades, along the front part - along the bottom of the areola. Typically, measurements are taken during inhalation and then during exhalation. The difference in these parameters is also important; it reflects the excursion of the sternum, that is, its mobility. Normal excursion should be within 5-8 cm.
Important! Before taking measurements, the doctor must treat the measuring tape with a 70% alcohol solution.