Definition of disease
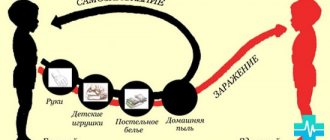
Purulent tonsillitis is an infectious disease caused by various types of microbes (most often streptococci). With this type of tonsillitis, the lesions are localized on the palatine tonsils. Infection, as a rule, occurs by airborne droplets, but contact and household transmission of infection through dirty dishes used by the patient is also possible. The peak incidence occurs in spring and autumn.
The term "angina" is not used in any medical textbook. However, the phrase “purulent tonsillitis” is popularly used to describe a condition in which pus forms on the tonsils. Foci of pus are observed in follicular or lacunar forms of tonsillitis. It happens that the same patient may simultaneously experience signs of these two forms of purulent tonsillitis.
Depending on the type of pathogen, tonsillitis is divided into viral and bacterial tonsillitis.
Causes of tonsillitis in children
Throughout life, a person constantly comes into contact with many microorganisms - fungi, viruses, bacteria. But in most cases, such meetings pass unnoticed, without affecting the well-being of either the adult or the child. This means that insemination took place in a small amount (which is the norm if body hygiene is observed) and the body’s defenses are working normally.
But in some situations, infection (the introduction of microorganisms and their reproduction) is inevitable. This occurs with a temporary decrease in immune strength:
- With local hypothermia (cold drinks, ice cream);
- With general hypothermia;
- In case of a long-term psycho-traumatic situation;
- After a recent illness;
- Against the backdrop of an unfavorable environment;
- In contact with a person with purulent tonsillitis (bacterial form) or when sharing household and personal items with him (dishes, toothbrush, etc.).
In these cases, bacteria or viruses attack the body, primarily the mucous membranes, which leads to the development of inflammatory processes, in particular to diseases such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis. Serious medical attention is often required to eliminate these diseases. Viruses in most cases cause a simple (catarrhal) form of tonsillitis, while bacteria (mainly staphylococcus) cause purulent tonsillitis (follicular and lacunar form of tonsillitis in children).
The incubation period for bacterial tonsillitis is two to five days after exposure. However, if the patient with whom contact occurred took antibiotics, then he was not infectious. 24 hours after starting antibiotics, the patient becomes non-infectious.
Causes
There is only one direct cause of purulent sore throat - infection with streptococcus or staphylococcus. In medicine, there are numerous cases of “family” epidemics, when the whole family became infected in a short time when using the same cutlery. The gap in the frequency of appearance of symptoms of purulent tonsillitis in this case ranges from 1 to 5 days.
Additional causes of purulent sore throat:
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- The presence of staphylococcus or streptococcus pathogens in the body;
- Weakening of the immune system.
Cases of purulent sore throat are common due to constant stressful psychological stress. For children, this often happens during the transition from preschool to school, during exams, and with any problems in studying and communicating with peers.
In children from six months to 1 year, purulent tonsillitis is one of the most common diseases. In children aged 3 years and older, the main reason for the development of inflammation of the tonsils and the formation of purulent plugs is considered to be a general decrease in immunity. The reason for a surge in infection can be sudden hypothermia, the presence of dental caries, breathing problems due to a deviated nasal septum or polyps.
Causes of sore throat
Every person’s body contains both beneficial and harmful bacteria. But thanks to the normal functioning of the immune system, harmful bacteria are suppressed due to the production of special antibodies. As a result, bacteria cannot overcome the protective barrier and remain in the body, so to speak, in an inactive state.
When the immune system is weakened, harmful bacteria get a chance to become active and begin the inflammatory process. As soon as this happens, the first symptoms are visible. The reasons for weakened immunity in children are varied:
- lack of vitamins in the diet
- hypothermia
- drinking a glass of cold water in summer or winter
- drafts
All these reasons contribute to a decrease in the body’s protective function. Even contact with children who have a sore throat is a cause for the disease. Therefore, it is very difficult to protect a child from acute tonsillitis, and if he does get sick, it is important to know the symptoms of the disease and how to treat it.
Symptoms
With the development of acute or exacerbation of chronic forms of purulent tonsillitis, a sore throat appears, which intensifies when swallowing. The child may complain of a feeling of discomfort in the oral cavity. At this moment, kids behave restlessly, are capricious and cry for any reason. General malaise and weakness always accompany the onset of tonsillitis. After a short period of time, in the acute form, a sharp increase in temperature occurs to 40º C or more. Sometimes the temperature does not decrease even after taking antipyretics.
With the viral nature of the disease, inflammation and swelling of the nasopharynx occurs, and breathing is impaired. The child refuses to eat and sleeps poorly. Due to purulent plugs that form on the tonsils and the back wall of the pharynx, bad breath appears. After the pus matures, a cough begins, with the help of which the body rejects phlegm.
Symptoms of bacterial (Fig. 1) and viral (Fig. 2) sore throat in children
When examining the oral cavity by a doctor, severe redness is observed at the back of the palate, tonsils and back wall of the pharynx, on which yellowish dots are clearly visible. These are purulent plugs. They give a high temperature that is difficult to bring down. When palpating the submandibular and parotid lymph nodes, their enlargement and soreness are noted.
It is difficult to determine a sore throat in an infant under 1 year of age. The baby just cries and cannot say that he is in pain.
If a child exhibits signs such as high fever, refusal to eat, sleep disturbances, or constant tearfulness, then an ambulance should be called. Don’t blame your baby’s discomfort on teething.
How to treat a child with purulent sore throat
Sore throat with ulcers in a child usually occurs in an acute form. Before the age of one year, doctors insist on referral to a hospital. Children aged 2-3 years can be treated at home if there are no clearly complicating diseases and conditions. The standard treatment plan for acute purulent tonsillitis in a child includes the simultaneous use of several groups of drugs.
Antibiotics to suppress bacterial growth. As a rule, penicillin drugs, amoxicillin and analogues are prescribed. At the first appointment, an allergy test is required. Severe forms of purulent tonsillitis require the use of cephalosporins. We do not indicate the names - only a doctor should make the appointment!
Antiseptics in the form of rinses and sprays - with iodine, miramistin, furatsilin. These are Iodinol, Hexoral, Ingalipt, Lugol. Some gargles and [sore throat sprays] have an unpleasant taste. It is allowed to use products with sage and chamomile extracts. Some formulations may contain anesthetics to relieve sore throat. Doctors of the old school may recommend applying streptocide powder, brought to a thick suspension, to the tonsils.
Antipyretic drugs based on paracetamol, Ibuprofen and analogues. Small children under one year, and sometimes up to two years, are prescribed rectal suppositories. Suspensions are given up to 5-6 years.
The support complex includes vitamins and multivitamins, probiotics to maintain normal digestion. Not all doctors highly appreciate the effectiveness of immunomodulators, but they can recommend taking them.
The prescription of specific drugs and forms depends on the age of the child and individual contraindications. You should not take risks and carry out treatment according to your plan!
What can you give to children with ulcers in the throat?
It is somewhat easier to quickly cure purulent sore throat in a child after 6 years of age than in a child. At this age, you can achieve effective gargling, use irrigating agents, and monitor your well-being by questioning.
Important to know: Symptoms and treatment of follicular tonsillitis
The temperature begins to drop only after 38.5 C, in infants after 38 C. Until this threshold, the body fights bacteria quite effectively.
Under the age of 3 years, sprays for sore throats and sore throats should not be used - these drugs can cause life-threatening spasms of the larynx or pharynx! You should not use lozenges and lozenges for a sore throat, as the child may swallow them, choke, or damage the mucous membranes.
Older children can be given salt, iodine and soda rinses. The use of any iodine preparations is not allowed for thyroid disorders!
Modern pharmaceutical remedies for purulent sore throat in children completely cover the need for treatment, so you can refuse self-made solutions for gargling and irrigating the throat.
Possible complications
Complications of purulent tonsillitis develop in the absence of timely correct treatment. In children, the most dangerous complication if the rules of preliminary diagnosis are violated is diphtheria. This disease in its clinical picture is similar to tonsillitis in the acute stage. Plaque is visible on the tonsils. At an advanced stage of chronic tonsillitis in children, tonsil removal may be prescribed.
A distinctive feature of diphtheria is that with this disease dense fibrous films can form that completely block the airways. If left untreated, the baby may die from simple suffocation.
Other complications of purulent sore throat:
- Development of peritonsillar abscess with accumulation of pus behind the tonsils (urgent surgical opening and constant monitoring in a specialized hospital are required);
- Rheumatism with the formation of heart valve defects, damage to the cartilage tissue of the joints, and the development of spondylosis;
- Meningitis and inflammation of the arachnoid membrane of the brain;
- Acute renal failure due to long-term severe intoxication;
- Secondary pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis;
- Toxic hepatitis;
- Endocarditis, serous myocarditis, disruption of the heart muscle.
The consequences of purulent tonsillitis can appear years later. This is usually expressed in the constant presence of streptococcus or staphylococcus pathogens, which is detected during a random examination. Thus, in 15% of women registered for pregnancy, hemolytic streptococcus is detected when examining a smear from the throat. And Staphylococcus aureus is found in 36% of women.
This pathological condition is dangerous not only for the health of the expectant mother, but also for the formation of internal organs in the fetus.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional methods of treatment are effective when used together with drug therapy.
Kill viruses and bacteria and disinfect the air in the room with chopped onions. It is placed in a plate in the child's room. Onions contain phytoncides that help fight viruses and bacteria. Due to the high content of vitamins, minerals and biologically active substances, onions are used as the main remedy against influenza and sore throat.
Another folk remedy for gargling is beetroot juice. It must be diluted in a glass of water and rinsed three times a day.
Apple cider vinegar is a popular home remedy. Its solution with boiled water helps to wash away mucus and purulent plugs from the surface of the throat and tonsils.
Another natural antiseptic from the garden is arugula. If this greenery grows in the garden, you can squeeze the juice out of it and gargle. Active biological substances kill infections in the respiratory tract.
Sea buckthorn oil has bactericidal properties. It is used to lubricate the throat and as a gargle. You can prepare a healthy drink with sea buckthorn oil and honey. Drink in small sips three times a day.
An effective folk remedy is a solution of lemon or citric acid with boiled water.
Contraindications to this method:
- for allergic reactions;
- as the only method of therapy;
- infants up to three months (after this age, the list of remedies is strictly limited).
At home, prepare fruit drinks, infusions and decoctions for your child using:
Treatment
Treatment of purulent tonsillitis should be comprehensive and include a number of measures aimed at eliminating infection and pus, relieving swelling and symptoms of intoxication.
By medication
The standard treatment regimen for purulent sore throat includes measures such as:
- Antibacterial therapy;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Symptomatic therapy;
- Antihistamines;
- Taking vitamin C and routine in large quantities to strengthen the vascular wall;
- Gargling.
It is not recommended to carry out any activities related to heating the area of inflamed lymph nodes. This can provoke the development of lymphadenitis.
The choice of drugs for the treatment of purulent tonsillitis in a child depends on the age of the patient and the form of infection. It is also necessary to take into account culture data for sensitivity to antibiotics. In early childhood, it is recommended to use antibacterial drugs in combination with antimicrobial agents, such as Biseptol-240 or Co-trimoxazole.
Recently, when treating purulent tonsillitis, pediatricians are increasingly prescribing the drug Sumamed to small patients. This medicine gives the fastest results with minimal risk to the baby’s health. But you can use other antibacterial agents, for example:
- Benzinepenicillin (mainly used in the form of intramuscular injections for severe disease in children and adolescents);
- Azithromycin or Azitral;
- Amoxicillin;
- Amoxiclav (for children from 6 months in the form of syrup and soluble tablets with banana flavor);
- Ciprofloxacin or Ciprolet (for children over 3 years old);
- Tsifran (intramuscular injections).
Antibiotics for purulent sore throat are usually supplemented with antimicrobial agents, such as:
- Biseptol - 480;
- Metronizdazole;
- Trichopolum;
- Streptocide.
The throat with purulent sore throat is the main source of infection and pain. You need to know how to treat your throat; The speed of restoration of the mucous membranes depends on this. Usually, for this purpose, various sprays are used to irrigate the mucous membranes and tonsils. These medicines have antimicrobial and regenerative properties. The most popular among them:
- Kameton;
- Bioparox;
- Hexoral;
- Miramistin;
- Chlorophyllipt;
- Stopangin et al.
Lugol for purulent tonsillitis can be used in the form of a spray and solution for lubricating the tonsils.
In addition, rinses are prescribed every 30 minutes during the day. Before gargling, you need to moisten your mouth with a weak soda solution.
Basic means for gargling with purulent sore throat:
- Hydrogen peroxide solution with a concentration of 3%;
- Iodinol at a concentration of 1% (can be used no more than 6 times a day);
- Potassium permanganate;
- A decoction of chamomile with the addition of sea buckthorn oil;
- Boric acid, diluted with warm water to a concentration of 2%;
- Rotokan or Stomatofit;
- Furacilin (1 tablet per 150 ml of warm water).
A triple rinse solution, which contains 5 drops of iodine, half a teaspoon of salt and soda per 1 glass of water, is effective for rinsing at home.
Folk remedies
In order to speed up the healing process, you can use folk remedies in combination with antibiotics. The following are the most popular recipes used for purulent sore throat:
- Grate the beets on a fine grater and squeeze a glass of juice out of it. Add 1 tbsp. a spoonful of vinegar and gargle with the resulting solution 6 times a day until recovery.
- Mix 1 part calendula flowers with 1 part eucalyptus leaves and 2 parts chamomile herb. 1 tbsp. Pour a spoonful of the resulting mixture into 1.5 cups of boiling water and boil over low heat for 2 minutes. Wrap the resulting broth and leave for 30 minutes. Gargle 2 times a day, and at first the temperature of the broth should be 26º C, and then every day it should be lowered by 1 degree, gradually bringing it to 16º. This procedure not only relieves inflammation, but also hardens the throat.
- Infusions of herbs (calendula, eucalyptus, chamomile, mint, lemon balm, licorice, sage) used for gargling give a good effect in the treatment of purulent sore throat. They remove plaque from the tonsils and eliminate inflammation. Based on similar collections, brew teas by adding raspberry and currant leaves.
- After each meal and rinsing, let your child chew or suck natural propolis. Every day you can consume 1 teaspoon of propolis, dissolving the portion for 20-30 minutes.
With purulent sore throat, it is very important that the child drinks plenty of fluids. Warm drinks (compotes, mineral water, raisin or rosehip decoction) will enhance the effect of folk remedies.
Local treatment and antipyretics
Purulent tonsillitis involves local treatment, which must be carried out correctly. It is necessary to do the procedure only after eating. The throat and oral cavity should be treated every 3 hours; after the procedure, you should not eat or drink. Lugol and Iodinol should be used for such therapy, however, these drugs are prohibited for children under 12 months. After 1 year, you can treat the oral cavity with these medications no more than once every day.
In order not to overload the body, the pediatrician will prescribe 1-2 drugs with different effects..
How to treat fever with sore throat? Like any inflammatory disease, purulent tonsillitis is accompanied by high body temperature, which rises all the time until the purulent plaque is eliminated. Usually, when taking an antipyretic drug, relief occurs for only a few hours, so it is important to choose the right drug. To effectively reduce the temperature, an antibiotic is prescribed for a period of 2–3 days. All this should be taken in combination with an antipyretic drug. Most often, Paracetamol in suspension, Calpol, Panadol, Efferalgan, and Ibuprofen are used to treat children. It is better to insert suppositories for babies, as they are absorbed faster. But teenagers can take Ibuklin.
You can take antipyretic drugs only if your body temperature has risen above 38°C.
When the temperature rises, antibodies are produced, that is, the body independently fights bacteria and viruses, and if at this time you take medicine and lower the temperature, this process will be interrupted, and the disease will develop further. If the child normally tolerates a temperature above 38°C, then it is possible not to bring it down. But in children under 12 months of age, this must be done, since a fragile body can react negatively to high temperature.
If the increase in temperature is accompanied by pain and cramps, then it is necessary to begin to bring it down already at 37.5°C. If it is impossible to reduce the fever with medications, you can use traditional recipes. If this does not help, the child’s condition worsens, and the temperature creeps up, then you should immediately call an ambulance.
Until the doctors arrive, it is necessary to give the child plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration; you can put a cold, damp towel on the stomach and head.
Prevention
Measures to prevent purulent tonsillitis in children are well known. It is necessary to accustom a child to lead a healthy lifestyle from childhood and carry out hardening procedures. It is recommended to harden your throat. Preventative rinses are perfect for this purpose: start with warm water, gradually lowering the temperature.
If a child often suffers from purulent tonsillitis, then make sure that he does not get hypothermic and wears warm socks. In order to prevent purulent sore throat, you can give your child immunomodulators to drink, for example Broncho-Vax or any others that the doctor recommends.
Ointment “Doctor Mom”: instructions for use
All available methods of treating adenoids in children are described here.
Selecting antibiotics for the treatment of sinusitis
Sore throat - what is it?
Tonsils are an obstacle to the path of microorganisms into the organs of the lower respiratory system. Microbes accumulate on the surface of the tonsils, multiply and cause a dangerous disease for children - tonsillitis. The disease is often diagnosed in children attending kindergarten or school. Sore throat in a one-year-old child occurs in an acute, severe form and requires mandatory hospitalization. When the first symptoms of the disease appear (lethargy, refusal to eat), you must call a doctor.
conclusions
So, purulent tonsillitis is a rather dangerous disease that threatens the child with serious complications. That is why parents need to take full responsibility for the treatment of the disease and follow the doctor’s recommendations. After recovery, you need to monitor the child’s condition, especially immunity, and take a number of preventive measures that can help prevent relapse. Frequent relapses will certainly lead to a chronic form of tonsillitis, and this is fraught with even more serious consequences. Follow all your doctor's recommendations conscientiously to reduce risk factors to a minimum.