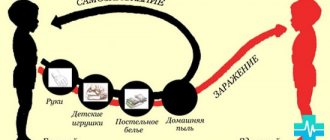
According to official data, the incidence of influenza in several regions of the Russian Federation has exceeded the epidemic threshold, that is, an influenza epidemic has begun. Since the influenza virus is easily transmitted by airborne droplets, we can expect the disease to spread throughout all regions of the country in the near future.
The flu, like most infectious diseases, begins with a slight malaise. Then the condition quickly worsens: the head, muscles and joints begin to ache very much, the body temperature rises, and general weakness appears. A little later, an annoying dry cough, pain in the chest when breathing, sneezing and a runny nose begin to annoy. If the immune system is strong enough, after a few days of complete loss of strength, these manifestations gradually decrease, but the symptoms will completely disappear no earlier than after 7-10 days. But this cannot be called a complete recovery - the body, weakened by the infection, will regain strength for at least another month.
The flu is more dangerous than it seems
Most people tend to underestimate the danger of the flu. However, this disease does not always develop according to the scenario described above. It happens that due to severe influenza intoxication, increased bleeding, disruption of the brain and internal organs develop, which leads to death a few days after the onset of the disease. This form of influenza is called hypertoxic. In addition, the disease is dangerous due to its complications: inflammation of the lungs, membranes of the brain or heart muscle.
Children are especially vulnerable to the effects of the virus. Their immune system is imperfect and cannot always adequately fight off infection. Therefore, the risk of severe illness and complications of influenza in young patients is much higher than in adults. According to research, up to 70 percent of all health problems in children are associated with influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections.
Prevention
Specific prevention of influenza in children includes vaccination on the eve of the epidemiological increase in incidence (at least 1 month in advance). Every year, the WHO (World Health Organization) predicts the strain of influenza virus that will be circulating at the time of the rise in incidence. Based on the forecast data, a vaccine is produced. Its administration is primarily indicated for children with chronic somatic or infectious pathologies. Non-specific protection measures are also carried out, which include:
- Limiting visits to places with large crowds of people (gyms, cinemas).
- Taking multivitamin preparations to maintain immune activity at the proper level.
- Washing hands after going outside.
- Ventilate the child’s room at least 2 times a day.
- Avoiding overwork and hypothermia.
- A balanced diet with sufficient intake of plant fiber.
- Use of Oxolinic ointment, which is applied to the skin and mucous membrane of the nostrils (non-specific protection against the penetration of the virus into the cells of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract).
Following simple preventive recommendations and timely treatment of influenza in children makes it possible to avoid complications and negative consequences. The severe course of the infectious process, the presence of chronic pathology, as well as the age of the child under 1 year are indications for a mandatory visit to the doctor.
Children at risk
Children from big cities are at particular risk. This is due to several factors. Firstly, almost all such children attend organized groups - kindergartens and schools, and many also attend various developmental courses and sports sections. Since the influenza pathogen is highly virulent (infectious) and is transmitted by airborne droplets (by coughing, sneezing and talking), it spreads at lightning speed in such groups. Once one sick child coughs at school, a few days later a significant portion of his classmates will be at home with a high fever.
The decrease in the immunity of the children's population of large cities also contributes to the spread of the influenza and ARVI epidemics. It is caused by both the polluted air of the metropolis and the characteristics of the diet, which is not always healthy and nutritious. Often, the child’s immunity is undermined by the parents themselves, who unreasonably, without a doctor’s recommendation, prescribe dietary supplements, antibiotics, adaptogens and other drugs.
Therefore, it is not surprising that from year to year the number of frequently and long-term ill children increases. In some regions, such problems are observed in more than half of the child population.
Meanwhile, a single comprehensive approach to the treatment and prevention of frequent respiratory diseases in children in healthcare has not been developed. This leads to an additional deterioration of the epidemic situation during the cold season.
To prevent the disease, there are preventive vaccinations. They are really effective, but they do not help in all cases. This is due to the high variability of the virus - its antigens (surface proteins that are recognized by the immune system) are constantly changing. Vaccines contain only a limited set of antigens and are effective only against viruses containing them. In addition, vaccination serves only as a preventative measure, and if the disease has already developed, treatment is necessary.
But the flu is caused by a virus, not a bacteria. This means that antibiotics are absolutely ineffective against it. There are no drugs that kill the virus that has entered the body. Therefore, the task of destroying the influenza pathogen falls entirely on the immune system.
One of its most important components of antiviral immunity is the production of interferons. These substances change the functioning of cells in such a way that they become immune to the virus and do not participate in its reproduction. In addition, under their influence, immune cells – lymphocytes and macrophages – are activated.
The more interferons are produced, the easier the course of the disease will be, the faster recovery will occur and the lower the risk of complications. However, the body is not always able to quickly respond to the introduction of a virus. Especially if it is a child’s body with reduced immunity.
How does the virus manifest itself?
First of all, the flu affects the bronchial system, larynx and trachea. It is in them that pathological processes caused by the main causative agent of the disease occur. In the lung tissue, circulatory disturbances can be observed, in the pleura there is fragility of small vessels and, as a result, small hemorrhages. The formation of serous focal inflammation is possible. The younger the child, the higher the chance of this process.
With influenza, the addition of pathogenic flora increases the risk of developing pneumonia. For this reason, it is very important to recognize the first symptoms of influenza in a child and take therapeutic measures.
Flu symptoms in a child may vary and will depend on the subgroup of the disease. Thus, type A virus is characterized by an incubation period of several days and is included in the group of ARVI (acute respiratory infection). Influenza in children type B is accompanied by an incubation period of 4-5 days. Both types of disease begin with an acute course and an increase in central body temperature to 39 and even 40 degrees. As a rule, the child complains of chills, loss of appetite, weakness, and body pain. The peak of the febrile state is observed at the end of the first day of the disease. This period is accompanied by the most pronounced signs of the pathological process.
Often the acute viral process of influenza provokes nausea and vomiting. To protect a child from severe flu and colds, preventive syrup, drops, and decoctions should be given. Symptoms and treatment corresponding to the clinical picture will be considered by more than one doctor, since in children the symptoms may concern other organs.
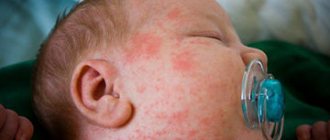
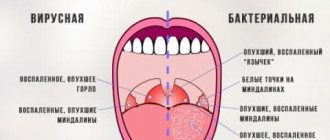
Then you can observe more standard symptoms of a respiratory viral disease - a cough, often dry, nasal congestion with a slight discharge of clear secretion, sore throat, especially pronounced when swallowing. When examined by a doctor, swelling of the tonsils and redness of the throat mucosa are diagnosed. The baby's outer skin may appear pale.
Influenza-like lung damage or segmental edema is a common feature of the disease and disappears on its own in the first couple of days. There are no clinical signs, but on x-ray examination the swelling is clearly visible.
In other cases, the period of fever can last up to 5 days, then the body temperature decreases, and the child feels an improvement in his condition, signs of intoxication disappear. With the addition of bacterial flora, the duration of fever increases to 10-11 days. In this case, general signs of flu may bother a child for 15-20 days.
How to protect your child from the flu? First of all, it is necessary to monitor the state of the immune system. Even the slightest immunodeficiency increases the possibility of infection many times over.
Increased defense capability
But this situation can be corrected - in the arsenal of modern pharmacology there are drugs whose action is aimed at stimulating the functioning of the immune system. One of them – the most researched and effective – is the original domestic drug cycloferon. The action of its active component methylglucamine acridone acetate is aimed at enhancing the production of its own interferons in the body. Due to this, nonspecific immune defense is enhanced and the susceptibility of cells to the virus is reduced.
Clinical trials of cycloferon have shown the effectiveness and safety of its administration to young patients. Therefore, the drug is approved for use in children from the age of four. It has proven itself especially well as a means for emergency prevention of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections, that is, when taken immediately after contact with a sick person or when the very first signs of the disease appear. But even if the disease has already developed, the administration of cycloferon reduces its severity and duration, and also serves as a good prevention of complications.
How to protect your child from the flu
Measures to prevent influenza and colds in children involve a whole range of measures. These include:
- A complete diet, enriched with all necessary elements. The most important are vitamins C, A and E, which have antioxidant properties. Fermented milk products with live bifidobacteria, which stimulate the immune system, are also useful.
- Regular walks outdoors, preferably in nature.
- Hardening and doing sports as much as possible.
- Lack of stress and unnecessary mental stress. You should not send your child to all clubs and sections in a row, worrying about his future. This can have a negative impact on your current health.
- Healthy sleep in a ventilated area also creates a powerful immune response to viral attacks.
During the epidemic, it is recommended to avoid visiting crowded places. Before going outside, you can lubricate your nostrils with oxolinic ointment, and when you come home, rinse them with warm water. For prevention purposes, older children use interferon, which is instilled into the nostrils three times a day.
We also recommend reading the article: “How to help a child who often suffers from colds.”
An important point is how to protect your child from the flu if someone in the family is already sick. First of all, the patient should be isolated as much as possible. It would be ideal if he could be allocated a separate room or at least fence off a corner with a screen. The sick person must have his own dishes, towel, and bed linen. They need to be washed and washed separately from other things. The baby should not be allowed to communicate with a sick family member. Anyone caring for an infected person should wear a protective mask and wash their hands with soap. Wet cleaning of the apartment is carried out daily using disinfectants.
Treatment regimen for influenza and ARVI in children
According to the instructions, for influenza and acute respiratory viral infections, the drug is prescribed in age-specific doses on days 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23 and then once every three days. The course of treatment ranges from 5 to 15 doses, depending on the severity of the condition and the severity of clinical symptoms.
As a means of emergency nonspecific prophylaxis during the seasonal rise in incidence, the drug is prescribed in the indicated age-specific doses on days 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, then five more doses with an interval of 72 hours.
Remember that the course of treatment and dose of the drug can only be determined by a doctor, depending on the severity of the condition and the severity of clinical symptoms.
Based on materials provided by POLYSAN"
Features of the influenza virus
All influenza viruses produce dangerous toxins. The most common are:
- neuromenidase;
- haemaglutenin.
Due to the action of these toxins, damage to nervous tissue and blood vessels occurs. Pinpoint hemorrhages appear, headaches, pain in muscles and blood vessels increase. Changes in the number of antigens responsible for the production of these toxins leads to the fact that the virus often changes its structure. Because of this, humans do not have permanent immunity against influenza.
The mechanism of influenza virus infection in children
Once the influenza virus enters the respiratory tract, it infects the respiratory epithelium (particularly the trachea). After entering epithelial cells, the virus begins to multiply intensively and produce toxins. Due to exposure to toxins, degenerative changes in the cells of the respiratory system occur (the structure of the cells changes to produce new virus cells).
After the virus has divided into many copies and the cell's resources are exhausted, the flu exits through the epithelial membrane. In this case, in 50% of cases the cell dies. All cells that are infected with the virus are attacked by the immune system (T-killer cells), as a result of the attack the basal layer of the respiratory epithelium and nerve endings are exposed. Exposed nerves lead to severe pain along the respiratory tract, and more severe irritation, which causes hoarseness and a dry, painful cough.
IMPORTANT! Due to the destruction of epithelial cells by the influenza virus, local immunity decreases. This leads to the development of a secondary bacterial infection.
When should you call a doctor?
According to WHO, about 2.5 million children die from influenza and its complications every year in the world, since this disease is accompanied by damage to the respiratory system and prevents adequate air intake.
Symptoms that indicate the need to see a doctor include:
- no improvement on the fifth day of treatment;
- elevated body temperature on the seventh day of the flu;
- child's refusal to eat and drink;
- vomit;
- difficulty breathing (shortness of breath, intermittent breathing);
- increased intensity of cough, especially with a deep breath.
Signs of urgent and mandatory seeking of medical help are:
- hemoptysis in a child;
- convulsions;
- swelling of the neck;
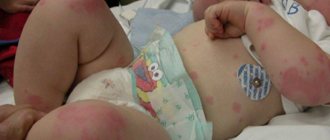
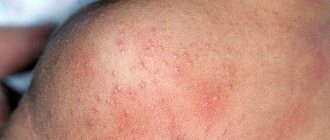
- skin rash;
- lack of effect from antipyretic drugs;
- pale or blue skin;
- vomiting and diarrhea;
- significant reduction in blood pressure;
- loss of consciousness;
- arrhythmia or decreased heart rate.
Can you cure the flu on your own?
Of course, self-medication is contraindicated for any disease, especially for children. However, since flu treatment is mainly carried out at home, there are several recommendations to promote a speedy recovery of the child.
Despite the lack of appetite, the child's body needs an increased amount of nutrients.
The flu diet should include:
- steamed protein dishes (lean meat, fish);
- weak natural broths;
- vegetable stew;
- dairy products;
- omelette.
During this period, it is undesirable to introduce fried foods, dry and crumbly foods (rusks, cookies) into the child’s diet, since they can additionally irritate the inflamed mucous membrane of the throat. You should also avoid foods that contain high levels of sugar, which reduces the activity of white blood cells (immune cells).
A significant point in the self-treatment regimen is the drinking regime. A sufficient amount of fluid will help the body get rid of toxins as quickly as possible and reduce the symptoms of the disease. Also, with the flu, increased sweating is often observed, so it is necessary to replenish fluid loss and prevent dehydration.
Drinks should be warm (temperature equal to body temperature) and not hot, as hot liquid can burn the mucous membrane of the throat and increase pain in it.
The most useful drinks for children and adults with the flu are:
- fruit drinks;
- herbal teas (you can add a small amount of honey);
- water (still);
- fruit juices diluted with water;
- compotes;
- pharmaceutical preparations for rehydration.
The room in which a sick child is located should be regularly ventilated, since the circulation of fresh, moist air will reduce the dryness of the mucous membranes of the nose and throat and enhance the activity of local immunity (stimulating the formation of mucus as a barrier to infection).
Thus, a gentle but nutritious diet, plenty of fluids and humidified air will have a comprehensive strengthening effect and will help the child’s body overcome the infection as quickly as possible.
We strongly do not recommend self-medication with medications, as this can aggravate the course of the disease and lead to the development of complications. To date, drugs with proven antiviral activity are not freely available, and drugs for symptomatic treatment should be prescribed individually and only by a doctor.