Rhinitis in children - symptoms:
- Headache
- Weight loss
- Sleep disturbance
- Fever
- Sweating
- Nasal congestion
- Fever
- Malaise
- Tearing
- Anxiety
- Sneezing
- Rapid breathing
- Smell disorder
- Burning in the nose
- Shallow breathing
- Copious nasal discharge
- Nose tickling
- Violation of the sucking process
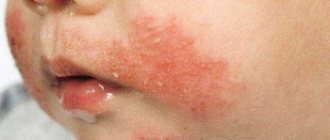
- Irritation of the skin under the nose
- Pressure in the bridge of the nose
Symptoms
Rhinitis in children can be either an independent pathology caused by bacteria, viruses or the action of allergens, or a consequence of previous infections (influenza, diphtheria, measles, etc.).
Depending on the form, a runny nose is classified into chronic and acute, depending on the characteristics of its manifestation - into seasonal, permanent and paroxysmal.
Symptoms of the disease in children develop in three stages:
- Irritation
Rhinitis of a viral nature, bacterial or allergic origin begins with a sensation of scratching, slight burning, and dryness of the nasal mucosa.
Congestion gradually develops. The duration of this stage ranges from several hours to several days.
- Watery discharge stage
As inflammation develops, watery discharge occurs, forcing the patient to constantly blow his nose. The use of scarves causes redness and swelling of the nasal septum and surrounding skin.
There is tearing, frequent sneezing, and inability to breathe normally. The duration of the stage is up to two days.
- Stage of purulent discharge
Nasal congestion and sneezing gradually go away, the discharge from watery becomes thick, containing impurities of pus. Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses begins to subside.
The total duration of the three stages is 7-10 days, if there are no complications of inflammation and adequate treatment takes place.
Features of the course of rhinitis in infants
Practice shows that rhinitis in infants, especially premature ones, occurs in the most severe form.
The distinctive features of the disease in newborns are:
- high probability of complications;
- the predominance of general symptoms over local ones;
- sudden onset of the disease;
- its bilateral distribution.
The cause of a runny nose in infants is their inability to clear their airways on their own.
Due to the narrowness of the nasal passages of newborn children, even minor swelling leads to serious breathing difficulties. The child is forced to take frequent and shallow breaths.
Other characteristic symptoms of the disease include:
- difficulties with breastfeeding: the baby is not able to breathe and suckle at the same time;
- restless sleep;
- nervousness, irritability of the baby;
- increased body temperature, in some cases fever.
Associated symptoms include loose stools, vomiting, and sudden weight loss. These signs are caused by swallowing air - a consequence of impaired nasal breathing.
When prolonged, rhinitis in newborns leads to oxygen starvation of the brain, which negatively affects the psychomotor development of the baby. In an effort to get more air, the baby throws his head back, which often provokes convulsions.
In a significant number of cases, infant rhinitis provokes dangerous complications: bronchitis, pneumonia, abscess, otitis media and others.
Features of acute rhinitis in older children
A runny nose in older children can be an independent problem or a complication of the following diseases:
- adenoiditis;
- flu;
- diathesis;
- diphtheria;
- whooping cough, etc.
In some cases, rhinitis becomes a consequence of individual intolerance to the administered vaccines.
Less commonly, rhinitis in an older child occurs due to the following factors::
- entry of a foreign object into the nasopharynx;
- prolonged exposure to the cold;
- allergic reactions;
- congenital or acquired disorders of the anatomical structure of the nose.
A feature of rhinitis in children and adolescents is its rapid development. The disease begins with a scratching, burning sensation in the nasal mucosa.
Then the following set of symptoms is added:
- excessive tearing;
- sneezing;
- impaired perception of tastes and smells;
- purulent or watery nasal discharge;
- congestion in one or both nostrils;
- migraine;
- a feeling of pressure, bursting from the inside in the area of the bridge of the nose.
Handkerchiefs and other methods of dealing with discharge from the nasal passages provoke redness of the skin of the nasolabial triangle and the appearance of painful cracks on it.
As the disease progresses, nasal discharge changes from watery to mucopurulent.
As this transformation progresses, the patient’s general condition normalizes: depression, irritability, loss of strength go away, and normal breathing is restored. Manifestations of the acute form of the disease subside within 7-8, less often 10 days.
Prevention
In general, preventive measures are aimed at eliminating the influence of possible factors for the onset of the disease. This includes timely treatment of viral diseases in the child, as well as avoiding severe hypothermia in his body.
Preventive measures should be aimed at:
- hardening the child;
- preventing the occurrence of any colds;
- minimize sudden temperature changes between indoors and outdoors;
- perform physical exercises (systematically);
- healthy and nutritious nutrition of a child is the main factor in strengthening his body and preventing diseases;
- ventilate the room where the child is, and it is also important to carry out wet cleaning;
- sunbathing as a child;
- adhere to basic rules of personal hygiene.
Symptoms of chronic rhinitis in children
Chronic rhinitis causes persistent changes in the nasal mucosa. Depending on the form of the runny nose, it grows, acquiring hypertrophied sizes, or becomes thinner.
Common manifestations of the disease include:
- impaired sense of smell;
- inability to breathe normally through the nose;
- feeling of dryness in the nasal cavity;
- nasal voice;
- frequent headaches;
- snore;
- cough, which worsens in the morning, after eating, with sudden changes in temperature;
- general lethargy, constant feeling of fatigue.
The severity of the listed symptoms and their combination varies for each individual case. What exactly will be the key sign of rhinitis depends on its form.
For example, simple chronic rhinitis in children is similar in symptoms to the acute form. Nasal discharge, nasal congestion, and impaired sense of smell are observed. When mucus drains down the nasopharynx, the patient may cough or gag.
Hypertrophic rhinitis provokes constant disturbances in nasal breathing, migraines, decreased acuity of smell and hearing. The voice of sick children becomes nasal, they experience increased fatigue, lethargy, and deterioration in school performance.
Vasomotor rhinitis is manifested by nasal congestion, discharge, tearing, and sneezing. Specific signs include facial redness, sweating, and in some cases, heart rhythm disturbances and migraines.
The atrophic form of the disease in children is diagnosed less often than others . Its main manifestation is crusts covering the membranes of the nasal passages, discharge with a strong unpleasant odor. Bleeding and a feeling of constant tightness in the nose are possible.
The allergic form of rhinitis is manifested by itching, burning, and sneezing. The patient constantly scratches the tip of his nose and cannot breathe normally due to congestion. The complex of symptoms is complemented by lacrimation, pain in the eyes, and impaired taste perception.
How to identify this type of runny nose
Chronic rhinitis is usually diagnosed by an ENT doctor. You should contact him at the slightest concern. After all, the child’s health is very important, and under no circumstances should rhinitis be caused.
When diagnosing, it is important to determine the nature of the chronic runny nose in order to further consider ways to get rid of it. Usually the doctor asks whether the child has constant nasal congestion, whether he sleeps with his mouth open, whether there is discharge, what color the mucus is, whether there is dryness in the nose and dried discharge, whether there has been an allergy to anything, whether there are any chronic diseases. Based on all this, notes are made that will help in further examination.
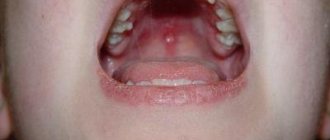
Next, the pediatrician examines the baby. Listens to the lungs, heart rhythm, examines the nasal cavity and mouth, throat, limbs, skin. With chronic rhinitis, the nasal passages are narrowed, and there is constant discharge in the nose. The shells are red or blue.
Your doctor may recommend a complete blood count, bacterial culture of nasal mucus, an allergy test, an x-ray, or a nasal tomography. There is also a new type of research - rhinomanometry. This is a measurement of air resistance in the nasal cavity.
Nasal swabs are taken to determine whether rhinitis is related to a cold or infection. Based on the test results, the doctor prescribes complete treatment. The chances of recovery are very high if you go to the clinic in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of rhinitis
To diagnose rhinitis in children, you need to go to an appointment with an ENT specialist, during which the doctor will collect an anamnesis with the help of the little patient and parents.
He will be interested:
- nature of symptoms;
- their intensity;
- moments of their occurrence;
- the patient has concomitant diseases or allergic reactions.
The next stage of administration is a visual examination of the mucous membrane, which can indicate the type of runny nose.
For example, with atrophic rhinitis it becomes covered with crusts, with vasomotor rhinitis it becomes pale and bluish, with catarrhal rhinitis it becomes red and lumpy. The examination is carried out using a special device - a rhinoscope.
When the first assumptions regarding the diagnosis are made, the doctor prescribes instrumental studies: X-ray, CT, endoscopy. Additionally, laboratory tests (blood, urine, mucus secretion) may be required.
What needs to be examined?
Before prescribing treatment for acute rhinitis to a child, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the disease; for this, parents should contact a pediatric otolaryngologist (ENT).
The doctor will collect a history of the patient’s life and illness and examine the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity using a rhinoscope.
To differentiate (determine the exact cause) of the disease, additional diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- X-ray of the paranasal sinuses - is a mandatory study in the presence of purulent nasal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- laboratory diagnostics (blood and urine tests) - allow you to identify the number of rods in the blood, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- allergy tests - prescribed for suspected rhinitis of allergic origin;
- bacterial culture of nasal discharge - is carried out if a bacterial etiology of the runny nose is suspected, in order to determine the causative agent and select an effective drug.
It is very important to distinguish acute rhinitis from a specific runny nose, which is one of the clinical signs of influenza, adenovirus infection, measles, scarlet fever and other infectious diseases.
Sometimes the patient is prescribed a consultation with other specialists - a surgeon (if a foreign body is suspected in the nasal cavity), an infectious disease specialist and an allergist (if allergic rhinitis is suspected).
Drug therapy
Treatment of rhinitis in children involves a combination of medications with the use of physiotherapy, correction of the daily routine and diet.
Medicines prescribed by a doctor to combat a runny nose are divided into four groups depending on the direction of action:
- Vasoconstrictors
They eliminate swelling, reduce the amount of mucus secreted, and therefore are considered an effective way to restore normal breathing.
Vasoconstrictor nasal drops of different brands have a similar principle of action, the difference lies in the active substance. Common options include Xylometazoline and Naphazoline.
The maximum duration of use of the drugs is 5-7 days, otherwise addiction will develop.
- Antiviral
Suppress the activity of viruses that cause the development of the disease . They are used under the strict supervision of a doctor and are used as a method of treatment and prevention. Products in this series are available in the form of tablets, ointments, suppositories, and nasal capsules.
- Antibacterial
Their active ingredient is an antibiotic that suppresses the activity of pathogenic bacteria that cause manifestations of acute rhinitis in infants and older children.
Most often, such drugs are used in the form of sprays, because It is this form that facilitates ease of administration and uniform distribution of the product in the sinuses. Antibacterial medications must be selected by a doctor and used strictly according to the scheme indicated by him.
- Antihistamines
The drugs are selected by the doctor depending on the factor that caused allergic rhinitis. These medications have a complex effect: they constrict blood vessels, reduce swelling, and fight inflammation.
Prohibited actions
Very often, parents do not take their child’s runny nose seriously, self-medicate and are in no hurry to seek medical help, putting their child’s health at unjustified risk.
Below is a list of actions that are strictly prohibited for rhinitis in children:
- Never start treating a runny nose with antibiotics - antibacterial drugs are an excellent breeding ground for viruses, so starting to give medicine without a doctor’s prescription, parents thereby suppress the baby’s immunity and contribute to a long and complicated course of rhinitis. In addition, antibiotics for viral infections are ineffective and dangerous.
- You should not instill antibiotic solutions into your nose, even if your runny nose is of bacterial origin - solutions that are administered intranasally can cause a severe allergic reaction in the form of swelling of the respiratory tract and suffocation.
- You should not overheat a child with rhinitis, turn on heating devices near his bed and block the windows - all this leads to drying of the mucus in the respiratory tract and the active proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in it. Accumulation and thickening of mucus in the nasal passages and nasopharynx can cause the development of tracheitis or obstructive bronchitis.
- It is prohibited to use “adult” dosages of vasoconstrictor drugs into the nose - this leads to an overdose and severe side effects from the blood vessels and heart.
Herbal preparations
Treatment of rhinitis in children involves the widespread use of drugs based on herbal raw materials. Homeopathic remedies relieve inflammation and swelling, suppress the activity of viruses, and stimulate the patient’s body’s defenses.
Their advantage is naturalness, a minimum of possible side effects and contraindications.
Pinosol
These are nasal drops created on the basis of eucalyptus extract and pine oil. Rhinitis in children is an indication for their use.
The drug helps:
- clear the nasal passages;
- soften the mucous membrane;
- reduce inflammation;
- remove nasal congestion.
Unlike vasoconstrictors, Pinosol is not addictive and has virtually no side effects. The optimal duration of its use is up to 14 days.
Eucasept
It is actively used for the treatment of runny nose of various origins. The drug is based on fir and menthol extracts.
It has an anesthetic and softening effect, relieves inflammation, relieves pain, and normalizes free breathing.
How to treat chronic runny nose
Having determined the symptoms and treatment of a runny nose, the doctor writes a prescription. Only a pediatrician can prescribe effective treatment for a child. He may prescribe antiviral medications. They are usually prescribed to strengthen immune defense if the body itself cannot cope with a prolonged runny nose.
Also, antibacterial therapy, that is, antibiotics, is necessarily prescribed. Based on a blood test, it is determined which antibiotic is suitable for a given infection in order to begin to fight it. Antibiotics are taken for at least three days. If they are really suitable, then improvement occurs after just three doses. Parents and children will notice this. It is recommended to take anti-dysbacteriosis medications along with the antibiotic.
Your doctor may prescribe allergy medications to relieve nasopharyngeal swelling, itching, sneezing, and eye discharge. If the temperature is elevated, Paracetamol or Nurofen is prescribed. It is worth remembering that it is not recommended to lower the temperature below 38.5.
Sometimes treatment for chronic runny nose is selected taking into account the characteristics of the child’s body. Homeopathic remedies may be prescribed. Their effectiveness is still debated. Some doctors may prescribe them, since they are not as aggressive as many medications, but they relieve inflammation well.
An ENT specialist may recommend physical therapy or heating, laser treatment. If the procedure is truly indicated, then it will have an amazing effect, recovery is guaranteed.
Since chronic rhinitis has a diverse nature and origin, an examination is first carried out.
If it is allergic, most likely it can be treated without antibiotics, but if it is a symptom of an infection or bacteria, then antibiotics will need to be taken.
It happens that sometimes surgery is necessary to get rid of the disease forever. It is done at the discretion of the doctor.
How to treat infectious rhinitis
To choose therapy, the doctor determines the nature of the disease: fungal, viral or bacterial. Depending on the type of pathogen, a set of medications is selected.
A set of medications may include:
- antibiotics;
- antifungal drugs;
- antiviral agents.
To eliminate swelling and normalize breathing, vasoconstrictor drops are prescribed. Additionally, nasal rinsing, physiotherapy, avoidance of foods that irritate the mucous membrane, and drinking plenty of fluids are recommended.
If a runny nose is accompanied by an elevated temperature, antipyretics are needed.
Do I need to take hormonal and vasoconstrictor medications?
Vasoconstrictors effectively relieve the symptoms of rhinitis, which is important at stages 1-2 of the disease. To avoid side effects and addiction, they should be used under medical supervision for no more than a week.
Their uncontrolled use can cause chronic runny nose.
Hormonal drugs are effective for rhinitis, but often cause side effects: dry mucous membranes, rash, bleeding. They are not prescribed if there is individual intolerance and the patient is under 4 years of age.
To avoid adverse consequences, you need to use medications under the supervision of a doctor.