Disease concept
Pemphigus of newborns in medical practice is usually called a type of staphylococcal skin lesion, characterized by a benign or malignant course. With benign pemphigus, blisters with a diameter of 0.20 to 0.5 cm appear on the baby’s body. These formations are filled with liquid with a translucent consistency. The localization of rashes is, as a rule, the area of the tummy, inguinal and cervical folds, and limbs. Bubbles can appear either singly or in groups of several.
Why viral pemphigus is dangerous: features of treatment of an infectious disease
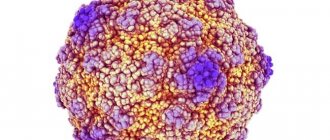
Viral pemphigus is a severe viral disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes of humans. As it develops, blisters with exudate form on the skin. The cause of viral pemphigus is infection with the Coxsackie enterovirus.
A microorganism can enter the body in two ways: airborne droplets and contact. The disease is diagnosed more often in children (affects mainly the mucous membranes), as well as in adult patients from 40 to 60 years old. Viral pemphigus is treated by a dermatologist.
The treatment plan is drawn up after the exact form of the disease has been established. Antihistamines, antipyretics, glucocorticosteroids, and antiseptic solutions may be prescribed. It is also important to follow a diet.
The doctor's recommendations should be followed until all symptoms disappear.
If the patient's body is weakened enough, the blisters spread over a large area of the body, affecting the outer surfaces of the lower extremities and genitals. With a mild course of the disease, the symptoms disappear within a week or 10 days, after which time the nail plates may fall off painlessly.
The main treatment of the pathology is to take drugs that modulate the immune response. Local treatment of blisters with antiseptics is important to prevent bacterial complications of infection.
Causes of pathology
Viral pemphigus of the palms and soles is caused by a special group of viruses – enteroviruses, more specifically – Coxsackie viruses, subspecies A16 and enteroviruses themselves, subspecies 71.
The first type of microorganisms causes damage, mainly only to the palms, which occurs easily and without complications.
Viral pemphigus in adults occurs most often over the age of 40 years; Children under 10 years of age and those who have recently had another viral infection are more susceptible to it. They become infected in the following ways:
- airborne droplets when talking with a sick person;
- when eating from the same container with a sick person;
- after a handshake or other physical contact with a patient, when liquid from a bladder deprived of a tire gets on the skin of a healthy person;
- when kissing;
- when particles of the patient’s feces enter the digestive system of a healthy person - if hands were not washed after going to the toilet, and the patient took someone else’s dishes, towels, toys, shook hands, touched the handrails of public transport, and the healthy person did not wash his hands afterwards.
The danger of viral pemphigus is that you can become infected not only from the patient, but also from:
- a person who is in an incubation period lasting 3-6 days;
- a carrier of the virus - a person who, due to the activity of his immune system, is not sick and feels well, but excretes the virus in his feces;
- recovered from this infection, for about those months after the blisters in the mouth or on the extremities have disappeared.
People with reduced immunity and those who have a hereditary feature of the upper layer of skin (epidermis), which gives them a tendency to develop viral pemphigus, are more likely to get sick.
The disease is characterized by seasonality: the virus is usually activated in spring, summer and autumn, while high and low temperatures kill the microbe in the environment.
People who have visited new places are more likely to become infected: the sea, nature, where other enteroviruses that differ from their own region “live” (the immune system of an adult usually develops protection against similar microorganisms in its own region).
Immunity is developed only to the strain of the virus that causes the disease. Other subspecies of enterovirus are still capable of causing viral pemphigus.
Watch a video about the causes and symptoms of pemphigus in pregnant women and newborns:
How does the disease manifest itself?
The first symptoms of viral pemphigus appear after 3-6 days of the incubation period. They are non-specific. This:
- fast fatiguability;
- drowsiness;
- worsening appetite and mood;
- temperature rise, usually to high levels.
Not always found, but may be:
- diarrhea;
- runny nose;
- headache;
- cough.
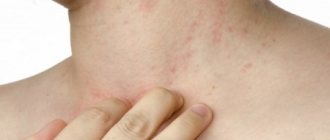
Such symptoms last 12-36 hours. Next, those symptoms of viral pemphigus appear, which make it possible to make this diagnosis. This is the appearance on the feet, hands, and sometimes the buttocks, thighs and genitals of blisters with the following characteristics:
- oval or elongated shape;
- with transparent contents, if a bacterial infection occurs, the color of the bubble changes to whitish;
- painful and itchy;
- around there is a reddish rim;
- after they burst, painful erosions up to 3 mm in diameter appear, bordered by a red rim;
- soon the ulcers become covered with crusts that fall off in 2-3 days, leaving no traces on the skin, in some cases only dark spots.
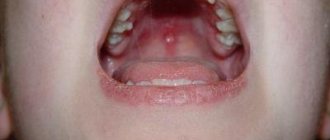
With viral pemphigus of the oral cavity, the temperature rises, yellowish blisters with a red rim around appear in the mouth. The rash is accompanied by halitosis. The blisters themselves hurt, the pain intensifies when food or drink gets on them, especially if they are sour, cold, hot or spicy.
In addition to a rash in the mouth, if a child is sick, there is coughing, vomiting, and later blisters appear on the extremities. They are located on the soles, palms, sides of the feet and hands. In more severe cases, the rash covers the elbows, knees, perineum and buttocks. The disease can lead to enlargement of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes.
Watch a video about diagnosing pemphigus:
Viral pemphigus of the oral cavity is very similar to a sore throat, so to make a diagnosis you need to see an infectious disease doctor. This step is necessary to ensure that penicillin antibiotics are not prescribed, which treat sore throat, but with enterovirus infection can cause the appearance of a special small-spotted rash.
A high temperature with viral pemphigus of any localization usually lasts up to 5 days, then subsides, and the patient feels relief. In general, about 10 days pass from the onset of the disease to the complete disappearance of all crusts. After this, the person, feeling completely healthy, secretes the virus in his feces for another 3 months.
If viral pemphigus of the extremities has been noted, after a week or a little longer the person’s nails may peel off. This process is painless and reversible - after 2 weeks, new nail plates grow.
Photo of a rash with viral pemphigus
Complications
Caused by enteroviruses or Coxsackie viruses, viral pemphigus can be complicated by such severe conditions as:
- pneumonia;
- encephalitis;
- meningitis;
- myocarditis – inflammation of the heart muscle tissue. It occurs mainly with Coxsackie lesions. This is due to the fact that there is a similar area in the structure of the virus and in the myocardium. The immune system, starting to attack the microbe, discovers that a similar locus exists in the structure of cardiac muscle cells. Mistaking it for a virus, the immune system attacks the heart;
- viral pemphigus during pregnancy, developing in the first trimester, can cause spontaneous abortion or fetal malformations that may be incompatible with life.
Enterovirus infection is usually mild, but in some cases its complications can cause death.
Features characteristic of the disease
To more accurately determine what pemphigus is, let’s highlight the main characteristics of the disease.
These include:
- The appearance of a rash in the form of blisters on various parts of the body. In addition, the baby suffers from the appearance of erosions and wounds on the body. Blisters can be single or multiple and appear on any part of the body and mucous membranes.
- Staphylococcal origin. Scientists believe that the main cause of the disease is a staphylococcal infection. These are pathogenic bacteria that can normally be found on human skin in small quantities.
- Highly infectious. Skin infection occurs very quickly and upon contact with a sick person, many people can become infected at once.
When a staphylococcal infection gets on the defenseless skin of a baby, pathogenic bacteria begin to multiply quickly. At the same time, the newborn’s immune defense is triggered. To prevent infection from spreading throughout the skin, immune defense encloses pathogens in so-called capsules. These are bubbles.
The skin of such blisters is very delicate. At the slightest touch, it is damaged and the contents of the capsule come out. This contributes to the spread of staphylococcal infection to healthy areas. To prevent damage to large areas of the skin, it is important to diagnose pemphigus in the early stages and begin treatment promptly. To do this, parents should immediately consult a doctor.
Advice from Doctor Komarovsky
Dr. Komarovsky warns that in rare cases, viral pemphigus in children appears in the eye area. This can lead to blindness in the child. To prevent this from happening, you should contact specialists in time and begin treatment.
vospitulya.ru
Pemphigus in children is a disease of viral etiology . The disease is accompanied by the formation of characteristic blisters on the skin that quickly spread throughout the epithelium.
Children of primary and preschool age are at risk. If treated incorrectly, pemphigus can cause serious complications and affect the child's quality of life. Therapy should be carried out comprehensively and in stages.
Concept and characteristics
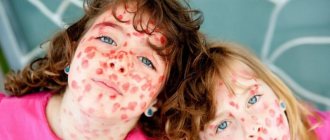
Pemphigus in a child - photo:
Pemphigus is an infectious disease that causes painful blisters to form on the skin. Visually, they resemble bubbles filled with liquid.
The progression of a viral disease leads to the merging of blisters and a rapid increase in their number. The pathological process is accompanied not only by itching and burning, but also by severe pain.
Pemphigus is considered a seasonal disease. The greatest activity of the virus is observed in the autumn and spring.
Causes
The causative agent of pemphigus is the Coxsackie virus. The disease can be transmitted by airborne droplets or by contact with contaminated objects. Symptoms of the disease do not occur in all children.
The main condition for the development of pemphigus is considered to be weak immunity.
If the protective functions of the child’s body are not impaired, then contact with a carrier of the virus can do without negative consequences.
increase the risk of infection for a child:
- weakening of the immune system under the influence of uncontrolled use of potent medications;
- congenital autoimmune pathologies;
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal disorders in the body;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- negative impact of the environment on the child’s body;
- pathologies associated with the central nervous system;
- contact with common objects without observing safety measures.
How to treat herpes on a child’s body? Find out about this from our article.
Classification
In medical practice, pemphigus is divided into several varieties. They differ not only in their location , but also in the process of their development.
Determining the specific type of disease is necessary to prescribe a specific course of treatment . To treat certain types of the disease, it is necessary to use special drugs and regimens for their use. Pemphigus can develop in mild, moderate, severe or chronic forms.
Types of pemphigus:
- Leaf- shaped (bubbles on the child’s skin begin to burst, and crusts form in their place; the development of the pathological process causes them to be layered on top of each other).
- Viral form (blisters can appear on any part of the child’s body, their appearance is accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition of the little patient; the blisters resemble the symptoms of chickenpox).
- Seborrheic form (this type of disease is characterized by damage to the scalp, the general symptoms of the pathological process do not change).
- Vegetative form (the pathological process affects the mucous membranes of the mouth, lips, area around the nose or on the child’s genitals; a distinctive feature of this type of pemphigus is the formation of purulent crusts with an unpleasant odor).
Symptoms and signs
The incubation period for pemphigus is seven days. The first symptom of the disease is a deterioration in the child’s general condition. The appearance of characteristic blisters occurs after two or three days.
In some cases, blistering may be accompanied by a rash. The further development of the disease resembles chickenpox. Blisters can appear singly or immediately cover a significant part of the skin.
A distinctive feature of pemphigus is the merging of bubbles with each other.
Symptoms of pemphigus are the following :
- formation of hyperemic lesions with flat blisters on the skin;
- runny nose, cough, sore throat;
- weakness and increased fatigue;
- the presence of characteristic crusts at the site of the blisters;
- deterioration of the child’s general condition;
- lack of appetite and weight loss;
- sleep disturbance and moodiness;
- feverish condition;
- increase in body temperature.
Complications and consequences
In some cases, pemphigus can become chronic. Such forms of the disease provoke serious damage to internal organs and impair their performance.
In childhood, such complications are rare and only as a result of the lack of the correct approach to treatment. Most often, pemphigus has a favorable prognosis and goes away without a trace in young patients.
Possible complications of the disease may include the following:
- meningitis;
- myocarditis;
- heart failure;
- pneumonia;
- sepsis;
- encephalitis.
Recommendations for the treatment of roseola in children can be found on our website.
Diagnostics
In most cases, doctors are able to identify pemphigus in children by visual examination.
If an additional infection or specialists suspect a complication of the pathological process, then an additional examination is prescribed.
Children who have had pemphigus are recommended to be examined by a dermatologist. After recovery, children need to be regularly examined by this specialist.
procedures can be used :
- general and biochemical blood test;
- cytological examination of fluid from blisters;
- checking blood for the presence of specific antibodies;
- histological studies;
- comprehensive stool analysis;
- cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
How to treat?
When drawing up a treatment plan for pemphigus, doctors take into account the individual characteristics of the child’s body , the degree of damage to the skin and the presence of additional infections.
With proper and timely treatment, the symptoms of the disease disappear within a week.
If the skin is affected to a minor extent , then treatment can only consist of the use of medications that eliminate pain.
Drugs
The need to use potent medications in the treatment of pemphigus arises in the case of significant damage to the skin or a serious condition of the child.
To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, antipyretic, hormonal, antiviral drugs, as well as drugs of other categories, are used.
When treating pemphigus, the following drugs :
- means to reduce body temperature (Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen);
- glucocorticosteroids (Dexamethasone);
- hormonal drugs (Prednisolone, Betamethasone);
- combination medications (pharmacy talkers);
- antihistamines (Fenistil, Cetrin);
- antiviral drugs (Viferon, Cycloferon);
- agents from the group of cytostatics (Azathioprine);
- antimicrobial drugs (Orasept);
- antiseptics (Miramistin).
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures for pemphigus are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor.
This technique becomes mandatory if there are complications or damage to large areas of the skin of a small patient.
Preparations for physiotherapeutic procedures are selected by specialists on an individual basis . Doctors take into account not only the general condition of the child, but also his age.
Types of procedures used:
- electrical stimulation of the bladder;
- electrophoresis with proserine or atropine;
- electrical stimulation;
- electrophoresis with calcium chloride;
- magnetotherapy.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine recipes are good for eliminating pain from pemphigus. They are allowed to be used, but only after consultation with a doctor and a comprehensive examination of the child.
Some forms of pemphigus require the mandatory use of potent medications. Self-medication with folk remedies can complicate therapy and slow down the healing process of a young patient.
Examples of folk remedies used for pemphigus in children:
- Lotions with nettle juice (fresh nettle leaves must be crushed, squeezed out the juice, a cotton pad is soaked in the resulting liquid, the preparation must be applied to blisters or scabs several times a day).
- Compresses with aloe juice (you need to extract the pulp from aloe leaves, soak a cotton pad in the juice and apply the lotion several times a day to the affected areas of the child’s skin).
- A healing infusion to strengthen the general condition of the child (in equal quantities you need to combine yarrow, chamomile, St. John's wort, birch buds and calendula, pour boiling water over a teaspoon of the resulting mixture, infuse and consume in small portions throughout the day).
- Lotions with oils (a cotton swab soaked in sea buckthorn, sunflower or olive oil should be applied to the affected areas of the skin several times a day, the procedure helps speed up the process of peeling off the crusts).
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Dr. Komarovsky strongly recommends that parents avoid self-medication of pemphigus in children.
Blisters that occur on the mucous membranes are more difficult to treat, and complications can cause extremely negative consequences.
For example, blisters in the eye area increase the likelihood of decreased vision. Proper child care plays an important role. Blisters must be handled with gloves. Otherwise, the risk of infection for an adult will increase.
Based on the opinion of Dr. Komarovsky, the following conclusions :
- diet (excluding sour, spicy and salty foods from the diet);
- during the period of illness, it is necessary to limit the child’s consumption of sweets;
- Hot foods and drinks should be excluded from the child’s diet;
- clothes for the child should be chosen from natural materials (the cut should be loose to ensure a constant supply of oxygen to the wounds);
- the room in which the child is located must be regularly ventilated and wet cleaned;
- It is not recommended to bathe children in the first week of disease progression (the healing process of wounds will worsen under the influence of moisture).
Forecast
Favorable prognosis for pemphigus is possible only with adequate and timely therapy.
If the symptoms of the disease are ignored for a long time or self-medication is used, the consequences can pose a threat to the child’s life.
Pemphigus has the ability to recur . When it occurs regularly, the protective functions of the child’s body are reduced. The baby becomes vulnerable to infections and viruses, many of which increase the risk of death.
prediction nuances :
- overdose of hormonal drugs causes complications;
- eliminating the use of corticosteroids slows down the treatment process and leads to relapses;
- self-medication can provoke the addition of additional infections that are dangerous to the child’s life.
Prevention measures
Prevention of pemphigus is aimed mainly at strengthening the protective functions of the child's body . In most cases, the virus affects weakened children.
If a child has suffered a serious illness or surgery, then special attention should be paid to strengthening the immune system.
Additionally, it is necessary to monitor the diet of children and the conditions in which they are located. Children should be taught personal hygiene from a very early age.
Measures to prevent pemphigus are the following recommendations :
- The child must have personal hygiene products (towel, toothbrush, etc.).
- Strengthening the child’s immune system from the first days of his life (long-term breastfeeding, proper diet, vitamins in accordance with age).
- The child’s clothes must be clean, and the room in which he stays must meet sanitary requirements.
- The child should know that it is impossible to come close to people with signs of a cold (for example, a person who is sneezing or coughing).
- All diseases (regardless of etiology) must be treated promptly and fully.
If your child develops symptoms of pemphigus, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. The disease is not a deadly infection, but lack of therapy can cause the addition of other pathological processes.
The presence of complications becomes the basis for unfavorable prognosis . Some consequences may not respond to treatment and disrupt the baby’s quality of life. Self-medication for pemphigus should be excluded.
You can learn about epidemic pemphigus of newborns
pediatrio.ru
In pediatrics, there are severe pathologies, the mechanism of their occurrence has not been sufficiently studied, which does not allow the root cause to be determined with maximum probability and eliminated. As a result, the prescribed treatment is not very effective, the disease progresses and leads to disability or death. One of these diseases is pemphigus - pemphigus, which is characterized by damage to the mucous membranes and skin.
Despite the danger of the diagnosis, parents should not panic, but do everything to alleviate the child’s condition. Moreover, the prognosis will largely depend on the form of the disease.
Causes
The causative agent of pemphigus is Staphylococcus aureus. The contact of these pathogenic bacteria with the baby's skin is the main cause of pemphigus in newborns.
You may be interested in: Scarlet fever in children: how to deal with the disease
Let's consider possible routes of infection:
- From parents to child. Staphylococcus aureus lives on the body of almost all adults, but no symptoms may occur. The baby is born literally sterile. When bacteria enter his body, pemphigus may develop.
- Infection from another sick baby through the hands of medical workers. This often happens in the maternity hospital or when visiting a doctor if the specialist does not follow safety rules.
- Infection can occur from any person suffering from purulent diseases of the dermis.
- Even if a person has suffered any purulent skin disease, Staphylococcus aureus remains for some time in large quantities on his skin. Upon contact with a child, it can infect him.
The severity of pemphigus will depend on the characteristics of the child’s immune defense, timely diagnosis and consultation with a doctor, as well as the correct treatment of the disease.
Diagnosis and course of treatment
The diagnosis of pemphigus is made to a child during an external examination, based on the appearance of the rash. Next, the dermatologist can refer you to an infectious disease specialist who will conduct serological tests to detect antibodies through blood, stool and cerebrospinal fluid tests (if complications such as encephalitis or meningitis are suspected). A cytological examination of the fluid inside the blisters may be ordered. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, appropriate treatment is carried out.
Treatment for pemphigus will depend largely on what form of the disease was identified in the child.
Viral form
Treatment of viral pemphigus involves the use of the following systemic drugs:
- antiviral: Viferon, Laferon, Cycloferon;
- glucocorticosteroids: Dexamethasone, Prednisolone;
- cytostatics stop the division of immune cells: Sandimmune, Azathioprine, Methotrexate;
- antipyretics: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Nimesil, Mefenamic acid;
- antihistamines relieve itching: Cetrin, Diazolin, Fenistil.
For external treatment of affected skin areas, the following may be prescribed:
- antiseptics: Chlorhexidine, Methylene blue, Miramistin;
- combination preparations of antiseptics and anesthetics: Oflokain, pharmaceutical talkers;
- antimicrobial local anesthetics for irrigating the oral cavity if viral pemphigus has affected the child’s mucous membranes: Forteza, Orasept;
- antipruritic lotions made from nettle juice, aloe, and walnut oil.
Since children with this diagnosis are usually treated in a hospital setting, to enhance the therapeutic course, therapeutic procedures can be carried out aimed at clearing the blood of antibodies:
- hemosorption using a carbon filter;
- plasmapheresis - replacement of the liquid part of the blood with similar solutions without microbes, immune complexes and antibodies.
Only a doctor can tell how to treat viral pemphigus, because in each individual case it can acquire some special features. As for other forms of pemphigus, the therapeutic course for them is also determined individually.
Other forms
The basis of treatment of non-viral forms of pemphigus in children comes down to the prescription of the following drugs and procedures:
- glucocorticoids in high dosages;
- since they can cause serious side effects, immunosuppressants are prescribed in parallel;
- intravenous administration of human immunoglobulin in high doses;
- administration of an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody;
- plasmapheresis;
- in special cases - antibiotics and antifungal drugs;
- Allotransplantation of bone marrow or stem cells is not recommended, as it can be fatal, but is still used in cases where the chance of survival is already minimal.
Scientists are still researching this mysterious disease and are looking for more effective methods to treat pemphigus in children in order to reduce the risk of complications and deaths. Many laboratories are working to discover new drugs that could help those suffering from this disease.
Parents can alleviate the condition of their child only by competent care and compliance with all medical prescriptions.
Who is at risk?
There are categories of infants who are more susceptible to pemphigus. This applies, first of all, to babies born prematurely.
In addition, children with the following conditions are at risk:
- Newborns whose umbilical wound was treated incorrectly.
- The presence of anatomical and physical features relating to the baby’s dermis.
- Failure to maintain baby hygiene by parents.
- Intrauterine growth retardation.
- The mother has suffered from severe early or late toxicosis.
- Purulent skin lesions in parents.
- Infectious diseases of the mother's genitourinary system.
- Failure to observe hygiene by medical personnel in a maternity hospital or other medical institutions.
If Staphylococcus aureus comes into contact with a baby's skin, the likelihood of developing pemphigus is very high.
Clinical signs of pemphigus in newborns
Symptoms of pemphigus in young children are very similar in all patients.
Typically the disease develops according to the following scenario:
- Increase in body temperature to high levels. These are, as a rule, indicators such as 38-39°C.
- The baby is capricious, sleeps poorly, refuses breastfeeding or formula.
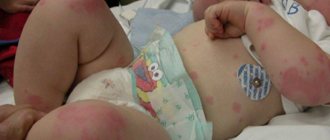
- A rash appears on the patient’s body in the form of blisters filled with cloudy contents. The liquid has a yellowish or grayish tint.
- The locations of the rashes are most often the tummy, the area near the navel, the back, buttocks, and limbs.
- As the infection spreads, blisters may appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes, and genitals.
- After opening the papule, red skin is visible in its place, and later erosions appear in this area.
- After erosion occurs, it gradually heals. In this case, crusts appear that burst, may bleed, and later fall off.
- When the blisters open, the infection spreads to new areas of the dermis, as evidenced by the appearance of new rashes.
If we talk about how many days pemphigus lasts, it can be noted that the duration of the disease can reach from 2 to 6 weeks. Here, much depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and the correctness of the selected therapy.
In infants with weakened immune systems or toddlers born prematurely, pemphigus often occurs with various complications.
Pemphigus of newborns
Neonatal pemphigus is a bacterial disease that causes red spots, blisters and ulcers on the skin. Pemphigus usually occurs in children with reduced immunity.
Local symptoms of the disease will be hyperemia in certain areas of the skin and painful blisters. General symptoms also occur: fever, weakness, anxiety. Children up to 15 days after birth can become infected with pemphigus. The cause of the disease is infection with staphylococcal infection.
There are several forms of pemphigus. Not only doctors, but also young parents should take part in treatment.
Pemphigus of newborns: causes
The causative agent of pemphigus is Staphylococcus aureus, which enters the child’s body through microdamage. The infection affects all layers of the skin. When an infection enters the body, it produces a toxic substance - exfoliatin, which has a pathological effect on the skin and damages it.
The skin of a newborn is very delicate, has weak immunity and can easily be damaged. Staphylococcus gets on the skin during childbirth from mother to baby, where the baby’s skin can be unnoticed.
In this case, omphalitis may occur - inflammation of the wound of the newborn's navel, and subsequently pemphigus of the newborn may occur. Staphylococcus aureus is present in 40% of women in the genitourinary system.
In addition, the mother may suffer from various skin diseases (or there is a focus of purulent inflammation in her body).
The reasons that increase the risk of pemphigus in a newborn are reduced immunity, birth trauma, prematurity or immaturity of the child at the time of birth. Also, a baby can become infected in a hospital; 30% of medical personnel may have the pathogen in their body.
If premises are poorly cleaned, instruments are processed, certain rooms are quartzed, bandages and medical wipes are processed, the hands of medical personnel are treated, or hygiene rules are not observed, staphylococcus may not be destroyed and may end up on the baby’s injured skin.
Also, maternity hospital medical workers can suffer from inflammatory skin diseases and become a source of infection when caring for newborns.
Pemphigus in newborns occurs when a number of random factors coincide and the child has reduced immunity.
Pemphigus of newborns: symptoms
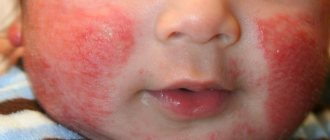
Pemphigus of newborns exists in two forms: milder (benign) and severe (malignant). The disease begins in a child with the formation of hyperemic rashes or peeling. The skin changes color first on the face (near the corners of the mouth) and tummy (around the navel), then it can spread to all parts of the body.
In place of these redness, puffiness, swelling appears and blisters form. Later, the blisters become flatter, the skin over them becomes thinner and breaks, and fluid leaks out. In place of the blisters, a shallow skin defect remains - erosion. With a favorable course, the bubbles, and after erosion, have a small size of up to 0.5 cm.
If the course of pemphigus in newborns is unfavorable, erosions can be up to 3 cm. Rashes appear on the face, tummy and can spread throughout the body. Blisters may appear in the mouth and genitals. After opening the vesicles, very painful erosions remain, which crust over after a couple of days.
This is how the healing process goes.
With pemphigus, newborn children lose their appetite, refuse breastfeeding, and subsequently their body weight may decrease. There is weakness, a rise in temperature to high levels, and anxiety appears.
Three stages of neonatal pemphigus can be distinguished: erythematous, exfoliative and regenerative. Erythema is translated from Latin as redness of the skin. At this stage, the skin changes color, inflammation occurs and rashes appear. Exfoliation is translated as delamination, peeling.
Fluid forms in the rash, the surface epithelium is damaged, and blisters rupture. At this time, a positive Nikolsky symptom is observed: during friction, the surface layer of the epithelium peels off. The epithelium also peels off when the edge of the bladder is pulled. At the regenerative stage, erosions heal.
Crusts form, which move away from the skin over time.
With benign pemphigus of newborns, only certain parts of the body are affected: arms, legs, tummy, groin area, neck, chest, back. The rashes are quite rare, isolated and small in size. The body temperature does not rise above 38°C. Sometimes the general condition of the baby is not disturbed at all. The child recovers completely in 2-3 weeks.
In the malignant form of pemphigus in newborns, the entire body of the baby can be affected; the rashes are multiple and can reach 3 cm. After opening the blisters, large and very painful erosions form. The epithelium between the blisters is broken and peels off after friction.
The skin also peels off if you pull on the edge of the bubble. There is a high temperature, above 38°C. This form of the disease is very severe. Intoxication of the body occurs and its symptoms are fever, weakness, refusal to eat, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting.
A sick baby may experience septicopyemia and sepsis. Recovery occurs within a month.
The following forms of malignant pemphigus are distinguished: syphilitic pemphigus of newborns, staphylococcal and epidemic.
Staphylococcal pemphigus of newborns is the most common. The causative agent is staphylococcus. The epidemic form of the disease is also caused by staphylococcus.
The name comes from the fact that this form of the disease can cause an epidemic - a rapidly spreading disease. Children with this disease must be isolated from others, because
the disease is highly contagious.
Syphilitic pemphigus of newborns is a sign of a syphilitic disease, that is, syphilis. The causative agent is Treponema pallidum. Infection of a child occurs in the prenatal period from a sick mother.
The peculiarity of this type of pemphigus in newborns is the rich color of copper-red skin, the blisters also have red contents containing the pathogen, localization of lesions on the soles and palms. Scars may appear that are characteristic only of syphilis.
This type of disease is the most severe and dangerous.
Pemphigus of a newborn: diagnosis
Epidemic pemphigus of newborns is easy to diagnose, but difficult to treat. To determine the correct diagnosis, all factors of the disease are taken into account. The time of disturbance of the newborn’s condition, the time of occurrence of rashes, and behavior are taken into account.
The cause of pemphigus and the possibility of the child coming into contact with a sick person are determined. It is necessary to clarify whether the mother or the medical staff had any skin diseases.
Next, a general external examination of the baby is carried out, the nature and appearance of the elements of the lesion are determined.
If the disease has entered the exfoliative stage, the doctor conducts a local examination of the lesions and checks Nikolsky's sign (when apparently healthy areas rub between the blisters, the skin peels off). If the symptom is positive, this gives grounds to diagnose pemphigus of the newborn.
To identify the causative agent, correctly determine the type of pemphigus and select treatment, the fluid from the affected element is cultured. Based on the results of the study, an antibiotic sensitive to this microflora is selected. To exclude syphilitic pemphigus, microscopy and PCR tests are performed.
In the presence of treponema pallidum, a diagnosis of syphilitic pemphigus of the newborn is made. A clinical blood test is also required to determine how severe the inflammation is in the baby’s body (based on the number of leukocytes and ESR).
Using the same analysis, it is determined whether a complication has arisen - sepsis.
Differential diagnosis of pemphigus in newborns is carried out with such diseases as: herpes, chicken pox, congenital syphilis, congenital epidermolysis, Leiner's desquamative erythroderma, ichthyosiform erythroderma, bullous and other forms of dermatitis, as well as allergic reactions. Consultation with a dermatovenerologist and infectious disease specialist is required. It is recommended to consult a neonatologist.
Pemphigus of the newborn: treatment
Staphylococcal pemphigus of newborns is treated in the hospital; the sick child must be isolated from other children.
When caring for a newborn with pemphigus, they strictly adhere to the rules of hygiene, use only sterile linen and instruments, and carry out quartzing every 4-5 hours.
Bathing the baby is carried out with the addition of antiseptic solutions and herbal decoctions (celandine, chamomile, oak bark) to the water. Daily linen change is required. Rashes are treated with ointments and aerosols with antibiotics.
Antiseptics are also used - Iodine, Diamond Green or Methylene Blue. At the stage of rupture of the blisters, baby powder with Xeroform is used to dry the affected elements. Unaffected skin is treated with Salicylic alcohol to prevent the spread of infection.
The most basic therapy for the treatment of pemphigus in newborns is the use of penicillin or cephalosporin antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Cefazolin, Cephalexin, Cefoxitin).
It is advisable to give preference to 1st or 2nd generation antibiotics so as not to develop immunity to stronger antibiotics in the baby.
When choosing an antibiotic, be sure to take into account the sensitivity test to a particular drug.
When treating pemphigus in newborns, anti-staphylococcal plasma and anti-staphylococcal gamma globulin are also administered. After using antibiotics, probiotics must be prescribed to restore the microflora - Linex, Bifiform, Lactobacterin.
For malignant pemphigus, infusion therapy is used for detoxification - medications and solutions are injected drip-wise to replenish fluid volumes in the body. Apply saline solution, Hemodez, Polyglucin, glucose solution. Symptomatic treatment is also carried out. For fever, antipyretics are used.
For a malignant form of the disease with large lesions, painkillers are used. With this form of the disease, sepsis and septicopyemia may occur. In this case, the dose of the antibiotic is increased, massive infusion therapy is performed, and blood plasma is transfused.
Be sure to carry out treatment to increase the immunity of the newborn.
With the malignant form of pemphigus, there are complications: abscess, otitis media, pharyngitis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, omphalitis, sepsis.
To prevent pemphigus in a baby, the disease should be diagnosed in time and comprehensive treatment should be selected. The prognosis is favorable, depending on the child’s immune defense, the extent of the process, and treatment.
There were deaths from neonatal staphylococcal pemphigus before the advent of antibiotics.
Pemphigus of newborns has no specific prevention; all measures must be taken to prevent the disease.
This includes identifying and treating diseases of the expectant mother, observing the rules of personal hygiene, adhering to proper care of the baby, and it is necessary to exclude the child’s contact with supposedly sick people.
Hospital and maternity hospital workers need to carefully process linen and instruments, carry out quartzing of premises according to schedule, carry out timely wet cleaning, isolate sick children, and eliminate sources of infection among medical personnel.
The information presented in this article is intended for informational purposes only and cannot replace professional advice and qualified medical care. If you have the slightest suspicion that you have this disease, be sure to consult your doctor!
Source: https://vlanamed.com/puzyrchatka-novorozhdennyh/
Diagnostics
An experienced specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis of a disease in a newborn after a visual examination of the baby’s skin. To confirm the diagnosis, a bacterial culture is performed. After this, the necessary treatment is prescribed.
You might be interested in: How to quickly treat stye on a child’s eye
Differential diagnosis is also important. Here it is important to exclude pathologies such as congenital syphilis, herpes, viral pemphigus, bullous dermatitis and others.
Treatment
The diagnosis of viral pemphigus can only be made by an infectious disease doctor, and it is he who will prescribe the correct treatment. Therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms. Therefore, external agents that have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects are used to treat viral pemphigus. This method promotes skin regeneration, thanks to which wound healing occurs faster. At this time, the child should be given medications that strengthen the immune system. Doctors do not recommend taking antiviral tablets, since after 10 days the disease goes away on its own.
Photos of the disease in children
In these photographs you can see what the disease looks like in young children.
You should not try to make a diagnosis yourself and select treatment for the patient. This can only worsen the course of the pathology.
Possible complications
If pemphigus in a newborn baby is not treated in a timely manner, extremely undesirable consequences for the child’s body may develop. If the doctor's recommendations are not followed, the disease quickly spreads to new areas of the skin, which leads to its severe course. In this case, therapy for pemphigus will last much longer, and the risks of various complications will increase significantly. Why is the disease dangerous for children?
- Development of blood poisoning (sepsis).
- Pneumonia in a child.
- The appearance of furunculosis. Furuncles can reach quite large sizes, requiring surgical removal.
- Staphylococcus aureus can cause damage to human bone tissue - osteomyelitis.
- The infection often causes inflammation of the middle ear - otitis media.
- If left untreated, there is a risk of developing lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodes in the body.
- A dangerous complication of staphylococcal infection is pyelonephritis - inflammation of the kidneys.
- Against the background of pemphigus, the threat of developing enterocolitis, an inflammatory process in the intestinal area, increases.
The most dangerous diseases that occur against the background of pemphigus in non-congenital infants include Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis. This is a malignant course of pemphigus. In this case, the body temperature rises to 40-41°C, the child refuses to eat, severe diarrhea develops, and the risk of dehydration, meningitis and other life-threatening and health-threatening conditions increases greatly. In the absence of proper medical care, death is possible.
To prevent such dangerous complications, at the first warning signs in a baby, you should contact a specialist as soon as possible.
Pemphigus of newborns: symptoms and treatment
Most mothers are very worried about their children. But little children are little troubles.
The most nervous days begin when the child begins to walk and run, the most sleepless nights - when the baby is no longer a baby at all and goes for a walk until the morning, without warning his worried parents.
In the meantime, he just lies in his crib, sleeps, whines, eats, smiles and sleeps again. Can anything happen to such a baby when he is under supervision 24 hours a day? Believe me, it can.
Bacteria do not care about age or your love for your baby. They don't care how many days or weeks the newborn is, what he eats, how or where he sleeps. They attack suddenly, appearing as if out of nowhere. The baby’s body is struggling, the child is suffering, the parents don’t know what to do or where to run.
But forewarned means forearmed. By the time the child grows up and stops getting sick completely, mothers can safely be given a certificate of completion of a course in pediatrics. After all, it won’t be possible to protect your baby from all diseases, but you can protect yourself from dangerous diseases if you know how they arise. It will be enough to simply protect the newborn from risk factors, and the sore will go away.
One of the most unpleasant and early childhood diseases is epidemic pemphigus of newborns. What kind of animal this is and how not to let it into the baby’s cradle, what to do if it nevertheless snuck onto the newborn, we will now find out.
What is pemphigus
This is a highly contagious lesion of the skin of newborns of staphylococcal nature, which manifests itself by the appearance of small purulent blisters on the epithelium, which grow, burst and erosions occur in their place. Now let’s try to parse this definition in normal language:
- highly contagious - this means that infection occurs quickly, and many children can become infected at once;
- staphylococcal nature - the causative agent is a bacterium called Staphylococcus Aureus, also known as Staphylococcus aureus;
- the appearance of blisters on the epithelium - that is, on the skin and visible mucous membranes (lips, tongue, oral cavity, in girls - labia);
- erosion – destruction of the skin surface.
In other words, this same staphylococcus gets on the baby’s skin. The epithelium of a newborn does not yet have its own defense system, so staphylococcus begins to actively multiply, “eating” the skin. The body doesn’t like this, it does the only thing it can so far - encloses harmful bacteria in capsules so that they do not spread to other areas of the skin.
But these capsules are very delicate and burst at the slightest touch. The purulent contents of such blisters immediately come into contact with healthy skin. And since there is a whole army of Staphylococcus aureus in such contents, re-infection occurs.
The result is an unpleasant, unsightly disease, but completely curable if you recognize the symptoms in time and seek help from a doctor.
Causes of pemphigus in newborns
The main cause of the disease is contact with Staphylococcus aureus on the skin of a newborn. And this happens most often in one of the following ways, from:
- a person who is a carrier of Staphylococcus aureus (while the person himself may not be sick);
- a child with pemphigus through the hands of medical staff;
- a person with severe purulent skin diseases;
- a person who has recently suffered a purulent skin disease.
But even if such people and children are not around the newborn, certain factors remain due to which the baby can still get sick.
Risk factors
The main factors that make the occurrence of neonatal pemphigus more likely include:
- improperly processed umbilical cord;
- anatomical and physiological characteristics of the baby’s skin;
- poor child hygiene;
- intrauterine growth retardation in toddlers;
- severe toxicosis in the mother;
- the presence of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system in the parent;
- regular neglect of hygiene and sanitation by mom, dad or medical staff.
Any opening left for staphylococcus to penetrate the baby's skin can lead to the appearance of all the symptoms of pemphigus in newborns.
Symptoms of pemphigus in newborns
The most important distinguishing feature of this disease is the age of the newborns. It occurs in the first 10-14 days of a toddler’s life. And it always develops according to the same scenario:
- first the body temperature rises to 38-39°C;
- the baby becomes restless and whines all the time;
- rashes appear on the skin of the newborn in the form of small bubbles with a cloudy liquid of a grayish-yellowish color;
- Most often, bubbles appear near the navel, on the stomach, back and buttocks;
- then the rash spreads to the feet and palms;
- with subsequent spread of the disease, the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes, nose and genitals may be affected;
- when the bubbles open, bright red spots appear in their place, as if corroded skin - erosion;
- erosions burst into purulent crusts, which dry out and then peel off;
- the process is repeated over and over again, the illness can last from three to five weeks.
In weakened babies born with low weight or too early due to premature birth, the symptoms remain the same. But it is they who may develop more serious complications of pemphigus in newborns.
Complications of pemphigus in newborns
If you ignore the symptoms or recommendations of doctors, the disease can actively progress, leading to a number of dangerous complications. They won't just make the recovery process difficult and lengthy. At such a tender age, they can seriously damage the overall health and usefulness of the baby.
The main possible complications of pemphigus in newborns include:
- sepsis (blood poisoning);
- pneumonia (inflammatory process in the lungs);
- abscesses (large boils);
- furunculosis (small abscesses on the skin and mucous membranes);
- osteomyelitis (bone tissue damage);
- lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes);
- otitis (inflammation of the middle ear);
- conjunctivitis (inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyes);
- pyelonephritis (inflammatory process in the kidneys);
A separate disease in neonatal dermatology includes the most terrible complication of pemphigus in newborns - Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis. This is a malignant variant of pemphigus. In this case, the appearance of the blisters on the child's skin looks more like a second-degree burn.
The temperature rises up to 40°C, there is diarrhea, refusal to eat, and the baby very quickly loses weight. Complications already with this disease occur more often and reach meningitis. And this option at such a tender age will be fatal for a newborn.
To prevent the occurrence of such complications, it is important to contact a pediatrician in time and begin timely and correct treatment.
Treatment of pemphigus in newborns
- The patient is required to be prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy. For this purpose, drugs with penicillinase-resistant penicillins or with the addition of clavulanic acid to the antibiotic are used. For example, Amoxiclav or Oxacillin. Cephalosporin antibiotics (Cefaloridin, Cefazolin) are also used.
- The dosage and duration of the course depend on the severity of the disease, the individual characteristics of the newborn and his weight.
- In addition to antibiotics, injectable albumin, B vitamins, ascorbic acid and retinol are used. These manipulations are aimed at stimulating the newborn’s body’s own regenerative resources. They also ensure the baby’s resistance to the development of complications.
- The skin around the blisters is treated with salicylic alcohol. If this is not available, boric alcohol can be used. The bubbles themselves are pierced and immediately cauterized with solutions of aniline dyes. Syntomycin emulsion is applied to the dried crusts.
- For the same purposes, aerosols and ointments that contain antibiotic substances (gentamicin, neomycin, erythomycin) can be used. In addition, it is recommended to bathe the baby every day in a bath with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Both general and local ultraviolet irradiation will not be superfluous.
- Any treatment will be effective if it is supervised by an experienced specialist. Self-medication in the case of pemphigus is not only dangerous, it can lead to various complications and a protracted period of rehabilitation. In this case, the parents’ task is to listen to the doctor and strictly follow all his instructions.
Prevention of pemphigus in newborns
Any disease is easier to prevent. A newborn has just come into this world; there is no need to expose him to unnecessary risks and suffering. And take care of your nervous system - you will need it later.
To ensure that Staphylococcus aureus never gets on your baby’s skin, you need to follow simple but mandatory precautions, not only for you, but also for the management of medical institutions:
- Treat all diseases of your genitourinary system in a timely manner, preferably at the stage when you first asked yourself the question of “preparing for pregnancy.”
- Medical personnel who deal with newborns must undergo regular and timely medical examinations. If any illness is discovered, the employee must be removed from work until complete recovery.
- Medical personnel who have or have suffered any purulent skin diseases should not be allowed to work with newborns.
- All strangers (that is, everyone except parents) must use medical gloves when in contact with the baby.
- Premises where infants are kept for a long time should be regularly treated with ultraviolet radiation.
- In the case of a baby, underwear and bedding should be changed as often as possible, undergoing washing and mandatory ironing with a hot iron.
- The mother should maintain personal hygiene and wash her hands with soap before contacting the child.
By taking these precautions, pemphigus can simply be prevented. This will protect the child’s health, mother’s nerves, and the family budget.
Epidemic pemphigus of newborns - video
In this video, the doctor explains what a childhood disease called pemphigus of newborns is. The doctor describes in detail the causes, course of the disease, and also talks about the necessary treatment and preventive measures.
Pemphigus of newborns is a very unpleasant and dangerous disease. A child can become infected right in the hospital, but symptoms will appear closer to the tenth day of his life.
The disease is not fatal, but without proper treatment it leads to serious complications and concomitant diseases, especially if the baby is already weak. Therefore, the prevention of pemphigus plays a huge role in the life of the baby and his family.
Have you encountered such a disease in your child? How many days was the newborn? What symptoms appeared first? How did you fight the disease?
Source: https://okrohe.com/deti/problemy/puzyrchatka-novorozhdennyh.html
Methods of treating disease in children
Due to the fact that pemphigus is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms related to bacteria, the disease is treated with the help of antibacterial drugs. In this case, doctors prescribe medications of the penicillin or cephalosporin series. Most often, the doctor prescribes the following medications:
- Amoxiclav.
- Cefazolin.
- Cephaloridine.
- Flemoxin Solutab and others.
In addition to antibacterial agents, vitamin therapy is used to increase the child’s immune defense. In particular, these are vitamins B, C and E. In addition to stimulating the immune system, vitamins are used to reduce the risk of developing various complications of the disease. The dosage and duration of treatment with certain drugs is selected by the doctor individually for each patient. Typically, taking antibiotics lasts from 7 to 10 days.
You might be interested in: Purulent sore throat in a child
Symptomatic therapy also includes the use of antipyretics. Among young children, paracetamol and ibuprofen-based drugs are usually used.
Treatment of pemphigus with medication and at home
Drug therapy to eliminate symptoms in newborns begins immediately after its diagnosis. Bacteriological culture tests must be collected to ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis.
Therapy consists of treating the newborn’s skin with special antibacterial agents: Amoxicillin and Flemoxin Solutab. Also, the skin around the injury is treated locally with Miramistin or hydrogen peroxide; in other cases, cauterization with iodine is acceptable. Doctors insist on removing the pustules and treating them with antiseptics, for example Chlorophylipt; this drug is harmless to newborns.
Children say! Showing packets of seeds. I ask what is depicted on them, and I get the answers: “Onions, beets, cucumbers, sausages—that’s like carrots!”
In severe stages of the pathology, it is possible to give a blood or plasma transfusion to a newborn, and administer vitamin preparations of groups B and C. The use of immunomodulators is possible. Sometimes diuretics and salts are used.
Important! Treatment of pemphigus in infants should be started in a timely manner, so that complications of the disease and its spread to other babies can be avoided. After birth, a baby with a similar diagnosis should be placed in a separate pathology ward.
Local skin treatment for pemphigus
In addition to taking antibiotics, antipyretic medications and vitamins, it is important to treat the affected areas of the dermis with topical medications. For this purpose, special solutions, ointments, creams and aerosols are used. Salicylic alcohol effectively copes with staphylococcal infections. The doctor can open the vial and instantly lubricate it with an antiseptic. These include brilliant green solution, Fukortsin or other medications. Opening papules on your own at home is strictly prohibited. This can provoke infection and the development of sepsis.
Expert opinion
Ksenia Dunaeva
User experience expert and comment moderator. Higher medical education and more than 5 years of actual practice.
Ask Ksenia
For a quick recovery, the doctor may also advise parents to bathe the baby in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. In severe cases of the disease, physiotherapy in the form of ultraviolet radiation may be prescribed. During the warm season, you can sunbathe. This will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the baby's skin.
Methods for preventing epidemic pemphigus in newborns
It's no secret that any disease is much easier to prevent than to treat. Young children are born very vulnerable to various infections. In this regard, it is extremely important to maintain the necessary hygiene.
In addition, it is important to carry out the following preventive measures:
- Competently and promptly treat various infectious diseases in the mother during pregnancy.
- Not only parents and loved ones of the baby, but also all medical personnel who come into contact with the baby must maintain hygiene. We are talking about using sterile instruments, washing hands, and regular preventive examinations.
- If one of the family members suffers from purulent skin diseases, for example, an older child or a grandmother or grandfather, you should not have contact with the baby.
- In the first days of life, the room where the baby is located should be treated with ultraviolet light.
- As for older children, if children are infected in kindergarten, quarantine must be introduced in accordance with the requirements of SanPin.
If the child is already sick, it is important to change his underwear as often as possible. The same applies to towels and bedding. Even if the mother does not show any signs of a staph infection, she should wash her hands thoroughly before touching the newborn.
These simple preventive measures will help prevent pemphigus in children and maintain their health, excellent health and family budget.
Preventive measures
Since the causes of pemphigus still remain a mystery, no one can give an exact guarantee that by following certain rules you will protect your child from this dangerous disease. But you can always monitor your baby’s health, strengthen his immunity, avoid unnecessary medication, and protect your child from injury and excessive exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation. This will only be beneficial. And, of course, if you know that someone in your child’s environment has pemphigus, temporarily limit the child’s contact with the carrier of the disease.