A newborn child has appeared in the family. With him came not only a feeling of great love, but also a sense of responsibility for his life and health. What difficulties can caring parents encounter in the first year of a baby’s life, what are the most common ailments, illnesses and diseases that parents will have to face - we will try to tell you all this in this mini encyclopedia.
What affects the baby's health?
The main diseases of newborns, which arose due to an imperfect immune response, can become quite severe due to its anatomical and physiological characteristics. Various pathologies arise in a child either during intrauterine development or after childbirth. Therefore, the classification of newborn diseases is quite broad.
The following factors will influence the baby's health:
- the course of pregnancy;
- How did the birth process go?
- pregnant woman's health;
- environmental conditions of the newborn;
- method of feeding;
- toxic effects in the womb on the fetus.
A child’s transition to unusual living conditions can lead to some profound shifts in metabolic processes, as well as changes in the functioning of its individual systems and organs. Infants are characterized by transitional health conditions, so these children need special treatment. Existing borderline conditions after some time can develop into more dangerous and serious illnesses.
What difficulties can await caring parents during the first time after childbirth, and what are the most common diseases of children at such a tender age?
Colic and gas
A common illness in young children is colic, severe pain in the baby’s intestines.
If the baby twists his legs, presses them to his chest, cries often and loudly, especially in the evenings, and often farts, you can confidently make this diagnosis yourself.
The cause most often is the swallowing of air with milk and improper nutrition of the breastfeeding mother.
After feeding, hold the baby upright to burp the air. Place it on your tummy more often. Review your mother's diet, excluding cabbage, spicy seasonings, nuts, coffee, and tomatoes. Brew dill water or fennel decoction for your baby.
By three months, colic and gas are usually gone. About colic - how to treat | About gas - how to treat | Tummy massage for colic | List of medications for colic
https://youtu.be/UKXAJoR-Xig
Birth injuries
This is a violation of the integrity of the bones, organs or tissues of the baby, which is mainly caused by mechanical factors during childbirth. These injuries are diagnosed in approximately 9-10% of infants. They have a negative impact on the development of the newborn and his physical health.
Depending on the underlying functional disorder and the location of the injury, the following birth injuries in infants are known:
- Bones and joints: traumatic epiphysiolysis of the bone tissue of the shoulders, subluxation of the joints, bone fractures and cracks. In such cases, the child is examined by a pediatric traumatologist, who usually prescribes an x-ray. If the collarbone is broken, the child may be given a Deso bandage; for fractures of the hips or shoulders, repositioning of the bones of the limbs, as well as the application of a plaster cast, is indicated.
- Soft tissue: muscle and skin injuries, tumor, and cephalohematoma. The tumor disappears three days after the birth process, and if there is a large-sized cephalohematoma, the child undergoes an x-ray of the skull bones in order to prevent the appearance of cracks.
- Organs, and bleeding into the adrenal glands and liver can be especially dangerous. The baby undergoes X-ray and ultrasound of the peritoneal organs and adrenal glands. To treat these conditions, symptomatic or hemostatic therapy is used. The prognosis for injuries inflicted on a child during birth will be determined by their severity and extent.
- Nervous system:
- injuries of the peripheral nervous system: paresis of the diaphragm, paralysis, injuries of the plexus of the shoulders;
- cranial injuries: intraventricular subarachnoid, subdural or epidural bleeding;
- spinal cord injuries: sprains, bleeding, rupture, and compression of the spinal cord; An accurate diagnosis is made by a neurologist by performing electromyography, MRI of the spine, lumbar puncture, and examination of cerebrospinal fluid.
No special medical supervision is required to heal these injuries. The consequences of injury will be determined by the condition of a particular organ. For example, if a newborn has bleeding into the adrenal glands, adrenal insufficiency may later develop. Injuries to the nervous system during childbirth are very dangerous, the consequences of which will depend on their severity.
ARVI
Cough, runny nose, moodiness, lethargy, lack of appetite - these manifestations are familiar to almost every mother. Including mothers of infants. Hypothermia, contact with sick adults - it’s quite easy for a child to get sick, especially considering the immaturity of the immune system. Treatment of acute respiratory viral infections with home methods is a possible experiment for adults, which is best not carried out on children (since they have an increased risk of complications). Be sure to contact your pediatrician and he will prescribe adequate therapy.
Unfortunately, there are health problems that do not have clear and distinct manifestations and can develop gradually. This is why medical examination of children is so important: during medical examination and testing, your baby’s body will be studied thoroughly by the specialists of our center, which will allow him to avoid problems and complications in the future.
Asphyxia
This is a rather serious pathological condition of a child, which usually occurs as a result of impaired gas exchange, causing hypoxia.
Also, the infant often experiences hypercapnia with the accumulation of large amounts of carbon dioxide. Respiratory and metabolic acidosis may develop, the enzymatic process may change, and dysfunction of the central nervous system, liver, and heart may occur.
According to the level of severity, doctors note mild, moderate and severe oxygen deficiency in infants. If a mild or moderate form of this disease is noted, the child has arrhythmic, atypical breathing, cyanotic skin, weakened audible heart sounds and heart contractions, and decreased reflexes. Decreased muscle tone may be noted.
With more severe asphyxia, the newborn’s skin gradually begins to turn pale, shallow or rare breathing is noted, the mucous membranes are cyanotic, the pulse is very difficult to palpate, the child has muffled heart sounds, arrhythmia and bradycardia may develop.
It is noteworthy that in the presence of white asphyxia, almost 50% of babies may die before the moment of birth or during the first week after it. The surviving children suffer from various developmental disorders and frequent chronic pneumonia.
Diarrhea
It is also popularly called diarrhea, a fairly common disease in children at an early age, which occurs when hygiene rules are not followed (not washed hands, dirty water, frequently used items) and manifests itself through acute pain, loose and frequent stools (more 5 times a day), even accompanied by blood, vomiting and nausea.
These symptoms are the cause of dehydration, during which the baby’s body loses fluid and salt, which negatively affects the baby’s body and condition. For example, up to two years of age, a baby loses 50-100 ml of liquid during loose stools, and the older the baby, he already loses 100-200 ml.
How to recognize dehydration with diarrhea? Firstly, it is expressed through anxiety, lethargy, weakness and drowsiness. Also, dry mucous membranes (eyes, mouth), sunken eyes, constant need to drink, the amount of urine decreases, and in some cases may disappear altogether. Secondly, the temperature may rise, and for children less than two months old the temperature drops. Thirdly, complete or partial refusal to eat.
What measures need to be taken? Firstly, you should also feed the baby, but when breastfeeding, you need to feed the baby more often, which will calm the baby, and for bottle-fed children, it is necessary to dilute the milk and give it in the amount required by the child. Children after 6 months should be given food more often, in small portions, freshly cooked and well processed and crushed. Secondly, food should be offered even after the 5th day of illness, but maintaining frequent feeding a couple of times more and for another couple of weeks, even if the child does not eat even half of the portion. Thirdly, it is necessary to consult a doctor on time.
Treatment of asphyxia
Treatment of asphyxia is based on eliminating oxygen deficiency, restoring full breathing, improving impaired metabolism, as well as eliminating existing circulatory disorders. So, doctors should use a catheter to suck out the blood in the respiratory tract as quickly as possible, as well as amniotic fluid and mucus.
After this, in the case of the development of a mild form of oxygen deficiency, the baby is provided with a helium-oxygen mixture, and in the last and most complex form of asphyxia, emergency ventilation is performed. A special apparatus is used for this.
Artificial ventilation is carried out until the baby begins to breathe independently. Oxygen is then supplied through the use of a special nasopharyngeal catheter; they are constantly kept in special oxygen incubators. Recently, hyperbaric oxygenation, performed in a pressure chamber, has been used quite actively.
When reviving babies who were born with severe asphyxia, craniocerebral hypothermia is often used: the baby’s head is cooled, swelling of the meninges is eliminated, the need for oxygen for the brain is reduced, and the microcirculatory process in the brain vessels is restored.
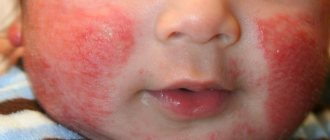
Allergic reactions
Another problem associated with diet is all kinds of allergies. As a rule, they manifest themselves cutaneously: in the form of diathesis or urticaria. With diathesis, the child experiences redness and roughness of the cheeks, and with urticaria, the symptoms can be more serious: itching, swelling, general weakness, a slight increase in temperature.
Don't ignore the signals your baby's body sends you. Eliminate foods that may cause allergies from your diet (for example, red fruits, citrus fruits, chocolate), and observe the reaction. If the rash, itching, etc. continue, contact our pediatrician, he will prescribe antihistamines, after first trying to find out the cause of the allergy. If you have severe allergies accompanied by respiratory symptoms, you should consult our allergist and conduct a special examination.
Respiratory distress syndrome
A significant place among the main and probable causes of mortality in newborns is occupied by the well-known syndrome of respiratory distress, which is usually observed in infants born slightly prematurely. The cause of illness in a newborn baby is called pneumopathy.
Doctors, after numerous studies, were able to establish a connection between this syndrome and pathological childbearing, difficult childbirth and existing diseases in the woman herself. Thus, this category includes uterine hemorrhages, endocrine diseases, as well as premature discharge of amniotic fluid, severe toxicosis during pregnancy, etc.
The burden of the mother's medical history is of no small importance. These negative factors, which can also be combined, cause early birth, as well as the development of complex pathological and physiological changes in the baby: disturbances in the gas exchange process, asphyxia of the baby, metabolic disorders, deterioration in the functional state of the vascular system.
The first symptoms of impaired respiratory activity in a baby appear immediately after birth. After about two hours, the symptom complex characteristic of respiratory distress syndrome may fully develop: rapid breathing, loud exhalation, increasing shortness of breath, changes in the shape of the sternum, and cyanosis of the skin appears.
The baby's breathing pattern may change; the doctor may listen to fine wheezing, which, however, is irregular. Heart sounds are usually tense and quite difficult to listen to due to the existing systolic murmur.
Not entirely favorable signs of this syndrome include liver enlargement, slow breathing, impaired consciousness; the newborn usually experiences muscle hypotension, general edema, hypo- and areflexia, as well as bradycardia.
Stomatitis
Diseases of children under one year of age are very diverse. But you should definitely remember about stomatitis, choosing the most common ones among them. This disease affects the oral mucosa.
Main symptoms:
- Sores and ulcers appear in the mouth.
- The child refuses food.
- The baby is acting restless.
The causative agent of this disease is candidal fungus - when it enters the child’s oral cavity through dirty clothes or toys, or perhaps other non-sterile objects, it leads to stomatitis. For treatment, it is necessary to apply the same recommendations as in the case of treating thrush, adding antifungal drugs to the treatment complex. Again, be sure to consult your doctor. The baby is still very small; independent treatment experiments are simply inappropriate here.
Therapy
Therapy for this condition in infants includes restoring normal ventilation of the lungs, correcting metabolic processes, as well as improving the condition of blood vessels and the heart.
To prevent the development of pneumopathy in a newborn, it is important to follow a set of measures to prevent toxicosis of pregnancy, prematurity, intrauterine asphyxia and early infection of the fetus.
Diseases of growth and development
Diseases of growth and development include various congenital, hereditary and some acquired diseases that lead to persistent physical impairment. and neuropsychic development. A significant role in the genesis of disturbances in the normal growth and development of the child’s body is played by the pathology of the prenatal period - embryopathies (see) and fetopathies (see). The main manifestation of embryopathies are congenital malformations of individual organs, as well as multiple defects, often incompatible with life. According to P. G. Svetlov, the nature of the defects that arise is determined solely by the age of the embryo, and not by the specific nature of the damaging agent (gene mutations, chromosomal aberrations, ionizing radiation, viral infection, teratogenic drugs). It has also become possible to carry out a differential diagnosis of embryonic diseases that cause the formation of developmental defects (due to chromosomal and gene mutations), viral embryopathies (when a pregnant woman gets rubella, cytomegaly). Malformations of individual organs that are compatible with life are one of the most important causes of delayed physical and sometimes mental development of a child.
Fetal diseases are the cause of intrauterine growth retardation and intrauterine dystrophy; babies are born at low birth weight both before and at term. A common cause of fetopathies are various intrauterine infectious diseases, which are recognized at birth on the basis of clinical, serol, and immunol data, studies (for example, high levels of IgM in the blood of a newborn) and specific serols, tests, etc. Placental insufficiency and diseases mothers also lead to intrauterine growth retardation.
Hereditary diseases (see), the vast majority of which manifest themselves in childhood, have a serious impact on the growth and development of a child. Various genetic factors, acting alone or in combination with damaging environmental factors, cause birth defects and diseases in approximately 5% of newborns. The table shows Stevenson's data (A.S. Stevenson, 1961) on the frequency of manifestation of the effects of these factors (per 1000 births), as well as on the magnitude of the genetic risk for the offspring.
According to a WHO research group, hereditary diseases account for up to 40% of child mortality in the UK. They amount to approx. 25-30% of all admissions to pediatric clinics in Canada and the USA.
Hereditary diseases are one of the main causes of childhood disability: deafness and blindness in children in approximately half of the cases are caused by hereditary factors.
The relative increase in the frequency of hereditary diseases in children is associated primarily with improved diagnostics, the introduction of genetic analysis methods into pediatric practice (see) and the use of screening programs for mass examination of the child population (see Screening).
Along with the study of typical monogenic forms of hereditary diseases and their variants, the relationship between hereditary, congenital and exogenous factors in the pathogenesis of hron, somatic and nervous diseases in children has been established. A hereditary (polygenic) predisposition to diseases has been proven, which manifests itself only when exposed to unfavorable environmental factors (for example, many congenital malformations, allergic diseases, most manifestations of obesity, vascular dystonia, etc.).
The mechanisms of development have been studied. 100 hereditary anomalies or metabolic diseases that manifest themselves almost exclusively in children as abnormalities of growth and development. The list of such diseases is annually replenished with new nozole forms. Elucidation of the primary mechanisms of action of the mutant gene at the molecular level allows the use of effective measures for the prevention and treatment of hereditary diseases in children. The severe consequences of a metabolic block can be prevented by nutritional correction methods (phenylketonuria, galactosemia, etc.), replacement therapy (hereditary endocrine diseases) or transplantation methods (hereditary kidney diseases, immunodeficiency diseases). The main requirement for diagnosing hereditary metabolic diseases is recognition of the defect even before the development of the full wedge, the picture of the disease, irreversible changes in the brain and internal organs. This requirement serves as an incentive for the development of the so-called. screening programs providing for mass examinations of newborns. In many countries of the world and in the USSR, such programs have been introduced that provide for the examination of all newborns for phenylketonuria (see), cystic fibrosis (see) and children for galactosemia (see) and a number of other hereditary metabolic abnormalities.
Studies of amniotic fluid (see Amniocentesis, Amniotic fluid) make it possible to recognize approx. 50 hereditary diseases, many of which have a high degree of genetic risk. The results of the study may serve as an indication for termination of pregnancy (medical abortion) or for the treatment of hereditary metabolic abnormalities in the earliest stages, and in some cases even in the prenatal period. Of particular importance is the antenatal diagnosis of diseases such as mucopolysaccharidosis, gangliosidosis, sphingomyelinosis, and Krebs-Henseleit cycle diseases, which lead to profound disability as a result of damage to c. n. With. and internal organs.
In accordance with the orders of M3 of the USSR, work continues to create medical-genetic consultations and offices in large cities of the USSR, designed to identify, record and medical examination of families with hereditary pathologies, as well as to study genetic prognosis (see Medical-genetic consultation).
Persistent deviations in the growth and development of a child are observed in diseases of the endocrine system, which may be associated with damage to higher regulatory nerve centers (intrauterine diseases involving the nervous system, brain dysgenesis, cerebral hemorrhages during childbirth), congenital hypo- and aplasia of the endocrine glands, or hereditary defects in the biosynthesis of hormonally active compounds. Growth deviations associated with insufficient secretion of growth hormone by the pituitary gland give a whole range of variations - from pronounced pituitary dwarfism to normal physical indicators. development.
Developmental disorders may be a consequence of hron, digestive and nutritional disorders (hypotrophy). The causes of malnutrition (see) in the post-war period changed significantly, which was reflected in the general structure of D. b. The increase in the material well-being of the population and the improvement of methods of feeding and feeding children have led to the virtual disappearance of malnutrition of nutritional origin. A sharp decrease in the frequency of infectious gastrointestinal tract. diseases led to a significant decrease in the frequency of malnutrition caused by infectious factors, and genetically determined syndromes of insufficient absorption became one of the leading ones (see Malabsorption syndrome). These syndromes are caused by disturbances in enzymatic breakdown and active transport of food ingredients into the gastrointestinal tract. tract (disaccharidase deficiency, monosaccharide intolerance, cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, malabsorption of certain amino acids, vitamins, etc.).
Hereditary enzyme pathology went.-kish. tract in children (see Enzymopathies) is no less common cause of malnutrition than congenital malformations of the digestive organs. The point of view also on hron, infectious pathology went.-kish. tract in children, edges continues to occur and is largely associated with insufficiency of local intestinal immunity.
Among the causes of transient developmental delay, it is necessary to name a specifically childhood disease - rickets (see), the predisposition to chrome in children is explained by the intensity of growth and the increased need for vitamins and minerals. The widespread use of methods for the prevention of rickets has led to the fact that severe forms of rickets do not occur, but the frequency of genetically determined rickets-like diseases (phosphate diabetes, renal tubular acidosis, de Toni-Debreu-Fanconi syndrome, etc.) has increased relatively. Such diseases are based on defects in the enzyme transport systems of the renal tubules, united by the general term “renal tubulopathies” (see [[TUBULOPATHIES | Hereditary tubulopathies]]).
Hemolytic disease
Clinical recommendations for hemolytic disease of the newborn depend on its form. This disease affects an extremely small number of infants - approximately 0.5% of the total number of children born. The disease develops in a child mainly due to Rh conflict or ABO system discrepancy. It is the most common cause of hemolytic disease of the newborn.
Typically, this disease manifests itself in infants in three forms:
- Anemic - develops due to the short-term effect of isoantibodies secreted by the mother. Damage to the fetus is minimal. Anemia usually develops after the first week of a baby's life, as the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin decreases, the spleen, kidneys and liver become enlarged, and erythroblastosis, polychromasia and anisocytosis may also develop.
- Jaundice - appears due to exposure of the newborn to isoantibodies. The baby may have signs of jaundice and anemia, and may have enlarged lymph nodes, the liver, and the heart. Further, the child will most likely experience a slight developmental delay. Due to the suppression of the immune system, children often suffer from sepsis, omphalitis and pneumonia during the first year of life.
- Edema - appears due to prolonged exposure of a pregnant woman to isoantibodies. In this case, the fetus develops further, since all toxic products will be excreted through the placenta. But still, his spleen, heart and liver may enlarge, extramedullary hemorrhage may form, protein-forming function may be disrupted, vascular permeability may be noted, and hypoalbuminemia may develop. Metabolic disorders in some cases can lead to fetal death.
Otitis
While feeding the baby, he may suck the breast a little and throw it away crying, even if he is hungry and his nose is breathing, you should pay attention to the fact that the baby’s ears may hurt. While suckling at the breast, the baby's eardrums are also retracted, and if they are inflamed, then feeding is painful for the baby, as a result of which he cries and refuses to eat. You can also determine otitis at home by gently pressing the baby’s ear tragus. If after such procedures the baby does not show any signs, then there is no reason to worry, and if after pressing the baby feels uncomfortable and painful, then there is a possibility of otitis. To check, you need to contact an otolaryngologist.
Most often in children, otitis media appears after inflammation of the nose, i.e. runny nose, as the infection travels through the auditory tubes into the middle ear. As a result, it is necessary to be very careful about your baby’s ears during a nasal disease. As the old saying goes, it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it later. After all, it’s not at all difficult to prevent otitis media; you just need to warm the baby’s ears with a heating pad, exposing one ear or the other. This procedure also makes it possible to clean the external auditory canals from wax, since when heated it softens and flows onto the heating pad. It is recommended to warm each ear for no more than 15 minutes.
Pathology therapy
Clinical recommendations for hemolytic disease of the newborn will be as follows. If a child has a severe form, it is necessary to perform a blood transfusion as quickly as possible. Afterwards, detoxification treatment is carried out: the child is given a copious amount of fluid orally, and an intravenous transfusion of blood and glucose substitutes is given. It is often called a hereditary disease of a newborn child.
Also effective is the photochemical method, in which bilirubin is oxidized under a lamp, turning into biliverdin, as well as non-toxic substances. The baby's skin is irradiated with a special blue lamp for about 15 hours a day for two to six days.
Phenobarbital helps activate glucuronyl transferase in the child's liver. To improve liver performance, doctors can prescribe the use of methionine, adenositrophosphoric and ascorbic acid, cyanocobalamin, tocopherol and pyridoxine, and to improve bile secretion, a magnesium solution of 25% concentration is prescribed.
Constipation in a baby
One of the most common problems that worry parents is constipation in children under one year old. Constipation is often accompanied by bloating and difficulty defecating. There may even be pain. For children under one year of age, constipation is normal, so parents should not worry too much. Infants should have normal bowel movements in the first months from two to four times per day. Per year - from one to two times a day. If stool retention in a child under one year old is observed for two days, then we can talk about constipation.
Causes of this disease
- The digestive system is being formed; in infants, the intestines are underdeveloped, so food is digested slowly.
- Transition from breastfeeding to artificial nutrition.
- Teething.
- Previous infectious disease.
- If at six months a child eats only breast milk or formula, then there may be a lack of plant fiber. This may also cause
- constipation
- The child does not move enough. Do gymnastics - place the child on his back, tuck his legs towards his tummy.
- Incorrect feeding - lack of food, complementary foods are introduced early, incorrect diet, monotony of food.
- Lack of breast milk in the mother, rickets and underweight in the child.
You cannot determine the cause on your own; only a doctor can do this. Therefore, at the first symptoms, be sure to consult a specialist.
Parents helping their baby with constipation
- Tummy massage is the best remedy. Do strokes with a warm hand in a clockwise direction.
- Encouraging the child to engage in physical activity.
- If a baby is constipated, a special diet is needed. A nursing mother should monitor her diet - try to exclude foods that cause constipation. Eat prunes and beets. Products that contain a lot of fiber are beneficial.
Sepsis
This is a pathological and quite dangerous condition of a newborn if not detected in a timely manner, which is usually caused by the entry of harmful microorganisms from an existing inflammatory or infectious focus into the child’s blood. It is often called disease of premature newborns.
It is noteworthy that staphylococcal infection is the most common infection recently. Its pathogenicity lies in the ability to independently produce enterotoxins, dermonecrotoxins, hemotoxins and leukocidins, as well as coagulase, hyaluronidase and fibrinolysin, which destroy colloidal particles.
Various diseases of a pregnant woman can be quite dangerous for the baby, since in this case the fetus’s immunity is weakened, as well as its intrauterine infection. But if the placental barrier is broken, the baby may become infected, and this can also happen during its progress during the birth process.
The entry points for infection into the organs of a newborn are usually damaged skin, navel diseases in newborns, navel vessels, eye conjunctiva, mucous membranes of the digestive system and respiratory tract. As a result, the child develops inflammation with the release of pus: conjunctivitis, pyoderma, omphalitis, otitis media, etc. Sepsis can be otogenic cutaneous or umbilical.
Sepsis is diagnosed after receiving the results of laboratory and bacteriological examinations of the baby, as well as with obvious clinical manifestations. Pathogenic staphylococcus is usually cultured from the throat and nose, umbilical wound, skin pustules, or even from blood. But negative examination results cannot 100% exclude the presence of sepsis, especially if it has clinical signs.
The main symptoms of an infant being infected with sepsis are the following: a long-wetting navel, late falling off of the navel, frequently repeated regurgitation, skin pustules, and insufficient weight gain. The combination of symptoms should in each case raise suspicion.
The temperature response of a newborn with sepsis may initially rise to 39 0C, after which the temperature drops to low-grade fever. Approximately on the third day, the baby experiences symptoms of toxicosis: heart sounds are muffled, the skin becomes grayish-pale in color, hyporeflexia and hypotension develop.
Most infants experience profuse vomiting, general weakness, and dyspeptic symptoms. After the second week of the disease, the spleen and liver often become enlarged, and weight gain may slowly increase or even stop.
The navel is not healing well
The navel heals within a week to a week and a half after birth. If it is constantly wet, blood and pus are oozing from the umbilical wound, measures must be taken. Treat the navel with a sterile cotton swab soaked in hydrogen peroxide. Remove any yellow crusts that have formed. After treating with peroxide, lubricate the navel with brilliant green. You cannot bathe the baby during the treatment period; you can wipe the body with a damp cloth. How to treat an umbilical wound | What to do if your belly button is bleeding
Sepsis therapy
Therapy should be aimed at eliminating the pathogen, correcting metabolic disorders, increasing the child’s immunity, and thoroughly sanitizing existing purulent sources.
Among antibacterial drugs, doctors prescribe antibiotics such as Methicillin, Oxacillin and Ampicillin. To prevent the development of dysbiosis and candidiasis in a newborn, it is recommended to combine antibacterial therapy with the use of levorin, nystatinom and bifidumbacterin.
In case of severe anemia, the child may be prescribed an emergency blood transfusion. Ideally, the donor's blood should be immunized with a special toxoid. To correct metabolic disorders, a newborn may be prescribed cocarboxylase and glutamic acid; if hypokalemia occurs (intestinal paresis, tachycardia, vomiting, regurgitation) - potassium acetate. If the infant has severe hypohydration, the administration of certain saline solutions is indicated.
It is advisable to include in therapy the use of antihistamines, which should alternate courses: Pipolfen, Suprastin and Diphenhydramine. For purulent and septic lesions, there is a need for surgical intervention.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis in an infant is a rather serious problem. With this disease, the eyes turn red and purulent discharge accumulates in their corners. After sleep, the child has difficulty lifting the eyelashes that have stuck together.
For relief, you can wash your eyes with infusion of chamomile, calendula, or weak tea leaves. You need to wipe each eye from the outer corner to the inner one with your own swab. The doctor will prescribe treatment, usually eye drops. Clean your eyes before each instillation of the medicine. If a child's eye is festering | Caring for a newborn baby's eyes
Jaundice
Jaundice is a visual manifestation of increased bilirubin in the blood. It is worth learning about the causes and consequences of jaundice in newborns. An increase in bilirubin occurs in absolutely all newborns in the first days of life, while jaundice of the skin is expressed only in 60-70%. Jaundice is more common and more pronounced in children with late passage of meconium, fasting and hypothermia.
Therefore, it is important to put the baby to the breast early and often, which will also facilitate the passage of meconium, and not allow the baby to become hypothermic.
If yellowing is very pronounced or occurs later than the seventh day after birth, or continues to increase after the fifth day and lasts more than three weeks, then it is necessary to determine the level of bilirubin in the child’s blood. When the level is more than 200 µmol/L, additional examination is necessary to exclude pathological jaundice. As you can see, the causes and consequences of jaundice in newborns require immediate elimination.
Skin problems
Jaundice
In the first days of life, the baby's skin may acquire a yellowish tint, even the whites of the eyes may turn slightly yellow. Don't be alarmed; your baby has neonatal jaundice. It is not dangerous and usually goes away by the end of the first month. Follow the rules of hygiene, walk more with your baby. About jaundice - causes, symptoms, how to treat
The newborn's skin is peeling
The skin of a full-term baby is covered with a special lubricant - a white oily liquid. It protects the delicate skin of a newborn from dry air (after all, before his birth he was in an aquatic environment) in the first hours of life. Gradually, the lubricant is absorbed into the baby’s skin almost completely.
If it was wiped off at birth, or the child was born late, which means practically without lubrication, the skin dries out and begins to peel. Frequently lubricating the baby's skin with sterile vegetable oil will help solve the problem. Why does the skin peel and what to do | About crusts on a child’s head
Diaper rash
The baby may experience redness, dry or weeping, in the groin, armpits, and neck folds. The reason is overheating and failure to comply with hygiene rules.
How to treat? Reduce the temperature in the nursery to +21…+22 degrees. Determine whether diaper rash is dry or wet?
If dry, lubricate with baby cream or sterilized vegetable oil. If it gets wet, use baby powder, preferably without additives or fragrances.
Rinse problem areas often with a light solution of potassium permanganate or just warm water. Don't bundle up your child. Take air baths and keep diaper rash areas open for better drying. About diaper rash (treatment and prevention) | Traditional methods of treating diaper rash
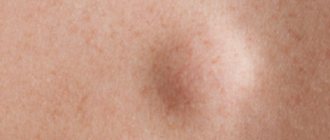
Prickly heat
What does prickly heat look like? Reddened skin with clusters of small red pimples, sometimes with white purulent tips. They usually appear on the butt, neck, head, groin, armpits, and can be on the back, chest, or behind the ears.
Sometimes prickly heat can be confused with an allergy. Parents should be alert if the child itches, is restless, and the rash quickly spreads throughout the baby’s body. A pediatrician will make an accurate diagnosis.
With prickly heat, the rash does not bother the baby. It is enough to wash the affected areas with an infusion of calendula flowers, chamomile, string, and a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Lubricate with baby cream, Bipanten cream, and boiled vegetable oil. You can use pharmaceutical powder. About prickly heat - treatment and prevention
Diaper dermatitis (diaper thrush)
The most striking sign of diaper dermatitis is the appearance of a small rash in the form of blisters, crowded together, but not extending beyond the clearly defined border of the affected area. You can see them in the groin, perineum, in the folds of the legs, around the genitals. For treatment, it is better to use ointments based on nystatin or clotrimazole (strictly as prescribed by a doctor). About diaper dermatitis
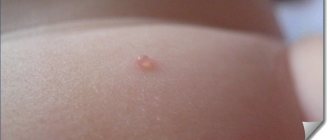
Pemphigus of newborns
Soon after birth, large bubbles (the size of a pea) filled with a yellowish liquid may appear on the baby's body. Gradually they burst, leaving a pink spot in their place. Pemphigus is treated with antibiotics and special ointments (prescribed by a doctor).
Newborn acne
Acne of newborns (infantile acne, neonatal pustulosis) - occurs in ~ 20% of newborns. A rash on the face in the form of pimples. The causes of acne in newborns are hormonal. Does not require treatment. Read more about Acne
Mipia
White dots similar to acne are visible on the baby's face. There is no need to treat them; they will go away within two to four months.
Important: proper skin care for a newborn baby
Treatment of jaundice
If the examination reveals the painful nature of jaundice (and its causes can be varied), appropriate therapy is carried out. And first of all, Ursofalk is prescribed for newborns for jaundice, reviews of which so far are only positive. It is approved for use at any age.
And if it is confirmed that the jaundice is physiological, but prolonged, phototherapy is carried out with special lamps. Currently, this is the most productive and harmless way to cure jaundice. The essence of phototherapy is the effect on the skin of light with a specific wavelength, which breaks down the pigment and promotes its excretion in feces and urine.
In addition, it is permissible to prescribe ursodeoxycholic acid, which dilutes bile and improves its decrease. For example, Ursofalk is used for newborns against jaundice. Reviews about the treatment of the disease with this drug are only positive. And therefore it can be safely used against such pathology.
According to recent studies, prescribing water, glucose or activated carbon to a child is not considered effective.
Regurgitation
Sometimes spitting up becomes a problem for new parents. After eating, hold your baby upright to burp air. Usually this measure is sufficient.
If regurgitation does not stop, consult a doctor, because this may be the beginning of more serious diseases (for example, dysbiosis). Why does a child regurgitate a lot after breastfeeding?
Pemphigus
Pemphigus is a disease of a newborn child from a series of acute infectious skin pathologies, characterized by the appearance of blisters with serous inflammatory contents, with a predisposition to the rapid spread of the process to healthy areas of the skin and oral mucosa. The disease is bacterial in nature and is caused by staphylococcus, less commonly streptococcus. Appears, as a rule, in the first weeks of a child’s life. The cause of the infection is considered to be: personnel caring for the child, the mother of the newborn, members of his family who are sick or have suffered from purulent skin diseases. In some cases, the umbilical cord is considered to be the basis of the infection. It should be noted that the occurrence of an infectious disease in a newborn child is also facilitated by such factors as the lack of protective properties of the skin, its anatomical and physical features, and insufficient hygiene of children.
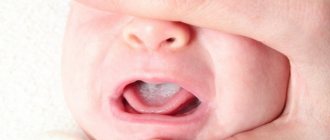
Oral thrush
White, uneven spots appear in the child's mouth on the tongue and inner surface of the cheeks. They are coarse and greasy, looking like pieces of cottage cheese or leftover milk. But, unlike milk stains, these are not washed off from the baby’s tongue. You can distinguish thrush like this - the remaining milk disappears during the break between feedings, the spots of thrush, on the contrary, spread throughout the oral mucosa.
It is necessary to treat thrush, because it causes pain in the baby’s mouth. He sucks worse or refuses to take the breast altogether.
When breastfeeding, a mother can also become infected with thrush. Therefore, before breastfeeding, treat the baby’s oral cavity with a gauze or bandage napkin soaked in a solution of baking soda (add 1 teaspoon of soda to a glass of warm water).
Sterilization of nipples and bottles is required; when breastfeeding, thoroughly rinsing the breasts before and after feeding. To treat thrush, special drugs based on nystatin are used. The doctor will select and prescribe them. Treating oral thrush in newborns