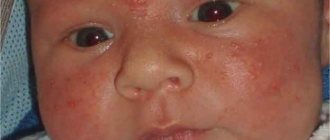
Birth injuries in newborns are quite common. They mean damage to the baby’s organs and tissues resulting from exposure to mechanical forces during the process of delivery, which entail a number of disturbances in the child’s compensatory and adaptive mechanisms and the corresponding reaction of the body to these damages.
We would like to clarify that in medicine the concepts of “birth injury” and “birth injury” are not the same thing. The damage can be toxic, hypoxic, infectious or some other, which indicates a pathological process and the root cause of the development of pathology. Birth trauma is a disease, a kind of response of the body when, following birth injuries, other pathological processes occur.
Causes
Conventionally, we can distinguish 3 groups of factors influencing the causes of injury: pathologies of the fetus, anatomical features and diseases of the mother, and the technique of conducting the birth itself.
The most common group is related to the condition of the fetus:
- prematurity;
- heavy weight;
- breech presentation, umbilical cord entanglement;
- incorrect cutting of the head;
- hypoxia or asphyxia;
- oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios;
- intrauterine pathologies.
Application of obstetric forceps is fraught with birth injuries
The next category concerns the pregnant woman. The risk of birth injury increases if the mother:
- narrow pelvis;
- late gestosis;
- hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the uterus;
- bending of the uterus (hyperanteflexia);
- age less than 18 or more than 35 years;
- diseases of the endocrine, cardiovascular or gynecological system;
- bad habits (smoking, taking drugs, alcohol);
- inhalation of harmful substances at work.
And finally, childbirth itself can be traumatic. Difficulties present:
- rapid or prolonged labor;
- stimulation with oxytocin, prostaglandins, antiprogestogens, bladder puncture;
- use of obstetric aids: application of forceps, vacuum extraction,
- pressure by the midwife's hand on the fundus of the uterus in order to accelerate the advancement of the fetus.
Causes of damage
Traumatization occurs due to mechanical impact during the birth process, as a result of which the tissue structure is disrupted. In other words, this phenomenon is said to occur when newborns have damage that occurred during their birth. The likelihood of a birth injury is not always affected by physician errors. Often, damage occurs due to the incorrect lifestyle of a pregnant woman, the structural features of the woman’s pelvis, the position of the fetus, and for a number of other reasons.
Features of the structure of the head of a newborn
The structure of the head in newborns has several significant differences. Before birth, this part of the body is the largest. In most cases, the fetus moves with its head in front. As a result, she experiences maximum stress. She manages to maintain her previous shape due to two qualities:
- elasticity;
- elasticity.
Fontanas in a newborn
The development of the first quality is influenced by fontanelles. These structures are cavities between the bones of the skull, filled with a dense membrane. The latter is formed from the dura mater of the brain and the periosteum. Newborns have four fontanelles.
The increased elasticity of the child’s skull is also due to the structural features of the sutures made of connective tissue. This structure ensures relatively free passage of the head through the birth canal. When a child’s skull experiences stress, it becomes slightly deformed, eliminating the possibility of injury to tissues and the brain.
Birth trauma in newborns occurs when there is strong compression. Such exposure leads to damage to the structural elements and tissues of the skull. After birth, the head remains deformed.
Risk factors
Such damage occurs under the influence of three specific factors. Let's look at them in more detail:
- The course of pregnancy. Birth-related traumatic brain injuries in children are caused by:
long pregnancy;- ecological situation;
- weak contractions;
- lack of coordination of tribal forces;
- tetanic contractions;
- obstetric turns;
- using obstetric forceps to pull out the baby (the most common reason);
- use of vacuum extraction of the fetus;
- medical errors made when performing a caesarean section.
mother's lifestyle;
- heart pathologies;
diseases of the endocrine and other internal systems;
large size of the child;
position of the fetus with the pelvis towards the birth canal;
Extension insertion of the head also leads to brain damage in newborns. More often the skull is injured under the influence of a group of factors. The development of congenital pathologies is facilitated by cesarean section performed before the onset of contractions. When the fetus is forcibly removed, negative pressure is formed inside the uterus. To get the baby out, the doctor has to make an effort. And if the position of the hands is unsuccessful, there is a high probability of injury.
Traumatic brain injuries
Unfortunately, head injuries are considered one of the main causes of disability or even death in newborns. The situation can be aggravated by aspiration of amniotic fluid or prolonged hypoxia due to placental abruption.
Causes
As a result of the fact that the head forms the birth canal and is the largest part of the body in circumference, it takes on the maximum load during childbirth. Due to the ability to change configuration due to the elasticity and elasticity associated with the presence of fontanelles, the bones of the skull during birth are superimposed on one another, and the volume of the head decreases, withstanding the pressure exerted on it. However, when the pressure is higher than usual or over a long period of time, damage to brain structures can occur.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The severity of the injury is judged by assessing the infant's behavioral state. Pathological manifestations may be:
- stupor - practically no reactions to external stimuli;
- lethargy - the child sleeps almost all the time, waking up in response to a strong painful stimulus;
- coma.
The localization of hemorrhages in the brain can be different, but it always poses a danger to the health and even the life of the baby
Brain lesions can be in the form of hemorrhages under the meninges (subarachnoid, epidural, subdural), directly into the brain (then hematomas are formed) or inside the ventricles.
Outwardly, it is not so easy to determine the presence of injury, since healthy babies are also able to react sluggishly to light, their pupils wander, there are manifestations of strabismus - and these are variants of the norm.
Normally, the brain should not protrude above the bony edge of the fontanel, and when palpated, a pulsation is felt. When compiling a clinical picture, they focus on the presence (or absence) of convulsive, hydrocephalic syndrome, increased excitability, and a decrease in the sucking and swallowing reflex.
The most informative diagnostic methods are considered to be neurosonography through the large fontanel, x-ray examination (allows you to assess damage to bone structures), and MRI.
Treatment
We recommend reading: Cracked collarbone in a newborn
Newborns with traumatic brain injuries are treated in intensive care wards, placed in special incubators. All manipulations related to care and feeding are performed in the crib.
Postpartum swelling is usually simply observed, while large cephalohematomas (greater than 6 cm) require removal of the contents using two needles. After the procedure, a tight bandage is applied to the head. Abrasions are treated with a solution of brilliant green. If the scalp is affected, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed and stitches are applied.
Fractures of the skull bones are almost always associated with the use of obstetric aids. But, thanks to bone elasticity, not all of them require surgical correction. For example, depressed fractures may heal spontaneously.
The most difficult treatment for birth injuries to the brain is associated with intracranial hemorrhages, since they are fraught with large blood losses and functional changes in brain function. Surgical treatment is carried out in 3 directions: puncture, staged and craniotomy.
Consequences of trauma during childbirth
We will not talk about severe birth injuries that cannot be corrected.
Let us note the most complex fascial injuries: Small cerebral dysfunction (MMD).
These are mild changes in the functioning of the central nervous system. They can manifest themselves in behavioral disorders, hyperactivity or laziness, learning difficulties, and speech disorders.
Torticollis.
It is manifested by an unnatural position of the baby’s head: tilting to the side with a turn. Torticollis can be one-sided or two-sided. This is a syndrome caused by changes in the soft tissues and nerves of the neck. Often the pathology can only be seen by a specialist.
Head asymmetry.
The disorder can be associated not only with birth trauma, but can also develop during the period of intrauterine development. It happens that caesarean babies who have not gone through the difficulties of natural childbirth have deformed skulls. Most likely, the mother of a baby with an asymmetrical head had scoliosis or an old injury to the sacrum.
Autism.
Isolation, decreased intelligence, social maladjustment. The origins of autism and autism spectrum disorders are unclear to this day. In addition to birth injuries, their causes also include genetic pathologies. Typically, parents notice behavioral abnormalities in a child before the age of 3.
Hyperactivity.
Attention disorder syndrome (previously called minimal brain dysfunction, hyperkinetic syndrome, etc.). Untreated childhood painful restlessness can become the basis for adult neuroses and difficulties in interpersonal relationships.
Hypertonicity.
The predominance of tension in the flexor muscles over the tone of the extensor muscles after 3.5 months of life requires special treatment. If you do not pay attention to this, the child will suffer from poor coordination and speech problems.
Delayed speech and psycho-speech development (ZRR and ZPRR).
According to studies in various cities of Russia, such deviations are observed in 50% of cases in 7-year-old children.
Internal organ injuries
Mechanical pressure on the fetus often leads to hemorrhages in the spleen, liver or adrenal glands. Symptoms are clearly visible 4-5 days after birth. Due to existing internal bleeding, muscle weakness, intestinal paresis, low blood pressure, bloating, along with regurgitation and vomiting are observed. Reflexes are depressed.
The diagnosis is established using ultrasound and x-ray of the peritoneal organs, as well as ultrasound of the adrenal glands. Therapy is aimed at stopping bleeding; sometimes laparoscopic intervention is used or laparotomy is performed.
The consequences of a birth injury of this kind depend on the severity and extent of the injury, as well as the speed of its detection and assistance.
When is it necessary to see an osteopath?
Prevention of the consequences of birth injuries
No one can predict the course of labor. But every woman is able to properly prepare in advance not only for childbirth, but also for pregnancy. This is not at all about taking tests and standard consultations with doctors. These are things that go without saying. We are talking about the need to visit an osteopathic doctor. Using his knowledge and skills, the doctor will determine whether your body is at risk for complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
Osteopathy methods will help to examine the organs and systems of the expectant mother and balance them as much as possible. An osteopath checks the position of the pelvic bones, spine, internal organs, and nervous system. They will receive the greatest load during pregnancy. Their position will influence the correct intrauterine development of the child. A woman who takes a responsible approach to pregnancy and childbirth, comes for consultations with an osteopath, most often gives birth without outside help.
Kinesiology is aimed at testing a person’s muscular reactions while walking, moving the body and individual parts of the body. A kinesiologist analyzes movement patterns, identifying possible pathologies. Not all kinesiology methods can be used to examine a pregnant woman because of their pain and rather harsh effects. The doctor chooses only mild options, following the medical principle of “do no harm.”
How osteopathy can help pregnant women
A systematic examination of the expectant mother by an osteopath is not dangerous for the child. 3-4 preventive sessions throughout pregnancy are enough. After taking it, women note improved mood, calmness, relief from lower back pain, and a reduction in varicose veins and swelling.
When exposed to soft osteopathic techniques, the following occurs:
- Balancing the pelvic bones, which ensures easy passage of the baby through the birth canal.
- Alignment of the position of the fetus in the uterus. This eliminates emergency situations of squeezing an arm or leg, or the umbilical cord during childbirth.
- Correction of breech presentation. It increases the risk of injury, for example to the delicate vertebrae of a newborn's neck.
- Removing uterine tone. Because of this pathology, childbirth occurs quickly and violently, causing birth trauma to the child.
- Relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles. This is important for the passage of the fetal head, especially in primiparous women.
- Correction of the position of internal organs squeezed by an enlarged uterus. The risk of gestosis and the need for instrumental intervention is reduced.
What to do after childbirth
Our congratulations on the birth of your child! Now is the time for the woman to see an osteopath herself after giving birth and bring her newborn baby for examination.
Even if childbirth passed without visible consequences, microtraumas can appear years later in childhood or even adulthood. The violation, like a time bomb, is waiting in the wings. Therefore, it is so necessary to show the newborn to an osteopathic doctor.
Soft tissue injuries
This type includes damage to the skin and subcutaneous tissue. They may look like scratches, abrasions, or other manifestations. Thus, when the sternocleidomastoid muscle is damaged, not only a soft compaction (tumor) is formed, but also torticollis develops. For treatment in this case, massage techniques, electrophoresis with potassium iodide are used, the position of the head is fixed with special orthopedic rollers.
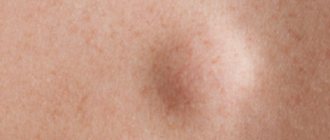
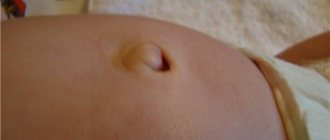
Cephalohematoma
This type of trauma can also include birth tumors and cephalohematomas. The tactics of their treatment are described above. It is worth noting, however, that cephalohematomas can be monitored for 3-4 weeks, but if there are signs of suppuration, it must be removed immediately. Since cephalohematomas are often accompanied by the intrauterine development of mycoplasmosis, PCR diagnostics are performed.
Traumatization of the musculoskeletal system
This type of injury is considered exclusively an obstetric defect. More often than others, the collarbone and limb bones are damaged. If the clavicle fracture is not displaced, it is diagnosed approximately on the 3rd day, when a callus forms in the form of a swelling. In case of displacement, newborns not only experience swelling, but also limited arm movements, the child cries when trying to carry out any manipulations with the damaged limb.
Rarely, during childbirth, the epiphysis of the upper or lower end of the shoulder or hip may become displaced. In such cases, limb traction is performed with temporary fixation. The regenerative abilities of the child’s body are amazing, so the bones are completely restored over time.
A fracture of the humerus, radius or femur is diagnosed by pain reaction, visual shortening of the limb, swelling, and of course, by x-ray. A pediatric traumatologist must be involved in the treatment of fractures in newborns. In some cases, for example, with a fracture of the collarbone, applying a tight bandage is sufficient, while in others the limb is immobilized with a plaster.
If the collarbone is fractured, it is enough to fix the injured arm with a bandage for a week
What is a hematoma or cephalohematoma?
A cephalohematoma is a special type of bruise on a child’s head. It is a bloody swelling in the area between the periosteum and the flat bones of the skull. In everyday language, this is a bruise caused by damage to soft tissue.
In order to pass through the birth canal, the baby needs to pass between the muscle ring and the mother’s pelvic bones. To do this, the baby makes a series of movements, which helps itself to overcome this passage.
The pressure inside and outside the womb varies. Therefore, at birth, the capillaries and blood vessels of the newborn burst and cause blood to accumulate.
Most often, a hematoma on the head of a newborn after childbirth goes away quickly and leaves no trace. After a while, the baby’s scalp becomes a normal color, the bruises fade, and after a couple of weeks they disappear completely. In medicine, there are cases when a tumor obtained during childbirth significantly increases in size and blood begins to be released from it. In this situation, you must immediately consult a doctor to avoid possible complications from the birth injury.
Cervical and spine injuries
During birth, the baby experiences colossal overloads: he is affected by forces that expel the fetus from the womb. And since most often the child has a cephalic presentation, injuries to the head and neck are common, encountering resistance from the pelvic floor and muscles throughout the birth canal.
Causes
Birth trauma to the cervical spine occurs most often due to traction of the head and neck in newborns. Under such circumstances, the bodies of the I-II vertebrae may become displaced, subluxation of the joints in the cervical vertebrae, rotational subluxation of the atlas, and damage to the intervertebral discs may occur.
Symptoms and diagnosis
There is no clear clinical picture to help establish the presence of a birth injury to the cervical spine or spinal cord. Pathology can be suspected by decreased reflexes (swallowing, sucking), impaired muscle tone, often in the direction of hypotension, shortened or elongated neck, and the presence of torticollis. The muscles of the cervical-occipital region are often tense, and when the spinous processes and paravertebral points in the cervical region are palpated, the child begins to worry, cry, and changes his facial expressions.
Children with suspected injuries to the cervical spine and spine undergo radiography in two projections. The study also uses neurosonography and Dopplerography of the vessels of the spinal cord and brain - this way you can understand whether there are disturbances in vascular blood flow, in particular, blood circulation in the vertebral artery basin or damage to the membranes of the spinal cord.
Treatment
If the clinical manifestations are mild, the alarming symptoms may disappear on their own within a few days. However, if serious damage is suspected, a comprehensive approach to treatment is necessary.
The main goal of therapy is to restore brain trophism. To do this, in some cases it is necessary to temporarily (up to two weeks) immobilize the cervical spine by applying special cotton-gauze collars (for example, Shants). Later, the collar is replaced with an orthopedic pillow.
Massage performed by an experienced and qualified osteopath gives good results in the treatment of birth injuries
The treatment regimen includes taking medications aimed at improving the functioning of the central nervous system and ensuring trophism of muscle tissue. Massages and electrophoresis with aminophylline, relaxing baths with pine needles and salt are effective. Therapeutic treatment may take about 6 months or more, and during the first year the courses of massage and electrophoresis are repeated. In any case, after restoration of functions, the child is still under the supervision of doctors - a neurologist and an orthopedist.
Consequences with possible complications
The earlier treatment of birth trauma begins, the less likely it is to develop complications. But the bones of the neck and spine in infants are very fragile and can stretch, thereby disrupting the outflow of fluid and affecting blood circulation. If nothing is done, the child may subsequently suffer from the following diseases:
- headaches, digestive problems;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia, hypertension;
- diseases of the joints and spine (scoliosis, osteochondrosis), flat feet, clubfoot;
- physical and mental retardation;
- underdevelopment of fine motor skills (“awkward fingers”).
What is birth trauma
Birth trauma is a reaction that occurs in the child’s body to damage that occurs during passage through the birth canal . Birth injuries can occur during normal delivery, as well as during pathological childbirth.
If the course of labor is unfavorable, fetal trauma can lead to severe damage to the brain and spinal cord, bones and spine . This leads to severe neurological diseases, mental retardation, disability, and in severe cases, death of the fetus or newborn.
Photo 1. Birth trauma is a phenomenon that occurs more often than it seems. Source: Flickr (Jonatan P.)
Injuries of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
These include the considered spinal injuries, when the spinal cord is affected, and damage to the peripheral nervous system:
- paresis of the facial nerve - appears during prolonged labor and prolonged compression of the nerve; the face is asymmetrical, the lips move to the healthy side;
- Duchenne-Erb's palsy - the brachial nerve plexus is damaged, causing the arm to not move;
- paresis of the diaphragm - occurs when using obstetric aids and fetal asphyxia;
- Dejerine-Klumpke palsy - partial paralysis of the branches of the brachial plexus leads to immobilization of the hand muscles and loss of sensitivity.
To clarify the diagnosis, an X-ray or MRI of the spine is done, and a lumbar puncture is taken. They are treated with massage, electrical stimulation, exercise therapy, as well as therapy aimed at eliminating circulatory disorders.
Are injuries possible during a caesarean section?
There is an opinion that if a child is born by caesarean section, birth injuries can be avoided. Most often this is what happens, but damage is still possible under the influence of various factors:
- A history of indications for cesarean section can cause trauma.
- Technique for caesarean section. During the operation, an incision of 25 cm is made, and the circumference of the baby's shoulders is slightly larger, about 35 cm. Therefore, removing the baby requires effort on the part of the midwife, which can result in damage to the cervical spine.
- The absence of passage through the birth canal negatively affects the development of the baby’s nervous system, because the restructuring of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems occurs according to a completely different scenario. This is a kind of stress for the body.
Caesarean section is not an absolute guarantee that childbirth will be without injury.
Therefore, if there are no direct indications for a cesarean section, you should not insist on the operation, thinking that in this way it will be possible to protect the child from all troubles. In addition, a cesarean section does not make it possible to carry the next pregnancy for 3-4 years.
Preventive actions
Is there any way to reduce the risk of birth injuries? Yes, if you follow some recommendations:
- plan your pregnancy in advance by undergoing a reproductive system examination;
- treatment of diseases, especially chronic ones, without delay;
- a pregnant woman should avoid crowded places during periods of viral and respiratory diseases to reduce the risk of contracting an infection;
- high-quality and balanced nutrition during pregnancy;
- timely observation by a gynecologist, passing all necessary tests;
- the expectant mother should lead a healthy lifestyle;
- During labor, listen to your midwife and push correctly.
So, injuries in newborns during childbirth occur frequently. Most of them do not pose a threat to the baby’s life, and the body recovers over time without outside help. However, in difficult situations it is necessary to trust specialists in the field of neurosurgery, neurology and traumatology. For her part, the expectant mother can do a lot to ensure that her child is born healthy.
Why do babies fall from changing tables?
Indeed, children spend the first 1-2 months of their lives in the position in which their parents placed them in the crib or on the changing pad. Therefore, they are given the false impression that they will not get away from it. Isn't it wonderful: putting a naked baby on a diaper so that he can take an air bath? And yet, this is where the child faces one of the most serious dangers - falling from the changing table.
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
Statistics say that every third baby under the age of 6 months had this type of injury. The main reason for it is leaving the child unattended due to an imaginary sense of security: he is surrounded on three sides by sides. Besides, how can a baby fall off of it if he hasn’t even learned to roll over? And yet, practice shows that he can master this skill precisely when he is left alone on the changing pad. In addition, babies who are not even a month old have a number of innate reflexes, in particular pushing off the support with their feet. As a result, a baby who seems so small may well do something that is not at all expected of him.