Diseases of the newborn period always require special attention. This is especially true for infectious lesions. Due to the fact that the baby’s body is still poorly adapted to the new environment, and the functioning of the immune system is still imperfect, inflammatory pathologies can lead to dangerous complications. This is especially true for premature newborns, as well as children who are bottle-fed. These babies are at risk and require increased attention from medical personnel.
An example of an infectious lesion is: vesiculopustulosis in newborns, pemphigus, omphalitis, etc. These diseases require hospitalization of the baby in a children's hospital, since without timely treatment they can lead to the development of sepsis.
Types of vesiculopustulosis
Depending on the source of infection, there are 2 types of disease:
- congenital vesiculopustulosis in newborns - contamination of the child’s skin occurs in utero or intrapartum (while passing through the birth canal). The first symptoms develop within 1-2 days after birth.
- acquired - occurs 7–10 days after birth.
Important! The reasons for the development of pathology may be non-compliance with hygienic rules for caring for the child’s skin (lack of daily bathing), the presence of pustular skin lesions in people in contact with the child (parents, grandparents, medical personnel).
Causes
The causes of the disease include the following:
Vesiculopustulosis in newborns is caused by staphylococci. The infectious microorganism begins to multiply on the baby’s skin under the following conditions:
- A woman suffered from a staphylococcal infection during pregnancy;
- Unfavorable epidemiological situation in the hospital where children are cared for: in intensive care wards, in delivery rooms, pediatric wards, in intensive care units;
- Insufficient hand cleaning of medical staff who care for small children;
- Poor quality care for the baby, hypothermia or overheating, the presence of diaper rash;
- The skin of infants has a special structure; it is prone to maceration, that is, it easily absorbs liquid and then becomes inflamed;
- Early refusal of breastfeeding.
When the microorganism comes into contact with the baby’s skin, it develops inflammation of the sweat glands, which is characterized by certain symptoms.
Vesiculopustulosis is caused by both gram-positive (staphylococcus, streptococcus) and gram-negative (klebsiella, proteus, E. coli) bacteria.
Recently, cases of fungal vesiculopustulosis have become known.
Factors predisposing to the development of vesiculopustulosis in newborns
Not all children are equally susceptible to developing this skin lesion. There are a number of factors that unite infants into a group at high risk of developing the disease “vesiculopustulosis”:
- prematurity;
- artificial feeding;
- the presence of developmental anomalies;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- the course of pregnancy against the background of gestosis;
- multiple pregnancy;
- asphyxia at birth;
- the presence of an atypically proceeding labor (rapid or, conversely, protracted);
- prolonged jaundice of the newborn, etc.
Note: when several risk factors are combined, the child requires especially careful hygienic care of his skin.
Clinical manifestations in newborns
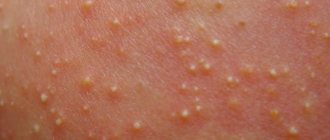
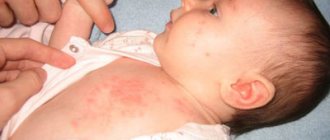
Most often, vesiculopustulosis in newborns affects the areas of greatest accumulation of sweat glands: axillary, inguinal folds, and scalp . It begins with the appearance of small (several millimeters in diameter) reddish spots.
The onset of skin rashes most often resembles prickly heat, and therefore does not cause sufficient concern among parents
The next stage in the development of rash elements are vesicles.
The vesicle is a small vesicle filled with transparent contents that may be surrounded by a rim of redness
This stage lasts about 1-2 days. The number of elements varies: from single bubbles to multiple extensive lesions.
The final stage of development of the rash is clouding of the transparent contents, pustules appear.
A pustule is a small cavity filled with pus
The pustules open on their own, which leads to the release of their contents onto the surface and infection of neighboring healthy areas of the skin. Afterwards, a weeping erosion remains in this place, healing by primary intention without the formation of scars or marks.
Note. Despite the fact that the process can cover a large area of skin, it usually proceeds favorably. The child's general well-being is not affected. An increase in temperature to 37ºC is rarely observed.
Vesiculopustulosis is rare in adults; it is believed that this disease is characteristic of the newborn period.
Main symptoms of the disease
Clinical cases of vesiculopustulosis are considered individually. There are general and specific signs of the disease. Dysfunctional manifestations form pathogenesis and etiological factors.
Characteristic symptoms:
- high body temperature (low-grade fever or fever);
- increased activity, anxiety;
- sleep disturbances with vesiculopustulosis;
- intense crying for no reason, the child fusses, rushes about, cannot be calmed down;
- lack of appetite;
- lips, mucous membranes are dry;
- hyperemia.
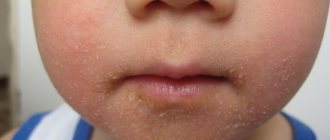
The head becomes covered with rashes due to poor care of the scalp; the course of the disease is often aggravated by incorrectly selected hygiene products. The effect of staphylococcus on the body is aggravated by pathogenic elements - Klebsiella, E. coli, fungal invasions.
Epidermal symptoms of vesiculopustulosis:
- small red dots similar to chickenpox form on the skin;
- the rash intensifies, the pustules grow;
- contents – serous fluid (cloudy at first, as the pathology progresses, the substance turns into pus);
- pustules are surrounded by a bright pink rim;
- elements merge, forming large areas of damage;
- the abscess increases in size, when it reaches the extreme point, it opens;
- bare areas of the dermis with vesiculopustulosis are presented in the form of weeping surfaces - painful erosions;
- damaged tissues become scarred. If the treatment tactics and methods were chosen correctly, the skin restores its barrier functions.
Vesicles appear on surfaces where sebaceous and sweat glands are located, poorly ventilated: on the head, where there are follicles, in the upper third of the back, on the buttocks, on the chest of obese babies.
If the doctor does not make a diagnosis in a timely manner and does not prescribe therapy, the pathological process of development of vesiculopustulosis will affect the basal layers of the epidermis and subcutaneous fatty tissue.
Treatment
Treatment of vesiculopustulosis in newborns begins immediately after diagnosis. It is most often carried out at home by a pediatrician. To prevent the spread of the process, bathing the child is canceled. The affected areas are treated with antiseptic solutions.
One of the antiseptics in children's practice is potassium permanganate or potassium permanganate. To prepare the solution, take boiled warm water, to which a couple of crystals are added. The color of the solution should be pale pink.
Important! It is necessary to dilute this solution carefully, as a high concentration can lead to burns to the delicate skin of a newborn.
The resulting erosions must be dried with solutions of methylene blue or brilliant green. The use of these drugs is targeted.
The baby's skin must be treated 2 times a day.
In case of extensive skin rashes and no effect from local treatment, additional antibiotic therapy is performed.
Important! You cannot squeeze out or open the formed vesicles and pustules yourself, because... this can lead to the spread of infection and the development of complications.
Appearance of a newborn with vesiculopustulosis
Complications
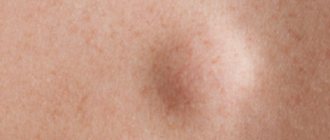
Vesiculopustulosis is a disease that has a benign course and a tendency to self-heal 1-2 weeks after its onset, however, if the child’s immunity is reduced or there is a lack of competent care, complications can develop. These include the formation of abscesses of various sizes:
- furuncle;
- carbuncle;
- phlegmon;
- abscess.
Important! A serious complication can be general blood poisoning - sepsis.
Prevention
Prevention of vesiculopustulosis begins before the baby is born. A woman's birth canal should be examined for the presence of pathogenic microflora and, if necessary, sanitized shortly before childbirth. After birth, early breastfeeding will help populate the baby's skin with maternal microflora. This measure will serve to protect the baby from aggressive hospital flora, including staphylococcal skin infection - vesiculopustulosis.
Hygienic procedures for caring for the skin of a newborn include:
- bathing the child daily;
- wiping the skin folds at least once a day with napkins moistened with boiled water.
Don’t forget about the role of breastfeeding in creating normal immunity..
Every mother wants to see her baby healthy. And a child’s skin is the first protective barrier against the penetration of microorganisms inside, which is why it is so important to monitor its condition.
Diagnosis of vesiculopustulosis
Vesiculopustulosis in newborns is diagnosed based on data obtained through examination and laboratory tests.
The first thing the doctor will do is collect the mother’s medical history and complaints. At the same time, the time of formation of bubbles and their development, which occurred from the moment of their appearance, are specified. The pediatrician will also ask if the baby’s body temperature has increased.
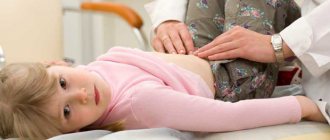
After this, a general examination is carried out, during which the pediatrician clarifies where exactly the bubbles are located, what is their prevalence, and whether there is fusion between them. The general condition of the baby must be assessed.
If necessary, the baby may be sent for a general blood test to determine the increased number of leukocytes and ESR.
After the blood test is done, it is necessary to identify the causative agent of vesiculopustulosis, since the treatment will depend on this.
This is done by inoculating the contents of the bubbles. Sometimes the blood of a newborn is used for these purposes. Culture allows you to determine the sensitivity of microbes to antibiotics, which is very important for the correct prescription of antibiotics.
In case of complicated course of vesiculopustulosis in children, other tests may be required, as well as consultations with doctors of other specialties:
- A general urine test, which will also help identify the causative agent of vesiculopustulosis.
- Examination by an otolaryngologist (ENT) if otitis media is suspected.
- Examination by a surgeon if abscesses or phlegmon form at the site.
- Examination by an infectious disease specialist.
- Examination by a pediatric dermatologist.
The basis of the diagnostic process of this infectious disease is a set of studies that were obtained during the initial examination by a dermatologist and laboratory data from materials taken for specific tests.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the specialist collects the mother’s medical history and complaints, that is, using a survey, determines the moment when the first bubbles appear on the child’s skin, monitors the nature of their changes over a certain period of time, and also measures the patient’s body temperature.