Main reasons
Most often, vulvovaginitis occurs in girls aged 3 years and older. This is explained by the fact that the child has already begun to wash herself, and perhaps she did not do it well enough. As a result, a cluster of microbes arose, which provoked an inflammatory process. In infants, vulvovaginitis can be a consequence of allergies.
The disease can be caused by different viruses: cytodentvirus, herpes or adenovirus. The bacterial type of lesion can be caused by:
- allergic reaction;
- insufficient hygiene;
- improperly selected antibacterial therapy;
- infectious disease.
The spread of microorganisms is facilitated by dermatological problems and mechanical damage to the mucous membranes.
Forms of the disease
There are several forms of the disease. Each of them has its own characteristics, so before starting treatment, the doctor must determine the type of lesion. The following forms of vulvovaginitis are distinguished:
- mycotic;
- trichomonas;
- viral or bacterial.
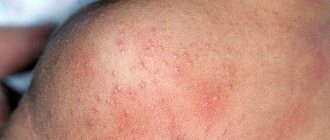
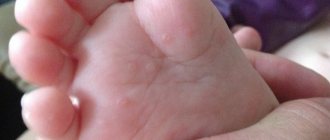
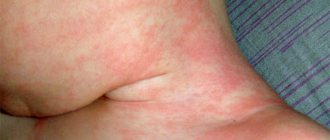
The mycotic form of the disease is often diagnosed in newborns and girls at puberty. A distinctive feature is the presence of a cheesy coating on the genitals, under which eroded areas form. Signs of mycotic vulvovaginitis are itching and redness of the skin.
The trichomonas form of pathology is observed in newborns and girls aged 12 years, when mature epithelium begins to form in the vagina. Due to glycogen, the epithelium becomes a good environment for the development of Trichomonas. The main signs of damage are hyperemia and slight swelling of the vulva. This form is characterized by foamy leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor.
The viral or bacterial type of vulvovaginitis develops with diphtheria, smallpox, and also against the background of respiratory diseases. A common cause of damage is strepto-staphylococcal infection. In this case, slight redness of the labia may occur.
Therapy is selected depending on the form of vulvovaginitis and the degree of its neglect. The sooner treatment is started, the more effective it will be.
Colpitis (vaginitis) - symptoms and treatment
The goals of treatment are to eliminate inflammation and restore vaginal microflora.
Treatment regimen for vaginitis
Treatment always consists of two stages. The first stage is the fight against inflammatory agents. This stage sometimes begins with a slight acidification of the vaginal environment (only if indicated). The second stage is the restoration of microflora in the vagina and intestines, followed by transition to preventive measures to reduce the risk of relapse.
Medicines
Treatment of specific and nonspecific vaginitis. Depending on the causative agent of the disease, systemic therapy with antibacterial drugs (amoxicillin, jazzomycin, clindamycin, ornidazole, metronidazole, tinidazole, etc.) may be required. Suppositories, capsules or vaginal tablets are prescribed locally, most often containing combination drugs (Poliginax, Macmiror complex, Terzhinan, Neo-penotran, etc.).
Treatment of candidal vaginitis (thrush). For thrush, antimycotic (antifungal) drugs of local and systemic action are prescribed.
Treatment of atrophic vaginitis. For atrophic vaginitis, the use of vaginal creams, tablets or rings with estrogen is indicated [13].
Lifestyle and aids
During treatment, sexual abstinence is recommended. After the main course of therapy, it is necessary to carry out a course of restoring the microflora in the vagina with preparations containing lactobacilli.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
In case of a chronic and often recurrent process, treatment should be comprehensive and include physiotherapeutic procedures (ultrasonic sanitation with the stage of restoration of vaginal biocinosis). It is important not only to eliminate inflammation, but also to restore damaged microflora, immune defense and remove the influence of the causative factor (sanitize foci of chronic infection, change personal hygiene products or contraception, compensate for diabetes with insulin).
It is also worth noting that there is an additional method of treating and restoring the vaginal microflora - this is low-frequency ultrasound sanitation with the Gineton-MM apparatus. Advantages of this treatment method:
- direct bactericidal effect of ultrasonic vibrations with a frequency of 22-44 kHz;
- effective hydrodynamic rehabilitation;
- increasing the concentration of the drug at the site of inflammation;
- vibration and hydromassage in sonified tissues, stimulation of microcirculation, improvement of trophism and tissue metabolism.
This method is used as an additional method to the main treatment [2][4][6][9][11].
Surgical operations
Surgery is not required to treat vaginitis.
Diet for vaginitis
Nutrition does not have a significant effect on the course of vaginitis. When taking antibiotics, alcohol should be avoided.
Restoring and improving quality of life
If you follow the doctor's prescriptions, a complete cure and restoration of quality of life is possible.
Treatment of vaginitis during pregnancy
During pregnancy, careful monitoring of the microflora is necessary. This is due to the likelihood of infection spreading to the fetus and membranes, the threat of miscarriage and premature birth, miscarriage and pregnancy loss. The drugs are prescribed by the doctor individually depending on the test results and the timing of pregnancy.
How to treat vaginitis without potent drugs
Vaginitis caused by a bacterial infection cannot be cured without the use of antibiotics.
Is douching used for vaginitis?
Douching is not required to treat vaginitis.
How is a partner treated for vaginitis?
For specific vaginitis, the woman’s sexual partner is treated with antibacterial agents. For nonspecific vaginitis, the partner is not treated.
Traditional methods of treating vaginitis
The use of traditional medicine often not only does not lead to a cure, but also aggravates the situation.
Symptoms
At an early age, parents should periodically examine the child's skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs for rashes and irritation. The following symptoms indicate the development of the inflammatory process:
- redness in the groin area;
- whims of the child immediately after urination;
- yellowish-gray discharge.
Girls at an older age may independently complain of burning and itching in the area, purulent discharge and the presence of blood in the urine.
Treatment of vulvovaginitis
Treatment of vaginitis depends on the reasons that caused it.
If it is a helminthic infestation, then antihelminthic therapy is prescribed.
If there is severe unbearable itching in the perineal area, sedatives (calming) and antihistamines are prescribed.
If, during a laboratory examination, yeast-like fungi Candida are detected in a smear analysis, antifungal drugs are prescribed in the form of ointments and creams.
There is such a thing as specific vulvovaginitis, that is, vaginitis caused by pathogenic microorganisms (gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia). This disease requires the prescription of antibiotics, possibly the prescription of vaginal sticks and ointments.
In addition to drug therapy aimed at destroying the infectious agent, it is worth noting that the treatment complex necessarily includes vitamins in the form of synthetic forms or products enriched with vitamins (fruits, vegetables, legumes). And, of course, the disease is considered cured when the vaginal microbiocenosis is restored.
Restoration of microflora is carried out by taking probiotics (1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th generations), prebiotics, eubiotics or fermented milk products
Therapeutic techniques
The choice of therapeutic technique depends on the causes of the lesion. If a foreign body is present in the vagina, it is first removed and then washed with antiseptic solutions.
Specific infections such as chlamydia and mycoplasma are treated with antibacterial drugs. It may be necessary to examine other family members to determine the presence of infections. When treating allergic vulvovaginitis, the contract with the allergen is terminated.
The most difficult thing to treat is the nonspecific type of vulvovaginitis, which is caused by opportunistic microflora. In most cases, this form of the disease is chronic. Its exacerbation can occur after acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis or flu. Therapy is carried out both local and general. Local treatment involves the use of rinsing solutions and special ointments. General – treatment of dermatological skin lesions and strengthening of the immune system.
Causes of vulvovaginitis
The question arises, where does it come from, this vaginitis, in a small child?
There are many reasons for vaginitis, but we will give the main ones:
- Allergic reaction
- Excessive efforts to wash the baby “to shine” - mothers wash away the natural protection of the vagina.
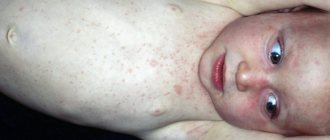
- Viral infections (ARVI, rubella, chicken pox and many others), when the virus spreads through the blood and lymph throughout the girl’s body, including the vagina. But it is worth noting that in such cases, vaginitis does not require treatment as such, since eliminating the cause itself, that is, the viral infection, will also lead to the disappearance of the symptoms of vaginitis.
- Vaginitis often occurs as a result of swimming in pools with chlorinated water. In this case, chlorine acts as an irritant, and irritation appears in the genital area. This condition is not observed in all girls, but only in those who have a reaction to chlorine, so you should not prohibit your child from visiting the pool due to this.
- Sea, public beaches, where there are a huge number of people per square meter
- A foreign body in a girl’s vagina (a bead, a small toy, a string).
- Also, the reasons for the development of vaginitis in girls are decreased immunity and endocrine diseases.
Vulvovaginitis in children is divided into specific, caused by an infectious agent - Trichomonas, chlamydia, tubercle bacilli and others, and nonspecific, caused by viruses, yeast-like fungi and other agents that are opportunistic, that is, causing the development of infection under certain conditions.
Preventive actions
Parents should be involved in the prevention of vulvovaginitis in little girls. It is important to clean the external genitalia regularly and thoroughly. Girls should be taught to take daily hygiene measures. You can use baby soap several times a week when washing.
Linen should be made only from high-quality and natural materials. Synthetics do not allow moisture to pass through, which creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Vulvovaginitis is a disease of the mucous membrane of the genital organs, which manifests itself through inflammation. If all hygiene standards are observed, such a disease can be avoided.
Vulvovaginitis in girls
About the article
42025
0
Regular issues of “RMZh” No. 3 dated 02/04/1999 p. 5
Category: Pediatrics
Author: Bogdanova E.A.
For quotation:
Bogdanova E.A. Vulvovaginitis in girls. RMJ. 1999;3:5.
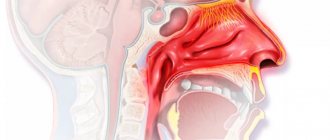
The inflammatory process in the area of the vulva and vagina (vulvovaginitis - VV) is more often observed in girls of preschool age. The diseases account for 60–70% of the structure of gynecological morbidity in girls.
This is due to certain physiological characteristics of the mucous membrane of the children's vagina and vulva associated with low levels of estrogen in the blood. The flat epithelium of the mucous membrane of these organs consists of a small number of layers, its cells do not reach full maturity, do not become keratinized, and do not contain glycogen, therefore, in the vaginal discharge of a girl there are no conditions for the existence of a lactic acid fermentation rod, which creates an acidic environment in the vagina of an adult woman. The vagina of a prepubescent girl has an alkaline reaction and most often a coccal flora, consisting of opportunistic microorganisms. A decrease in the child’s body’s defenses after an illness or in case of insufficiency of the immune system can lead to an imbalance between the vaginal microflora and the body. In the case of a significant decrease in the body's defenses, the opportunistic flora exhibits pathogenic properties. Pathogenic flora from the oropharynx, nasopharynx, intestines, and skin may become active and penetrate into the vagina. On the other hand, with childhood viral infections, rashes can be observed not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina, causing burning, itching and vaginal discharge, especially during peeling. Clinical picture of VV
in girls: vaginal discharge, hyperemia of the skin of the perineum, vulvar mucosa, there may be rashes on the mucous membrane and skin of the labia, traces of scratching, thickening of the anal folds.
In vaginal smears, the number of leukocytes exceeds 30 in the field of view, and an abundance of flora is noted. Bacterial VV
Bacterial (nonspecific) VV can begin acutely or have a torpid course with or without periods of exacerbation.
With bacterial VV, there is hyperemia of the vulva, perineal skin, labia, and moderate yellowish vaginal discharge. There may be elements of pyoderma on the skin of the thighs and around the labia, and areas of hyperemia on the walls of the vagina. After vaginoscopy and taking smears, it is advisable to rinse the vagina with a weakly disinfecting solution (potassium permangonate, rivanol, chlorhexidine, etc.) or simply saline, insert a suppository with sulfanilamide or a broad-spectrum antibiotic, and lubricate the skin of the labia and perineum with zinc ointment or (if pyoderma) with mercury ointment. Such treatment can be carried out daily until the results of microbiological and immunological studies are obtained. Even before the final results of the study are obtained, therapy may have a positive effect. At the same time, it is necessary to carry out sanitation of foci of chronic infection, treatment of skin diseases and antiallergic therapy. After obtaining laboratory data, the diagnosis and treatment regimen are clarified. Vaginal procedures are carried out daily for 7 - 10 days, then switch to hygienic baths. General restorative therapy should be longer and combined with hardening activities and physical education. VV due to enterobiasis
We are talking about an inflammatory process, usually caused by the introduction of intestinal flora into the vagina.
The causative agent of VV is Escherichia coli or Enterococcus. A symbiosis of these two microorganisms is often observed. A thorough interview with parents helps clarify the diagnosis. Parents note the child's restless sleep, his complaints of itching of the skin of the perineum and external genitalia. Sometimes the child wakes up crying and screaming from pain in the external genital area. Attentive parents may see pinworms on the skin or in the child’s stool. When examining the genital organs, attention is drawn to thickening of the anal folds, their hyperemia, and traces of scratching around the anus. In cultures of vaginal discharge, E. coli, enterococcus and other types of intestinal flora are found. In such cases, it is advisable to take a scraping from the perianal folds for pinworm eggs. Treatment.
Daily rinsing of the vagina for 7 days, toileting the external genitalia and anal area and administering suppositories with kanamycin or another antibiotic to which the pathogenic flora is sensitive.
At the same time, it is necessary to carry out therapy for enterobiasis. For this purpose, pyrantel
or other drugs that destroy pinworms are prescribed.
The effect of these drugs is based on blocking the nerve endings of the parasite; they do not affect the human body. These medications are prescribed at the rate of 10 mg per 1 kg of child’s body weight, i.e. A single dose of 250 mg tablet is sufficient to treat a girl weighing up to 25 kg inclusive. Treatment must be repeated after 1 month. Parents should pay attention to defects in the child’s hygiene, to the possibility of enterobiasis affecting the entire family (and therefore, we strongly recommend treatment of enterobiasis to all family members), as well as to the daily toileting of the child’s external genitalia. VV due to a foreign body
Parents of girls with VV due to a foreign body in the vagina complain of bloody-purulent profuse discharge.
Heavy discharge leads to maceration of the perineal skin and pyoderma. Rectoabdominal examination and vaginoscopy can detect the foreign body of the vagina, usually surrounded by disintegrating granulations. Characteristic is an increase in discharge during the study due to a violation of the integrity of the granulations and trauma by their dense foreign body during palpation. Vaginoscopy or examination in children's vaginal speculum is very important to clarify the diagnosis and conduct a differential diagnosis with pampiniform sarcoma of the vagina, which is usually observed in girls 2 to 4 years old and can manifest as bloody-purulent discharge. However, with this severe malignant disease, grape-like growths are visible in the vagina, the decay of which causes bloody discharge. Treatment
is removal of the foreign body.
In many cases, a foreign body can be removed with a finger inserted into the rectal ampulla. Gently pushing an object palpated in the vagina with your fingertip often allows you to move the foreign body to the entrance to the vagina, where it becomes more accessible and can be grabbed with a clamp, crushed or bent (if it is large) and removed. It should be remembered that objects such as hairpins and hairpins can be deeply embedded in the vaginal wall and can be quite difficult to remove. Grains of sand, pieces of cotton wool and fabric can be washed with a stream of liquid under pressure. A rubber catheter is inserted into the vagina, onto the end of which a 20 mm3 syringe is placed. A weakly disinfecting liquid or saline solution is poured into a syringe and injected into the vagina with pressure from the syringe. In this case, it is useful to slightly move the tip of the catheter inserted into the vagina so that the flow of fluid enters all its parts. A foreign body may be carried away with the flow of fluid. After removing the foreign body, the vagina is washed with a disinfectant solution (for example, a solution of potassium permanganate). Toileting the vagina for 2 - 3 days usually leads to a cure for the inflammatory process. Atopic EVs
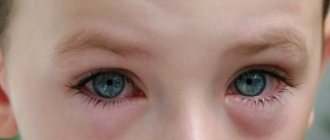
Atopic EVs are observed in girls with exudative diathesis and allergic manifestations.
They may experience a sluggish, sometimes subsiding, sometimes worsening inflammatory process. When examining the genital organs, scanty leucorrhoea, thinning of the mucous membrane, “dryness,” and focal hyperemia of the vulva are noted. A variety of flora is detected in the vagina, often opportunistic. To assess the presence of an anaphylactic reaction, Ionov and K.M. Glukhov determines the spontaneous degranulation of peripheral blood basophils and the number of mast cells in the vaginal wash. The detection of spontaneous degranulation of peripheral blood basophils over 14% and two mast cells or more in smears from vaginal lavage confirms the presence of atopic EV. Treatment.
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate contact with the allergen, adjust the diet, and eliminate foods that cause diathesis.
Antihistamines are prescribed (for example, diazolin 1 tablet 2 - 3 times a day, clemastine 1 tablet 2 times a day, ketoprofen 0.5 tablets 3 times a day). Local treatment includes baths of medicinal herbs (chamomile, oak bark, etc.), application of ointments (with zinc, bismuth) to the external genital area with the addition of antihistamines and small amounts of estrogens. Clinical manifestations and treatment of mycotic and trichomonas IVs
in girls are similar to those in adult women.
In recent years, new causative agents of inflammatory processes in the vulva and vagina in girls have been identified. These are chlamydia, myco- and ureaplasma, genital herpes virus types I and II. All these pathogens are transmitted sexually or from the mother during childbirth. Chlamydia VV
is characterized by a long course, and inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyes and joints is often detected simultaneously in girls.
The pathogen is detected by immunological methods and by examining cells from vaginal smears for the presence of chlamydia. Antibiotics (macrolides), interferon in suppositories, and eubiotics are prescribed. Genital herpes
manifests itself as ulcerative rashes on the mucous membrane and skin of the labia.
Patients complain of burning and pain in the genital area. Ulcers heal within 2 - 4 weeks. The disease is characterized by a persistent course with repeated ulcerative eruptions. Treatment is acyclovir. Another type of viral infection of the genital organs is human papillomavirus infection
.
It causes the formation of papillomas on the skin and mucous membranes. Treatment is removal of papillomas with an electric knife, laser or by freezing (cryodestruction). The personal hygiene of the girl and hygiene in the family are very important, as well as timely and complete treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs in spouses. All this is an effective measure to preserve the health of children. Content is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share the article on social networks
Recommend the article to your colleagues