Viral conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane that connects the eyes and eyelids. The pathology occurs against the background of colds: acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, pharyngitis, laryngitis and other diseases affecting mainly the respiratory system.
This form of conjunctivitis often occurs in preschool children. Their immunity has not yet been formed, which is why children easily become infected with viral infections, which cause complications, including in the eyes. One of these complications is conjunctivitis, which occurs during or after infection.
Share
Tweet
Share
Cool
Send
The essence of pathology
This disease affects the conjunctiva, a thin transparent tissue that lines the visible part of the sclera and the inner surface of the eyelid. This causes the small blood vessels in the area to become inflamed, enlarged, and more visible.
Incubation period
In newborn children, the immune system is very weak, so symptoms of the disease appear 4-8 hours after contact with a carrier of the infection. In older children, from 2 to 7 years old, the first signs appear after 2-3 days. The duration of the incubation period is individual, depending on the age of the child and the ability of his body to resist infections.
Is the pathology contagious or not?
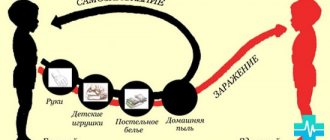
Viral conjunctivitis is highly contagious. This means that the disease is highly contagious. The pathology is transmitted by airborne droplets or household contact. If a child attends a kindergarten where half of the children suffer from viral conjunctivitis, he is likely to become infected from them.
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in children
Therapy for a viral eye infection involves not only treating and restoring the mucous surfaces of the visual organ, but also boosting the child’s immunity in order to, if possible, protect him in the future.
Herpetic species
The doctor prescribes ointments and drops with antiviral, anti-inflammatory, interferon action.
The affected skin of the eyelids on the outer surface can be treated with brilliant green. To combat the herpes virus, the doctor will prescribe one of the ointments: Zovirax, Tebrofen ointment, Bonafton. A small amount of the substance must be placed under the lower eyelid. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe Valacyclovir, Acyclovir.
In the future, to develop immunity in a child, it is necessary to use antibiotics. For example, erythromycin or tetracycline ointments are suitable for this purpose.
Adenoviral species
During treatment, antiviral agents are prescribed. Drops used: Oftalmoferon, Poludan, Aktipol. They not only have an antiviral effect, but also regenerate tissue. Tebrofenovaya, florenal, bonaftone ointments are also used for adenoviral conjunctivitis.
Eye disease and subsequent recovery are often accompanied by dryness and discomfort. To reduce them, ophthalmologists prescribe drugs that act as tear substitutes.
Epidemiological species
First of all, with such a disease, it is important to isolate sick children and maintain personal hygiene.
The child's eyes need to be treated with disinfectant solutions several times a day. After this, a solution of interferon and deoxyribonuclease is injected dropwise into the conjunctiva 6-8 times a day in the acute phase, 2-3 times thereafter. The course of treatment is at least two weeks.
Classification
The causes and symptoms of conjunctivitis depend on its type. Below are the forms of this disease.
Adenoviral
This form of the disease occurs in children of any age. An exception is infants in the first year of life who are breastfed. Such babies are protected by special antibodies found in mother's milk. The rest of the children attending school, sports section or kindergarten are at risk, since the disease is contagious.
The causative agent of this form of conjunctivitis is adenoviruses types 3, 4, 7. They are transmitted through conversation or physical contact with an infected person, as well as the use of his personal belongings. At first, the child shows signs of a cold; after 2-3 days, white filmy deposits form on the conjunctiva of his eyelids and transitional folds. A characteristic symptom is swelling of the eyelids, which is easily palpable and soft to the touch.
Signs and classification of viral type of conjunctivitis
The following general symptoms are observed during infection:
- pain in the eyes (especially in their corners);
- severe redness of the eye vessels;
- inflammation of the conjunctiva and its acquisition of a red tint;
- fear of light.
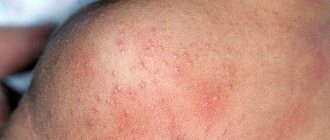
Photo of viral conjunctivitis in a child
More often, the disease initially affects only one eye, and only then the viruses penetrate the second.
There are several types of infection, each of which is characterized by a specific course.
| Type of disease | Typical symptoms |
| Adenoviral | Previously, a respiratory infection occurs that affects the throat. The child's temperature rises and the lymph nodes in the preauricular area become enlarged. Involuntary spasms of the eyelid are possible. Small transparent discharge from the eyes is characteristic. Films and bubbles may form on the conjunctiva. |
| Enterovirus and herpetic | The child's eyes hurt badly. Hemorrhages are observed in their individual areas or throughout the entire membrane. The white turns red. Body temperature rises, cough and sore throat are noted. Mostly symptoms are observed only in one eye, but with a long course the infection can spread to the second eye. |
| Epidemic | It is characterized by a long incubation period (up to 9-12 days). Symptoms may disappear after a week even without treatment, but then reappear. When there is an infection, the child is bothered by lacrimation. There is a feeling of a foreign object in the eye. |
Acute viral conjunctivitis is marked by redness of the eyes. A clear liquid is released from them abundantly. Swelling of the eyelids is possible, and there is often a high body temperature.
The chronic form of infection is sluggish. The child constantly experiences itching and burning in the eyes. For a long time he feels the presence of a foreign body in both eyes.
Differences between viral and bacterial conjunctivitis
Before starting therapy, the doctor needs to find out whether the child has a viral or bacterial type of disease. There are many criteria for distinguishing one form of infection from another.
| Criterion for distinguishing diseases | Viral | Bacterial |
| Course of the disease | Slow, gradual | Fast-paced and intense |
| Presence of purulent discharge | As a rule, they are absent or insignificant. More often than not, clear fluid is released from the eyes. | Pus is present in large quantities and has a yellowish tint. |
| Localization | More often it affects only one eye, less often it spreads to the second. | The infection usually affects both eyes. |
The difference between viral conjunctivitis and bacterial conjunctivitis in a child also lies in the degree of redness of the eyes. With a viral infection, the sclera becomes very red; with a bacterial infection, hemorrhages occur rarely and are point-like.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of the disease include:
- burning, itching and lacrimation;
- swelling and redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes and eyelids;
- mucous discharge;
- sensation of a foreign body or sand;
- photophobia;
- inability to open eyes due to dried mucous discharge.
Specific symptoms depend on the form of the disease.
Prevention
Prevention consists of children observing the rules of personal hygiene and using individual care items. When the first signs of infection appear, the baby must be protected from other people and provided with quality care. Timely treatment starts to avoid complications.
During the winter season, it is recommended to ventilate the room more often and humidify the air.
Sometimes viral conjunctivitis occurs in newborns against the background of other infectious diseases. During passage through the birth canal, the child can become infected with urogenital infections that the mother suffers from. They often provoke inflammation of the conjunctiva. But high-quality antiseptic treatment of the birth canal makes it possible to avoid infectious diseases in the first days after birth.
Author of the article: Evgenia Yuryevna Medvezhova, specialist for the website glazalik.ru Share your experience and opinion in the comments.
Treatment
A child with a viral form of conjunctivitis cannot go to kindergarten or school. During treatment, he must be isolated from other children. Therapy is prescribed by a pediatrician or pediatric ophthalmologist. Self-medication can lead to unpleasant consequences in the form of complications.
What not to do?
When treating conjunctivitis, you should absolutely not apply compresses, tape or blindfold your eyes. This creates a favorable environment for the development of viruses and other microorganisms.
Drugs
Treatment of the disease is local: the doctor prescribes the use of drops and ointments aimed at eliminating microorganisms and relieving unpleasant symptoms.
Drops
Before instilling the product, wash your hands thoroughly and prepare cotton swabs. If you are treating an infant, place him on the changing table, gently pull down the lower eyelid and drop the product into the eye, then blot it with a cotton ball. Repeat the procedure with the second eye using a clean cotton swab.
Diagnostics
Most often, the disease is determined during a basic external examination of the patient by an ophthalmologist . A survey of mother and child is also used to establish a complete picture of the disease.
However, in some cases, a specialist may resort to taking a smear or scraping. Most often, this is done in order to establish the type of pathogen and prescribe more effective treatment.
In some cases, doctors resort to the following diagnostic methods:
- immunoenzyme research technique;
- cytological technique;
- immunofluorescence diagnostics.
If a child has a fever, rashes and severe pain in the eyes, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor for informed advice.
Don't want to wear glasses? – Learn about vision restoration using the Zhdanov method.
Timely treatment is the key to the absence of complications
Find out the causes of flashes in the eyes here.
Diagnosis of the disease.
It is not difficult to determine conjunctival disease. But this cannot be done based on characteristic symptoms alone, since it is important to diagnose the virus that caused the disease, therefore, in case of inflammation, a smear is taken from the conjunctival cavity.
The material obtained in this way is examined under a microscope. In addition, it is possible to do a culture and determine the degree of sensitivity to antibiotics.
Laboratory research can reveal, with a high degree of probability, the effectiveness or ineffectiveness of the therapy used, and develop the most appropriate tactics for further action.
Causes
The root cause of the occurrence and development of viral conjunctivitis in a child is a causative virus, which, penetrating the body, contributes to the appearance of inflammatory processes that affect the membranes of the eyes. The main causative agents of the disease are:
- adenovirus. Pathologies caused by this type of virus have a severe course, which is especially typical for young children;
- viruses that contribute to the development of acute respiratory viral infections can also provoke the occurrence of viral conjunctivitis;
- herpes virus;
- enteroviruses.
The main route of infection is airborne .
A predisposing factor is considered to be a decrease in the natural defenses of the child’s body, poor nutrition, lack of vitamins, a sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity, as well as the presence of chronic diseases that weaken the child’s body.
Read about the symptoms and treatment of cataracts in children here.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
This disease is also divided into several subtypes:
A type of infection that occurs through direct contact with the pathogen Neissera gonococcus. This is a gonococcal type of bacterial conjunctivitis.
Infection with this disease occurs during childbirth, usually if the mother suffers from gonorrhea, the child becomes infected with gonococcal conjunctivitis. Also, the cause may be a violation of hygiene rules when caring for the baby.
The disease appears on the 3rd day in the form of cyanosis of the eyelids, and a serous-bloody substance is released. More often observed in girls. It can develop into ulcers on the membrane of the eye, which can lead to its destruction. In this case, timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease is extremely important.
The disease, which is provoked by the Klebs-Leffler bacillus, is a diphtheria subspecies. The following symptoms are identified: loss of appetite, general weakness, headaches, enlarged lymph nodes. Then swelling of the eyelid and discoloration appear. The mucous membrane is pale in color and may become covered with a thin film, which may cause slight bleeding when removed.
In case of exposure to the pathogen diplobacillus Morax-Axenfeld, a diplobacillary type of conjunctivitis is isolated. Manifests itself in the form of discomfort, burning and pain in the eyes. The edges of the eyelids become thicker and redder, and small cracks may appear.
purulent discharge due to bacterial conjunctivitis
When exposed to the main causative agent of pneumococcus - pneumococcus. First, swelling of the eyelid appears, then small pinpoint hemorrhages form on the mucous membrane of the white of the eye. At subsequent stages of the disease, a film may form on the conjunctiva.
Symptoms and signs
After the virus enters the child’s body, an inflammatory process gradually develops .
However, during the incubation period, which is 4-12 days, this does not manifest itself in any way.
Over time, your baby may experience symptoms as:
- The appearance of specific vesicular formations on the mucous membrane of the eyelids.
- As a result of an increase in the eye capillaries and the occurrence of irritation, the child experiences dry eyes, itching, burning, and redness.
- In one eye, abundant discharge of purulent contents occurs, then this process can spread to the second eye.
- Enlarged lymph nodes located in the ear area, their pain on palpation.
- The child is afraid of bright light and feels the presence of a foreign body in the eye.
- The inflammatory process provokes clouding of the cornea of the eye, as a result of which the child may complain of decreased vision. In some cases, this situation persists for a long time after healing.
Recommendations for the treatment of farsightedness in children can be found on our website.
Reasons why it occurs
Usually this disease does not come from the outside, but is caused by the same infections that provoke acute respiratory diseases.
Important! Most often, when the upper respiratory tract is affected by herpes infections, the disease spreads to the eyes.
In most cases, bacterial diseases begin to develop against the background of a viral eye disease, so treatment is often accompanied by the use of antibiotics .
In children under six months of age, this eye disease can be caused by blockage of the tear duct . As a result, the membrane of the eye is not protected by the tear secretion secreted by these channels, and this leads to the spread of infection to the conjunctiva.
Foreign bodies, dust and dirt getting into the eyes can also be considered as a cause of infection . In 15% of cases, the disease is caused by such external factors.
Symptoms of the disease: how it manifests itself
Depending on the pathogen infection that provoked conjunctivitis, this disease may have different characteristic signs, but in most cases the common symptoms are :
- Profuse or moderate lacrimation .
- Swelling of the upper and lower eyelids , accompanied by redness.
- Redness of the conjunctiva itself.
- Feeling of itching and burning in the eyes.
- Discharge of clear purulent fluid (exudate), which causes the eyelids to stick together .
- Photophobia may occur , which manifests itself even when looking at not very bright light sources.
Sometimes the disease can become chronic .
In this case, most of the symptoms disappear, but severe itching, burning, and a constant desire to scratch the eyes remain ( which is absolutely forbidden to do, since rubbing the eyes leads to increased irritation ).
Depending on the state of the immune system, the age of the patient and the characteristics of the body, symptoms in children may be more or less pronounced, and some of them may be completely absent.
The infection usually affects one eye first, but within a few hours it spreads to the other..
Quick and effective treatment of the disease is possible only with the correct determination of the nature and its cause.
Is conjunctivitis dangerous?
The prevalence of conjunctivitis in groups of children has allowed the formation of a strong public opinion about the mild course of the disease. Indeed, in most cases, the disease is short-lived, since the immune system of a healthy child is able to cope with it quickly. Therefore, many begin to treat the baby on their own without consulting a doctor, trusting the experience of other parents.
This approach can cause complications and the development of dangerous ophthalmological diseases. With viral conjunctivitis in children, a bacterial infection often appears, which the baby brings into the eyes through his hands, experiencing itching, burning and other unpleasant symptoms and not receiving adequate help. A child with a strong immune system can quickly cope with the disease. If the protective functions of the baby’s body are weakened, the treatment will be long-term, even with the use of antiviral medicine. Among the dangerous complications of viral conjunctivitis are blepharitis, keratitis, phlegmon and other inflammatory processes affecting the cornea and the surface of the eyelids. Treatment of complications of conjunctivitis in children is long-term, more than one to two months.
Complications and consequences.
Conjunctivitis is a disease that can be easily and quickly treated if you notice it in time, do not neglect it and consult an ophthalmologist. It is much more difficult to get rid of an advanced disease and its consequences. Let's look at the main complications of conjunctivitis:
- Blepharitis is an eye infection associated with inflammation of the eyelids. Difficult to treat, affects vision impairment;
- Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea, which provokes the appearance of a cataract;
- Dry eye syndrome – decreased ability of the eye to produce tears;
- Hypopyon is a disease in which purulent growths appear in the lower part of the eye.
Conjunctivitis is a fairly common viral disease in children. With timely consultation with an ophthalmologist and proper care, the risk of complications is eliminated, and the baby will look at the world with healthy, wide-open eyes!