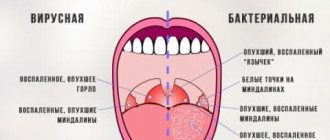
Adenoviral infection is one of the types of severe forms of ARVI, which affects the lymphatic system with all the accompanying symptoms . Even some medical workers cannot determine the disease by eye, so a general diagnosis is often made - an acute respiratory disease.
Symptoms and treatment of adenovirus infection in children according to Komarovsky involve the use of drugs to relieve signs of the disease, as well as the normalization of the baby’s daily routine, and careful monitoring of his condition.
Causes of the disease
This disease is a consequence of the entry into the body of an adenovirus that is highly resistant to environmental influences. Sowing the pathogen indoors requires its presence in the air for the next 4 weeks, the first two of which are the most dangerous.
The pathology is most severe in children under three years of age, but it can affect any age group of children.
There are predisposing factors that increase the baby’s risk of getting sick. Among them are:
- general, local hypothermia;
- decreased immunity;
- passive smoking;
- imbalance of vitamins and minerals in food;
- artificial feeding;
- other infectious diseases in acute and chronic form.
Of course, a child is most likely to catch an adenovirus in a group of peers, among whom there is an already sick child. At the same time, the chance that an immature body can independently cope with an infiltrated infection is only 10-15%.
It is transmitted, like any respiratory infection, through airborne droplets
. Fecal-oral and contact-household transmission of adenoviral disease is less common.
Clinic of the disease
The symptoms of the disease directly depend on the stage at which it occurs. There are mild, moderate and severe forms of adenovirus infection. On average, the incubation period ranges from 1 to 7 days
. At this stage, it is not yet possible to observe any signs of the disease, but the child can already infect the people around him.
Symptoms of adenovirus entering the body:
- a significant and sharp increase in body temperature up to 39-40 degrees;
- sore throat when talking or swallowing;
- cough;
- headache;
- breathing through the mouth, runny nose;
- tearfulness, drowsiness, lethargy - as signs of general intoxication;
- indigestion, but diarrhea should not be accompanied by pus or blood;
- In infants, high fever can provoke seizures.
At home, it is almost impossible to determine an adenovirus infection in a child, since these symptoms may indicate other pathologies in the body. To find out the root cause of their child’s poor health, parents must contact specialists.
Symptoms of infection
First of all, with the typical form of the disease, the child’s temperature rises to 38°-39°. It is difficult to bring it down with antipyretics. It can last up to 7 days.
There is a sore and sore throat and difficulty swallowing. The child does not eat well. Due to nasal congestion, he does not sleep well. Due to intoxication with waste products of the virus, he develops weakness and headache. Infants often develop seizures.
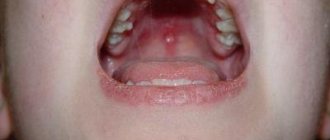
A runny nose occurs. At first, the mucus is abundant and transparent, then thickens and acquires a green tint. Purulent inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils occurs, and a white coating appears on them.
Due to damage to the intestinal mucosa and inflammation of its lymph nodes, the baby has a stomach ache, frequent loose stools mixed with mucus, and vomiting. This symptom most often occurs in children under 2 years of age.
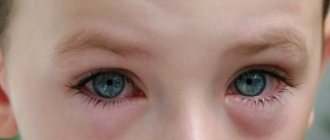
The patient is tormented by a lingering cough (at first it is dry, then becomes wet). On days 4-6 of the disease, the child may develop conjunctivitis. The eyes turn red and purulent discharge appears. There is pain and photophobia. Eyelids swell.
The baby becomes lethargic, pale, and his cervical lymph nodes become enlarged. Possible enlargement of the spleen and liver.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis in a child with similar symptoms, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician. He will conduct a survey and a thorough examination, and prescribe additional diagnostic methods.
This is necessary in order to differentiate viral infection from other pathologies.
What examinations are carried out:
- Survey
At this stage, parents must provide the doctor with complete information about their child’s medical history
. You should talk about where the child could have caught the virus, when it happened, how the disease manifests itself and how many days the symptoms last.
- Inspection
During the examination, the doctor notes lethargy and apathy in the baby, drowsiness. The skin is pale and there may be clammy sweat from fever. The disease is accompanied by profuse nasal discharge, which is clear or whitish in color. The pharynx is hyperemic and edematous. A gray coating is observed on the tonsils. A phonendoscope helps to listen to dry wheezing in the early stages of the disease and wet wheezing during the recovery period.
- Laboratory diagnostics
Analyzes of biological fluids should be studied in order to exclude complications of the disease. You will need to donate blood and urine for laboratory testing. The results will be standard for any type of ARVI. The presence of viruses in the body can be diagnosed by an increase in the number of lymphocytes and monocytes; leukocytes may be slightly reduced from normal. The nasopharynx area is also washed to detect secondary infections.
Treatment
Dr. Komarovsky’s main advice regarding the treatment of adenovirus infection is to provide suitable conditions for the sick baby. To make you feel better, you can use symptomatic medications, but only after examination by a specialist.
Parents should pay attention to the fact that most drugs are approved for use at 2-3 years of age. Therefore, you must carefully read the instructions before using medications.
Treatment of adenovirus infection:
- Eliminating a runny nose
At this stage, you can use rinsing or instillation, depending on what the child tolerates better. From infancy, it is allowed to use drops containing sea salt. For example, Aquamaris, Aqualor. Some of them have a vasoconstrictor effect and stop a runny nose in a short time, for example, Snoop (used no earlier than two years of age). This group of medications should be used for no more than a few days, as local dysbiosis and addiction develop.
- Elimination of relevant symptoms
The temperature should be brought down if it rises above 38.5 degrees for 3 days. If there is no improvement within this period and the child continues to have a fever, it is necessary to consult a doctor again. Paracetamol or Nurofen are most often used for children. These substances, in addition to antipyretic, have an analgesic effect. These drugs can be found on pharmacy counters in the form of sweet emulsions, so taking the medicine will not be difficult.
- Additional measures
The children's room must be ventilated at least 3 times a day, and wet cleaning must also be carried out. In addition, you should provide the child with plenty of warm drinks and try to maintain bed rest.
. If the baby is sick, the mother must ensure uninterrupted access to breast milk.
How to treat: what E. Komarovsky says
E. Komarovsky’s opinion regarding this virus is that adenovirus infection can be treated without medications.
The main thing is to create favorable conditions for the body to begin an independent fight against the virus. The patient's room should have at least 50% humidity and be cool enough, not higher than 20℃. To do this, it is advisable to have a humidifier, but you can hang wet towels in the room. The patient should be dressed warmly and not allowed to become overcooled. Bed rest and a minimum of physical activity are required.
The doctor places special emphasis on drinking regimen. A sick person must drink in sufficient quantities. All liquid to drink should be warm. Ordinary clean water, homemade fruit drinks and compotes, and weak tea are better suited.
On a note! Feeding is not necessary unless he asks. Food should be light and soft so as not to further injure the throat.
Dr. Komarovsky advises to bring down the temperature only if it is above 38.5℃. Elevated body temperature promotes the production of its own interferons, which kill the virus. The exception would be children prone to seizures.
The doctor advises paying special attention to infants, because... they are more likely to experience complications
To make breathing easier, E. Komarovsky advises using saline solutions, and in extreme cases, drops and sprays with a vasoconstrictor effect.
Prevention
Regarding the prevention of adenovirus infection, Komarovsky also gives quite clear recommendations. To avoid the virus entering the body, it is necessary to avoid visiting establishments where there are large crowds of people. Especially in the off-season. Other measures are secondary.
Parents should strengthen the child’s immunity in every possible way and balance his diet. A mother makes a huge contribution to the baby’s health by providing him with breastfeeding at least in the first year of life.
If all the rules are followed, the infection can also enter the body without leaving any serious consequences for health.
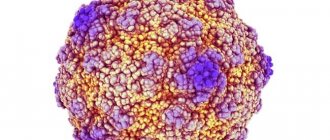
Adenovirus belongs to the group of DNA-containing microorganisms. This means that the pathogen is resistant to environmental influences. At room temperature, the adenovirus persists for about half a month. All dangerous properties do not disappear after double freezing. The pathogen can be destroyed only by boiling or ultraviolet irradiation.
Adenoviral infection in children is a contagious disease that is transmitted both by airborne droplets and by contact: nutritional or fecal-oral (dirty hand disease). The source of infection is a sick person. The virus is found in nasal secretions and stool. Children become infected because they do not always wash their hands, and when swimming in open water they swallow water. Patients shed viruses 3-4 weeks after infection.
In kindergartens and schools, the infectious disease is transmitted mainly by airborne droplets. In a closed room, adenoviruses accumulate and are deposited on toys, notebooks, and textbooks.
After infection, the child does not experience any health problems for 3-12 days, although he poses a danger to surrounding children.
Most often, adenoviral infection in children develops between the ages of six months and three years. When a child is breastfed, the risk of infection is low due to the immunoglobulins contained in mother's milk. Antibodies are produced to the adenovirus, which provide immune protection for 5-8 years. But immunity is type-specific. That is, a person receives protection only from the type of virus that caused the disease. And today there are about fifty of these species. Therefore, adenovirus infection of breastfed children develops with a fifty-fifty probability, because no more than two types of the pathogen “live” in one geographic region.
What kind of infection is this and why does it occur?
Adenoviral infection is a type of acute respiratory viral infection
An adenovirus is a DNA-containing virus that is quite stable in the external environment. This is an important feature that predisposes to long-term recurrent cases. Viral bodies can live on objects and in the air for 2 weeks.
If a room is poorly ventilated, but viruses from sick people constantly enter it, then a permanent reservoir of infection is created in it. If there are often sick and healthy children in the room (a group in a kindergarten, a class in a school), infection occurs, and isolating the patient is not enough.
The main routes of transmission of the virus are airborne droplets and fecal-oral (with food, water, dirty hands). The source of infection is a sick person. The virus can also be contained on things used by the patient, dishes, clothes, toys, hygiene items, and in the surrounding air. Animals are not the source of the virus, but it can survive on their fur. Both adults and children get sick.
If no measures are taken, the virus can live quietly on environmental objects for up to 2 weeks. Important cleaning, freezing and boiling do not save from the virus - it survives in boiling water for 30 minutes, and tolerates freezing, retaining its pathogenic properties. The most effective means against adenovirus are ultraviolet irradiation, an autoclave and disinfectants. Ventilation helps to avoid the accumulation of the virus in the room and the creation of a self-sustaining source of infection.
What are the symptoms in children?
The infection has different clinical manifestations
The virus causes a huge variety of manifestations. The most common symptom complex resembles ARVI and is manifested by a runny nose, cough, and a slight increase in temperature. Redness of the eyes, watery eyes and sluggish development of the disease can be used to suspect an adenovirus. Also, adenovirus is characterized by a cyclical, “endless” course of the disease, especially if parents neglect to ventilate the child’s room for fear of aggravating his condition.
The prodromal period is not typical - the disease immediately begins with a high fever and signs of a runny nose. General malaise and headache occur. It is difficult for a child to concentrate on any task, this is especially noticeable among schoolchildren whose academic performance drops sharply during illness. Younger children become capricious during illness, cannot eat, and sleep poorly.
The most severe manifestations are observed in the nasal area - abundant, thick discharge appears, making nasal breathing so difficult that the baby cannot breathe through his nose. When examining the throat, enlarged tonsils and a reddened posterior wall of the pharynx are visible.
Intestinal symptoms occur in about half of the cases, which is why adenovirus infection can be confused with intestinal flu. Abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence, diarrhea and vomiting appear. The baby's appetite disappears, and after eating, intestinal symptoms intensify.
Can it cause complications?
The infection can spread to the lower respiratory tract and cause pneumonia
Adenoviral infection occurs over a long period of time and cyclically, which leads to a decrease in local immunity. Like all viral infections, adenovirus negatively affects the immune system and causes a significant decrease in not only local, but also general protective mechanisms.
Therefore, the most common complication is secondary bacterial infections:
- Purulent pharyngitis
- Purulent sore throat
- Tracheitis and bronchitis
- Pneumonia
- Otitis media
- Bacterial conjunctivitis
- Purulent sinusitis
Among these, the most dangerous complication is pneumonia, which can become hemorrhagic in nature - hemorrhages appear in the lungs, which impede gas exchange in the lungs.
The virus is not the main cause of these complications, but creates favorable conditions for them. For the same reason, infectious complications may appear in those organs that have not been exposed to the virus - skin infections; in adolescents - an imbalance in the microflora of the genital tract.
Eye damage that lasts for a long time can lead to disruption of the transparency of the cornea - the formation of foci of cloudiness or a cataract that completely covers the eye. If this pathology is not corrected surgically in time, permanent blindness will develop in the affected eye, which cannot be corrected by any methods. Penetration of infection into the internal environment of the eye leads to the development of disturbances in the outflow of intraocular fluid and changes in the transparency of the lens (cataract).
Adenoviral infection in children, symptoms
Despite the fact that adenovirus can cause diseases that are completely different in localization, today only two main infection syndromes are known:
- Acute respiratory distress;
- Pharyngoconjunctival fever.
In the first form of adenoviral infection in children, the symptoms are similar to influenza, but differ in the severity of the course and the possibility of the addition of bacterial flora. The course of the acute respiratory disease type is characterized by general and local manifestations. Common symptoms include the following:
- Slow onset of the disease: lethargy, malaise, lack of appetite;
- Chills alternating with a feverish state.
Local manifestations are localized in the area of the “entrance gate”:
- Nasal congestion;
- Runny nose;
- Redness and swelling of the tonsils;
- Coughing.
With adenovirus infection in children, which occurs as pharyngoconjunctivitis, the body temperature first rises: from 38 to 40°C. This condition lasts for two to five days. At the same time, inflammatory changes occur at the level of the pharynx (pharyngitis) and eyes (conjunctivitis). The child's eyes become reddened, and a thin film forms on their surface. As a rule, one eye is affected first, and then the second.
Causes of the disease
What causes parvovirus infection in children? Its causative agent is virus B 19. It is also believed that certain physiological reasons play an important role in the occurrence of parvovirus infection in children. Among them:
- burns; - expansion of capillaries; - outdoor games; — diseases of internal organs; - impact or squeezing of the skin.
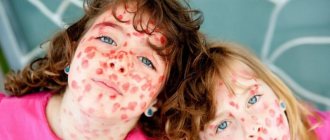
Parvovirus infection in children can have symptoms very similar to other illnesses. Treatment, based on external signs, is often prescribed for scarlet fever, measles or rubella.
The first distinctive signs of infectious eczema are similar to viral diseases (flu, colds). The child develops a fever, as well as redness of the skin in the cheek area. The body is covered with a rash. After the virus has had its effect on the baby’s body, within two days you can observe:
- chills, accompanied by sudden changes in temperature up to 39 degrees:
- pain in the abdomen and head;
- general malaise;
- red rash.
- pain in the joints and throat;
- runny nose.
Complications of adenovirus infection
Viral infection in young children is prone to generalization. The adenovirus enters the respiratory tract and causes pneumonia. Otherwise, it is called hemorrhagic, because when blood vessels are destroyed, blood accumulates in the alveoli, making breathing difficult.
With adenovirus infection in children caused by type No. 8, damage to the cornea of the eyes occurs, which can provoke the formation of cataracts.
During illness, children under one year of age often suffer from intestinal disorders. When the adenovirus is localized in the lymph nodes of the mesentery, mesoenteritis develops, the symptoms of which are similar to acute appendicitis.
Treatment of adenovirus infection in children
There is currently no specific therapy. Antiviral drugs do not have the desired effect. Adenoviruses are also not sensitive to any antibiotics or sulfa drugs. However, taking into account the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the child’s body, doctors prescribe antibacterial drugs, since the treatment of adenovirus infection in children is carried out not to destroy the virus, but to prevent serious complications.
Sick children are prescribed bed rest for a week. The diet provides sufficient amounts of protein and fluid. At high temperatures, antipyretics are prescribed. If shortness of breath occurs, the child is given desensitizing medications to prevent status asthmaticus.
To prevent pneumonia due to adenoviral infection in children, distractive treatment is carried out: they put mustard plasters on, use a UV lamp.
Pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky is engaged in popularization activities with parents, convincing them that viral diseases do not require any special treatment methods, which are used by relatives without a doctor’s prescription.
To treat adenovirus infection in children, Komarovsky proposes to create conditions under which it becomes impossible for the virus to multiply. Consequently, the symptoms of the disease are smoothed out until they disappear completely.
This requires little:
- Ventilation of the room;
- Warm clothes;
- Increased air humidity;
- Drink plenty of fluids.
For persistent runny nose, vasoconstrictors will do more good than harm. According to Dr. Komarovsky, a sick child should breathe through his nose! No other medications are required without a doctor's prescription.
Adenoviral infection in children is an acute respiratory disease, which is one of the types of acute respiratory viral infections, belonging to the group of seasonal catarrhs and characterized by damage to lymphoid tissue, the connective membrane (conjunctiva) of the eyes and the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
The share of this infection in the general etiological structure of ARVI accounts for at least 20%. According to statistics, up to 25–30% of all registered cases of virus infection in young children between influenza epidemics are due to adenovirus infection. Babies from 6 months to 3 years of age are most susceptible to the type of virus that causes a similar inflammatory process.
In the first months of life, children have passive transplacental immunity, transmitted from the mother, so they are not susceptible to infection. Adenovirus infection in preschool children is diagnosed during epidemiological outbreaks or year-round. It is difficult to find a child who has not suffered from such an illness: often all children have been treated for adenovirus infection at least once, or even several times.
Prevention of complications
Prevention of complications of ARVI is that you need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Many people make the same mistake: the child feels better after the fever subsides and is allowed to get out of bed
But with influenza and parainfluenza, it is very important to maintain bed rest. It is advisable to avoid any stress
Even reading requires a certain amount of effort. Failure to comply with bed rest and stress on the body can lead to complications from the musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular system and kidneys.
Prevention of complications also includes proper nutrition. If in the first days the child does not want to eat, there is no need to insist. But after 3-4 days you can already prepare something light for him.
It is important that he drinks as much fluid as possible
Etiology
To date, from 32 to 57 serotypes of viruses of the Adenoviridae family are known from various sources. The causative agents of the disease in preschool children are 1, 2, 5 or 6 serological types, in adults - 3, 4, 7, 8, 14 or 21 serological types. Conjunctivitis and pharyngoconjunctival fever are caused mainly by virus serovars 3, 4 or 7.
Adenovirus variants with a diameter of 70 to 90 nm have double-stranded DNA and three antigens: A-antigen, B-antigen and C-antigen. They have increased resistance to environmental influences: they remain viable for up to two weeks under normal conditions; They tolerate drying and freezing well, are insensitive to the effects of antibiotics, but die from boiling, exposure to chlorine-containing agents and UV rays.
Parvovirus B19 - infection (B34.3)
Parvovirus B19 replicates in erythroblasts and is transmitted through respiratory secretions, contact and blood. Patients are contagious before the appearance of the rash, with aplastic crises - for at least a week after the crisis. Incubation - 4-21 days.
Drug sensitivity. There are no specific means.
Clinical manifestations. The infection (“Fifth Disease”) occurs with a slight disturbance of the condition, low temperature, sometimes with arthralgia and a characteristic rash (Table 7.1), which fades and flares up with changes in air temperature. It causes crises in patients with aplastic anemia, and anemia in people with immunodeficiency.
Parvovirus B19 causes embryo- and fetopathy in pregnant women - both miscarriages (about 10%) and the development of hydrops fetalis.
Diagnostic tests. IgM antibodies appear from the 1st day of the rash and from the 3rd day of aplastic crisis, they persist for 2-4 months. IgG antibodies appear from the 7th day of the rash and remain for life. It is possible to detect viral DNA using PCR. With fetopathy, the level of alpha-fetoprotein in the blood of a pregnant woman increases.
Treatment is symptomatic, for immunodeficiency - intravenous immunoglobulin
Pathogenesis
Routes of infection:
- Airborne. Characteristic of the early period of the disease, when the patient secretes pathogens with nasopharyngeal mucus.
- Fecal-oral. Possible in the late period, when adenoviruses are excreted in feces.
- Water. Infection of a child occurs through water, which is why another name for the disease is swimming pool disease.
The source of infection is an adult or child who has an acute infection and releases pathogens into the environment, as well as virus carriers - people with an erased form of the disease or who are asymptomatic.
After treatment, type-specific immunity is formed, so re-infection is possible, but with other serological types of adenovirus.
The adenovirus enters the body through the conjunctiva, intestinal mucosa or respiratory system. Having reached the lymphoid formations of the intestine, epithelial cells, lymph nodes, the pathogens begin their reproduction, synthesizing viral DNA in the nuclei of the affected cells and leading to the cessation of their division and death. After 16–20 hours, mature particles of new adenoviruses are formed.
The incubation period ends with the development of viremia, caused by the release of viruses from dead cells, entering the bloodstream and spreading throughout the body. As a result, the mucous membranes of the pharynx, nose, thin connective membrane of the eyes, and tonsils are affected. Inflammation leads to swelling of the mucous membranes, redness, pain, and the release of copious serous exudate.
Once in the lungs and bronchi, adenoviruses actively multiply in the mucous membranes of the alveoli and the bronchi themselves, provoking the formation of necrotizing bronchitis or viral pneumonia. Inflammatory processes of the bronchopulmonary system are caused by a combined infection: bacteria are often associated with viruses. The infection can affect the intestines, spleen, kidneys, and liver. In rare cases, the brain is affected and swelling develops, leading to the death of a small patient.
Symptoms of adenovirus infection in children
Signs of the disease appear sequentially after an incubation period lasting up to 12 days, usually no more than a week. Adenoviral infection can manifest itself as one of the following syndromes:
- Catarrh of the mucous membranes of the respiratory organs.
- Keratoconjunctivitis and acute conjunctivitis.
- Pharyngoconjunctival fever.
- Mesadenitis, or mesenteric lymphadenitis.
- Diarrheal syndrome.
Catarrh of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract
– the most common variant of this infection in children. Manifests itself in the form of laryngotracheobronchitis, tonsillopharyngitis, rhinopharyngitis. It is characterized by an acute onset with a rise in body temperature to 39.8–40 0C and moderate or mild symptoms of intoxication: loss of appetite, lethargy, moodiness, headache, joint and muscle pain.
Catarrhal changes appear along with fever. Difficulty in nasal breathing is accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane with discharge from the passages of first serous, then mucopurulent exudate. The pharyngeal mucosa is hyperemic and swollen, whitish pinpoint plaque forms on the tonsils, and the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged.
Pharyngoconjunctival fever
occurs against the background of inflammation of the tonsils, mucous membrane of the pharynx and eyes. Be protracted, sometimes wavy in nature. Often, a high or elevated temperature does not subside for 1–2 weeks. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged and easily palpable. Sometimes the child has an enlarged spleen or liver (moderate splenomegaly or hepatomegaly).
Keratoconjunctivitis and acute conjunctivitis
caused by inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyes. First one eye is involved in the process, then the inflammation spreads to the second. The child is worried about lacrimation, pain, pain in the eyes, and a sensation of a foreign body. He begins to avoid bright light.
Upon examination, a pediatric ophthalmologist detects swelling and moderate redness of the eyelids, granularity and hyperemia of the conjunctiva, and sometimes the appearance of a whitish-grayish film on it. Conjunctivitis can be catarrhal, membranous or follicular. At the beginning of the second week of the disease, the development of keratitis, characterized by corneal syndrome, is possible.
Mesadenitis
with inflammation of the mesenteric lymph nodes of a viral nature, it manifests itself as paroxysmal pain in the navel area or in the right lower abdomen, reminiscent of attacks of acute appendicitis. Accompanied by fever and vomiting.
Diarrheal syndrome
in children it is an independent manifestation of adenoviral infection or one of the signs of mesenteric lymphadenitis or catarrh. It is more often observed in children under one year of age with an intestinal form of infection. At the height of the disease, the frequency of bowel movements reaches 7-8 times. Mucus without blood is found in the stool.
Forms of infection:
- light;
- moderate severity;
- heavy;
- complicated;
- not complicated.
In severe cases of the disease, parenchymal organs are affected, and severe adenoviral pneumonia often develops, complicated by severe respiratory failure.
Other complications that develop with the addition of a secondary bacterial infection include the development of focal serous-desquamative pneumonia, otitis media, and sinusitis.
Types of disease
Experts distinguish three main forms of conjunctivitis depending on the source of the inflammatory process: viral, bacterial and allergic. Not only the method of treatment, but also the safety of others depends on correct diagnosis, since infectious forms of the disease are contagious to other people and quickly spread in groups.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
About 30% of cases of conjunctivitis are bacterial in nature and are caused by pathogenic microorganisms entering the mucous membrane of the eyes. The most common causative agents of infection on the organs of vision are:
- staphylococcus (in newborns and infants up to one year - Staphylococcus aureus);
- streptococcus;
- mycoplasma;
- chlamydia;
- Trichomonas.
Conjunctivitis caused by staphylococci
The bacterial form of conjunctivitis does not spread so quickly within a group, but is still contagious, therefore, when cases of the disease are detected, it is necessary to disinfect the room in which the patient was for a long time (school classroom, work office, group in a kindergarten), treat common objects and isolate the infected person.
You can distinguish a bacterial infection from a viral one by its characteristic symptoms. The main difference is the formation of thick yellow pus (with gonorrhea, green discharge may appear). In the morning, dense crusts form on the patient’s eyelids, which are dried purulent contents. They can be easily removed using a cotton swab moistened with boiled water or strong tea.
Pneumococcal conjunctivitis
Other symptoms of bacterial eye damage include general signs:
- itching and burning in the eyes;
- increased temperature (not found in all cases);
- weakness and general malaise;
- lacrimation.
The temperature with bacterial conjunctivitis can rise to 38 degrees, but about half of the cases of the disease occur against the background of normal or slightly elevated (to subfebrile values) body temperature.
Treatment of bacterial conjunctivae
Viral conjunctivitis
In the vast majority of cases, the disease is viral in nature and is caused by various groups of viruses: adenoviruses, enteroviruses, herpes virus, etc. The incubation period ranges from 3 to 12 days. During this period, the person is already infectious to others, but signs of the disease have not yet appeared. It is with the long incubation period that doctors associate the high rate of spread of viral conjunctivitis within groups.
The symptoms of the viral form of the disease differ from the bacterial type, so diagnosis usually does not cause difficulties. Signs of viral conjunctivitis include:
- clear discharge from the eyes;
- painful sensations in bright light;
- a feeling of heaviness and a feeling of “sand” in the eyes;
- redness of the eye sclera and white membranes;
- burning and tingling in the eyes;
- clouding of the cornea of the eye.
Treatment of viral conjunctivae
Diagnostics
Diagnostic criteria that serve as a basis for suspecting adenoviral infection:
- fever;
- polyadenitis;
- catarrh of the respiratory tract;
- signs of conjunctivitis;
- hyperplasia of pharyngeal lymphoid tissue;
- sequence of symptoms.
Positive laboratory results confirm that a disease caused by an adenovirus is developing in the body:
- immune electron microscopy (IEM);
- immunofluorescence reactions (RIF);
- enzyme immunoassay (ELISA);
- analysis for complement fixation reaction (CFR);
- determination of hemagglutination inhibition reaction (HAI);
- bacteriological culture of a scraping or smear from the conjunctiva;
- examination of a swab from the nose and throat for microflora.
Differential diagnosis of various forms of this disease is carried out with infectious mononucleosis, influenza, other types of acute respiratory viral infections, yersiniosis, mycoplasma respiratory infection, diphtheria of the eyes and pharynx.
Treatment of adenovirus infection in children
Hospitalization is required only for children with a severe course of the disease and serious complications. More often, treatment is carried out at home. A pediatrician called to your home helps you choose a therapy. Sometimes consultation with an infectious disease specialist, otolaryngologist or ophthalmologist is required.
Recovery is facilitated by bed rest, which is mandatory throughout the entire period of fever, plus the next 2-3 days after the temperature has returned to normal. The child is recommended to have a fortified diet with sufficient amounts of protein, as well as frequent drinking. Liquids in the form of jelly, fruit drink, dried fruit compotes, hot milk, herbal decoctions or infusions help remove toxins from the body - waste products of adenoviruses.
General etiotropic treatment is carried out with antiviral drugs (children's anaferon, arbidol, kagocel, ribavirin), taken according to the regimen. It is possible that the doctor may prescribe desensitizing agents (fenkarol, suprastin, tavegil) and one of the vitamin-mineral complexes (alphabet, multi-tabs, etc.) in an age-specific dosage.
Syndromic therapy consists of antipyretic (children's Panadol), mucolytic (lazolvan, broncholitin or ACC) drugs. Aggravation of adenoviral infection by bacterial complications requires the prescription of antibiotics.
Local treatment consists of intranasal application of oxaline ointment or cycloferon liniment, instillation of interferon into the nasal passages, inhalation with herbal infusions or soda solution after a decrease in temperature.
If the conjunctiva is affected, apply antiviral eye ointment, for example, acyclovir, behind the eyelid; instillation of eye drops, sodium sulfacyl solution or deoxyribonuclease, for example, into the conjunctival sac.
To reduce febrile temperature, wiping with an alcohol or vinegar solution is effective. The elbow and knee bends, the inner surfaces of the arms and thighs, as well as the sides of the neck are treated. This helps to avoid the use of antipyretic drugs or significantly reduce their frequency of administration and dose.
The prognosis for a disease that proceeds without complications is favorable. The child recovers in 10–14 days, with a mild form sooner.
Mortality among young children is observed in severe cases of the disease, aggravated by serious complications of a bacterial nature.
Komarovsky spoke about a dangerous intestinal infection for young children
In recent years, in the fall and winter, more and more people are faced with an unknown disease. In addition to the already familiar symptoms of a common cold (cough, runny nose, sore throat), all the signs of severe intestinal poisoning are added. People called the new disease the stomach flu.
But the famous pediatrician Evgeny Komarovsky believes that this is how norovirus infection manifests itself - a very serious disease, especially dangerous for young children. On his Instagram page, Evgeniy Olegovich spoke in detail about norovirus and gave answers to the 8 most frequently asked questions.
Where did norovirus come from?
It turns out that a viral intestinal infection was first identified in 1972 in the American city of Norfolk (Ohio). This is where the name of the disease comes from - norovirus. Over the course of several years, norovirus infection has literally spread throughout the world, causing not only outbreaks, but sometimes even entire epidemics.
How is norovirus transmitted?
Norovirus infection is considered highly contagious and is transmitted, as doctors say, by the fecal-oral route. Moreover, there can be three ways of infection:
- Water - through water from a water supply or open reservoirs.
- Food - through poorly washed fruits and vegetables.
- Contact - through dishes, bedding, toys and any other things with which a sick person has been in contact.
By the way, the sick person himself is contagious not only during the illness, but also for 2-12 days after recovery (depending on the severity of the infection).
Who is most likely to get norovirus?
According to doctors, all people are susceptible to norovirus infection, regardless of age, gender or place of residence. But the main risk group includes children (especially under 2 years of age), the elderly and those with a low level of immunity.
As a small consolation, doctors talk about an interesting observation: people with blood groups 3 and 4 suffer least from norovirus infection. But the owners of group 1 suffer first of all.
[adsp-pro-1]
Is it possible to get norovirus a second time?
Unfortunately, humans do not develop any immunity to norovirus. And in just a couple of months you can catch this dangerous infection again.
What are the symptoms of norovirus infection?
The incubation period for norovirus is very short – 1-3 days. After this, the disease immediately gains strength. The main symptom is painful nausea and incessant vomiting. In addition, the patient is worried about severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, muscle and headache, weakness, and drowsiness.
Literally immediately, the troubles with the gastrointestinal tract are accompanied by cold symptoms - fever, sore throat, runny nose, cough.
Well, it is clear that with such a “bouquet” the patient loses his appetite and sense of taste (if he can even cram any food into himself).
How is norovirus treated?
The fact is that most people have a mild form of norovirus infection (and this is good news). Therefore, symptomatic treatment is usually carried out, that is, if you have a headache, we take a painkiller, if you feel sick, you take an antiemetic, etc.
But, since norovirus causes the body to lose a lot of fluid, it must be replenished. The best option is to drink special pharmaceutical solutions - Regidron, Re-sol, Ionica and others.
The calcium and sodium salts they contain help with fluid retention and prevent dehydration.
And, in addition, more familiar drinks are also perfect - green or herbal tea, juices (preferably diluted), compote or berry jelly.
[adsp-pro-2]
And, nevertheless, if the patient is at risk or his condition does not improve, it is imperative to call a doctor. Because, unfortunately, sometimes norovirus can cause very serious complications (even death).
Do I need to follow a diet?
In no case should a person sick with norovirus be given foods that increase peristalsis or cause fermentation - any fresh fruits and vegetables, fresh bread, milk. Well, it’s clear that you’ll also have to temporarily abstain from smoked-salted-fried-fatty foods.
What is allowed? Just a little: pureed soups and purees, fermented milk products (the least fatty), crackers. And, perhaps, that's all.
So, how can you protect yourself from this norovirus?
To be honest, practically nothing. Because there is no vaccine for norovirus, and it itself is so tenacious and contagious that even the slightest contact can cause illness.
But it’s still worth trying to protect yourself. And to do this, try to monitor hygiene as carefully as possible - wash your hands more often, do not drink tap water, do not eat unwashed vegetables and fruits.
And, of course, don’t forget about boosting your immunity - giving up bad habits, eating healthy food, and spending more time in the fresh air. Then the nasty norovirus will simply have nothing to cling to.
Source: https://mama-likes.ru/advices/komarovskij-ob-opasnoj-kishechnoj-infektsii.html
Prevention
There is no specific prevention, just like vaccination. The remaining measures are suitable for preventing any type of viral infection:
- hardening of the body;
- seasonal course intake of vitamin and mineral complexes;
- during epidemics, taking immunomodulators, such as Immunal.
- isolation of sick children from healthy ones;
- in case of contact with a sick child, preventive use of children's anaferon or other antiviral agent.
- during illness, regular (2 times a day) wet cleaning of the room and daily ventilation; in the hospital, quartzing the room.
Komarovsky about infectious diseases (video)
Adenovirus infection in children is diagnosed very often today. This disease is an infectious disease that most often occurs in young children. It is accompanied by damage to the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract itself. During the cold season, adenovirus is diagnosed quite often. Let's talk about this disease in more detail below.
general information
This disease is transmitted, according to experts, by the so-called airborne route. Adenovirus infection in a child under six months is relatively rare, since in one-month-old children it is very strong. However, after six months, the immune defense begins to gradually weaken, therefore the virus can very easily settle in the body.
Adenoviral infection. Treatment
In children, as a rule, this type of disease is very mild. That is why specialists often prescribe outpatient treatment. However, in this case, strict bed rest and rest are prescribed. A small patient should lie down all the time as long as there is an elevated temperature. In addition, parents must provide adequate nutrition. If the baby refuses him, under no circumstances should he be forced. If the body temperature is above 38 degrees, prescribed
antipyretic drugs. For a dry cough, special ones are considered an excellent option, and for a runny nose, you can instill vasoconstrictor drops (no more than 5-7 days).