What eye color do newborns have?
Eye color is formed from the genetic material of the parents. Typically, most newborn Caucasian babies have cloudy eyes that are blue-blue, gray or light brown. This blurriness is determined by the small amount of melanin a person has at birth.
Melanin is a pigment substance that colors hair and skin in an individual shade. The pigment protects against UV radiation and is produced in response to its exposure. The accumulation of pigment is a long process; it takes from several months to several years for a sufficient amount of it to form in the body.
How to determine eye color in newborns, table
Many mothers and fathers want to know some of the features and traits of their child even before his birth. Fortunately, today there is 3D ultrasound, which helps you see the facial features of your newborn, and already a few months before delivery you know who he will look like.
However, if you are interested in knowing what color the baby’s eyes will be, then just select the initial data of mom and dad and get the result. To make your research more comfortable, you can use the table below.
Causes of changes in the shade of the iris in infants
Under certain situations and conditions, the shade of the baby's eyes changes:
- When there is a lack of substances needed by the body, the eyes acquire a dark tint.
- With negative emotions and stress, the eyes darken as the pupil dilates.
- When crying, the eyes have a greenish color due to redness of the area around the eyes.
- Lighting and weather conditions make the eye color brighter or duller.
- Lack of sleep, infectious diseases and injuries change the color of the eyes of newborns when the filling of the blood vessels of the eyeball changes.
Factors that determine color
The iris has a fibrous structure, in the depths of which there are cells that produce pigment substance.
Nationality
Residents of India and China are distinguished by dark skin and dark eyes , since historically representatives of these countries live in places with a high concentration of sunlight, like representatives of the countries of the African continent.
In black people with brown eyes, newborns may initially be brown-eyed (due to high melanin content) . Fair-skinned Europeans have a variety of eye colors (green, gray, blue, brown).
The eye color of a Negroid newborn is often dark brown
Among the inhabitants of Iceland, 80% of the population have green or blue eyes. Green eyes are common among Western Slavs, Germans and Swedes. In Turkey, people with green and blue eyes make up only 20%. The newborn baby in such cases will be blue-eyed.
Heredity
According to the law of inheritance of traits (Mendel's law), traits are dominant and recessive. The dominant gene contains the leading trait (brown eye color). In turn, light colors are recessive. The genes are located in 2 copies on chromosomes 15 and 19. The EYCL1 gene is located on chromosome 19, which determines blue and green eye colors.
On chromosome 15 there is the EYCL2 gene, which is responsible for the blue and brown iris. The combination of gene copies determines the child's eye color.
If both parents have the same eye color, the child will repeat that shade.
If the newborn's grandparents have light eyes, then the child's eyes will be different from the eyes of the parents.
Mendel's law can also control the inheritance of the location of pigment-producing cells in the layers of the iris, thereby shaping the individual characteristics of the eyes of newborns.
Melanin amount
The amount of pigment is reflected in the eye color:
- Blue and gray eyes- characterized by a low content of melanin, and the pigment-producing cells are located in the lower layers of the iris. The increased density of collagen threads and the distribution of light in the iris gives a similar shade.
- Green eye color - cells that produce melanin are randomly located in the middle and lower layers of the iris.
- Brown and black eye colors are people with the highest levels of melanin. Also, pigment cells are located in the upper layers of the iris and therefore contribute to maximum light absorption.
- In the absence of melanin (albinism), the eyes have a red tint . This occurs due to the visibility of the blood vessels of the eye through the iris.
Is it possible to predict the final eye color of a child?
It is impossible to accurately predict the color of a child's eyes. Mendel's law is the main hypothesis that allows us to guess the shade of the eyes. But for this you need to know not only the eye color of your parents and grandparents, but also your distant ancestors.
Melanin and eye color:
- Blue and blue eyes. The cause of blue or gray-blue eyes is a low density of pigment cells in the upper layer of the iris, a high amount of melanin is located in the deep layer of the iris with an increased collagen density. The brightness of the eyes depends on the cells in the outer layer. The fewer there are, the brighter.
- Brown and black eyes. Brown and black eyes are characterized by a high concentration of pigment cells in the upper layer of the iris. Melanin blocks the sun's rays, protecting the eyes from UV radiation. The more melanin-producing cells, the darker the eyes appear.
- Green-eyed children. Green eyes occur when there is a small amount of melanin distributed in the middle and lower layers of the iris in a chaotic manner. The color of the eyes is influenced by the presence of lipofuscin (yellow aging pigment). Small inclusions of pigment determine different variations in the color of the iris. The placement of pigment cells in the layers of the iris directly affects the eye color of newborns. When the amount of melanin in the deep and middle layers of the iris changes, then the eyes begin to acquire a turquoise, and subsequently green tint.
- Yellow tint to the eyes. Yellow eye color is associated with less melanin in brown eyes. At the same time, a large number of lipofuscin cells may be located in the upper layer of the iris, causing the brightness of the shade. Closer to the age of 12, children with yellow eyes acquire a brown tint. There are 1-1.5% of people with a yellow iris in the world.
- Red eyes in babies. Red iris is a genetic disorder called albinism. These eyes do not have the pigment melanin, so the blood vessels are visible through the iris.
With albinism, there is no change in the color of the iris, since melanin is absent and the cells cannot produce it. Albinism is not a mutation. This is a recessive trait. The distant ancestors of such a person had a lack of melanin. The emergence of this pathology was due to the combination of two recessive albinism genes.
Eye color pathologies
Common causes of changes in iris color are:
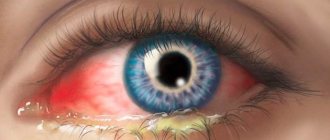
- Heterochromia is a pathology in which the color of the iris of one eye is different from the other or its parts.
- Glaucoma - the iris becomes cloudy and becomes lighter.
- Changes in the body's hormonal levels during puberty or illness. In this case, the color of the eyes may darken.
- Diseases of the central nervous system, such as Horner's syndrome, change the color of the iris to a lighter color.
- Inflammatory diseases - the eye acquires a greenish tint.
- Foods change eye color in newborns when the body's rate of production of the pigment melanin changes.
Amino acids contribute to this:
- Beta carotene.
- Tyrosine and tryptophan.
- Vitamin E.
- Selenium.
- Lycopene.
Heterochromia in children
Heterochromia is a rare hereditary pathology of the color of the iris, occurring in only 1% of the population. This is the result of a total or local change in the amount of melanin in the iris.
The simple form of heterochromia does not change vision. Complicated, in turn, affects the ability to see, manifesting itself: atrophy of the iris, clouding of the lens, cataracts, loss of visual fields.
Classification of heterochromia:
- Congenital and acquired.
- Abnormal darkening and lightening of the iris.
- Complete, sector and central heterochromia.
The cause of heterochromia can be a previous disease that has affected the pigment system in the organs of vision, as well as medications used to treat eye diseases, but most often it is a genetic predisposition.
If heterochromia is hereditary, then the development of pathology cannot be prevented.
In the case of acquired heterochrony, restoration of the same eye color is quite acceptable. It has been statistically proven that heterochromia occurs more often in females.
Albinism
Albinism is a disorder characterized by the absence of melanin in the body . This is a genomic change that occurs in 1 in 10,000 newborns worldwide. This violation is not tied to a specific nationality.
If only one in a couple has the albinism gene, the likelihood of having a healthy child is high. If there are two, the child will be an albino in 100% of cases. Albinism is associated with marriages between immediate family members. The main cause of the pathology is the absence of tyrosinase.
Aniridia
Aniridia is a disease characterized by the absence of the iris. This rare pathology occurs in 1 in 70,000 people. The pathology affects vision; in severe cases, the disease leads to complete blindness.
There are 2 types of aniridia: congenital and acquired:
- The formation of acquired aniridia occurs due to eye injuries: penetrating wounds and blows.
- Congenital aniridia occurs as a result of a mutation in the PAX-6 gene on chromosome 11. With a dominant type of inheritance, the probability of occurrence is 50%; with recessive inheritance, the disease can appear in 25% of cases, but then aniridia is accompanied by mental retardation of varying degrees.
In addition to the absence of the iris, the channels contribute to disruption of the circulation of intraocular fluid. This affects the increase in intraocular pressure. The retina of the eye is subjected to excessive irritation, because of this twilight adaptation suffers, and visual acuity decreases. In addition to the listed disorders, nystagmus is formed - uncontrollable twitching of the eyes.
What determines the color of a newborn's eyes?
The color of any person's eyes depends on the amount of melanin that is in the iris. The greater the amount of this pigment, the darker the baby's eyes will be. However, melanin is practically not produced during fetal development, since its production requires light.
In addition, heredity affects the amount of melanin. In the world, a large number of people have a dark shade of the iris, the reason for this is the genetic dominance of traits associated with a large amount of dark pigment.
So, for example, if one parent has a dark iris and the other has a light one, then most likely the newborn will have dark eyes. The color of a newborn's eyes can change throughout life. For example, it is believed that during times of stress, illness, moving, lifestyle and eating habits, the color may become darker or lighter. This occurs due to increased melanin production in various physical or psychological conditions.
Can diseases cause changes in eye color?
Diseases, as well as treatments, can cause changes in eye color. Drugs and diseases of various body systems change the color of a newborn's eyes, when not only the amount of melanin and its distribution throughout the iris changes, but also the integrity of the collagen fibers.
Reasons for changing eye color:
- Infections of the eyes and iris.
- Diseases of the central nervous system.
- Glaucoma and drugs for the treatment of glaucoma.
- Injuries, blows to the eyeball.
- Hormone-dependent diseases, taking hormonal medications.
- Chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus).
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease characterized by metabolic disorders of the endocrine system, leading to disruption of all eye structures.
Eye damage manifests itself as inflammation of the iris and fundus. Pathologically curved vessels form in the fundus. Small capillaries intertwined with the fibers of the iris rupture. In this case, small brown-red hemorrhage spots appear.
The iris brightens and becomes cloudy along the edges, gradually spreading towards the center. In some cases, the eyes appear brighter due to the blood-filled whites of the eyes. With the development of lens cataracts, the pupil does not differ from the main color of the iris, so the impression of a veil on the eye is created.
Anemia
Anemia is a condition of the body in which the concentration of hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells are reduced, and impaired transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide leads to the development of bleeding symptoms.
Lack of oxygen in the blood leads to thinning of the vascular wall, causing damage to its integrity. Hemorrhages in the iris are one of the symptoms of prolonged anemia. Eye color changes depending on the severity of anemia, when the saturation of blood vessels and capillaries with oxygen begins to differ from normal.
The more severe the anemia, the paler the eyes may appear.
In this case, blood stains from hemorrhage into the iris stand out clearly against the background of light, pale eyes.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the formation of cancer cells on the skin from cells that produce melanin (melanocytes). Most often, this disease affects people with blond or red hair and eyes of green, gray and blue shades. Of the non-cutaneous localizations, ocular melanoma is the most common.
The main factors influencing the appearance of this type of tumor:
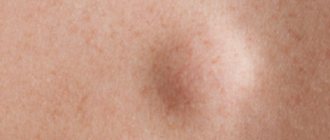
- Degeneration of birthmarks.
- Giant spots (over 10 mm in diameter). In 18%, melanoma occurs.
- Heredity.
- Light skin, blue or green eyes.
- Irradiation with ultraviolet rays.
Detection of eye melanoma at an early stage results in recovery in 80-90% of cases.
If the disease has been advanced and metastases have appeared, then the prognosis is not good. In melanoma of the eye, a dark brown or black spot appears near or on the iris of the eye, thereby changing the shade of the eyes to dark.
Wilson-Konovalov disease
Wilson-Konovalov disease is a genetically mediated disease that results in long-term copper poisoning due to impaired transport and pathological accumulation of the element in the body.
The basis of the disease is a mutation of the gene responsible for the transport and metabolism of copper in the body. Depending on the location of accumulation of the element, hepatic and neurological forms are distinguished. In the neurological variant of the disease, the manifestation of the disease can be found on the iris of the eye
A Kayser-Fleischer ring is copper that has accumulated on the outer edge of the iris. The ring is bright red or bright orange in color, making it easy to see with the naked eye.
Does eye color change in newborns and at what time?
For many parents, a real shock is the moment when their babies' eyes change color. In fact, it is worth understanding that this happens differently for each child. So, for example, you can put your newborn to bed with one iris color, and he will wake up with another. While others may take several years to develop the final color.
So, let's figure out when newborns' eye color changes completely. Most often, this process lasts up to 2 years. However, in modern medicine there are even cases where the formation of the color of the iris ended by 5-6 years of life.
Do not forget that changes in eye color are also possible in adulthood, as a result of changes in the state of the body.
The influence of eye color in a child on visual acuity
Eye color does not affect visual acuity.
Absolutely every newborn sees twice as bad as an adult, since the visual apparatus is not fully formed. Newborns cannot distinguish faces, but only react to light. At the age of 1-3 months, a baby can distinguish 50% of normal vision from the surrounding world.
Eye color is a unique combination of parents' genes. Newborns have blue or brown eyes depending on the amount and location of melanin in the thickness of the iris. It is impossible to say with certainty what a child’s eyes will be like and when they will change completely until early adolescence.
Author of the article: Lana Erkel
Article design: Svetlana Ovsyanikova
Age of change in eye color in children
In order to bring at least some clarity to the process of changing eye color in children from birth to adulthood, we will consider this process in more detail.
- As mentioned earlier, most children have blue or dull gray eyes from birth.
- Also, brown-eyed babies can often be found.
- Newborn babies with a green iris are rare.
Basically, the first color of the organs of the visual apparatus that differs from blue is a heredity factor.
Let's look at how and when the eye color of babies changes, depending on their age.
First half of the year (3 months)
The first changes in color usually begin at three months:
- This process will begin most quickly in children with a large amount of melanin. At this time, the brown color is most often formed.
- The rest do not appear or are constantly changing.
- Also, constant eye color can be observed already at this age in green-eyed babies from birth.
From six months to a year
Dramatic changes in the iris begin to appear by the age of six months or one year:
- At this time, the green color will definitely be fully formed. The only thing that will happen to them next is a change in shade. They may either lighten or turn dark green.
- By this time, a blue-eyed child has every chance of changing the color of the visual apparatus to gray or acquiring a brown color.
- The brown color of the organs of vision, as a rule, does not change upon reaching this age, but certain circumstances may occur that will affect the production of melanin; they may turn gray or green.
- Gray eyes can also change from heavenly to brown.
Three to five years
The period from three to five years is the final period in the formation of eye color and with a high probability can show the final color that the child will have for the rest of his life.
- The blue color (if it has not changed to brown or gray during this time) will most likely become light blue, sky blue, cornflower blue, etc.
- Green-eyed babies, as time shows, at this age can only change shade.
- A brown eye can become fiery brown, yellow brown, dark brown. But it is also possible to change the pigment substances to gray or green, followed by a change in shade.
- Gray eyes during this period can remain either gray or change to brown if melanin production increases, or heavenly. If during this period there were changes in the eyes from gray to blue, then during the further development of the child only changes in their shade will occur.
The final eye color, according to statistics and a number of studies, will be formed after five years.
In order to present all these situations more clearly, let's present them in the form of a summary table:
Change in eye color from birth to final color: click to enlarge
But even all these described situations must be combined with the assumptions that were obtained by geneticists.