Causes of purulent discharge from the eyes in children
Eye diseases that can cause purulent discharge from the eyes in newborns and infants:
Dacryocystitis of newborns
Many children are born with poorly developed tear ducts. This means that tears cannot drain properly into the nasal cavity. Because of this, secretions from the eyes accumulate in the lacrimal sac and inflammation begins. In this case, as a rule, only one eye of the baby becomes watery and purulent.
Treatment in the first 3 months of the child is carried out with medication. Anti-inflammatory drops are instilled and massage of the lacrimal sac is applied. In most cases, dacryocystitis goes away. Sometimes it is necessary to probe the lacrimal ducts.
Neonatal conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye during the period 28 days after birth is called neonatal conjunctivitis.
Bacteria that cause inflammation: Staphylococcus aureus, chlamydia, streptococcus, etc.
Gonococcal infection of newborns
With gonococcal infection, newborns have very profuse purulent discharge, with pronounced swelling of the eyelids. Damage to the cornea and development of corneal ulcers may occur.
Eye injury during childbirth
In case of pathological birth, eye damage and infection of the eye are possible.
Inadequate eye care immediately after birth
Immediately after birth, newborns are given special antiseptic drops for prevention. In the case when drops are not used, the risk of developing conjunctivitis in newborns is increased.
Inflammation of the mother's genital tract
Inflammation of the mother's genital tract leads to infection of the child and the appearance of signs of eye inflammation.
Causes of suppuration in the eyes of a newborn
Why red eyes in a newborn baby - what to do
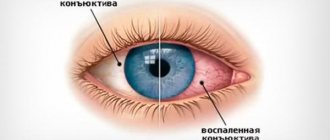
Conjunctivitis manifests itself in different ways and has different causes. This:
- Infection with bacteria, most often staphylococcus or streptococcus. This problem is characterized by abundant formation of pus. There can be so much of it that the eyelashes will stick together. Eye hyperemia is moderate;
- Infection with viruses and infections. The most common causes are adenovirus or herpes virus. Discharge is not typical here. But the whites may turn red more. And against this background, bacterial damage can occur, then pus will appear;
Adenoviral conjunctivitis
- Allergy. This conjunctivitis develops upon contact with an allergen. Most often there is redness of the white of the eye, profuse lacrimation, and swelling of the eyelids.
If a newborn baby's eye becomes infected, this may be due to a blockage of the tear duct with a plug. The problem occurs in the first weeks of a baby's life. Natural lubrication stagnates and inflammation occurs. Something that can be done at home to solve the problem is massage of the nasolacrimal duct, it helps the plug to move away. Sometimes this does not help, then the surgeon makes a puncture.
If one eye gets sick, a similar problem will soon appear on the other side. Conjunctivitis is highly contagious. Discharge from the organs of vision is an alarming symptom. It is important to act correctly if they appear.
Green discharge
This is a very bad sign. Green pus in a child's eyes indicates extensive bacterial infection. There is already strong, deep inflammation of the conjunctiva. You should immediately visit a doctor and begin treatment. If therapy has already been started, but does not bring results, you cannot wait, the specialist is called again. If your baby has a stye, greenish pus may also come out of the eye.
Yellow discharge
Yellow pus from a child's eye
If a child’s eye is purulent and the discharge is yellow, then this is a clear sign of bacterial conjunctivitis. The pus is usually dense, thick, and when it gets from the mucous membrane onto the eyelid it quickly dries to a crust. A film may stretch on the eye itself, which interferes with vision.
Pus is released even in the middle of sleep, not only in the corners, but along the entire length of the eye. Drying by morning, it forms a dense crust. This purulent discharge is a sign of the functioning of the immune system. This happens not only with inflammation of the conjunctiva, but also with fungal keratitis.
Bloody discharge
They talk about an acute form of inflammation of the conjunctiva or large barley. Require immediate medical attention.
Brown discharge
This is a consequence of untreated yellow discharge. Pus stagnates in the eye and takes on a different shade. An unpleasant odor may appear.
If brown pus is released primarily (that is, there was no yellow pus), then this is a sign of bacterial inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct. The passage of tears is limited, and stagnation occurs. The pus released is very thick and dark.
Discharge after sleep
There is nothing wrong with this, but provided that a tiny piece of crust appears in the morning after sleep very rarely. When there are so many crusts that it is impossible to open your eyes, this is a symptom of bacterial conjunctivitis.
The child's eyes are stuck together due to a purulent crust
If there is a moderate amount of discharge, but it appears consistently every day, then this may indicate chronic inflammation of the conjunctiva. You should consult your doctor.
For a runny nose or cold
With diseases that affect the upper respiratory tract, the child's eyes may become slightly inflamed and watery. This is a normal reaction of the body to a harmful agent. Light white discharge is a common symptom of ARVI or chlamydia. The latter, by the way, happens in newborns - they become infected with chlamydia from their mother while passing through the birth canal.
If hyperemia becomes pronounced and the child is restless, then it is probably an adenoviral infection - a frequent accompaniment of colds. If the eye becomes infected, then bacterial infection has occurred.
According to Dr. Komarovsky, in general, all inflammation of the conjunctiva is associated with respiratory diseases, snot and red throat. For the problem to be only related to ophthalmology and not affect anything else is rare, according to him.
Causes of purulent discharge from the eyes in pregnant women and children over one year old
ARVI and influenza
Pus that may be present in your child's eyes may be due to a viral infection. Knowing the causative factors, as well as how to cope with them, can prevent the development of purulent discharge from the eyes in an infant.
Sinusitis
If your baby has a cold, he may develop sinusitis (inflammation of the sinuses). Important symptoms: fever, pain in the forehead and eyes, lacrimation and suppuration of the eyes.
Allergy
If your baby has a runny nose and you notice redness and small mucous-yellow discharge, then it may be an allergy.
Conjunctivitis
The eyes of children and pregnant women often fester due to infectious inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by both bacteria and viruses. Symptoms of conjunctivitis begin in one eye and then spread to the other eye.
Prevention of conjunctivitis in newborns
A disease in which the conjunctiva becomes inflamed is called conjunctivitis. Inflammation is most often accompanied by the appearance of pus. This problem occurs not only in older children, but also in newborn babies. Among the causes are bacterial, viral and fungal infections received from the mother, staff in the maternity hospital or roommates.
Since the consequences of the disease are serious, including blindness, it is important to prevent its occurrence. Therefore, the neonatologist necessarily carries out prevention. The specialist will not forget:
- Rinse the newborn's eyes;
- Use antibiotic drops;
- Place antibacterial ointment under the eyelid.
All this is part of the first toilet of a newborn, carried out in the maternity hospital immediately after the baby is born.
A neonatologist performs the first toilet of a newborn
Interesting. In rare cases, such measures are not only of no use, they are also harmful. For example, if a child is allergic to albucid (a substance that treats ophthalmia), the conjunctiva will still become inflamed.
A child's eye is festering, treatment
Situations that require immediate attention and medical attention include the following symptoms:
- severe swelling of the eyelids and very profuse purulent discharge
- increase in body temperature
- the child complains of decreased vision and pain in the eyes
- child rubs his eye
- eye redness and watery eyes
It is important to know that the spread of infection in children occurs very quickly and rapidly. Therefore, it is necessary to seek medical help in a timely manner.
During treatment, when using eye ointments and drops, it is necessary to first remove pus from the eye. Any types of medications (drops and ointments) are effective only after rinsing the eye.
What complications can there be?
Why does a child's feet peel - what to do?
If the pus in the child’s eyes is not removed or the baby is not treated in any way, this can lead to the development of the following complications:
- Blepharitis. This is when the inside of the eyelid (its mucous membrane there) becomes inflamed. The problem is dangerous because it is difficult to treat, but quickly becomes chronic.
- Keratitis. The most dangerous possible consequence. This is an inflammation of the cornea of the eye. It is difficult to cure; keratitis often turns into a chronic disease. Then he faces complete loss of vision.
- Entropion. Turning of the eyelids inward. This disrupts a person’s natural defenses against harmful agents: viruses, bacteria, infections. Consequently, the child begins to get sick more often.
- Hypopyon. Purulent discharge accumulates in the eye, and it is impossible to clean it out on your own. Often the problem can only be solved by surgery.
- Xerophthalmia. This is a disease that affects the lacrimal gland. As a result, the eye is less moisturized, and bacteria and viruses are more likely to settle on the dry mucous membrane.
Traditional treatment
You cannot start treatment on your own, because if you choose the wrong medications, you will only harm your baby. All medications and procedures for the child must be prescribed by an ophthalmologist and pediatrician. Doctors identify the root cause why the pus appeared, and only after that they select the optimal medications. However, there are several recommendations that parents can follow regardless of whether the milk gave suppuration or other factors contributed to this. The recommendations presented are safe and suitable for children of any age.
Hygiene procedures
If the eye is covered with pus, you need to try to eliminate it as quickly as possible. It is recommended to pay attention to hygiene procedures:
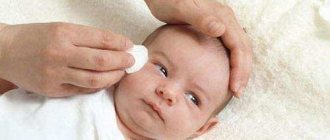
- washing the mucous membrane of the child;
- removing crusts from eyelashes and eyelids with a cotton swab;
- rubbing with herbal solutions (chamomile, calendula).
Before using medicinal herbs, you need to make sure that the baby is not allergic to them.
If you have completed all of the above procedures, you can proceed to the next stage - massage. It must be done with clean hands and light movements. The main area of stimulation is near the nose and the inner corners of the eyes. This promotes more efficient functioning of the sebaceous glands. Purulent formations are eliminated through the tubules over time. How do you know if you started doing massage correctly? If at the end of the procedure a yellow substance is released, it means you are doing everything well. Further treatment depends on the individual characteristics of the child’s illness.
Allergy treatment
Allergies in a baby usually manifest themselves to mother's milk or pharmaceutical infant formula. If the child is bottle-fed, you should try a different formula, changing the manufacturer.
If the newborn does not accept breast milk and the mucous membrane festers, there may be a problem in the mother’s diet: the diet should be reconsidered, the allergen should be identified and eliminated.
If a child has been diagnosed with conjunctivitis, a different approach to solving the problem is necessary. The first step is to eliminate the infection, and then the doctor identifies the factors that caused the development of the disease.
When there is an infection, the eye turns sour, so you need to remove the pus quickly, otherwise the disease will progress quickly. To do this, the doctor prescribes a solution of furatsilin. If the infection is serious, then the baby will have to be treated with antibiotics.
Medical procedures
If there is slight suppuration, the doctor prescribes the following medications that can be used to wash the eye:
- chloramphenicol;
- antibacterial ointments;
- furatsilin solution.
If after treatment the tear duct does not uncork, doctors are forced to do probing.
This procedure is done under local anesthesia, so the newborn does not feel pain. Using a probe, the doctor carefully removes the film that is blocking the tear duct.
After the procedure, parents need to follow all hygiene rules, because infections very quickly affect the eye and sour back.
Nursing mothers need to reconsider their diet. Everything that is consumed ends up in the milk, and this can trigger an allergic reaction.
Which doctor treats this?
The eyes are treated by an ophthalmologist; there is an office in the children's clinic. Since appointments there are usually scheduled a week (or even two) in advance, you can visit the pediatrician on duty and ask him to redirect the little patient to a specialized specialist or go to the hospital.
Examination by an ophthalmologist
Since conjunctivitis is contagious, the methods described above are only possible when consultation with an ophthalmologist is urgently needed. If the discharge has just appeared and there is little of it, you can call a pediatrician at home, he will prescribe primary treatment. Perhaps it will be enough and the baby will recover. After the examination, the doctor will tell the parents everything: what to wash the eyes with, what to drip.
Attention! It is impossible to treat even a newborn, even a 1.5 year old child with folk remedies or home remedies. Only a doctor can prescribe therapy.