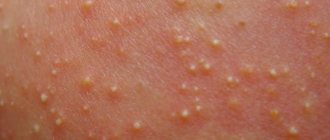
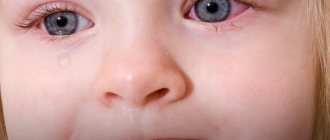
The skin behind the child's ears cracks and peels
Various factors can cause the skin behind a child's ears to crack.
If parents pay attention to such a symptom in a timely manner and seek help from a specialist, then there will be no special problems with treatment. The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe therapy with appropriate medications.
Self-medication for pathologies with such a symptom is not recommended, as this can negatively affect the child.
Causes of cracks behind the ears
The cause of cracks behind the ears in a child may be too hard water.
Often parents are faced with the problem of cracks behind their child’s ears. The main factors that provoke their appearance include:
- Sudden changes in ambient temperature and insufficient humidity.
- Swimming in hard water.
- Genetic predisposition to allergic reactions.
- A diet that includes frequent consumption of a variety of sweets and rich foods. If a woman during pregnancy or breastfeeding is addicted to allergenic foods, this can negatively affect the baby.
- Weakened immune system of the child's body.
- Functional disruptions of the digestive system and metabolism.
- Mechanical damage in the area behind the ear, accompanied by the penetration of a fungal infection.
- Hygiene products and synthetic detergents, the composition of which can cause an allergic reaction (shampoo, soap, gel, powder).
- A baby's delicate skin and excess weight can cause diaper rash behind the ears due to constant rubbing.
Such negative factors can affect the occurrence of the following diseases characterized by the presence of this symptom:
- exudative diathesis;
- scrofula;
- eczema;
- dermatitis;
- otomycosis.
If the crack gets wet
When a child begins to get wet behind the ear, this is a clear symptom of the presence of a pathological process in the body of a dermatological nature.
Weeping diathesis
This disease is often diagnosed in infants and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- scaly crusts of yellow-gray color;
- rash;
- redness of the skin behind the ears, followed after a few days by the appearance of blisters filled with liquid;
- constant itching and burning;
- pain in the area of the burst blister.
Weeping diathesis occurs in a child due to an allergic reaction to food or mother’s breast milk. In this case, parents urgently need to identify the allergen and eliminate it from the child’s life.
Important: Unconsciously scratching the wet area behind the ear can cause infection in this area.
Allergy
Due to contact of the child's parotid area with an irritant contained in a hygienic detergent, the temples of glasses or the metal of earrings, an allergic reaction on the skin may occur.
Not least important in the occurrence of this pathology is the genetic factor. Children of parents with allergies are often more predisposed to allergies of various forms.
Children are diagnosed with a chronic pathology such as gneiss.
In this case, the skin behind the ear is susceptible to the following symptoms:
- dryness;
- burning and itching;
- redness due to inflammation;
- the lobe and area behind the ears are peeling;
- if spots become wet behind the ear, this indicates an acute course of the disease. Swelling and crusts appear;
- cracks.
As in the previous case, it is necessary to remove all objects in contact with the affected area and consult a dermatologist about medications to eliminate the symptoms that appear.
Scrofula
This non-infectious disease manifests itself in children under 10 years of age and is considered the initial stage of atopic dermatitis. Basically, the affected area is considered to be the area behind the ears, but if the process is advanced, scrofula can also appear on other areas of the skin (forehead, cheeks). The main symptoms are:
- the formation of whitish-gray spots behind the ears, gradually spreading to a large area of the head;
- unbearable itching;
- peeling;
- rash and the appearance of lichen;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the spots are covered with golden-colored crusts. When they peel off, a wet, reddened skin remains, so the child’s earlobe may become wet.
The main reasons for the manifestation of such a disease in a child are considered to be an abundance of sweets, insufficient walking time, the presence of cancer, syphilis or tuberculosis in parents, a lack of vitamins and a weakened immune system.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Z3O2P6k0l4
The sooner parents see a doctor, the easier it will be to get rid of this pathology.
Diagnostics
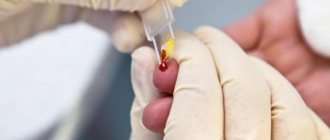
At the appointment, the treating specialist will conduct an examination and clarify with the parents the possibility of a hereditary factor. To understand the cause of cracks behind the child’s ear and make the correct diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe certain examinations:
- a general blood test to determine the presence of inflammation;
- bacterial culture of ear secretions. It is taken if otitis is suspected in order to clarify the type of pathogenic microorganism and the necessary antibiotic to combat it;
- allergen detection tests;
- a smear from the skin behind the ear to identify the fungal parasite and, if necessary, its sensitivity to drugs;
- immunogram.
Based on the research results, the doctor selects the necessary medications for therapy.
How to treat
After determining the cause of the crack behind the child’s ears, the following types of medications are prescribed:
- antihistamines in the form of tablets (Suprastin, Loratodin) or drops (Tavegil, Parlazin) to relieve itching;
- ointments with a drying effect (zinc ointment) will help get rid of weeping lesions;
- after water procedures, it is recommended to treat the area behind the ears with Bepanten or creams with depanthenol for a healing effect;
- Corticosteroid ointments can be used to treat severe cases. From 6 months, children are recommended to apply Celestoderm B;
- if an infectious infection occurs, then antibiotics are added to therapy. At the same time, it is important for the child to combine such treatment with taking medications to restore intestinal microflora (Linex, Bifiform);
- immunomodulators and vitamins;
- Weeping cracks should be treated with Levomekol;
- crusts are removed by preliminary softening with prednisolone ointment;
- fungal infection is treated with appropriate medications.
Physiotherapy through the use of ultraviolet rays has a wound-healing and anti-inflammatory effect.
As folk remedies for scrofula, you can use lotions made from string and chamomile, and for weeping diathesis, a bath with oak bark is an excellent remedy.
It is important during treatment to carefully select food products and maintain ear hygiene.
Prevention
To prevent cracks behind the ears in a child and the possible consequences of this symptom, follow these rules:
- pay attention to any allergic manifestations after your child consumes a new product;
- walk in hot weather for no more than 1 hour in the shade;
- carry out timely wet cleaning of the room and ventilation;
- strengthen the child's immune system;
- carry out careful hygiene in the area behind the ears;
- select anti-allergenic detergents and hygiene products;
- moisturize the skin with special baby creams;
- carry out timely treatment of the parotid area in the presence of scratches, cuts and other microtraumas;
- During pregnancy and lactation, monitor your diet and do not overuse allergenic foods.
Allergic reactions and various skin dermatitis are not uncommon in childhood, so you need to carefully monitor your baby's skin. If you know that your child is predisposed to allergies, then try to take all preventive measures to avoid dangerous complications.
Rate:
(Total: 2 / 5.00) Loading…
Source: https://StopOtit.ru/treskaetsya-i-shelushitsya-kozha-za-ushami-u-rebenka.html
Disease prevention
To prevent scrofula it is necessary:
- observe the rules of hygiene - bathe and wipe all folds of a newborn baby on time;
- keep the home and children's room clean, do wet cleaning;
- spend more time outdoors, sunbathe according to the season;
- get enough sleep; children must have a quiet hour during the day;
- eat properly and balanced, take vitamin complexes (VitaMishki, Pikovit);
- up to 3 years of age, completely limit the consumption of sweets - sweets, chocolate, marshmallows, etc.;
- maintain immunity (harden yourself, play sports, walk in the fresh air).
The most important preventive measure to prevent the development of the disease is to monitor the child’s hygiene
The skin behind the ears of a child cracks and peels: causes of formation in infants
Crusts behind the ears of a child are not uncommon. The symptom most often becomes noticeable during hygiene procedures. Such peeling usually has an unpleasant odor, which causes inexperienced parents serious concern about the health of the baby. In addition to being an aesthetic problem, the crusts cause discomfort, causing severe itching.
As a result, the baby begins to be capricious and cry, sleep is disturbed, and appetite disappears. In such cases, it is necessary to identify the cause that caused the problem and, by eliminating it, get rid of the symptom. The article will discuss why the skin behind the ears cracks in a small child, how to eliminate the symptom, and what are the measures to prevent this problem.
Baby hygiene - effective prevention of skin diseases
Consequences of poor child hygiene
Crusts and peeling behind the ears of a baby are often the result of poor hygiene of the baby.
When a baby drinks milk (regardless of the type of feeding: breast or artificial), some liquid gets behind the ears. In addition, dirt and sweat accumulate in these areas.
All these components mix with each other, and the process of rotting begins, which causes an unpleasant odor, itching and irritation.
Causes of crusts and peeling
Milk crusts in a child
The main provoking factors that can lead to the formation of scales and cracks behind the ears in a child include:
- Neglect of hygiene rules.
- Staphylococcus. If hygiene standards are observed, but the problem does not disappear, the help of a pediatrician will be required. The bacterium is detected using a special analysis - microflora culture. Staphylococcus is an opportunistic microorganism that is present in most people. If the body's protective functions work normally, and hygiene procedures are carried out regularly, correctly and in a timely manner, the bacterium does not cause harm. In the opposite situation, its active reproduction and spread occurs.
Important! If, in addition to crusts and peeling, the baby has a fever, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Redness and pus formation are often observed around the crusts. With such symptoms, it is forbidden to take a bath or apply heat to the source of inflammation. Treatment is carried out using antibacterial agents, the areas behind the ears are treated with antiseptic ointments.
- Allergic reaction. Often a newborn's ears become flaky due to certain types of allergies. Most often, a negative reaction is associated with the consumption of certain products. The most common allergens are:
- Chocolate, honey;
- Citrus;
- Other fruits (grapes, persimmons, bananas);
- Nuts;
- Melon, tomatoes, eggplants, carrots, beets;
- Milk and dairy products;
- Cocoa, coffee, tea;
- Eggs;
- Meat;
- Seafood;
- Mushrooms.
If the baby is on IV, it is better to switch to another milk formula, and also exclude complementary foods from the diet. If negative symptoms persist, other allergens may be the cause of the appearance of crusts:
- Various baby care products (ointments, powders, shampoos);
- Washing powder and other household chemicals;
- Dust;
- Animal wool;
- Plant pollen;
- Poplar fluff;
- Mom's new cosmetics;
- Toys.
Important! If a negative reaction in a child still persists even after the suspected allergens have been excluded, it is worth visiting a doctor.
- Seborrheic dermatitis. The symptom in the form of crusts behind the ears (as well as on the neck, head) occurs due to excessive secretion of sebum, as a result of which the layer of the epidermis separates and crusts form. Dermatitis can be caused by allergic reactions, endocrine disruptions in a woman during pregnancy, and the use of certain medications. A mild form of pathology is not accompanied by dangerous symptoms and is limited only to aesthetic problems in the form of peeling skin. A severe form is characterized by the spread of a negative sign to other parts of the body. The child is not only bothered by itching, his general health worsens, and his sleep is disturbed. In the first case, the doctor prescribes a diet and external remedies for seborrhea. In the second case, the doctor prescribes ointments containing steroid hormones, antibiotics, and drugs to strengthen the body.
- Scrofula. This is what people call a type of atopic dermatitis. The disease mainly affects children from the first months of life to 10 years. When the flaky particles are removed, you may notice fresh, pink skin that looks like it has been burned. Scrofula can be caused by allergic reactions (for example, to food). Dermatitis also occurs against the background of decreased immune defense, due to a lack of vitamin D or non-compliance with hygiene and sanitary standards.
Interesting. As practice shows, scrofula often occurs in “late” babies.
Dermatitis can be caused by such serious pathologies as syphilis, tuberculosis, and malignant tumors that the child’s mother suffered from. It has been noticed that scrofula often affects children conceived by parents who abused alcohol.
At first, the disease can be confused with ordinary diaper rash. Then the skin begins to peel off, forming a golden crust with cracks (which gives the name to dermatitis). If left untreated, such formations will spread to other areas of the skin.
A crust behind a child's ear
Symptoms of crusts and peeling
Irritation on a child’s bottom - what to do if the buttocks are red
If a crust has formed behind the ears of a newborn baby, the symptoms may be as follows:
- Unpleasant odor emanating from the site of inflammation;
- Itching;
- Redness;
- Restless behavior;
- Sleep disturbance;
- After removing the particles, there are no ulcers or wounds;
- In some cases, an increase in temperature.
A crust behind the ear as a sign of scrofula
Why are crusts and peeling dangerous?
Vomiting water in a child under 1 year of age - what to do when he feels sick
The harm from the appearance of crusts behind the ears in a child lies mainly in the reason that contributed to this. If a serious pathology acts as a provoking factor, then the baby requires adequate treatment.
How to get rid of crusts
Since most often crusts behind a child’s ears are formed due to non-compliance with hygiene rules, appropriate procedures will help eliminate the unpleasant symptom. So, to save your baby from the problem, you need to follow these instructions:
- Immerse the baby almost completely in water, leaving only the face on the surface. Thanks to this, the crusts soften and are easier to separate.
- After the procedure, wipe the skin behind the ears dry and remove the crusts using a cotton swab or disk.
On a note. If the crust that appears behind the baby's ear is difficult to remove, it must be softened with baby cream or special oil purchased at the pharmacy. The crust should soak for 2-3 minutes, then it can be carefully removed.
- Treat the area with sea buckthorn oil - the product will help relieve irritation and soothe the skin.
- After a couple of minutes, wipe the areas with a clean, dry cloth (which will absorb any remaining oil).
- Moisturize the skin with cream (otherwise the overdried dermis may crack).
- If the room temperature is too high, it is better to apply powder to the skin.
- Your child's ears need to be cleaned regularly.
Features of treatment for children of different ages
As a rule, therapy for this disease does not depend on the patient’s age. If you suspect scrofula or diathesis, the skin is dry, cracking, or wet wounds appear behind the ears, you should contact your pediatrician as soon as possible (see also: dry skin on the legs and arms of a child). He will refer you for consultation to a pediatric dermatologist and allergist.
The next stage is the prescription of medications to relieve itching and remove crusts. If left untreated, a secondary infection may develop due to constant trauma to the skin when scratching; the wound behind the ears rots and enlarges. With timely treatment, scrofula can be cured in a short time.
It is important to strengthen the child's immunity. The defenses of a healthy baby’s body are able to cope with scrofula on their own.
Drug therapy
- Ointments. For the treatment of scrofula, Sudocrem, Tsindol, zinc ointment, Topicrem, Drapolene are used. They dry the wet crusts well, which then come off easily. Typically, these products are applied 2-4 times a day to clean skin, without washing off for several hours.
- To moisturize the skin with cracks and dryness, Bepanten is used.
- Cauterization with Fukortsin. This is a crimson-colored drug that effectively disinfects and cauterizes disease-affected skin. The child may complain of a burning sensation in the areas treated with Fukortsin. It is used if there is no improvement after 3-4 days of treatment with ointments.
- Enterosgel and other sorbents are used to remove toxins and cleanse the body. They also remove allergens.
Hygiene procedures
When scrofula does not cause symptoms other than crusts on the scalp and does not progress, it may not be treated. In this case, they get by by simply combing out the scab, that is, the crusts. Before this, the skin is generously lubricated with nourishing baby cream or Vaseline oil, and they are combed out with a regular comb. When removing crusts from a child under one year old, you need to be careful not to damage the fontanel.
When drug therapy is carried out, before using ointments it is important to thoroughly clean the skin and carry out other hygiene procedures. It is useful to take antiseptic baths with herbal decoctions.
Special diet
Strong allergens must be excluded from the diet of a child or nursing mother: candy, chocolate, citrus fruits, nuts, milk, etc. For scrofula, a food diary is kept, where parents write down everything that their child ate. This will allow you to track which products the reaction occurs to. You are allowed to eat low-fat broths and meat, hypoallergenic vegetables and fruits, and water-based porridge. Subsequently, other foods are gradually and carefully introduced.
Newborns and bottle-fed infants must be given only adapted formulas. It is unacceptable to feed your child goat or cow milk, as it causes very severe allergies.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers an extensive list of recipes against scrofula. Before using them, you should consult your doctor.
Due to its effectiveness, baths with chamomile decoction are in great demand in the treatment of scrofula.
For scrofula in a child, baths with:
- chamomile decoction;
- oak bark;
- walnut leaves;
- decoction of currant leaves;
- tea tree essential oil.
An infusion of string is used internally and externally. It dries the skin perfectly and has an antiseptic effect.
The skin behind the child's ear is peeling
- 1 The skin behind the child’s ears is peeling 1.1 The skin behind the child’s ears is cracking and peeling
- 1.2 Causes of cracks behind the ears
- 1.3 If the crack gets wet 1.3.1 Weeping diathesis
- 1.3.2 Allergies
- 1.3.3 Scrofula
7 The skin behind the ear gets wet and peels!
14 Features of treatment for children of different ages
The skin behind the ear peels, cracks, crusts and gets wet: reasons, how to treat with medication and folk remedies?
20 The skin behind the ear peels, cracks, becomes crusty and becomes wet in adults, children, and infants: causes
23 Why the skin in the ears and behind the ears dries, flakes, turns red and peels: treatment with folk remedies
28 The appearance of crusts as a result of the action of staphylococcus
Various factors can cause the skin behind a child's ears to crack.
If parents pay attention to such a symptom in a timely manner and seek help from a specialist, then there will be no special problems with treatment. The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe therapy with appropriate medications. Self-medication for pathologies with such a symptom is not recommended, as this can negatively affect the child.
It gets wet behind the ear and the skin peels!
I noticed how hot it became, my daughter was constantly scratching her ear, especially the left one,
The skin behind the ear began to peel, it used to happen when I was very little, if I lay down and drooled or milk flowed. it was because of the moisture.
now what could it be? Has anyone come across this?
registry
Our diathesis appeared at almost 8 months. They treated him with “Defender” cream, immediately removed everything from the diet, and ate only the mixture. "Defender" does not remove the cause of the rash, etc. etc., but simply relieves redness and irritation.
We went to the doctor, and it turned out that this diathesis was caused not by food, but by teeth. There was a waterfall of drool, my son rubbed it and it caused a rash on his cheeks, his ear got wet because when he wants to sleep, he touches his ear and scratches it. If this is an allergy, then it is better to take a course of “Fenkarol” or “Suprastin”.
Heals well.
Source: https://dou99.ru/uho/za-uhom-u-rebenka-shelushitsya-kozha
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Experienced and respected pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky believes that the appearance of any skin rash occurs in three ways:
- due to non-compliance with the diet;
- through infection from a sick person through touch;
- by airborne droplets.
In order to avoid the development of the disease, you need to follow simple rules:
- maintain hygiene;
- do not introduce complementary foods very early;
- do not give children exotic fruits and products, so as not to cause allergies;
- do not overfeed the baby;
- do not bathe your child in water that has been chlorinated;
- wash children's clothes with special hypoallergenic products;
- bathe the baby using soap and detergent no more than 2 times a week;
- Avoid contact of the baby with strong household allergens: pets, sprayers, aggressive household chemicals.
Source: VseProRebenka.ru
My child has peeling skin behind the ears, what is it?
» Miscellaneous » The child’s skin behind the ears is peeling, what is it?
- In the process of carrying out hygienic manipulations, it is necessary to pay attention not only to the ears, but also to the space behind them. When taking a bath, you need to lower the baby's head into the water so that only the face remains on the surface, this will soften the crusts and remove them without any problems.
- Immediately after the water procedures, you need to take a piece of bandage, wrap it around your finger, moisten the material in vegetable or medicinal pharmaceutical oil (for example, sea buckthorn) and treat the clean and dried skin behind the baby’s ears.
- After a few minutes, carefully wipe the treated areas, removing any remaining plaque and medication.
- In most cases, the main causes are hereditary predisposition. Children whose parents suffered from syphilis, tuberculosis and various cancers have a high risk of developing scrofula.
- For topical use, sudocrem, zinc ointment, bepanthen or fucorcin are recommended.
- Traditional medicine recommends bathing the baby every evening in decoctions of medicinal plants (oak bark, tricolor violet, etc.) to relieve itching and inflammation. Infusions and decoctions are also used internally (for example, coltsfoot).
Tip: Increased attention should be paid to the area behind the baby's ears during the summer months. If sweat constantly accumulates in the hidden area, the baby will suffer from diaper rash, irritation and inflammatory processes. In some cases, you can even use powder to prevent moisture buildup.
Such manipulations are also good for preventing the condition. As a last resort, it is recommended to wipe the problem area every day with a cotton swab dipped in warm water. Twice a week we apply moisturizing cream or a little vegetable oil to the skin to soften the tissues.
Scrofula in children behind the ears
Scrofula is the name of exudative diathesis, known since the time of our grandparents, which is considered a manifestation of dermatitis at an early stage. Basically, this disease affects the area behind the ears and most often affects children from two to ten years old. Scrofula behind the ears in infants is much less common.
Scrofula behind the ears - symptoms
Other signs may include discharge from the ears and nose and inflammation of the eyes.
Scrofula behind the ears - causes of occurrence
How to treat such unpleasant scrofula behind the ears?
womanadvice.ru
- Scrofula in adults
- Gneiss in adults
If an adult gets wet behind the ears, it can be a symptom of various diseases. First of all, weeping skin indicates the presence of some kind of skin disease, so treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Often, constant moisture behind the ears can be accompanied by itching, peeling of the skin, irritation and burning. The causes of a constantly weeping area behind the ear are determined using secondary symptoms.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Symptoms of skin disease
- the appearance of red diaper rash behind the ears and under the hair, after some time they become yellow, but the hair does not fall out or break (we recommend reading: reasons why hair falls out in a 6-year-old child);
- as the disease develops, the area of the lesion increases, it spreads to the neck, face, arms and legs;
- the skin becomes cracked, becomes wet and peels (we recommend reading: what to do if the skin on the head of a 5-year-old child is peeling?);
- severe itching;
- peeling of the earlobes;
- bloating, digestive system disorders;
- inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes (we recommend reading: what causes inflammation of the lymph nodes in a child’s neck?);
- joint pain, swelling;
- redness of the eyes.
An adult’s health deteriorates significantly, the temperature rises, sometimes to critical levels. In this case, a diagnosis of skin tuberculosis may be made.
The disease is also severe in newborns. The fact is that the baby’s immune system is still completely immature; it is not able to resist other diseases with scrofula. In addition to the symptoms described above, frequent colic, cramps, increased muscle tone, and discharge from the nose and ears are added. You can see what scrofula looks like in a child in the photo above (using the example of weeping wounds).
Ways to get rid of the problem
If the cause is not a disease, then you can start the fight on your own.
- It is better to take boiled water for washing, cool it to 37 degrees.
- Adding herbal infusions to water will help relieve inflammation and dryness. Oat decoction helps a lot.
- After taking a bath, the skin should only be blotted with a terry towel, but not wiped.
- Lubricate the areas of peeling on the head and face with olive or almond oil.
- Give your child enough fluids.
- Adjust the mother's diet. A nursing mother should avoid fried, spicy and sweet foods.
Dry skin causes flaking to spread throughout the body. This leads to the development of wounds, ulcers and cracks, which will bring more discomfort to the baby.
Preventive measures
- Hygiene products and powders should not contain excess dyes and chlorine. At first, you can wash using laundry soap, and then select special baby powders.
- Clothes for babies should be chosen from high-quality natural fabric.
- A humidifier will help maintain optimal humidity levels in the room.
- Bath your child no more than once a day.
- Before going outside, lubricate the cheek area with protective cream.
The health of a baby depends on proper care for it. Attentive parents will not miss the changes that occur on the skin. If the situation worsens, you should contact a specialist.
Source: grudnichky.ru
Dryness of certain areas of the body
On the head
You can often notice that the skin on a baby’s head is peeling. The most common cause is inflammation of the sebaceous glands (seborrheic dermatitis). The sebaceous and sweat glands are not yet sufficiently developed. In this case, there is a strong secretion of sebum, which causes peeling. By the age of one year, these symptoms should go away.
If pathology of the sebaceous glands, an inflammatory process in the body or endocrine disorders are detected, then the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis on the face, head and other areas persist for a long time.
Sometimes crusts can be found in places where a child’s skin peels. 20 minutes before taking a bath, the crusts on your head should be lubricated with oil and while bathing, carefully comb out the softened scales with a soft brush.
On the face
When a child's eyebrows or forehead peel, the reasons may be the following: unfavorable weather factors (heat, wind, frost) or an allergic reaction to foods and medications.
To prevent your eyebrows and forehead from drying out, you need to eat right and avoid medications. You can wipe your face with a decoction of chamomile or calendula.
Behind the ears
If peeling is found behind the ears of a child, the reasons may be as follows.
- Improper hygiene when the ears are not cleaned well enough from accumulated dirt.
- Staphylococcal bacteria.
- Allergy. In this case, peeling can be observed throughout the body.
- Diaper rash can cause redness and flaking behind the ears.
On the cheeks
Peeling of the cheeks can be caused by several factors:
- Diathesis. Allergic reaction to an irritant. Peeling and redness of the cheeks are accompanied by diarrhea, abdominal pain, rash, and itching on the body. Redness usually worsens in the evening.
- Eczema. The disease begins to develop in infants precisely from the cheek area. The skin is red, dry, flaky, and cracks appear.
- The cheek area remains unprotected during walks, so wind or frost dries out the skin, causing redness and peeling.
You cannot remove crusts without first softening them. This leads to irritation and wounds, which can lead to infection. .
Causes of the problem
The most common causes of peeling on the body, head, and face in infants are the following.
- In the first months after birth, the baby's skin becomes accustomed to the environment. Peeling in this case is a natural process. Parents should only monitor the child’s condition more closely. If there is no redness or rashes, the baby eats well and is calm, then there is no reason to worry.
- Improper hygiene associated with frequent use of shampoos, soaps, body lotions during and after bathing. They should be used no more than twice a week. It is better to add decoctions of pharmaceutical herbs (chamomile, sage) to the water.
- The use of potassium permanganate and other products that dry the skin leads to peeling.
- In hot weather, you cannot be in the open sun, and the baby must wear a hat (cap, panama hat). In cold weather, as much of the body area as possible should be covered. You cannot use creams before going outside.
- Dry and hot indoor air. As a result, the baby sweats. You need to carefully monitor humidity and air temperature.
- Allergic reaction. Peeling is most often associated with the first complementary foods. Other symptoms may also appear: stool and digestive upset.
All these causes are easily eliminated and do not require additional treatment. You just need to make adjustments to your diet and hygiene.
There are other reasons why you may experience peeling skin:
- Fungal disease.
- Inflammatory skin disease (atopic dermatitis).
- Infectious diseases: scarlet fever, rubella.
- Congenital ichthyosis (sebaceous glands produce abundant secretions that quickly harden).
- Problems with internal organs (intestinal, kidney diseases).
In these cases, in addition to peeling, the baby also experiences other symptoms. It is necessary to undergo an examination and contact a pediatrician, dermatologist, allergist, gastroenterologist.
Treatment
It is easy to treat crusts behind the ears using folk remedies. They help reduce itching, inflammation, wonderfully nourish the skin, and also speed up the healing process of wounds. Here are the most common ones.
Birch tar
The healing properties of this product are known to everyone who knows at least something about traditional medicine. It can be used for a variety of skin conditions, including flaky skin.
Here, for example, is a recipe for psoriasis. An ointment is prepared based on tar:
- 2 tablespoons of tar, mixed with 3 tablespoons of honey;
- then the mixture is filled with two liters of castor oil;
- egg white is added.
After the product has been infused in a dark place for three days, it should be applied to the affected area 1-2 times a day.
Tea tree oil
This oil helps to effectively fight inflammation, fungus and remove itching. Particularly effective for seborrheic dermatitis. You can use the recipe: mix 10 drops of oil with a quarter cup of jojoba oil.
The mixture is applied to the affected area and washed off with water after 10 minutes.
Aloe vera
This plant effectively fights skin infections and relieves itching. To use it, you need to cut an aloe leaf and apply fresh juice to the flaky skin behind the ear. After drying, wash off.
Olive oil
This product helps soften crusts, eliminates itching, moisturizes and heals the skin. Easy to use: apply a small amount of oil to problem areas and massage. After 10 minutes, rinse with warm water.
Experts recommend using it three times a week until the condition improves.
Egg mask
Thanks to proteins and minerals, it is an excellent nourishing and moisturizing product.
To prepare it, you need to beat the egg yolk and apply it to the affected area behind the ear. Leave on for a short time and rinse off as usual.
Lemon juice
The acid contained in the fruit narrows the sebaceous glands, helping to fight infection.
If you have sensitive skin, then it is better to dilute the juice half and half with water.
For this method, squeeze the juice out of half a lemon, moisten a cotton swab or bandage, and apply it to the affected areas for 10 minutes. Then it is washed off again.
Unusual consequences of an allergic reaction
The child’s body’s response to the action of various allergens can also manifest itself in the form of crusts appearing on the skin behind the ears. True, such a symptom is rarely localized strictly in one place; usually the rash spreads throughout the baby’s body. If the baby is breastfed, the mother will have to reconsider her diet.
First of all, you need to exclude sweets, caffeinated drinks, and whole milk from it, and make sure that the baby is tolerant of fruits and vegetables. Sometimes such a specific reaction is provoked by certain meat and fish products, eggs. For a formula-fed baby, it is worth replacing the usual adapted formula, reconsidering supplementary feeding or complementary feeding.
In addition to food, allergies can be caused by the following factors:
- Children's cosmetics, washing powder, fabric conditioner.
- Pet hair.
- Pollen from outdoor or indoor plants.
- Dust in the room, especially with low air humidity.
If it is difficult to understand the current situation on your own, you need to contact an allergist. Simple tests will help identify allergens that will simply need to be excluded in the future.