A child has many moles on his body - this is not a cause for concern. Nevi are benign formations that arise due to increased production of the melanin pigment. When the formation does not cause concern, it is not necessary to remove it. It is important to monitor the condition and prevent injury; moles rarely turn into malignant tumors.
Do moles grow with the child?
Moles appear immediately after the baby is born or appear under the influence of certain factors. In infancy, you can see several birthmarks on the baby’s face and body. In most cases, marks appear when hormonal levels change.
In medicine, several stages of the development of nevi in children are noted:
- newborns and early childhood: 6 months – 2 years;
- age 5-6 years;
- puberty: 10-12 years.
The formation of the element is associated with an increase in the level of melanocytes in the skin structure.
The main location is the gap between the inner and outer epithelial layers. The more active melanin is produced, the darker the skin will be. Cells containing melanin act as sun protection. The pigment significantly reduces the adverse effects of ultraviolet rays, reducing burns and negative effects on the skin.
The appearance of pigmented areas is a natural process for a child’s body.
The skin that rubs against clothing and areas exposed to chemicals and hormonal drugs are subject to pigmentation. The period of occurrence and development of moles depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
Removal methods
Birthmarks need to be removed when:
- localization in a place of increased trauma;
- bleeding, pain;
- changing size, color, shape, structure.
It is necessary to postpone the removal of nevi in children under the following conditions:
- hyperthermia of unknown cause;
- herpes;
- infectious diseases;
- inflammatory process on the skin;
- immunodeficiency.
Nevi are removed after preliminary diagnosis by a dermatologist.
The doctor collects anamnesis, examines the mole with a dermatoscope, and issues a referral for laboratory diagnostics (general and extensive blood tests). If there are no indications, it is better not to remove the formation.
- The medicinal method includes the prescription of cauterizing drugs (cryopharma, stefalin, lapis pencil). Use is allowed only after consultation with a doctor.
- Hardware methods. The choice of removal technique depends on the size and location of the tumor.
| Name | Peculiarities |
| Radio wave | Exposure to the Surgitron apparatus using high frequency waves (up to 4 MHz). Radioknife is used for small moles located on the surface of the skin. The advantage of the procedure is the absence of scars and scars. |
| Cryodestruction | For fresh birthmarks, removal is carried out with a cotton swab moistened with liquid nitrogen. Nevi located in the deep layers of the skin are removed with a cryodestructor. The disadvantage of this method is the danger of damaging healthy cells. |
| Diathermoelectrocoagulation | Removal occurs by high frequency electric current. The advantages of the method are the absence of bleeding and the ability to conduct histology of cut biological material. It is allowed to use electrocoagulation to remove moles on the face, head, and neck. Complete healing of the wound occurs after 7-10 days. |
| Laser | Non-contact and bloodless removal using laser. Impact on the problem area of the skin. |
The procedures are performed under local anesthesia.
- Surgical excision is performed in a hospital setting. The birthmark is removed with a scalpel. Surgery is resorted to in difficult cases when the nevus degenerates into a malignant tumor. The damaged area takes a long time to heal, and there is a possibility of infection of the wound.
- Traditional methods include lightening nevi with chalk mixtures, celandine ointment, and chamomile. Methods help to temporarily disguise a cosmetic skin defect. It is not recommended to use cauterizing substances (acetic essence, table vinegar, iodine) on moles. Uncontrolled use of cauterizing agents poses a health hazard and leads to burns.
You cannot remove the formation yourself (by tying it with hair). It is not recommended to carry out the procedure in a beauty salon. A doctor should remove the nevus. After disposal, the biological material is sent for histology.
After excision of moles, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Avoid contact of the damaged area with water and cosmetics.
- Avoid direct sunlight.
- Do not take wound healing medications without a doctor's prescription.
Reasons for the rapid growth of a mole
A child’s mole has grown larger – a situation that makes parents worry.
Congenital marks have a specific classification:
- hemangioma;
- spots with a light orange color (stork bite);
- saturated wine stain (fire stain).
Hemangioma is a vascular formation that appears some time after birth.
The size of the nevus immediately increases rapidly. By the age of ten, the element becomes pale and disappears without a trace.
A stork bite is a pigmented cell cluster that occurs on the eyelids, back of the head, and in the bridge of the nose. It looks like a large speck, rich pink in color.
Common are bright red nevi on the scalp, which increase in size as the child grows and disappear with age.
Acquired moles are divided into:
- intradermal;
- epidermal;
- combined.
The first two varieties resemble peas, and the combined type is a smooth formation at the same level as the skin in the form of a brown speck.
The reasons for the increase in nevi are the following factors:
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Hormonal changes.
- Mechanical damage to the skin surface (impact, rubbing, scratch, cut, insect bite).
- Viral infection.
Genetic predisposition contributes to the enlargement of a mole. The more birthmarks mom and dad have, the higher the risk of their formation in the baby.
According to statistics, fair-skinned, premature babies have a higher risk of developing nevi than dark-skinned babies. Girls are more susceptible to the appearance of congenital formations.
When (at what age) do children develop moles - 3 reasons
After the baby is born, the first moles appear in the first months of life. Without knowing the reason for the appearance of nevi in newborns or older children, parents can become very panicky. They are afraid of the possibility of degeneration into a malignant form. A pediatric dermatologist can dispel all fears and clarify things.
Features of children's moles
Moles are dark spots that appear on the skin of the face and body of most people after birth.
The peculiarity of moles in newborns is that with age they completely disappear or their number increases significantly. Moles in children form when pigment cells containing melanin accumulate in one place.
Predisposition to pigment elements occurs during embryonic development. Nevi can be localized in various places, and also have a variety of shapes, colors and sizes. These benign formations are sometimes prone to the process of malignancy. Over the course of a lifetime, the number of nevi changes many times.
The appearance of moles in children
Why do they appear in children and what are the norm?
When moles appear in children, dermatologists attribute this to one of the reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. The hereditary factor is the most common and natural. The number and localization of children's nevi directly depends on these parameters characteristic of his father, mother or grandparents.
- Internal reasons. Pigment formations often appear or disappear against the background of hormonal changes in the body. This is most pronounced after two years, and then during puberty. The natural increased formation of moles is characteristic of the period when a woman is carrying a child.
- External reasons.
In addition to the factors affecting the child's maturation, exposure to direct sunlight also changes the activity of melanocytes. Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, a mole can change its size, color, and even degenerate into an oncological pathology - melanoma.
Doctors are also trying to link the appearance of pigment elements with injuries to the skin. There is an assumption that increased childhood pigmentation develops during a period associated with injuries, insect bites or viral infectious diseases.
In newborns
Moles in newborns look like light, barely noticeable birthmarks. they are considered safe if their diameter does not exceed 6 mm.
and elements with a diameter of over 10 cm can provoke the development of melanoma.
Visually, such formations resemble spots, nodules, nodes or warty formations of a dark brown color or with a different color (Mongolian spot, blue nevus).
from six months to two years
Moles actively begin to appear in six-month-old children, and continue until the age of two. This is typical for children at this age, as they spend a lot of time in the open sun. 1% of children of this age experience melanocytic nevi.
from five to seven years old
Further, moles in children begin to actively form at the age of 5-7 years. This age category is characterized by dramatic changes in weight and height. The favorite localization of nevi in children is the lower torso, upper back, forearms, chest, proximal parts of the upper and lower extremities.
in adolescence
Most often, moles appear in adolescents during puberty. During puberty, when hormonal levels change greatly, moles acquire a bright color and become larger. On the body of teenagers you can find many small moles that appear at great speed.
kinds
Among the large number of moles in a child, there are 2 main categories of such formations: vascular and pigmented. The borderline and complex form of nevi can appear in the plural. Complex pigment formations can reach 10 mm and have a spherical shape with a dense consistency.
Borderline nevi include uniform, pigmented spots that have an oval or round shape. Such structures are smooth, have clear boundaries and lack hair.
Vascular moles in a child
Vascular moles are often diagnosed in a child. They consist of many blood vessels. The color of such formations varies from pink to bright red. Vascular nevi can be flat or convex. These neoplasms do not have malignant cells. They are removed not to prevent the development of melanoma, but for aesthetic reasons.
Common nevi
Parents should not be particularly alarmed by ordinary nevi that appear on the body of their babies. They have a smooth surface and their color varies from light brown to black.
Such formations are not prone to malignancy and do not cause significant discomfort.
The number of moles in each person varies, but if there are more than 20 of them, then they need careful monitoring.
Wine stains
When a baby develops purple-red spots with a slightly convex structure, such formations are called port-wine stains or fiery nevus. This spot on the skin of newborns remains unchanged with age. Any part of the body or face is suitable for localizing such spots.
A fiery nevus is an area of skin with dilated small blood vessels.
When the face becomes covered with port-wine stains, it is advisable to have the child examined by a neurologist, since in clinical practice there are cases of a relationship between a fiery nevus on the face and pathological abnormalities of the brain.
Stork bites
Flat red spots on the baby's skin have a popular name - stork bites. They typically appear on the baby's forehead, eyelids, between the eyebrows, around the nose or mouth, and in the back of the head. As the child grows older, they become lighter and by the age of two it is not possible to visualize them. They appear only during the whims of the child, when he is very tense.
How can they be dangerous?
Moles are completely safe formations, but they require targeted control. Parents are recommended to examine the child’s body from time to time in order to analyze the condition of existing nevi and record the formation of new ones. Patients with a large number of large pigmented elements should consult a pediatric dermatologist regularly.
Doctors identify suspicious and potentially dangerous moles in children. They classify as suspicious neoplasms that did not appear immediately after birth, but at an older age. Those formations whose diameter is more than 10 mm or those that have sharply changed their color (turned black, become spotted) are considered potentially dangerous.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
It is recommended to regularly monitor the condition of nevi and keep records of new formations. If any changes, even minor ones, appear, it is still better to make an appointment with an oncological dermatologist. A visit to the doctor should not be postponed if the following symptoms appear:
- the skin pattern disappears on the surface of the mole;
- the formation acquires a glossy shine;
- the edges of the pathological element become uneven and the shape becomes asymmetrical;
- the mole dynamically increases or decreases in size;
- the nevus itches and a burning sensation appears in it;
- peeling appears around the pigment element;
- hair falls out on the skin adjacent to the nevus;
- the mole changes color or ulcers appear on it;
- the formation begins to bleed;
- daughter pathological elements appear;
- A red rim or white spot appears around the nevus.
If a child has more than 10 moles on his body, this is a reason to consult a dermatologist. A skin passport will be created for the baby, containing the number and size of the largest tumors.
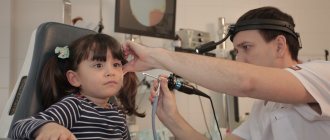
During the examination, the doctor examines changes in the skin using a dermatoscope.
Every 6 months, preventive examinations allow us to identify new dangerous elements and see the dynamics of the development of old ones.
Doctors recommend removing moles in children if they have spread across the skin under the eye or are uneven in color. A convex pathological element is removed when it completely or partially changes color and also has other pathological symptoms. The degree of danger of malignancy of any pigmented neoplasm is assessed by an oncologist.
Children have mostly normal nevi that do not cause any particular discomfort (no itching, bleeding, peeling, change in color or size). However, vigilant parents even prefer to consult with a doctor about such formations, who will examine the child and explain that it is necessary to choose a sunscreen and use it for preventive protection.
If the baby’s body or face has multiple nevi, then parents should show it to a dermatologist and oncologist.
If the formation turns out to be benign, then the parents will be able to sleep peacefully. And if melanocytic nevi are identified, it will be possible to begin adequate therapy in a timely manner.
, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter. We will definitely fix it, and you will get + to karma
(1 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Diagnosis of a growing nevus
Parents who notice that a dark and flat mole is growing in their child should definitely consult a pediatrician or dermatologist for advice. The doctor will conduct an examination and determine the type and danger of the stain. The degeneration of a benign lump into oncology in infancy is rare. It is necessary to observe the reaction and behavior of a child with marks.
Growths occur on skin areas with reduced immune defenses.
A weakened body is the main factor in the change in color and shape of the birthmark.
The doctor may additionally conduct an examination:
- dermatoscopy - examination of the spot on an enlarged scale, the method determines the malignant type of mole;
- Digital dermatoscopy – obtaining a clear image with a nevus approaching several times.
It is difficult to determine the type of growth on your own; you should visit a specialist in a timely manner.
Types of operations
The issue of removal is an individual decision for each person. But there are times when it is necessary to follow a specialist’s decision. If examination shows that the tumor is malignant, it should be removed immediately.
Types of operations:
- electrocoagulation. This method is used to remove both small hanging moles and flat ones. During the procedure, discomfort may occur. Scars may remain at the surgery site;
- laser removal. The procedure is painless and quick. The disadvantage of this method is that a new one may appear at the site of removal;
- surgical removal. During the procedure, the tumor and part of healthy skin are removed. Upon completion, stitches are applied. The main advantage is the impossibility of tumor formation again.
So, each person decides how to get rid of this problem independently, but only after consulting a doctor.
Is it necessary to remove a child's mole?
Small flat spots do not pose a threat to the life of a small person. Statistics show that in 40% of cases of tumor formation, oncology occurs. A small number of marks on the arm or back is not a cause for concern if the spots are not subject to friction.
If you constantly find new marks with a diameter of more than 5 mm, you should see a doctor. He will conduct a professional diagnosis and advise on possible treatment options. You shouldn’t delay going to the hospital when your baby accidentally rips off a bulging formation: the injury is the impetus for destructive phenomena in the body.
A special laser is used to remove dark spots in childhood on the temple, neck, and nose. After the manipulation, the baby may be left with a burn; it will take some time for rehabilitation.
You can remove spots on your leg using radio waves. The main advantage of this technique is that it does not affect healthy skin areas.
Removal takes place without pain or bleeding.
A reliable and safe method of getting rid of a mole is cutting it out with a surgical scalpel. There are no contraindications, the risk of relapse is reduced to a minimum level. The disadvantage is the presence of a scar. This method is not recommended for use in children. It is better to opt for laser removal
Dangerous changes in moles
As the child’s body grows, the number of nevi that appear also changes. It may decrease or increase. The nevi that we are used to seeing appear on a child’s skin at the age of 5–6 years.
If there are a large number of moles, it is necessary to monitor each one. This is the only way to notice in time the degeneration of a nevus into a cancerous tumor.
Nevi are considered dangerous if they can develop into cancer or look very similar to a cancerous tumor. Such neoplasms are susceptible to malignancy. That is why experts strongly recommend getting rid of such formations. They should be removed as soon as possible. After the procedure, the tissue is sent for histology. If it turns out that the tissue was cancerous, chemotherapy should be given, which will destroy all the cancer cells remaining inside the body.
The classic signs of a malignant neoplasm are:
- The appearance of an additional structure on the mole (bump, bulge, ulcer, crust, etc.).
- In a short period of time there has been a significant increase in size.
- Continuous itching in the area of the mole.
- Painful sensations of varying intensity near the formation.
This symptomatology is classic, but it is not always present. Doctors suggest that the most accurate indicator of a malignant nevus is its difference from others found on the body.
Dangerous accompanying symptoms
Any spots on the baby's body should be controlled by parents. Periodic examination allows you to notice the first signs of transformation of moles into melanoma:
- Asymmetry: in its natural form, a nevus is an even geometric figure, an oval or a circle, the halves are symmetrical in relation to each other. The growth of one part of the spot is an important symptom for examination.
- A healthy mark has smooth edges, while a pathological mark has blurred borders with jagged sides.
- Change in color: uniform color and color is normal, the presence of inclusions or a change in tone is a sign of deformation of the spot.
- If the diameter exceeds 6 mm, you should visit a doctor.
- Hair loss in the affected area.
If one of the above symptoms is detected, you must seek help from a medical facility to avoid dangerous consequences.
Description
Hanging moles are a benign tumor that occurs due to the accumulation of melanin located in epithelial cells. As a result of this process, moles become larger. They are dark in color, with smooth, slightly raised edges above the surface of the skin. If they are damaged, there may be a risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor. Such formations on the body are very dangerous and unpleasant. The person feels uncomfortable. They can easily be injured or torn off. They tend to be reborn. Also, many are confused by their appearance.
Possible complications and precautions
The main feature of a progressive pathological process is that the tumor grows rapidly in a short period of time (over the course of a month). When a white mark forms around a birthmark, do not be alarmed; this is a sign of Setton’s nevus. It occurs as a consequence of sunburn and disappears on its own after some time. A dangerous signal is the growth of moles throughout the body. This phenomenon requires specialist supervision.
Precautions to be taken:
- Limit children's exposure to the sun between 11 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Protect your skin from ultraviolet rays with sunscreens and lotions.
- In hot weather, wear a hat and walk with your baby in the shade.
- If the tumor is injured, it is necessary to treat it with hydrogen peroxide and immediately contact a specialist.
Treating stains using folk remedies at home is prohibited due to the risk of complications.
Inspection of suspicious elements should be carried out at an early stage to avoid undesirable consequences.
On the neck
Moles located on the neck pose a double risk.
They constantly interact with clothing parts, which can lead to injury. And if it does occur, you should immediately treat it using hydrogen peroxide and cauterize it with brilliant green. Injured moles can bleed for a long time and take a long time to heal if they are not treated.
Interaction with sunlight is also dangerous, especially in the warm season, when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet rays. Exposure to the factors mentioned above can lead to the formation of a malignant tumor.