The temperature of the human body is maintained within a certain narrow range.
This is done using the following mechanisms:
- dilation of skin blood vessels - this increases blood flow to the surface of the body and active loss of excess heat;
- stimulation of sweat glands - liquid evaporating from the skin promotes rapid cooling.
Sweat can be produced without an adequate stimulus, i.e. when there is no hyperthermia. This is how the sympathetic nervous system in most cases responds to some painful processes occurring in the body.
When children are hot, they move actively and become wet; this does not surprise or frighten parents.
When a child sweats at night or during the day for no apparent reason, many simply panic, especially if this happens often.
The term "cold sweat" is most often used to refer to sweating at normal temperatures when the body is not hot to the touch.
What causes cold sweat?
Cold sweat in a child is a reason to monitor the conditions in which he sleeps. If your child's room is hot, sweating may be inevitable. Sweating is sometimes observed after active games; it intensifies if the child is dressed warmly inappropriately for the season. Infants sweat intensely during feeding, since this process takes a lot of energy. All these causes of sweat are not scary. If they are neutralized, sweating will disappear and the baby will feel comfortable.
It also happens that profuse sweating is a sign of disruption of the internal organs and systems in the baby’s body.
If parents are sure that the baby is not overheating and there is an optimal air temperature in his room, but he continues to sweat in his sleep, this may be a symptom:
- lack of vitamin D, which can cause a disease such as rickets;
- lymphatic diathesis;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- endocrine disorders;
- VGSD;
- acute respiratory infections;
- allergies.
Sweating can be caused by taking certain medications. Sometimes it will persist for several days after the baby has recovered.
Why is fever dangerous?
Hyperthermia, on the one hand, is considered a beneficial phenomenon that confirms the good functioning of the immune system. The protective mechanism makes adjustments to physiological processes, redirecting blood flow to vital organs. With “white” fever, the toddler’s legs are the first to suffer, as they do not receive enough of their portion of lymphatic fluid.
Despite the fact that an increase in temperature creates unfavorable conditions for pathogenic organisms, in some cases, fever harms the child, especially if the disease is caused by a virus. In this case, pathogens multiply inside cells. By influencing the pathogen, the defense system also kills the infected cell - it and the virus have the same protein coagulation temperature.
Another danger of “white” fever is the disruption of the interaction of the 2 components of thermoregulation (production and output). Therefore, antipyretic drugs themselves do not always work, which is why the baby’s hydro-salt balance is lost, and the body may overheat.
Convulsive syndrome
As a result, the body produces toxins that affect the central nervous system. When a high temperature persists for a long time, the child begins to have convulsions, delirium and even death are possible.
Sweating in infants
Infants are considered children under one year old. Their thermoregulation is not easy to adjust to environmental conditions, so cold sweat usually occurs due to overheating.
You shouldn’t risk your child’s health, it’s better to be safe than sorry
Sometimes the cause of this condition may be a very soft bed or sleeping objects made of synthetic materials. If the child is not overheated, sweating should not occur.
When sweating continues to appear, you need to show the baby to a doctor, since there is a risk that the baby has health problems. Grudnichkov also breaks into a sweat due to psycho-emotional disorders.
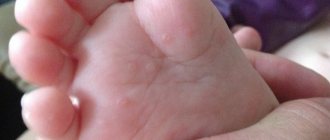
Allergies in babies under one year of age often manifest themselves as profuse sweating at night. The occurrence of cold sweat in a child during sleep may be associated with teething.
Children under one year old may sweat while sucking on their mother's breast, which is explained by the fact that they put a lot of effort into this. It also happens that sweating in a dream is a sign of rickets.
If a baby under one year old sweats due to pathological changes in the body, in addition to sweating, other symptoms may appear:
- cough;
- tearfulness;
- skin rash;
- temperature increase;
- lack of appetite;
- restless behavior, moodiness;
- bad dream.
The main signs of "white" fever
Why does a child under one year old have a fever, what to do?
Hyperthermic syndrome is a pathological variant of a febrile state, leading to dysfunction of vital systems and organs. It manifests itself as a consequence of a neglected situation.
Depending on what became the main cause of the phenomenon, fever is divided into 2 types. In children, “red” hyperthermia is more common, which is characterized by the corresponding color of the skin, wet limbs that are hot to the touch, and rapid breathing. The prognosis for this type of fever is favorable, since heat production in the body corresponds to heat transfer.
Despite the temperature rising to febrile levels, “red” hyperthermia does not affect the child’s behavior. “White” fever should cause concern for the mother.
Dangerous symptoms
High temperature and cold extremities in a child are the main signs of “white” fever. The phenomenon got its name due to the symptom of a “white spot” that occurs at the point where a finger presses on the dermis. Other “landmarks” include:
- marble-pale dry skin;
- bluish tint to lips and nail beds;
- breathing failure;
- chills;
- convulsive state with trembling of arms and legs.
White fever
The baby’s behavior is also disrupted - he becomes lethargic, indifferent to everything, eats practically nothing and sleeps poorly.
Sweating in school-age children
The situation with thermoregulation in children stabilizes after a year, but sweating can make itself felt when they overheat.
Sometimes you have to take pills for hyperhidrosis
If a child has a cold sweat, this may occur against the background of severe headaches. When there are pressure surges or pathologies of the nervous system are observed, vascular spasm occurs.
Often at this age, the cause of sweating is considered to be a negative reaction to taking medications. In this case, you should go with your child to the doctor so that he can find an alternative to this or that medicine.
School-age children often experience stress and severe emotional stress, which leads to depression, when cold sweating is a natural phenomenon.
If cold sweats appear, this may indicate more serious causes, so in order to rule them out, you need to consult with your doctors.
Conditions that cause night sweats include:
- tuberculosis;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- hepatitis.
Prevention
Preventive measures can not only improve the condition of the child’s feet, but also strengthen his immunity. You can reduce the level of hyperhidrosis of the legs in children in the absence of pathological causes using the following simple steps:
- therapeutic foot massage;
- hardening;
- careful foot hygiene, rinsing with herbal decoctions;
- use of orthopedic shoes made of natural materials (especially winter ones);
- socks and tights must be cotton, without the addition of synthetic threads;
- regular ventilation of premises;
- clothing for the weather.
Note! Foot massage can be done in a variety of ways. An interesting method is to walk barefoot on warm rice or buckwheat. This procedure improves blood flow, innervation, and stabilizes thermoregulation processes. The duration of exposure is 15-20 minutes. You shouldn't jump or run - you just need to stand or walk around. For infants, you can apply warm cereal in bags and massage the baby’s legs with it.
Hyperhidrosis in the leg area in a child is considered a symptom of physiological and pathological causes, therefore, if this condition persists for a long time, you should consult a pediatrician to assess the health of a child of any age.
Diagnostics
What diagnostic measures are required depends on the general health of the child.
The doctor will tell you how to properly care for your child’s skin.
He may be assigned:
- vitamin D test;
- blood analysis;
- urine test;
- glucose tolerance test;
- Ultrasound of the brain and thyroid gland;
- cardiogram.
How to measure temperature correctly?
Mercury or electronic thermometers can be used to measure body temperature. Currently, most parents prefer improved models that are safe. Mercury thermometers are easy to break, but they are more accurate.
Temperature can be measured in the following ways:
- orally – in the mouth;
- rectally - in the anus;
- in the armpit;
- on the forehead and in the ear - special infrared sensors are used.
The most famous way to measure temperature is under the armpit. Rules for the procedure:
- do not take measurements after meals or physical activity;
- place the thermometer in a clean and dry armpit;
- keep your hand tightly pressed (it is better for parents to hold the baby’s shoulder) - the temperature in the armpit should be equal to the body temperature;
- do not raise your hand for 5-7 minutes when using a mercury thermometer, until characteristic signals occur when using an electronic device.
It is more convenient for newborn children to measure the temperature rectally, since they cannot hold their hand. Basic Rules:
- lubricate the tip of the device with oil or Vaseline;
- put the baby on his side or back with his legs bent;
- slowly insert the thermometer into the anus 1.5-2 cm;
- hold the baby in position for the required time.
It is better to measure the temperature in the mouth for children over 4 years old, since children cannot hold the thermometer correctly. Measurements should not be taken after consuming cold drinks or food. The tip of the device must be placed under the tongue and held with the lips for a certain time.
Cold sweat before and after illness
Sweating during a viral or infectious disease is a natural phenomenon. It can occur with ARVI, pneumonia and the common cold.
A disease such as pneumonia is not always characterized by an increase in temperature; it also happens that it occurs without pronounced symptoms at all. The only thing that can remind you of it is profuse sweating, dry cough, chest pain.
Asymptomatic pneumonia most often occurs in children with weakened immune systems, when the body finds it difficult to fight infection. Pathogenic microbes travel through the bloodstream throughout the body and provoke pathological changes in the functioning of all organs.
Sweating in children may be a sign of serious illness
With ARVI and colds, the main symptom is cold sweat that occurs at night. In this way, the body tries to remove accumulated toxins. Severe sweating in a child with ARVI may indicate the presence of complications caused by the disease.
If during a cold the child took a large amount of antipyretic drugs, then after recovery, sweating may still occur as the body temperature begins to gradually return to normal.
When antibiotics are taken and the temperature drops significantly, cold sweat may appear. This phenomenon is considered normal, but provided that it is distributed evenly. Otherwise, you will need to consult a doctor.
What body temperature is considered elevated?
The marker with which the individual indicator is compared is considered to be a parameter of 36.5°C. In healthy children, it may differ slightly within 0.2-0.3°. As for newborns, their body temperature is slightly elevated, this is considered normal. The entire gradation of indicators is presented by the following data:
- subfebrile – 37-38°;
- moderate-high – 38-39°;
- high – 39-40°;
- dangerous – 40-40.5°.
The baby has cold hands and feet at normal temperature
A moderate-to-high temperature may not always mean that a serious illness is present. Here you need to take into account the general condition of the toddler and the presence of signs confirming the problem.
Important! A reading above 39.1° is called hyperthermic and is a cause for concern, regardless of how the baby tolerates the rise in temperature.
Treatment
If parents notice that their baby is sweating at night and has a low temperature, first of all they need to address the cause that led to this process. Treatment may be delayed if sweating is the result of complex diseases.
If your child sweats a lot during sleep, you should pay attention to this.
The doctor will draw up a treatment regimen and select drugs that slow down the secretion of secretions at the cellular level and medications that affect the activity of the nervous system.
If health problems are detected in an infant, you should definitely consult a neurologist.
Parents' actions when the temperature rises
The first action of many mothers when the thermometer reading is high is to immediately give the baby an antipyretic. Before doing this, you should find out why the baby has a fever, and also try to identify accompanying signs.
When to lower your body temperature
Doctors recommend not lowering low-grade fever to allow the body to fight the disease. There is a nuance here: if with a “red” fever you can reach 38.5°, then with a “white” fever you should not wait for the mercury to creep beyond the low-grade fever line.
Regardless of the form of hyperthermia, antipyretic medications are prescribed to children at risk if the thermometer shows above 37.5°. This category includes:
- babies in the first months of life;
- those suffering from febrile seizures;
- children with central nervous system pathology;
- having metabolic problems of a hereditary nature;
- who have chronic lung and heart diseases.
When conducting home therapy, the mother monitors the baby’s temperature every 30-60 minutes. If the indicator has dropped to a safe level and remains stable, the drug effect can be stopped and the immune system can be allowed to reduce the levels to normal without additional intervention.
First aid
Having diagnosed a child with a high fever and cold feet, the mother should immediately provide the baby with all possible help. Activities include the following:
- intramuscular administration of a lytic mixture containing an antipyretic (Analgin), a vasodilator (No-shpu, Papaverine or Dibazol);
- if the baby is over a year old, they are additionally given an antihistamine (Diazolin, Pipolfen, Suprastin);
- rub the entire body (with gentle movements so as not to damage the skin) - this stimulates blood circulation;
- a warm heating pad (37°) is applied to the feet.
How to bring down a fever
Injections can be replaced with tablets: Analgin, Ibufen or Paracetamol. A single dosage of medications is selected taking into account the age of the baby.
To normalize heat exchange, the baby should be warmed by wrapping it in a blanket (provided that the indicator does not go off scale beyond 38.5°). It is better to keep the room temperature within 18-20°.
Additional measures
If the immune system “decides” to increase body temperature by at least 1°, the body will need an additional volume of fluid: 10 ml is needed for every kilogram of body weight. The toddler can drink warm water, tea, milk. A decoction of raisins in combination with dried apricots and dried fruits will give the best effect.
It is advisable to keep Viburkol anal suppositories (or similar ones) on hand. They not only have antipyretic and analgesic properties, but also have an anti-inflammatory and calming effect. The drug copes well with cramps and helps neutralize toxins.
When to call an ambulance
If no antipyretic effect is observed within half an hour, it is necessary to call a specialist at home or (if possible) take the baby to the hospital. The following signs indicating the severity of the condition should be the reason for contacting an ambulance:
- whimpering and sobbing of the baby;
- weakened voice;
- dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes;
- the appearance of acrocyanosis and pallor;
- change in skin color.
It's time to call an ambulance
Advice. Lethargy, weakened attention of the toddler, convulsive syndrome - all these are reasons to seek medical help.
What will happen when the doctors arrive?
The doctor who arrived by ambulance first assesses the situation and talks with the mother to clarify the nature of the problem. If the specialist ascertains “red” fever, which does not pose a threat to the baby’s health, then, after providing the necessary assistance and giving the mother recommendations for care, he will leave, leaving the child at home.
If “white” hyperthermia is diagnosed, the baby will most likely be taken to the hospital. Reasons for hospitalization will also be:
- the hoarse moaning voice of a baby;
- hysterical crying;
- if the child does not sleep at all or, on the contrary, does not wake up;
- when the baby is indifferent to his surroundings and does not respond to stimuli.
In special cases, resuscitation of the baby begins on the way to the hospital - in the ambulance.
When does a child need medical attention?
If the body temperature is low, the child needs help at home:
- warm newborns with your body and attach them to the breast;
- put on warm clothes for the baby;
- drink hot tea.
If actions do not lead to normalization of the value, you should consult a doctor. Symptoms that require immediate consultation with a specialist:
- severe lethargy and apathy;
- drowsiness;
- loss or complete absence of appetite;
- causeless whims.
Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist, graduated from Samara State Medical University with a degree in Pediatrics. Read more »