Vulvitis in women, the symptoms and treatment of which are determined by the cause that provoked the disease, ranks first in the list of gynecological diseases. The pathology is accompanied by unpleasant, uncomfortable sensations in the vaginal area. Lack of treatment is fraught with the spread of infection deep into the reproductive system.
What it is?
An acute inflammatory process that affects the external reproductive organs in girls is called vulvitis. This is a fairly common pathology in pediatric gynecology. The peak incidence occurs between the ages of two and ten years. In adolescence, there are practically no cases of vulvitis.
The external genitalia include the vagina, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and the external urethra. These organs are covered on the outside by mucous membranes lined with epithelial cells. Due to various reasons that provoke the disease, inflammation develops. It triggers a whole cascade of inflammatory reactions that provoke the appearance of uncomfortable symptoms in the baby.
Various provoking factors can lead to the development of vulvitis:
- Incorrect or overly active hygiene procedures. Daily washing with antiseptic agents can lead to changes in the pH of the vaginal environment. With regular use of such products, the mucous membrane of the external genital organs dries out excessively and becomes very susceptible to any infection.
- Infection with various helminths . When multiplying, these parasites produce a large amount of toxic products that can cause various irritations and redness in the genital area.
- Severe hypothermia. This leads to a decrease in the level of local immunity. Too low a body temperature contributes to impaired blood flow in the genitals, which causes an inflammatory process.
- Chronic diseases. Most often, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system provoke inflammation in the reproductive organs. To eliminate unfavorable symptoms, it is necessary to prescribe treatment for the underlying chronic disease, which also provoked inflammation in the genitals.
- Traumatic. Babies often explore their bodies in the first years of life. During this, they may accidentally injure themselves. In adolescents, vulvitis may occur after using tampons during menstruation.
The variety of reasons leading to the development of vulvitis contributes to the emergence of different variants of the disease. This classification is very important. It helps to correctly determine the form of the disease, as well as establish the necessary algorithm for diagnostic measures and treatment prescriptions.
There are several types of vulvitis:
- Allergic. Occurs in various types of allergies. An atopic variant may occur in infants. In some cases, it occurs as a result of wearing diapers for a long time. Their long-term use leads to disruption of vaginal pH and more rapid development of various irritations.
- Bacterial. Occurs as a result of infection by bacteria. Most often these are staphylococci, streptococci, hemophilus influenzae, and aerobic microorganisms. They cause predominantly purulent forms of the disease. Treatment requires antibiotics.
- Viral. They develop as a result of infection with various types of viruses. The most common culprits of the disease are herpes. With a decrease in immunity, the baby develops inflammatory changes in the area of the external genitalia.
- Fungal. Most often develop as a result of candidiasis infection. They can also occur in frequently ill and weakened children. Quite often recorded in girls suffering from diabetes. To eliminate adverse symptoms, the prescription of antifungal drugs, mainly in the form of ointments or creams, is required.
- Traumatic. Occurs after various injuries. The mucous membranes of the external genitalia in childhood are very loose and easily injured. When a bacterial infection enters through various microdamages, a secondary infection can develop.
- Adhesive. Appear during chronic vulvitis. They occur only in cases where timely treatment was not provided. With this form, fusion of the labia occurs. Doctors consider impaired urination to be one of the first symptoms of this variant of the disease.
Causes of itching
Irritation in a child’s intimate area can occur due to various reasons. Redness and itching are a specific reaction of the skin and mucous membrane of the genital organs to an external or internal irritant. This phenomenon is often observed in girls aged 7–12 years, although the problem can appear at 5. In some cases, the malaise can be eliminated by changing hygiene products, in others serious drug treatment will be required.
Poor hygiene
In the first years of a child's life, the responsibility for care lies with the parents. Violation of a girl's personal hygiene leads to problems. Rare and improper washing causes irritation and redness of the intimate area. Unwashed hands and dirty underwear can cause inflammation in the perineum.
The infection occurs due to hypothermia of the body in winter. In summer, it is provoked by swimming in dirty ponds and contact with sand and earth on the genitals.
Care products
The cause of the trouble may also lie in the incorrect selection of personal care products. They are often replete with all kinds of dyes, fragrances, additives and other harmful chemical components. Delicate baby skin reacts negatively not only to soap and shampoo. Wet wipes, diapers, soap, toilet paper and even baby cream can cause redness.
Symptoms
Vulvitis can occur with the development of numerous unfavorable symptoms. With a mild course of the disease, they do not appear clearly enough. In such cases, only a pediatric gynecologist can detect the disease. A more severe course of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of a whole complex of unfavorable symptoms that are quite difficult to treat.
The main clinical manifestations of vulvitis include:
- Swelling and inflammation of the external genitalia.
- Redness in the vaginal area and genitals.
- Severe discomfort in the anogenital area.
- The appearance of discharge. They can be of different colors and consistencies. Bacterial infections cause yellow or green purulent discharge. With viral vulvitis, a gray discharge is formed, with a fairly liquid consistency. Fungal infections are accompanied by the appearance of abundant whitish discharge that crumbles easily.
- Urinary dysfunction. The urge to urinate becomes more frequent. The portions of urine are reduced, but the total amount per day does not change.
- Pain in the external genital area. Inflammation provokes increased pain during urination.
- Increased body temperature. In severe cases, fever may develop. A sluggish disease is not accompanied by a change in body temperature. It may not exceed the norm during the entire acute period of the disease.
- Changes in behavior and general condition. Girls become more nervous and capricious. In some cases, sleep is disrupted. The baby's mood becomes very depressed.
Treatment
To eliminate adverse symptoms, effective treatment is required. When the first manifestations of vulvitis appear, the baby should be shown to a pediatric gynecologist. The doctor will conduct a clinical examination and prescribe all the necessary tests and studies. Colposcopy and bacterial culture of the discharge make it possible to accurately identify the causative agent of the infection, as well as determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
The following are used in the treatment of vulvitis:
- Painkillers. Help eliminate pain in the area of inflamed external genitalia. Prescribed in the form of ointments, creams and various sprays. To treat vulvitis, you can use Miramistin, Furacilin, Levomekol and other drugs.
- Antiseptic. Eliminate irritation and redness. Infusions prepared from medicinal plants also successfully cope with adverse symptoms. For treatment, decoctions of chamomile, calendula, string, and oak bark are used. They can be used in the form of baths, lotions, and also for hygienic treatment of the genitals.
- Anti-inflammatory . Prescribed to eliminate severe inflammation. They help eliminate the consequences of allergic vulvitis, accompanied by severe itching and burning. Various antibacterial and hormonal ointments are used: tetracycline, hydrocortisone, erythromycin and others. They should only be applied to clean and pre-dried genitals.
- Antihistamines. They help eliminate severe swelling of the genital organs, as well as eliminate itching and burning. These drugs are especially effective in the treatment of allergic forms of vulvitis. Prescribed in tablet form for 5-7 days. These include “Suprastin”, “Claritin”, “Fenistil”, “Tavegil”, “Diphenhydramine” and others.
- General strengthening. These include rectal suppositories that help activate the immune system. In pediatric practice, interferon-based drugs are most often used. Regular use of multivitamin complexes will help strengthen the immune system and make the baby stronger, which is very useful for fighting the disease.
Dr. Komarovsky will name the causes of vulvovaginitis in girls and warn mothers against using soap too often when cleaning girls.
Vulvitis is an inflammation of the female external genitalia due to injury or an infectious process. Vulvitis can affect the vestibule of the vagina, labia, clitoris, and the outer part of the urethra. The disease ranks first among all gynecological infections in girls 1-8 years old. It is about 65-70%.
Primary vulvitis in girls is more often due to the anatomical features of the genitals. With prolonged and recurrent vulvitis at a younger age, menstrual irregularities and problems with reproduction may occur in the future.
Vulvitis - diagnosis
Inflammation of the vulva can be detected during an examination of the patient in a gynecological chair. The gynecologist collects the patient’s medical history, taking into account her complaints. To make a final diagnosis, the information obtained is supported by colposcopy and laboratory results. Before treating inflammation of the vulva, they try to establish the type of pathogen. Among the diagnostic techniques used:
- smears from the vagina and urethra;
- bacterial sowing;
- cultural inoculation to determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
Causes
At birth, girls' genitals are sterile. Gradually, opportunistic microorganisms appear on their mucous membranes. At first, the vaginal environment has a slightly alkaline or neutral pH. There are no lactobacilli in the smear; there are leukocytes and mixed microflora. Lactobacilli appear around puberty. Gradually, the vaginal environment oxidizes and glycogen begins to be produced. It becomes similar in composition to the microflora of sexually mature women in girls with the advent of menstrual cycles.
The immediate causes of vulvitis are nonspecific or specific infections:
- viruses (adenovirus, influenza, papillomavirus);
- fungi;
- protozoa;
- chlamydia;
- gonococci.
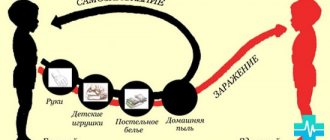
Ways of transmission of infection:
- in newborns, infection can occur when passing through an infected birth canal;
- at a younger age, the everyday route predominates (in places of public use, if hygiene rules are not followed);
- in case of sexual experience in adolescents - sexually.
Vulvitis often occurs in the presence of helminthic infestations or penetration of foreign objects (grains of sand, insects, blades of grass) into the genitals.
Secondary vulvitis in girls develops as a result of the spread of infection into the vulva from other foci (tonsillitis, caries).
Find out the instructions for using Linex for children.
How to tie a sling - a scarf for a newborn? Read the answer in this article.
Fungal infection of the vulva occurs due to:
- taking antibiotics;
- endocrine disorders;
- weakening of the immune system.
When an allergic reaction occurs to certain irritants (fragrant detergents, sanitary pads, chocolate, citrus fruits), atopic vulvitis develops. It doesn't happen often.
The genital mucosa can be damaged by frequent, diligent washing with soap, wearing tight underwear, or improperly selected diapers.
Abnormalities of the genitals also predispose to vulvitis:
- absence of posterior commissure;
- abnormal development of the external genitalia;
- low location of the urethral opening.
Why is vulvitis dangerous in women?
Faced with the disease, a woman asks the doctor a question about why vulvitis is dangerous and how it is treated. Untimely or incorrect treatment of the disease is fraught with the transition of the inflammatory process to other organs of the reproductive system. Endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, adnexitis are common complications of vulvitis in women, the symptoms and treatment of which are discussed in the article. In some cases, after healing of erosive surfaces, adhesions are formed in their place - synechiae, which interfere with normal sexual life and childbirth.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of vulvitis in children are in many ways similar to other genital infections (colpitis, vulvovaginitis).
Signs of the disease:
- burning and itching;
- pain in the genital area, which becomes more intense when urinating;
- swelling and redness of the clitoris, labia, vulvar mucosa;
- Sometimes there are erosions and ulcers on the mucous membrane.
Vulvitis in girls is characterized by vaginal discharge (leucorrhoea). They can be different, depending on the type and cause of the disease. They are mostly clear, but can sometimes be purulent or bloody. If the cause of the disease is E. coli, the leucorrhoea has an unpleasant fecal odor and a greenish-yellow color. If the infection develops when the vulva is affected by staphylococci, they are viscous and yellow. Vulvitis of a fungal nature is accompanied by a cheesy, white discharge.
General disorders of the body and gynecological diseases
If an intimate place itches, not all girls are ready to tell even a loved one about it. If the mother notices that the child is constantly touching himself between the legs, he should immediately see a doctor.
Allergy
Rash and irritation in the groin are especially typical for children in the first year of life. This is often due to the use of low-quality diapers. Prolonged contact of delicate skin with urine and feces disrupts the protective functions of the skin, which causes diaper dermatitis.
Sometimes a child breaks out due to the powder or conditioner used to wash children's clothes and bedding. The culprits of the ailment are products used to treat bathtubs, basins, and ladles.
In older girls, allergies may be associated with cosmetics - gels, rinses, soap, shampoo, cream. Taking certain medications, especially antibiotics, can also cause genital dermatitis.
Parasites
Itching can be caused by a helminthic infestation, most often pinworms. The female lays eggs around the anus at night when the baby is sleeping. Parasites can crawl onto the external genitalia, causing irritation and itching in the girl’s intimate area.
Severe itching is caused by scabies, a contagious parasitic disease. The scabies mite can settle in the intimate area, in the dermis layer. Sebum and sweat are a favorable environment for the parasite to multiply. Scabies is transmitted to children from their parents through the bed, bathroom, and toilet.
Another problem is pubic lice, they cause severe itching. Girls who already have hair in their bikini area can become infected.
Inflammatory processes
Often girls develop vulvitis, colpitis or thrush. These diseases are associated with the penetration of a bacterial, viral or fungal infection. Along with irritation and itching, pimples and pustules appear on the skin and mucous membranes. The smell, color and consistency of vaginal discharge depend on the microorganisms that caused the inflammatory process.
Little girls sometimes insert small objects into their vaginas. Being in the body for a long time, they provoke inflammation. Discharge of pus with blood appears, itching and pain occur.
Thrush is caused by hypothermia, immune system disorders, and prolonged use of antibiotics.
Genital herpes is viral in nature. The blistering rash is accompanied by tingling and itching. Diabetes mellitus leads to disruption of metabolic processes in the body. Blood and urine become a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria and fungi.
Other infections
The initiators of unpleasant itching in girls can be classic sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis) or a urogenital infection - chlamydia. Since infection occurs mainly through sexual contact, teenage girls who have early sexual intercourse become ill.
During birth, a child can become infected from a sick mother. It is easy to “pick up” an infection through bedding, towels, washcloths and other hygiene items.
Diagnostics
The disease can be diagnosed by a pediatrician. But a pediatric gynecologist must examine, observe and treat the child. He examines the genital organs, uses instrumental vaginoscopy and vulvoscopy.
To identify the causative agent of infection, laboratory diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- culture and microbiological examination of smears;
- scraping using PCR method;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- stool test for worms;
- scraping for enterobiasis;
- allergy tests.
Examination of girls by a gynecologist
Some women believe that a gynecological examination can only be performed on girls who have reached puberty, but if a girl complains of itching in the vagina, her labia are inflamed or there is discharge, then the help of this specialist cannot be done without.
Gynecological examinations for girls are different from those for adult women. A vaginal speculum and bimanual examination are not used; instead, the doctor will take smears from the vestibule of the vagina, if necessary, examine the vagina using a vaginoscope, which does not damage the hymen, and prescribe a transabdominal ultrasound. These diagnostic methods will not damage the hymen, but will allow you to determine the cause of the itching and eliminate it.
Useful information on the topic:
- Diagnosis of vaginal itching
- Vaginal itching without discharge
- Itching in the vagina before menstruation
- Itching in the vagina
- Itching during pregnancy
- Treatment for vaginal itching
- Causes of vaginal itching
A selection of effective treatment methods
Treatment of vulvitis in girls consists of a set of measures depending on the etiology of the infection.
Nutrition and regimen
In case of an acute process, girls need to be provided with bed rest. During illness, you should change your diet. Reduce the intake of foods that promote the formation of acids and spices (fried foods, meat broths, smoked foods, pickled vegetables, sour fruits). You need to increase alkalizing foods in your diet (milk, fresh and boiled vegetables). If vulvitis is of an allergic nature, a hypoallergenic diet is indicated. It involves eliminating allergenic foods from the diet:
After an acute period, to restore the microflora of the vagina and intestines, you can diversify the menu with fermented milk products.
Local therapy
It is indicated for the elimination of hyperemia and swelling of the genital organs, relieving the unpleasant symptoms of burning and itching. For this purpose, disinfectants are used in the form of baths, irrigations, and lotions.
Local antiseptics:
- Potassium permanganate solution (light pink);
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin;
- Furacilin;
- Quinozol.
Herbal infusions:
Find out about exercises to correct dyslexia in primary schoolchildren.
How to get rid of lamblia in a child? Treatment methods are described in this article.
At https://razvitie-malysha.com/zdorovie/sredstva/ambrobene.html, read the instructions for using Ambrobene solution for inhalation.
Effectively treat inflamed areas with ointments:
- Tetracycline (after 8 years);
- Oletetrinovaya;
- Sangiviritin 1%;
- Erythromycin.
The ointment should be applied carefully to previously washed and dry genitals. Long-term use of ointments is not recommended. If the inflammation does not go away, you need to show the child to a doctor to adjust the treatment.
If the disease is recurrent, estrogens (Folliculin, Estriol) are applied topically to accelerate reparative processes.
Systemic treatment
When the nature of vulvitis and its causative agent are determined, the doctor can prescribe medications for oral use.
Candidiasis vulvitis is treated with antimycotic agents:
In parallel, areas of inflammation are treated locally with antifungal ointments (Clotrimazole, Decamine ointment).
If trichomonas are detected within 7-10 days, the following are prescribed:
For prolonged trichomonas vulvitis with relapses, Solcotrichovac is administered intramuscularly (3 injections of ½ ml every 14 days). A second injection is carried out after a year - ½ ml once.
Gonococcal infection is treated with cephalosporin antibiotics:
In the presence of chlamydia and mycoplasmas, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed:
Vulvitis against the background of helminthic infestations begins to be treated with anthelmintic drugs:
Normalization of general condition
In case of vulvitis, it is necessary to take desensitizing agents to relieve swelling and itching:
Enzymatic agents to normalize digestion:
Immunomodulators to increase the body's protective functions:
Folk remedies and recipes
Traditional medicine methods can be highly effective in treating vulvitis in girls. Recipes:
- Infuse 1 spoon of St. John's wort in 200 ml of boiling water for 1 hour and strain. Take 50 ml orally three times a day.
- Pour 1 spoon of dried viburnum flowers into a glass of water. Leave in a water bath for 10 minutes. Filter and drink 1 spoon three times a day.
- To relieve itching and burning, externally use baths and washes with a decoction of chamomile or oak bark (2 spoons per 1 liter of water).
How to deal with itching
Treatment of the intimate area depends on the causes of the itching. If this is a violation of hygiene rules, then you can cope with the problem without medications. In the acute period, bed rest is indicated. The diet should contain a lot of fresh and stewed vegetables, milk and mineral water. Rich broths, fried meats, smoked meats and marinades, sour vegetables and fruits should be excluded.
In case of an allergic nature of the disease, honey, nuts, citrus fruits, eggs, seafood, and strawberries are removed from the menu. The girl is prescribed medications that relieve swelling, reduce itching and inflammation:
- sedative herbal preparations – motherwort, valerian;
- enzymes to normalize intestinal function;
- vitamin complexes;
- immunostimulants.
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are added taking into account the sensitivity of the bacteria or broad-spectrum drugs. At the same time, it is recommended to take antifungal agents. If the disease is of viral etiology, interferon inducers are prescribed. For complications and frequent relapses, hormonal medications are indicated. Pirantel and Piperazine are used for helminths.
Local therapy
You can relieve swelling and redness using sitz baths, irrigations and lotions. To do this, use a solution of furatsilin, potassium permanganate of a pale pink color. The skin can be lubricated with an oil solution of chlorophyllipt, erythromycin and tetracycline ointment.
A decoction for sitz baths is prepared from medicinal plants. You can use chamomile and calendula flowers, celandine grass, St. John's wort, string, and also use eucalyptus, oak bark, and nettle. The decoction is prepared according to the instructions on the packaging of plant materials. The procedure lasts no more than 15 minutes and should be repeated 3 times a day. The water in the basin should be warm.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures against this disease should be based on careful care of the genitals of girls and instilling hygiene rules from an early age:
- For infants, change nappies and nappies immediately after soiling.
- After each bowel movement, wash the perineum from front to back.
- Wash underwear with a hypoallergenic detergent and rinse it well.
- Change panties twice a day.
- Soap should not be used to wash the perineum more than once a day. Its pH should be neutral.
- Linen should be made from natural fabrics that do not contain aggressive dyes.
- Do not use aromatic oils, powders, creams.
- Have separate hygiene items (washcloth, towel).
Video. Dr. Komarovsky about the causes of vulvitis and vulvovaginitis in girls:
First, let's define the terms. Vulvitis is an inflammation of the female external genitalia (vulva). Vaginitis or colpitis is inflammation of the vagina (vagina). In girls, vulvitis is often combined with vaginitis. Doctors use one term: vulvovaginitis . The signs of vulvitis and vulvovaginitis are similar, as are the reasons and sequence of actions of parents. Therefore, it makes sense to consider these diseases in one article.
How come I didn’t keep track!
Mothers, upon discovering redness of the vulva and discharge in their daughter, panic. Where could a child “catch this infection”? How did I not keep an eye on the child? Don't rush to panic! You noticed the problem in time, which means everything is not so scary.
At the age of one and a half to two years, the cause of vulvitis is most often a violation of the thermal regime in combination with defects in hygiene. Simply put, untimely changing of diapers and improper washing. The girl needs to be washed under running water from front to back. But holding a child this way is quite difficult; it requires skill. Therefore, many parents neglect medical advice. They place the baby on his arm, belly down, and expose his buttocks to the stream of water. In this case, water carries microorganisms from the anus to the genital slit. These microbes are completely safe for the intestinal tract. But if they get on the vulvar mucosa, they can lead to disease. And rarely changing filled diapers creates ideal conditions for the growth of bacteria.
In older children, other causes of vulvovaginitis come to the fore.
- Helminthic infestation, most often pinworms. Parasites irritate the anus, the child scratches the perineum and infects the mucous membrane of the vulva.
- Excessive curiosity of the child regarding his own genitals. While exploring, he constantly rubs them with his hands and brings in dirt.
- Decreased immunity and activation of one’s own microflora. Normal microbes begin to multiply actively and cause damage to the vulva.
- Synechia (fusion or adhesion of the labia minora) interferes with the girl’s quality hygiene, promoting the accumulation of bacteria on the vulvar mucosa.
- Injury caused by an accidental fall, play or rough washing.
- Allergy. Sometimes vulvitis is the first sign of increased sensitivity of the body to a product, cosmetic or detergent.
Vulvitis detected. What to do?
Vulvitis and vulvovaginitis cause pronounced burning and itching sensations. Therefore, your baby needs immediate help. The first thing you can do is put the child in a basin with a weak solution of soda or a decoction of medicinal herbs. Chamomile, calendula, string and celandine are perfect for these purposes. The basin or bath should be scalded with boiling water. Pour clean, warm water. Take soda at the rate of one level tablespoon per three liters of water. If you prefer medicinal herbs, then brew one heaped tablespoon of dry herb with five hundred grams of boiling water and let it brew for about half an hour.
The procedure itself is carried out in a warm room or bathroom, under the supervision of parents. Adults need to be calm and considerate.
After a bath, the baby should be carefully dried with a diaper well ironed with a hot iron. Treat the perineal area with a solution of miramistin or chlorhexidine. This should be done every 3-4 hours. It is allowed to give the girl paracetamol or ibuprofen in an age-appropriate dosage, once.
If your actions do not bring results, the signs of vulvovaginitis bother the baby and the next day, you need to consult a gynecologist or pediatrician. This should also be done if the symptoms of vulvovaginitis reappear after some time. The doctor will find out the exact cause of the disease and prescribe comprehensive treatment.
Vulvitis - treatment
Doctors determine how to treat vulvitis and what medications to use in a particular case based on the results of the studies. Therapy is carried out comprehensively and involves both general and local effects on the source of inflammation. At the same time, doctors try to exclude not only the pathological process itself, but also the cause that caused it. The acute form of the disease requires bed rest and abstinence from sexual intercourse for the entire period of treatment. Among the main areas of therapy:
- anti-inflammatory treatment;
- antibiotic treatment;
- desensitization course;
- increasing the body's defenses.
Medicines for vulvitis
All medications used for vulvitis are prescribed by a doctor. When choosing dosage forms, doctors give preference to topical medications. All kinds of baths and washes help to quickly eliminate inflammation, relieve swelling and relieve itching and burning. For such procedures, antiseptic solutions are used that have a detrimental effect on pathogenic microorganisms. To eliminate inflammation of the vulva, treatment is based on the use of local drugs:
- ointments, gels;
- suppositories;
- creams.
Vulvitis - treatment with ointment
In most cases, treatment of vulvitis in women is not complete without the use of creams and ointments. This form is simple and effective to use. Anesthetic ointments for vulvitis act directly on the focus of the inflammatory process, eliminating the cause of the disease. The medicine for treatment is selected according to the type of pathogenic microorganism. Among those used:
- antifungal ointments – Clotrimazole, Candide, Pimafucin;
- hormonal - Flucinar, Ovestin;
- regenerating – Actovegin, Radevit;
- antibacterial – Triderm, syntomycin ointment.
Suppositories for vulvitis
Thinking about how to cure inflammation of the vulva, women resort to vaginal suppositories. This choice is completely justified: the drug is easy to dose and easy to use. By following medical prescriptions, using the medicine according to the course of treatment developed by the doctor, it is possible to quickly stop the inflammation and prevent it from spreading deep into the reproductive system. Effective anti-inflammatory suppositories include:
- Polygynax;
- Ginesol;
- Terzhinan;
- Viferon.
What if you don’t go to the doctor, but treat yourself with home remedies as needed?
Acute vulvitis or vulvovaginitis usually goes away without a trace. If, of course, mom took timely and sufficient measures. If this is not done, the consequences can be very unpleasant.
- Acute vulvitis will turn into chronic, affecting the uterus and ovaries, and later, when the girl grows up, it will cause her problems with conception.
- Synechiae appears or progresses. The labia will become fused to such an extent that it becomes difficult to urinate. This will lead to an ascending infection of the bladder and kidneys. Treating urinary tract diseases is much more difficult, more expensive and takes longer.
- A focus of chronic infection will appear in the girl’s body, which will constantly reduce immunity. The child will fall into the category of constantly ill, which will slow down his physical and mental development.
What needs to be done to ensure that a girl never develops vulvitis?
- Maintain good hygiene. Wash your baby girl properly and do not let her diapers overheat.
- Be more attentive to the baby. If you notice that she is interested in the structure of her genitals, do not pull her down. She had previously studied arms, legs, and faces. Let him examine his own crotch. If you forbid her to do this in front of you, she will do research whenever you lose sight of her. And so - everything is under control, with clean hands, and you will soon get tired of it.
- Check your child for worms in a timely manner and, if they are found, be sure to get rid of them.
- Boost your daughter's immunity in every possible way. To do this, walk more outside in the garden and park area, engage in active sports, swim, run, and strengthen yourself.
- Feed your child only safe, age-appropriate foods. Try to avoid exotic foods and those that can cause allergies.
Have you encountered anything similar before? Share your impressions so that our readers can protect children from this unpleasant disease.