Have you dreamed of a touching, cheeky baby with bandages on his arms and legs, like on the cover of a parenting magazine, but instead you were presented with a red, wrinkled creature with a huge head and cloudy eyes? Don’t be alarmed, it won’t be long before the strange alien turns into that same magazine cherub. In the meantime, get to know him better and find out what a newborn should look like. What in his appearance should alarm you, and what is completely normal?
What is lanugo
The original thin fluff covers the body of the fetus even before it is born. It does not contain pigment and is present in absolutely all people and animals. Hair is the rudiments of the first follicles that form in the womb. This delicate fluff of a newborn is called lanugo. According to popular belief, hair on a newborn's ears appears when the mother experiences heartburn. But this has not been scientifically proven.
Hairs begin to form as early as the 12th week of fetal development and remain on the body for almost 8 months. They grow for a reason, but perform a very important function. In the mother's belly, the baby's body is covered with a special substance, the so-called vernix lubrication. It is similar to wax and protects the baby from the effects of amniotic fluid. It is also of great importance for easier passage of the baby through the birth canal at the time of birth.
The hairs on the fetal body retain such lubricant, preventing it from slipping off. Most often, lanugo falls out on its own before childbirth, around the 40th week of pregnancy. Most premature babies are born with such a fuzz, since the hairs have not yet had time to fall out. However, sometimes lanugo lingers on the body. Hair often remains on the ears of a newborn, but it happens that the forehead, back, and sometimes even the baby’s arms and legs are covered with it. We will consider further what this depends on.
Leather
At the moment when the baby is born, his skin may be bluish or bright red, while it is covered with a white cheesy lubricant, which throughout intrauterine life protected the skin from getting wet. It is better not to wash off this lubricant, since it has bactericidal properties; gradually the lubricant will be absorbed into the skin itself.
The palms and feet initially have a bluish tint - the circulatory system has just begun to rebuild, and little blood flows to the limbs. When the baby begins to actively move his arms and legs, they gradually turn pink.
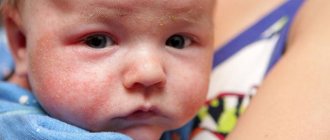
There may be reddish-bluish vascular spots on the scalp, neck, upper eyelids or bridge of the nose - they occur due to dilation of blood vessels. If you notice brown, bluish, dark brown or black pigment spots that rise above the surface of the skin, you should consult a dermatologist and pediatric surgeon.
Sometimes a rash in the form of pinpoint blisters appears on the skin of newborns. With the development of sweat glands, such a rash disappears without a trace.
On days 3-5, the skin sometimes begins to peel off - especially on the stomach and chest, most often this happens in post-term babies. It goes away on its own, without special treatment.
2-3 days after birth, in 60-70% of children, the skin begins to turn yellow. This is the so-called newborn jaundice . The face, the area between the shoulder blades, the torso and limbs turn yellow. The whites of the eyes, the mucous membrane of the mouth, hands and feet also turn yellow. On the fourth day, jaundice begins to decrease, and by the end of the first - the middle of the second week it disappears completely.
If you discover that your treasure's skin is covered with hairs, this is not a reason to panic. Most newborns retain their original down, lanugo, on their skin. There is especially a lot of it on the shoulders, under the shoulder blades, and in premature babies - on the cheeks. Usually after 2 weeks this fluff decreases or disappears completely.
Causes of increased hair count
The amount of hair on a baby’s body depends on several reasons:
- Heredity. If the parents have thick, thick hair, the child may be born with a head of hair and abundant lanugo.
- Nationality. Southerners have thicker hair - these are Spaniards, Italians, Caucasians, and residents of eastern countries.
- Race. The amount of hair also depends on whether people belong to a certain race, for example Mongoloid and Negroid. Their hair is very strong and thick.
If a newborn baby has hair on his ears, then think that maybe one of the factors listed above is to blame.
What hair can be like
Children are born with different amounts and colors of hair. There are newborns who are completely bald, their bodies covered in places with grease. There are options for having a light, barely noticeable fluff. Parents are most frightened when a child has long, thick and dark hair that resembles stubble all over the body or in certain areas. When the hair is on the back or arms, it is not so noticeable when the baby is in an envelope or clothes.
Many parents are confused by the hair on their newborn's ears. Both mothers and fathers wonder how to get rid of excess hair. However, there is no need to force this, since the lanugo falls out quite quickly on its own. It only takes a few weeks for the hair to roll out and disappear from the baby's body.
New parents are also surprised by hair color, which often does not correspond to the genotype. For example, blondes give birth to a baby with black hair. It all depends on the amount of melanin pigment, which is formed at the genetic level and a certain hormonal background. The endocrine system takes part in the process of its production. A child's true hair color will only appear by age 5.
What to do and how to roll it out?
Born with little hair, babies lose it within four months. After the first hairs completely fall out, the baby begins to develop coarser hair. Everyone's hair growth rate is different.
By the age of 11, all children have fully formed hair. If your child's hair grows slowly or is practically absent, do not worry too much. Most likely the reason for this is improper care or identified nutritional disorders.
Baby's hair may not grow well for the following reasons:
- Metabolic disorder.
- Rickets.
- Heredity.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Stress.
Having found out the reasons why your baby has problems with hair growth, you should start working on eliminating them.
- If the baby is breastfed, you need to balance not only his diet, but also the diet of his mother. The diet should contain sources of phosphorus, calcium and protein such as spinach, fish, and egg yolk.
- You should take vitamins that promote better hair growth and strengthen hair follicles. To do this, you can buy special vitamin complexes containing vitamins PP, E, B 12, B6, A and C.
- It is necessary to consult an endocrinologist.
- If your baby is acting restless, you should make an appointment with a pediatric neurologist.
- If parents have a genetic predisposition to early baldness and poor hair growth, the child’s hair should be strengthened from birth with the help of special cosmetics.
- If you have symptoms such as decreased muscle tone, bone deformation, or severe sweating, you should see a pediatrician to rule out the diagnosis of rickets.
Hair growth problems can also be caused by the wrong choice of cosmetics for washing your hair. Therefore, it is important to choose the right product that will strengthen your hair and promote its growth.
Additional hair care measures include the following:
- A scalp massage that stimulates blood flow in the hair follicles, causing them to grow faster.
- Replacing shampoo with baby soap.
- Wash your hair once a week with egg yolk or kefir.
- Rinse with infusion of nettle, chamomile or burdock.
- Burdock mask that stimulates hair growth.
Quite often you can see bald patches on a child’s head. They appear on the baby’s head as a result of the first fuzz falling out. Since it falls out where friction occurs, bald patches most often form in the temporal part and on the back of the head. To avoid their appearance, it is necessary to regularly turn the baby in the crib from one side to the other.
Seborrheic dermatitis, which is yellow scales, can also be the cause of slow hair growth or lack thereof. They must be removed, otherwise the hair will continue to grow poorly. To remove crusts, you need to follow the following procedure:
- An hour before washing your hair, you need to rub warm, pre-boiled vegetable oil into the seborrheic scales. This can be sunflower oil or regular baby oil.
- After this, you need to put a scarf on the child’s head so that the crusts soften under the influence of temperature.
- Softened scales should be carefully combed out with a comb.
- Wash your hair thoroughly.
Bald patches can also occur due to improper hair care in girls. So, if you make your braids very tight or use elastic bands, thinning spots may form on your temples.
Due to the fact that the hair is tightly pulled with an elastic band, it breaks and then the hair follicles stop growing in this place.
A condition in which hair does not grow in children is called alopecia. The causes of the development of the disease are most often neurological in nature, since baldness occurs due to malfunctions of internal organs, dermatological diseases and nervous disorders.
We suggest you read: How to properly highlight yourself at home: using foil, a cap, a comb. How to do your own highlighting with color stretching?
Lack of hair can result from:
- Fungal diseases - lichen.
- Injuries to the hair follicle that occur when the hair is frequently pulled or braided tightly.
- Alopecia areata, a severe autoimmune disease in which hair falls out and does not grow.
- Trichotillomania is a type of neurosis in which a child constantly pulls or twists his hair.
If your baby has hair growth problems, you should first visit a pediatrician, who, if necessary, will refer you to a trichologist, neurologist or dermatologist. If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, your child may be left without hair for life.
Children's hair is very thin and delicate, so adult shampoos are not suitable for it. The best option is a special shampoo with a neutral pH of 6. However, not only the right choice of cosmetic product will help to avoid early baldness. In order for the child’s hair to please his parents, they need to follow the following recommendations:
- You can wash your hair no more than once a week, as shampoo dries out the scalp.
- The water used for washing should be warm.
- Hair should be rinsed thoroughly so that no shampoo remains on it.
- There is no need to wipe your hair dry; it should be dried by patting it with a soft towel.
- To prevent hair from breaking and stretching, comb it only when dry.
- The child should have his own comb, preferably with natural bristles. For an older child, you can buy a wooden comb with blunt tips and wide teeth.
Child's hair grows slowly: reasons and what to do?
The worry that many mothers experience if their child’s hair grows slowly is justified: hair growth is an indicator of the baby’s health.
But you shouldn’t panic if the baby’s hair is thin and sparse, and the baby himself is not even a year old. Hair goes through a developmental stage just like all other organs of a baby.
Before talking about possible anomalies, it is necessary to clarify three factors that influence normal scalp growth:
- Hair on the head or body of a child and an adult is a typical, simple atavism left to us from distant ancestors, according to Darwinian teaching;
- Hair is a thread-like appendage of the skin, exactly the same as nails, because both consist of 95% keratinoids - the main cells of the epidermis;
- Another 2% is allocated to other microelements with vitamins, and 3% to moisture;
- The hair on the head is the most “nutritious” organ - the hair follicles receive the necessary substances from 225 thousand sebaceous glands, and there are 250 thousand such glands in the body;
- The sebaceous substance, which nourishes each hair follicle in which the hair root is located, delivers to the root all the nutrients that the body is rich in and necessary for hair growth;
With such attention from the nutritional system, it is not surprising that hair is the fastest growing organ in the human body.
- In addition, hair concentrates the entire mass of chemical and organic elements that the body has.
Therefore, a hair mineralogram analysis (the study of micro- and macroelements in the body) will give a more accurate result than the usual urine and blood tests.
Blood serum contains data on 8-10 elements, while a tuft of hair contains from 30 to 50!
Such a complex and rich organ of a child, like hair, must have a long development cycle - this is the first reason for slow hair growth.
- The first hairs appear in a child in utero, in the 3rd month of pregnancy and cover the entire fetus entirely, like skin, leaving only the palms and soles of the feet “bare”;
- This skin is called “lanugo” and its density depends on the genetic characteristics of the baby’s mother and father. The “shaggier” the parents, the denser and longer the lanugo of the fetus will be;
- This structure of hair density will remain in the child for the rest of his life, even after, by the end of the 6th month of gestation, the skin “peeles off”, dissolving in the amniotic amniotic fluid;
- The child will retain fairly thinned lanugo on his shoulders, forehead, ears and on the outer sides of his arms and legs. The most persistent hair remains on the head of the formed fetus.
Read the article on the topic: Hair on the ears of newborns{amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;.
- The same picture with hair can be observed in babies born prematurely;
- Babies who have patiently waited for their birth lose remnants of lanugo as they pass through the birth canal, and the so-called “birth hair” remains on the head for natural reasons;
- True, by 4-8 weeks after birth, the baby’s hair may fall off - this is a physiological norm, you should not be afraid;
- Those children who received the “hairiness” gene will have their hair quickly restored. For those who have not received this gene, hair will grow slowly, and you will have to wait up to a year for thick growth, or even longer.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Trichogram and phototrichogram - a complete examination of the hair and scalp
Genetic predisposition is the second natural factor in thick hair or lack thereof.
- A human child is the most defenseless and imperfect creature among all other animal children.
- After birth, only a human child is so “clinically” unstable to the slightest external influences, so susceptible to diseases and needs especially careful care.
For gentle baby care, see the course Happy Motherhood: Methods of Gentle Care{amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;
- The reason for this is imperfect hormonal levels, which are regulated by the endocrine glands. Imperfect glands mean imperfect background;
But the work of the baby’s heart, the cleanliness of his skin, the strength of his bones and, of course, the growth and condition of his hair largely depend on the well-coordinated work of the endocrine system.
- The first stage of “improving” the endosystem is completed by the age of 2. At this age, it is already possible to predict what color and thickness the child’s hair will be;
- The second stage will last up to 5 years. But even here, hair can disappear and grow, changing thickness and shade;
- Stage three – awakening of the sexual sphere and the release of sex hormones into the blood – puberty. Only after this period has passed, the final formation of hair follicles in the scalp ends;
- Those hairs that have established themselves after adolescence can be considered “real”;
- While the endocrine glands are completing their formation, the child’s hair can grow either slowly or quickly, or become thick, or thin right before his eyes.
To begin with, the mother and father of a crying infant should make sure that the reasons for the crying do not lie in something else. Babies can cry for a variety of reasons - from hunger, cold or heat, damp diapers or uncomfortable diapers, pain. If the little one is well-fed, clean, the room is cool and damp enough, the diaper does not cause allergies, the child is healthy and does not arouse suspicion from the pediatrician, but the roar is such that the neighbors have already asked several times if everything is okay in the family, it’s worth a try detect the bristles if they are not visually visible.
Diagnosing indistinguishable bristles, which can be reliably hidden from the eyes of others in the layers of the skin, will require some patience from parents. First, the child should be bathed in warm water, the skin should be steamed well, then carefully blotted with a sheet or soft diaper. Avoid hard towels and rubbing movements.
Parents can find a lot of advice on the Internet on how to remove stubble, but above we have given only child-safe ways to remove coarse and unpleasant hair. Other methods can pose a danger to the health and even the life of the baby. Let's talk about this in more detail.
Advisers who recommend taking the child to the bathhouse should be sent there too. It is strictly contraindicated for a newborn to take a steam bath. The baby’s skin is thin, the network of blood vessels is located close to the surface, the thermoregulation of a baby differs from that of an adult, and therefore even a short stay in the bathhouse can lead to hyperthermia with all the ensuing consequences - disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system. Overheating can be deadly for a baby.
Advice to apply anything and combine it with cling film wraps is generally extremely harmful and can have the most negative consequences - from blockage of the sweat and sebaceous glands and the occurrence of skin rashes to overheating of the body and the death of the child.
Parents should understand that coarse bristles should not be shaved or cut. Mechanical removal may lead to subsequent infection and the development of severe systemic infection. Plucking and removing with scissors increases the likelihood of injuring the skin and also causes severe pain to the baby.
When to worry
There are cases when experts consider abundant hair growth in a newborn as an anomaly. Let's consider the following options:
- Stigmas. These are the so-called minor anomalies, among which there is a significant increase in the amount of hair in the baby. Hypertrichosis can be expressed by fused eyebrows or a triangular headland of hair on the forehead.
- "Island" hair covering. It is also considered a deviation from the norm, especially if the abundant presence of hair is not characteristic of the child’s race, nationality, or heredity;
- Hair on a child's ears remains for a long time, and also appears on other parts of the body, except the palms and feet. This is characteristic of Wolfman syndrome, most often combined with abnormalities of the outer parts of the ears. This is a fairly rare phenomenon, found mainly in India.
If you doubt whether your child has remnants of lanugo on his body or has any abnormality, consult a doctor for advice.
Getting rid of lanugo
The hair on a newborn's ears will go away on its own; doctors recommend not to do any manipulation with it. This may take from several weeks to several months. Natural causes of hair loss include hormonal changes in the body after birth. Now the newborn does not have a close connection with the mother’s body, and this is also reflected in the condition of the hairline. Even after being born with long dark hair, the baby gradually loses it, and bald patches appear. There is no need to be afraid of this, the process of baldness is quite normal, all children go through it.
To avoid wiping the hair only in one place, where the baby most often moves or there is friction with bedding or a cap, try turning the baby on the other side, not putting a hat on him, and placing him on his stomach more often. The fetal fuzz should completely disappear by six months. By this time, old hair is replaced with new ones.
You can speed up the process with hygiene procedures. These are frequent warm baths with wiping problem areas with a mitten or soft sponge. In water, the hairs get wet and are easily removed without special products.
Navel and umbilical wound
After tying the umbilical cord, the so-called umbilical stump (remnant of the umbilical cord). It gradually dries out, becomes dense and brown-black. Usually the stump falls off in the first days of life, leaving an umbilical wound. The wound must be monitored to prevent infection. To do this, it is treated with an alcohol solution of chlorophyllipt, hydrogen peroxide or ordinary brilliant green. If the wound does not heal well or gets wet, be sure to tell your pediatrician about it.
Sometimes a swelling appears in the navel area when screaming or worrying. If your belly button is protruding, place your finger on it. Did you feel something like bubbles? This is a reason to contact a pediatric surgeon - perhaps the baby has an umbilical hernia.
Inessa Smyk
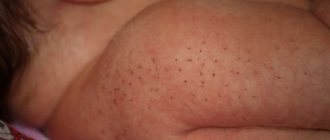
The appearance of stubble
However, in some cases, the embryonic fluff is in no hurry to fall out, and the hair curls and becomes stiff. The photograph of the baby clearly shows such bristles, which are popularly nicknamed “pokers” because of their curved ends.
Doctors explain this phenomenon by the adhesion of baby hairs and the remains of dead cells of the upper layer of skin to the secretion secreted by the sebaceous glands. This phenomenon occurs up to 3 months of age.
In any case, the doctors reassure us that this problem does not pose any danger to the child. So don’t worry too much about figuring out how to remove stubble from a newborn, since pediatricians believe that it should disappear on its own.
The difference between stubble and lanugo
The baby's embryonic fluff is soft and thin; over time, it rolls up and falls out completely painlessly for the child. If the hairs have not fallen out before birth, the process is completed in approximately the first two weeks.
The bristles do not cover the entire body; more often they are located between the vellus hairs. They feel more rigid and twisted to the touch. Such hairs are in no hurry to come out, and they can cause a lot of inconvenience to the child. They are often found on the ears. Even after taking a warm bath and wiping with a special mitten or sponge, they do not fall out.
Coarse hair on the ears of a newborn, according to young mothers, bothers children, pricks and causes discomfort. There are several ways to easily get rid of excess hair without harming your baby. Let's look at the most popular ones, according to reviews from mothers and doctors.
How to remove ear hair from a newborn
The accumulation of hair on the ears does not go away on its own, especially if it is not thin fluff that grows there, but hard bristles. What can mothers do to get rid of them painlessly? Everyone knows that hair is wiped more often in places of frequent friction, so you need to rub your ears using different methods. This can occur during active movements of the child; wearing a bonnet or cap will also contribute to the friction of the fabric against the hair on the baby’s ears.
While bathing, rub them lightly with soft gloves, swabs or a sponge washcloth. All rubbing actions will help you quickly deal with the problem of unwanted hair.
Rules for caring for a child's hair
The baby's delicate skin and hair need special care:
- For girls, buy hair accessories that are not tight.
- If your hair is long, change the parting location frequently.
- Hair should be combed dry. For babies under 2 years old, use special brushes. It’s good if their bristles are natural. For older people, wooden scallops are better suited.
- After washing, try not to rub your head, but simply pat dry with a soft cloth towel.
- Rinse the shampoo well so that it does not remain on your hair.
- Wash your baby's hair with warm water. You can pour it in advance into an enamel bowl and let it sit for several hours.
- Use special children's cosmetics with a neutral composition, without allergic additives.
After using baby shampoo, rinse your hair with herbal decoctions, such as chamomile, burdock root or birch buds. From time to time, replace cosmetics with natural shampoos; they can be easily prepared at home: add a chicken egg yolk, a little lemon juice and vegetable oil to a few tablespoons of carrot juice. Rinse off with warm water.
Rolling out bread ball and dough
Since ancient times, excess hairs have been rolled out using a crumb rolled into a ball. To do this, you need to take freshly baked bread, remove only the soft part with your hands and roll out a round even ball in your palms.
After taking a warm bath, the baby’s body will warm up, the skin pores will expand, and only then can you begin to act. The ball is rolled over the hair on the newborn's ear for 2 or 3 minutes. Then gently blot the friction points with a dry and soft diaper. If you notice redness on the skin, the best way, according to our grandmothers, is to wipe such spots with a few drops of breast milk. It has not only a soothing, but also an anti-inflammatory effect on the baby’s delicate skin.
Another effective way to roll out bristles with dough. It consists of 2 tablespoons of water, a little flour and a teaspoon of vegetable oil. Knead the dough and roll out a small but tight ball. They roll out hairs that stick to the dough. They will be noticeable visually.
Factors affecting hair growth in a child
The condition of the hair on a baby’s head largely depends on:
- Heredity.
- Hormone balance.
- Individual characteristics of the child's body.
- Food.
- Stress resistance.
- Care.
- Diseases. Hereditary, chronic, infectious.
Many mothers believe that if they shave their baby's head, the hair will grow better. This is wrong. Our ancestors tried not to touch their baby's hair until they were 1 year old. There is a rational grain in this, because the baby’s skin is very delicate, the epidermis can be damaged and hair growth will noticeably worsen.
Hair growth on the head is uneven. At one time the hair noticeably lengthens, at another it seems that it is not growing at all. The beauty and thickness of a child’s hair is influenced by heredity and a balanced diet.
If the reasons for slow hair growth are hereditary, then nothing can be changed, you just need to wait a little. Problems with nutrition entail not only a deterioration in hair growth, but also in the child’s well-being. Only a doctor can select special vitamin complexes.
We invite you to read: Hair loss in infants for 3–4 months on the head and back of the head
Lanugo begins to be formed by the embryo's body already at the 12th week of its development. Thin hairs have a structure identical to the skin and protect against excess release of waxy substances from the body. This fluff does not have follicles, so one small hair is quickly replaced by another.
In those born at 7-8 months of pregnancy, lanugo can be expressed as hard, well-defined hair covering the area of the back and shoulders, and the edge of the oval of the face. Over time, these hairs wipe off on their own, without additional intervention. If the hair does not disappear within 2-3 months, this indicates developmental abnormalities caused by disease or hereditary factors.
Corneli de Lange syndrome. With it, active hair growth on uncharacteristic parts of the body is accompanied by a delay in development and growth. Not only external but also skeletal abnormalities occur.
Hirsutism. Hormonal imbalance as a result of non-standard functioning of the endocrine system due to a hereditary factor. The hair on your baby's back grows quickly. Peak growth occurs during adolescence. It is normal and does not require special treatment. Hair is removed using cosmetic procedures.
Hypertrichosis. It occurs as a result of disruption of the nervous system, metabolism, the development of a malignant tumor, or a natural genetic abnormality in the type of DNA. The latter is not a cause for concern.
Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. Leads to active production of androgens. Brings the body closer to the male type. Female characteristics develop poorly. There is rapid growth, development of muscle mass, and a decrease in voice tone.
Excess body weight. Promotes the development of insulin-resistant dependence. This affects the production of male hormones by the adrenal glands. Untimely treatment inhibits sexual development. In girls it leads to ovarian dysfunction.
If by three months the hair on the child’s back does not disappear, you need to contact several specialists: a pediatrician, a neurologist, a geneticist, to rule out serious diseases.
Honey cakes
Before using this method to remove excess hair on a baby’s body, check if he is allergic to honey. To do this, apply a small amount to your hand and wipe with a damp cloth after a couple of minutes. If there is no red spot left, you can use this method calmly.
Heat the honey a little in a water bath so that it melts but is not hot. Then they lay it on the bristles and cover it with a bandage folded several times. Everything is wrapped in plastic film on top. This compress should be held for 5 minutes, and then removed and wiped with warm water. With this procedure, everything will go away; the hair on the ears of a newborn baby will gently come out of the skin and will not appear again.
treatment
Lanugo itself is not a medical condition, but a natural biological response to certain health conditions and life stages. As a result, it is not something that requires direct treatment.
In infants, lanugo is common and not a cause for concern. Babies naturally lose hair within a few days or weeks after birth.
Adults who develop lanugo as a symptom of anorexia or other health conditions will lose lanugo hair as these conditions are successfully treated. For people suffering from anorexia, hair disappears when it is restored through improved nutrition.
Reviews about these methods
Parents' opinions were divided. Some are categorically against forcible removal of bristles and say that their babies’ hair disappeared on its own, some at the age of 8 months. Others decided to try traditional methods. Rolling out the bread crumb helped get rid of unnecessary hairs in two days.
For others, only water procedures and wiping with a glove helped. Within two weeks, all the bristles came out and did not appear again.
The article describes in detail why a child may grow hair on the ears, back or forehead after birth, how to treat their appearance, and how to distinguish lanugo remnants from developmental abnormalities and hormonal imbalances. Simple folk methods of getting rid of unnecessary hairs on the body without causing harm or pain to the baby are also described.
Balanced diet
Regardless of whether a child’s hair grows well or not, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of a balanced diet. To do this, try:
- Increase the amount of protein foods. Hair consists mostly of protein, so eating protein foods every day will have a positive effect on the condition of your baby's hair.
- Prepare food from foods that contain a lot of fatty acids.
- Introduce more retinol and beta-carotene into your diet. They are abundant in sour orange fruits and vegetables.
- Stimulate the production of vitamin D. Stay outside more and eat greens, such as spinach, broccoli.
- Refuse fast and unhealthy food.
It would be a good idea to add fermented milk products to your diet every day; they contain calcium and other nutrients necessary for hair growth.