Pregnancy is an amazing process that occurs in a woman’s body and directly affects her. Every lady can notice many changes that are immediately noticeable from the outside. This is a unique and amazing process, because in nine months a woman’s body is able to recreate a full-fledged organism from one cell.
Many expectant mothers are interested in how the baby lies in the stomach, how it develops over the days, weeks and months. Fortunately, modern technologies allow us to find out this; it is even possible to watch a video of a child’s development, starting from one cell and ending with the birth of a baby.
How to understand how a baby lies in the mother's belly
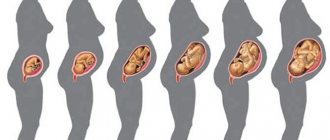
Up to 32 weeks, the position of the fetus in the uterus is called unstable.
That is, the baby can even turn several times a day, either head down or bottom down. Children spin especially actively with polyhydramnios, when the walls of the uterus are stretched and do not limit the child’s movements. At 31-33 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus takes the position in which it will be born. At this time, he no longer rolls over, but only moves his arms and legs, unbends and turns his head to the sides. In most cases, before birth, the baby lies with his butt up (this is called cephalic presentation), with his back turned to the left and outward, and his face turned to the right and inward. If the baby is lying incorrectly in the stomach, then at 32 weeks, obstetricians recommend that the mother do special exercises to help the baby roll over.
If the child lies head up, the woman will feel frequent tremors low above the womb in the area of the inguinal folds on the right or left. If the child lies across, the mother’s belly becomes unusually wide. Sharp, more painful movements arise from the fetal legs, and prolonged pressure occurs when the head is straightened. There may be pain in the area of the umbilical ring due to its stretching.
In the most common variant - cephalic presentation of the fetus - the right hypochondrium of the pregnant woman gets the most damage. As a rule, the baby takes this position closer to childbirth, when he already has enough weight and strength for strong pushes. Even just straightening its legs, stretching out after sleep, the baby can put quite painful pressure on the area of the mother’s liver and lower ribs.
Category: Advice for pregnant women Topics: fetal position, kicks, movements Link to material: How to determine by movements: how the baby lies in the womb
Firstly, the expectant mother should listen to her feelings. If the strongest shocks are felt in the area of the ribs, then most likely the child has turned his head down.
If the child hits the mother in the stomach below the navel, or the blows are sent to the pelvis (and bladder), then it is possible that the child is in a breech position.
The stomach is also very indicative in this regard. In its upper part you can see the rounded volumetric part of the child. It's either the head or the butt. By pressing it from top to bottom, you can feel that the baby’s body is lowering, which means you pressed on the butt and the baby is in a cephalic presentation. When the volumetric part moves separately from the body, then most likely it is the baby’s head (that is, a breech presentation is possible).
You can more accurately determine how the fetus lies in the stomach of a expectant mother in the following ways:
- By heartbeat.
- According to the “belly map”.
We will talk about them further.
This is the easiest way. It requires a stethoscope or stethophonendoscope - a simple device for listening to tones. Any doctor has it. The procedure can be performed either by a gynecologist or by someone close to you.
The woman lies on her back and the stethoscope is applied to her stomach. They usually start from the bottom, then listen from the sides. Where the beats are heard most clearly and rhythmically is where the baby’s heart is located. The normal heart rate of a baby is 120-160 beats per minute; if you deviate from these numbers, you should consult a gynecologist.
A muffled heartbeat may indicate breech presentation. And the heart will be located higher than with the head. Usually in these cases it is located at the level of the navel.
American midwife Gail Tully (Minnesota) proposed her own system for determining the position of the child in the womb.
Its essence is as follows:
- On paper, a map of the abdomen is depicted in the form of a circle, which is divided into four parts. The upper one contains the fundus of the uterus, and the lower one contains the pubic bone. In this case, the woman’s right side is the left side of the card, and the left side is the right side.
- The places where strong and weak kicks are felt are noted, where sometimes a large bulge appears, on which side the stomach is harder. Where the kicks are the strongest, the baby’s legs are most likely located, and where the kicks are light and less impulsive, there are the arms.
- If the fetal heartbeat was determined for the expectant mother in labor, then the baby’s heart should also be marked with the appropriate sign on the map.
- When filling out the map, you must remember that the child’s position is in opposite planes. These are the stomach and back, legs and arms, head and buttocks. There is a danger here of confusing the feet with the head - if they protrude, then the bulge will be round; The baby's arms and legs are bent, the hard place in the stomach opposite the legs is the back. There is no need to invent anything. Notice clearly what is there.
- Next, you can take any toy that has all the body parts that the child has, and place it on the map accordingly. If the child is in the correct cephalic presentation, then the toy will be upside down. Next, you need to turn it in the direction where the legs are. If the mother feels the baby's hands in front of the abdomen above the pubis, most likely the baby is in the posterior position of the occipital presentation - face forward and his back is next to the mother's back.
- The name of the position is determined. It includes answers to the questions: is the baby’s back turned to the left or right side of the mother, which part of the body enters the pelvis first (back of the head or sacrum, face or forehead), and which side of the woman’s body (back, front or hip) is it turned to. The position of the fetus is encrypted in Latin letters and is a kind of key during delivery.
One of the best birth positions is left lateral occipital presentation (LOT), which means the baby is positioned with his back to the mother's left side, head down and facing the woman's hip.
But not all types of cephalic presentation are safe for mother and fetus. With facial, frontal and anterior cephalic presentation there is a risk of neck injuries and even death of the child. In such cases, surgery may be prescribed. Facial presentation is considered the most dangerous.
It should be noted that drawing up a “belly map” is a pleasant activity and, according to psychologists, strengthens family ties.
If you have been diagnosed that the baby is in the wrong position in the womb, this is not a reason to panic. The doctor will prescribe you special exercises that will help change the presentation of the fetus. What is it:
- Lie on a hard surface on one side and then on the other, alternating them, turning over every 10 minutes 5-6 times. Do this exercise 3 times a day.
- Lie down on a hard surface, rest your feet against the wall and raise your pelvis (you can put a pillow on it). Try to do this exercise for 30 minutes 3 times a day.
- Get on your knees, rest your elbows on the floor. Stand in this position for 15-20 minutes, 3 times a day.
- If the baby is in a correct breech position, your doctor may advise you to wear a brace to prevent the baby from turning around again.
We suggest you read: Belly belly after childbirth: how to remove it and how long does it take to go away?
If you are expecting a child, you must understand that in many ways the birth of a healthy and strong baby depends only on you personally, on your lifestyle, nutrition and inner attitude. Take care of yourself and your baby! Have an easy and quick birth!
Pregnancy is an amazing process that occurs in a woman’s body and directly affects her. Every lady can notice many changes that are immediately noticeable from the outside. This is a unique and amazing process, because in nine months a woman’s body is able to recreate a full-fledged organism from one cell.
Many expectant mothers are interested in how the baby lies in the stomach, how it develops over the days, weeks and months. Fortunately, modern technologies allow us to find out this; it is even possible to watch a video of a child’s development, starting from one cell and ending with the birth of a baby.
"Coup" plan
If your due date is approaching and your baby is still in the wrong position, don't panic. You should never panic at all, especially if you are pregnant. There is an action plan!
Step 1. Corrective gymnastics...
... will help “persuade” the baby to take the correct position before childbirth. It is carried out after 24 weeks or at certain times in the third trimester. General contraindications to any set of exercises: threat of miscarriage, placenta previa. But there are other features of pregnancy in which doing gymnastics can be dangerous. Before performing any (!) exercises, be sure to consult your doctor!
With breech presentation
- Lie on your side, but not on a soft surface. Lie on one side for 10 minutes, turn to the other, lie down for another 10 minutes. Turn from side to side 3-4 times. Such simple exercises should be performed 2-3 times during the day.
- Lie on your back with your pelvis raised. To do this, place pillows under your legs and lower back. The legs should be 20–30 cm higher than the head. You can spend 10–15 minutes in this position 2–3 times a day.
- Take a knee-elbow position. Stay like this for 15–20 minutes. Repeat 2-3 times a day.
What happens: When performing such exercises, the motor activity of the fetus is stimulated, and it gets more opportunity to turn.
In transverse (oblique) position
- Lie on your side in accordance with the position of the fetus: the head on the left - on the right side, on the right - on the left. The legs are bent at the knee and hip joints. Lie down for 5 minutes.
- Take a deep breath, turn to the opposite side. Lie down for 5 minutes.
- Straighten the leg (in the 1st position - the right one, in the 2nd position - the left one), the other leg remains bent.
- Grab your knee with your hands and move it to the side opposite to the position of the fetus. Bend your torso forward. With your bent leg, describe a semicircle, touching the anterior abdominal wall, take a deep, extended exhalation and, relaxing, straighten and lower your leg.
What happens: A slight mechanical “pushing” of the baby by the muscles into the correct position.
Step 2: Additional steps
- In the transverse position, it is recommended to sleep on the side where the fetal head is located.
- With a breech presentation, turning the baby head down stimulates swimming (after consulting a doctor!).
Step 3. Visit to an osteopath
After the 35th week, a doctor in a hospital setting can rotate the fetus (in transverse and oblique cases, less often in breech presentation). During the entire “operation,” the condition of the mother and child is monitored. The procedure has contraindications and a high risk of complications and injuries, so it is performed in extreme cases.
Step 4. Consolidate the result
As soon as the efforts have been crowned with success and the little “striker” has decided to take the correct position, it is important to help him “get a foothold.” To do this, purchase a prenatal bandage, wear it throughout the day and do a special exercise (consult a doctor!).
Sit on the floor, spread your knees to the sides and press them as close to the floor as possible. Press your feet together. Stay in this position for 10–15 minutes. You can do this several times a day.
What happens: stretching of the ligaments and muscles of the pelvis, which promotes the insertion of the head into the pelvis.
How should a baby lie at different stages of pregnancy?
Until the 32nd week of pregnancy, the fetus does not occupy a stable position in the uterus, because it can turn several times a day, either head down or bottom. This happens especially often if a pregnant woman has polyhydramnios, or the walls of the uterus are stretched, which does not limit the movement of the child.
At the 33rd week of pregnancy, the baby is already in a stable position in which it will be born. He can no longer turn, he can only move his arms and legs, straighten and turn his head to the sides.
In the womb, the fetus is not in one position. It constantly moves and turns.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, the baby grows noticeably and, due to the small space in the uterus, it becomes more difficult for him to turn over. It is then that the question of its presentation becomes relevant. After all, by about 33-34 weeks the baby usually takes a certain position, which basically does not change until birth.
For natural physiological relief from the burden, it is important that the baby is head down. If the presentation turns out to be breech or transverse, then there is a high probability that the baby will be born as a result of cesarean section.
Having determined the presentation of the fetus, you can influence its position before birth. Special gymnastic exercises and complexes, and even, according to psychologists, self-hypnosis and visualization, allow you to change the baby’s position and ensure a less traumatic birth.
Most babies are born with a cephalic presentation (94-96%), but the danger of incorrect placement of the baby still exists.
There are also cases when the fetus literally a few hours before birth changes the incorrect position of the body to the correct one, but it is at least naive to count on such a turn of events.
Seven interesting facts about the “moving” of the baby during pregnancy
Movements (in the original language “kicks” - kicks) indicate the correct development and well-being of the baby
Movement is a sign of good development and health of the unborn child. Kicks show that your child is active. Can you feel them when your baby makes various movements in the womb? hiccups, rolls over, etc. When your baby stretches his limbs in the first half of pregnancy, you may experience fluttering in your belly.
2. The infant's response to environmental changes
The baby moves or extends its limbs in response to some external stimulus, such as noise or food consumed by the mother. Pinky is a sign of normal development and there is no reason to worry about it.
Lying on the left side increases the number of fetal movements
The “left side lying” position during pregnancy increases blood flow to the fetus. As a result, the baby receives enough oxygen for its development, and you may feel an increase in movements.
The baby moves more after the mother eats
The baby begins to move after 9 weeks of pregnancy
When does the fetus begin to move in the womb? In fact, babies start kicking shortly after 9 weeks of pregnancy. However, these first kicks can only be detected during an ultrasound and are too early for the mother to identify them. After the 24th week of pregnancy, you may feel your baby kicking quite often. During the second and subsequent pregnancies, the baby's movements are noticeable soon after the 13th week of pregnancy.
A decrease in the number of movements may indicate a deterioration in the child’s condition
After 28 weeks of pregnancy, doctors often advise counting fetal movements. Decreased activity may be a cause for concern and indicate an insufficient oxygen supply. Also, a decrease in embryonic activity may be associated with a drop in sugar levels. If the baby does not move within an hour, even though the mother has eaten, drink a glass of water or walk around. You should consult a doctor if you are unable to count 10 movements in 2 hours. More research will be needed to identify the causes and, if necessary, take appropriate action as early as possible.
Eighth week onwards
In the first week, the baby is a collection of cells; by the seventh day, the unborn child is a lump of hundreds of cells. Now this is called a zygote. Moreover, every day the cells divide more and faster.
The second week is not yet an actual pregnancy, although the unborn baby is attached to the wall of the uterus, now the follicle is maturing, after this stage it will be decided whether the woman will be able to bear a child or not.
From the third to the twelfth week there is an embryonic period; only in the fourth week can a girl notice the absence of menstruation and some changes (drowsiness, toxicosis, loss of appetite and others) associated with pregnancy. Now the test will one hundred percent confirm the fact of pregnancy.
Only at this stage the formation of the body and internal organs is practically completed; in the ultrasound image one can clearly distinguish the head, arms, legs, fingers, eyes, mouth and other parts of the body. Now the child weighs only 5 grams, but is already beginning to behave more actively.
From the third to the ninth month he is already a full-fledged person, every day he discovers some new opportunities for himself, new abilities appear.
Pregnancy 6 months. Why are movements most often felt on one side of the abdomen?
Hello! More and more often, I began to notice that the baby’s movements occurred only on the left side. On the right side of the abdomen, tremors occur rarely. The doctor said it's normal, but I'm worried. Has anyone had this happen? Should I worry? I would also like to ask why the child is more active at night? During the day I hardly feel it. This is my first pregnancy and I have no one to ask for advice. Don't consider it difficult to help me. Thank you)
Hello! More and more often, I began to notice that the baby’s movements occurred only on the left side. On the right side of the abdomen, tremors occur rarely. The doctor said it's normal, but I'm worried. Has anyone had this happen? Should I worry? I would also like to ask why the child is more active at night? During the day I hardly feel it. This is my first pregnancy and I have no one to ask for advice. Don't consider it difficult to help me. Thank you)
How to correct your child's position yourself
If the mother has polyhydramnios, and also if the woman is overweight and has a large layer of fat, it is difficult to independently determine the position of the fetus. Difficulties also arise if the placenta is attached to the anterior wall or the tone of the uterus is increased and the muscles of the abdominal wall are very tense.
It is also necessary to understand that the closer to childbirth, the greater the opportunity to correctly determine the position of the baby. In the early stages, this is difficult for any woman to do, and there is no direct need for it.
And if you have tried all the methods and still have doubts about the correct position of the fetus, do not delay in visiting a gynecologist. After all, modern medicine has all the means to help you. Just be sure that it is within your power to make labor easier and ensure a less painful birth of your baby.
Especially for beremennost.net – Elena Kichak
Even if the doctor made his verdict: breech or transverse presentation, then the mother herself is able to help her baby take the correct position. All you need to do is do some exercises every day on an empty stomach. However, before doing this, consult your doctor; in some cases, performing this exercise is contraindicated.
The simplest and most accurate way to determine the position of the fetus in the uterus is ultrasound. In any stage of pregnancy, literally from the first seconds, the doctor knows the exact place of attachment of the amniotic sac and the position of the baby.
After 28 weeks, during an examination, the obstetrician can already, by pressing his palms against the woman’s stomach, determine by touch how the baby is lying:
- across or along the axis of the mother’s spine;
- what part of the body is located in the area of the fundus of the uterus (under the liver): is it a dense head or a soft butt.
The third method is used when the cervix has shortened and opened slightly, that is, during the first stage of normal labor or when there is a threat of premature termination of pregnancy after 22 weeks. During a gynecological examination, the doctor probes with his fingers the parts of the fetal body that are about to exit the uterus.
This can be a soft butt with a breech presentation, a nose and chin with a facial presentation, and piles of tiny fingers with a foot presentation. In full-term pregnancy, the baby's head is most often present. Then the gynecologist feels dense bones with a soft fontanelle in the center. By its configuration, obstetricians even determine which side the baby is turned.
Head presentation
If the baby's position before birth is upside down, then this is the most favorable outcome; natural childbirth is indicated in this position (of course, if there are no other contraindications). But even in this position of the baby, the role of a successful outcome depends on the following factors:
- labor activity;
- position of the child’s neck (flexed or extended);
- where the baby’s face is facing and many others.
There are some options for positioning the baby in a cephalic presentation:
- facing the abdominal cavity or spine;
- slightly turned to the left or right;
- longitudinal, oblique or transverse position.
The most successful position for cephalic presentation is longitudinal, with the small fontanel forward, but most often babies are born with the occiput forward. A fetus of 20 weeks can already actively move, developing its muscles; while the baby is moving, it will not be difficult to feel its position. At this stage, he actively moves, turns over, but the time comes when the baby has little space, and he accepts his final position, and this issue is being resolved right now.
Breech presentation
Otherwise called pelvic. How does a baby lie in the stomach during a breech presentation? Booty down. This case should be taken very seriously; you need to take into account the position of the baby’s head, types of postures and many other factors. Very often, doctors prescribe a caesarean section. Sometimes it happens that even with this position of the child, doctors allow natural childbirth if:
- the child is not large;
- Mom has a wide pelvis;
- There are no contraindications to natural childbirth.
We suggest you read: Why does a child have light-colored stools?
Breech presentation can be determined using an ultrasound, which you will have either in the last weeks of pregnancy or just before giving birth.
Transverse presentation
If the fetus lies transversely, from the twentieth week of pregnancy the doctor will tell you his verdict; in this position, the head is on one side and the butt is on the other. Why is this presentation dangerous? Previously, doctors could correct the child's position by directing him in the right direction, but it required a lot of work and patience, and a caesarean section was very dangerous. Now doctors are playing it safe by immediately sending the woman in labor for surgery. There is an exception in this case: twins, when one child is located across. In this case, the second fetus has the opportunity to turn around correctly, using the free space.
Exercises
Exercises can be very diverse: “cat”, “downward-facing dog”, circular movements of the pelvis, “figure eight”. Or more complex: take a chair and pillows. Lie on the floor, raise your legs, place them on a chair. Place pillows under the basin. You should get a straight line, the angle to the floor is 45 degrees.
Although these are very simple and straightforward exercises, they will help you and your baby during childbirth.
Why does the child move very low?
Is the baby moving in the lower abdomen - good or bad? Having finally waited for the first movements of the fetus, the pregnant woman enthusiastically devotes herself to communicating with her offspring. You can learn a lot from the nature of the movements, their activity and duration. After all, at a period of more than 20 weeks, the child pushes strongly in the lower abdomen, that is, quite distinctly, the movements are usually already clearly noticeable, and mothers begin to slowly get acquainted with the characteristics of their little man.
By the way the baby moves, one can guess his temperament. Therefore, where movements are felt most, they often learn about the location of the fetus in the uterus. Thus, the greatest activity for the lower abdomen may be characteristic of the pelvic or transverse position. Of course, if your pregnancy has already exceeded 20-24 weeks.
But after 22-25 weeks the baby is usually placed head down and awaits birth. However, even after this period the possibility of changing the baby’s position still remains. Some even do a big somersault on the eve of giving birth. Babies turn either with their butts or their heads towards the birth canal.
The second, of course, is more desirable. But although breech presentation classifies childbirth as special, its natural outcome is usually positive. The same cannot be said about the transverse position of the fetus. In this position, the baby is positioned with the butt and head in the lateral parts of the uterus, and the shoulder is facing the exit.
Another reason why a child moves in the lower abdomen may be weakness and sagging muscles of the abdomen and uterus. This is more often observed in those expecting their second and subsequent children. The reason for this development could be uterine fibroids or fibroids. His head simply does not fit next to the tumor, and he turns his pelvis towards it.
Polyhydramnios also gives excessive freedom of movement and the ability to lie across. However, lack of water, which limits movement, can also be a reason. The small size of the fetus, as well as the unusually large one, on the same principle as water, are risk factors. Also, due to placenta previa and a narrow pelvis, the head may not be inserted into the small pelvis.
In a word, numerous deviations and anomalies can contribute to disruption of the normal course of the fetus’ preparation for childbirth. But in modern conditions all this is easily detected. Appropriate measures are taken and even “transverse” babies are born healthy.
When diagnosing a disease that manifests itself as pain in the abdomen, the area where the pain is localized is of great importance. The right side of the lower abdomen in humans is called the right lower quadrant, and many vulnerable organs are located here:
- a vermiform appendix that opens into the rectum - the appendix;
- a significant part of the intestine, parts of which are susceptible to a number of diseases - from inflammation and obstruction to cancer;
- ureter - the organ responsible for the flow of urine into the bladder from the kidneys;
- in women - fallopian (uterine) tubes.
Acute appendicitis is a common cause of pain in the lower abdomen on the right
If there is pain in the right lower abdomen, the first thought should be a suspicion of appendicitis. Inflammation of the appendix should not be ruled out until it is definitely established that the cause of the pain is another disease. Inflammation of the appendix requires urgent surgical intervention, otherwise suppuration of the appendix with subsequent rupture, peritonitis and serious complications, including death, is possible.
Acute appendicitis is one of the most common causes of pain in the right side of the abdomen. With this disease there is a characteristic picture:
- The initial pain occurs in the pit of the stomach; at first tolerable, it gradually increases and moves to the lower right corner of the abdomen - the iliac region.
- The pain radiates to the rectal area; standing, let alone walking, is painful; When walking, the body involuntarily bends to the right. When lying down, the lower abdomen on the right hurts, and the pain intensifies when trying to roll over to the left side.
- In addition to pain, you are worried about nausea and fever.
- You cannot name the reason why the right side in the lower abdomen hurts.
If your lower abdomen hurts on the right, and your sensations fit into the above diagram, call 03 immediately!
The common misconception that appendicitis begins with acute, cutting pain leads to big troubles. This is wrong! Remember: at an early stage, inflammation of the appendix causes a dull, constant pain in the lower abdomen on the right, which can be tolerated. Moreover, it can begin in the upper left part of the abdomen.
Severe pain in the lower abdomen on the right: diagnosis of “acute abdomen”
This concept - “acute abdomen”, applies not only to appendicitis. It combines various and very dangerous conditions that occur with peritonitis of various origins, acute pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), in which the right side of the lower abdomen hurts. Characteristic signs are acute, almost unbearable diffuse pain throughout the lower abdomen with a predominance on the right side, general poor health, severe bouts of vomiting, and high fever.
During palpation, tension in the muscles of the anterior peritoneal wall is recorded. The situation requires immediate hospitalization in the surgical department of the hospital. Important: before a medical examination, the patient should not take analgesics or other painkillers, as this can “blur” the picture and cause an incorrect diagnosis.
We suggest you read: Gases in a newborn: how to help a child with gases (treatment)
Other reasons why the lower right side of the abdomen hurts
Pain in the lower abdomen on the right, varying in location and nature, can also be caused by:
- infectious intestinal diseases: inflammation of the colon mucosa (ulcerative colitis);
- inflammatory process in the ileum (ileitis);
- Crohn's disease is a nonspecific inflammation observed in the gastrointestinal tract;
If there is pain in the right lower abdomen in women
If the patient complaining of pain in the right lower abdomen is a woman, an ectopic pregnancy or diseases of the reproductive organs should be suspected. Ectopic pregnancy is a very dangerous condition; it is caused by the fact that the fertilized egg is implanted not in the uterus, but in the fallopian tube, most often due to tubal obstruction.
Requires urgent surgical intervention. Also, the lower abdomen on the right side hurts in women due to many sexually transmitted diseases (trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia). If the pain becomes chronic, it is necessary to exclude a cyst (especially in the rupture stage) or an ovarian tumor. Increased pain during menstruation gives reason to suspect the proliferation of cells in the inner layer of tissue of the uterine wall - endometriosis.
What to do for pain in the lower right abdomen
If you experience very strong, sharp, dull, cutting or sharp pain localized in the right lower abdomen, you should contact a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, or surgeon. It is wise for women to consult a gynecologist. If you suspect an “acute abdomen”, you should immediately call an emergency doctor. It is also worth paying attention to possible accompanying symptoms, for example: compaction, tension, etc.
Fetal presentation: types, features
First, let's figure out what fetal presentation means. It’s simple, this term describes how the baby will progress at the time of birth. The doctor carefully looks at the ultrasound to see how the baby is positioned in the stomach so that the woman has time to prepare for childbirth (this is especially true for cases in which the pregnant woman is indicated for a cesarean section).
Let's name the main types of fetal presentation:
- Head presentation of the fetus is considered the most optimal and correct. In this case, if the child does not have any pathologies, childbirth takes place naturally. The ideal option is if the baby faces the occipital region towards the birth canal. Complications can arise if doctors diagnose a low presentation of the fetus, which can cause labor to begin prematurely. There are several positions of the fetal head. They depend on the flexion or extension of the neck. The following head positions are distinguished:
- anterior cephalic presentation of the fetus - when the head passes mostly along the birth canal (it is better in such cases to do a cesarean section to avoid birth trauma to the baby and mother);
- frontal - when the baby’s neck is strongly extended, which makes the head area too large, so it cannot pass through the birth canal (with such a presentation, only a caesarean section is performed);
- facial presentation of the fetus is the most dangerous, because the baby’s neck is fully extended, he must pass through the birth canal not with the back of his head, but with his face (in order not to break the baby’s neck, a caesarean section is required).
- Breech presentation of the fetus is the position of the child in which he faces the exit with his legs or buttocks. Therefore, there are 2 types of posterior presentation of the fetus:
- breech presentation of the fetus - it occurs in 35% of cases, with the buttocks facing the exit, the legs are extended at the knees and bent at the hip joint (with such a breech presentation of the fetus, childbirth can occur naturally, but this is very risky for the health of the baby and the woman in labor - ruptures cannot be avoided);
- foot presentation of the fetus - the baby can be facing the birth canal with legs straightened at the hip and knee joints, one leg fully bent at the hip joint, and the other straight, with two legs bent at the knee joint.
- Transverse presentation of the fetus (also called oblique) - the baby is located in the womb horizontally in relation to the exit along the birth canal. Doctors usually recommend that such women in labor have a cesarean section, because if you try to turn the baby around in the womb, there is a high probability that he will be injured.
- Longitudinal presentation of the fetus - when the baby is located in the womb vertically in relation to the exit along the birth canal. It can occur with both cephalic and pelvic presentation.
Below we will present you with photos of the positions of the baby in the stomach that we just told you about, so that you can visually imagine what it looks like.
Malposition of the fetus: truth and myths
...improper position of the fetus is a 100% indication for delivery through cesarean section
No! A caesarean section is recommended in 60–70% of cases of abnormal position of the fetus in the uterus. But most often, the indication for it is not only a non-standard location, but also a number of related reasons. Natural childbirth with breech presentation is classified as pathological: its course and outcome are significantly complicated, which forces the issue to be decided in favor of a cesarean section. And in case of transverse or oblique position, facial presentation, surgical intervention is absolutely necessary.
... natural birth with breech presentation is most dangerous for boys.
Yes! When a boy is born from this position, there is a risk of injury to the scrotum, especially if the buttocks and legs are raised high. This can lead to infertility and other problems in the future. Another danger is direct thermal and painful irritation of the baby’s scrotum during a vaginal examination of the mother, moving through the birth canal, which provokes premature breathing of the baby. Therefore, a caesarean section is indicated.
...if you put headphones “with music” on your stomach, the baby will become interested and roll over.
No! In most cases, if the baby turns over, it means that he has matured enough to prepare for childbirth and was able to physically perform this “trick”. And the music has nothing to do with it. If the baby is “unwilling” or unable to roll over, these methods will especially not work.
...breech presentation negatively affects the joints.
Yes! Possible underdevelopment of joints and congenital dislocation.
...pregnancy with breech presentation is more often accompanied by complications than with cephalic presentation.
Yes! About 3 times. Complications are often accompanied by hypoxia and delayed fetal development, an abnormal amount of amniotic fluid, and entanglement of the umbilical cord.
Malpresentation of the fetus: causes
Malpresentation of the fetus can occur due to certain factors:
- a pregnant woman has polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios;
- pathologically narrow pelvis of the expectant mother;
- low position of the placenta;
- strong and tight entanglement of the baby’s umbilical cord;
- the umbilical cord is short;
- the woman has tumors in the uterus;
- if a woman has previously given birth by caesarean section (in general, in this case the cause is a scar);
- the woman's uterus is abnormal;
- uterine tone is reduced;
- the woman is multiparous or has several children;
- the myometrium is thinned.