In newborns very delicate skin, which is subject to constant damage, and an incompletely formed immune system that is unable to resist many diseases. And when parents notice red spots on their child’s body, they begin to panic because they don’t know why they appeared and what to do with them. First of all, you need to find the reason for their appearance.
Common Causes
This rash can be caused by various factors. Some of them are harmless, while others can cause a significant threat to the baby’s health. The appearance of such a rash should alert parents. Without determining the diagnosis, it is not recommended to start self-medication. The most common causes of red spots on a child’s stomach are the following:
- Chicken pox.
- Allergic reaction.
- Manifestation of rubella.
- Manifestation of prickly heat.
It is worth taking a closer look at each reason separately.
Allergic reaction
An allergic reaction in a child can manifest itself in the form of urticaria and diathesis. If allergic red spots on a child’s skin itch, photos of which are presented below, then the following factors may be the causes of such a reaction:
The most common allergen in this case is cow's milk. The fact is that the baby’s reaction to this product is formed in the first year of his life during the transition to artificial feeding. Seafood and fish rank second among allergenic foods. However, with age, fish protein intolerance in a child does not disappear. The following foods contain many allergens:
Various preservatives, food additives, dyes and emulsifiers can also provoke an allergic reaction.
There is also a so-called drug allergy, which develops due to prolonged use of any medications or due to their overdose. If the red spots that arise for this reason in a child are itchy, treatment for skin allergies, the photo of which is presented in this article, should consist of eliminating this drug from use. In most cases, an allergic reaction is caused by penicillin antibiotics. It is worth paying attention to the fact that drug allergies do not go away over time. If, due to taking medications, an allergy occurs on the child’s stomach, a photo of red spots with a description of which is presented in this article, then this reaction persists in the baby for life. Currently, there are special diagnostic methods that can determine intolerance to certain drugs.
In addition, irritating substances can also be of chemical origin. Various compounds of heavy metals can sometimes be found in clothing and household chemicals. A small red rash on the child’s body appears in areas of contact with an external irritant. In addition, red dots can also be localized throughout the body, accompanied by itching.
Rough spots on a child's body
Skin is a mirror of human health. If it is clean and does not have any pathological manifestations, the presence of a somatic disease is most likely not present. Any appearance of pathology on a child’s skin is the reason for urgent contact with a specialist. Let's figure out what rough spots are, why they appear on a child's body, what their description is and what they look like in the photo.
What are rough spots on a child’s body?
Rough spots on the skin are pathological changes in the epithelium and dermis of the skin, which must be carefully examined. Visually, rough spots appear in different ways:
- The formations are identical in size, without a tendency to merge. All elements are the same and have not changed since their appearance. There are no signs of hyperemia or any pigmentation. The elements appeared immediately and they did not change quantitatively anymore. Sometimes the rash may be itchy. This clinical picture is typical for contact dermatitis or fungal infection.
- Pathological elements are different in diameter and tend to merge with each other. Elements have their own development and gradually change from the moment of their appearance. First, one or two formations appeared and gradually they increased in number and in diameter. There is hyperemia and it gradually increases along with the growth of pathological elements. This picture is typical for pink zhiber, herpetic infection, allergic reaction.
- The elements appeared gradually, and then they changed morphologically, pustular elements gradually appeared and the rash gradually began to suppurate. Hyperemia around the formations is a sign of acute inflammatory skin disease. Most likely, the cause of such a rash was an opportunistic flora that caused a disease such as pyoderma, acne or eczema.
Causes of rough spots on a child’s skin
Rough spots on a child’s body do not appear without reason; they are often caused by pathogenic microorganisms, and photos and descriptions of pathological elements only prove this.
Possible causes of rough spots on a child’s body:
- Fungal infection.
- Bacterial infection.
- Herpetic infection.
- Atypical dermatitis.
- Infectious toxic dermatitis.
- Allergic dermatitis.
- Contact dermatitis.
What can a child complain about when he has rough spots on his skin?
When the child is small, an attentive mother can easily notice rough spots on the child’s skin and compare the pathological elements with photos and descriptions on the Internet.
If such pathological formations are detected, parents are obliged to consult a doctor, because this can be dangerous to the health of the child himself and others.
If the child is an older mother, due to age-related changes, the nature and gender of the child, she may not notice the occurrence of such elements in a timely manner. The child will complain about:
- The appearance of a rash.
- Itching at the site of the rash.
- External skin change.
- Redness and pain around the rash.
Possible irritation and increase in rash from contact with clothing, after physical activity, in contact with sweat, in contact with soap or shower gel.
How to treat rough spots on a child’s body
Before treating rough spots on a child’s body, you need to make sure the diagnosis is correct. Descriptions of diseases and photos of their clinical picture will help with this. Simply taking antiallergic drugs will not give any results, since the cause of the disease will remain.
In case of herpetic infection, it is recommended to apply Acyclovir ointments and powders to the rash until bubbles appear. When bubbles have already appeared and some of them have turned into crusts, only drying medications (brilliant greens, fucarcin, alcohol, etc.) will help.
Don't waste money on useless medications. If the effectiveness of the ointment is not expressed, from 7 years of age you can use tablets and injections of Cycloferon.
In the case of a bacterial infection, it is necessary to use local antibacterial agents that will act on the immediate cause of the disease. If the disease is widespread, it is necessary to add an antibiotic orally. This may be Ampicillin or another broad-spectrum drug according to age.
If an allergic reaction occurs, it is necessary to carefully understand the causes of the allergy and urgently eliminate the allergen.
You need to understand that the presence of an undiagnosed allergy at some point can lead to the risk of death of a child from anaphylactic shock or angioedema, because the accumulation of allergen in the body only enhances the inflammatory response of the immune system.
Fungal infections of the skin in a child are treated with several factors:
- Antifungal drug locally.
- Stimulation of the immune system.
- Maintaining the child's personal hygiene.
Fungal infection in children is the first sign of immunodeficiency and poor care; if these causes are corrected, the disease can go away on its own.
Rough spots on a child’s body are a big problem that requires a professional assessment. There is no need to look for photos and descriptions of the rash on the Internet, contact a specialist from the very beginning, do not start the disease.
Sources:
vseprorebenka.ru
natele.net
allergology.ru
Source: https://www.Kleo.ru/items/zdorovie/lechim-pyatna-na-tele-rebenka.shtml
Fighting allergies
But how to cure allergies and red spots on the stomach of a child, a photo with a description of which is presented in this article? First of all, you first need to identify the main allergen. At the first stage of therapy, all allergenic foods are also excluded from the diet. The specialist prescribes antihistamine medications, as well as ointments for external use. In advanced forms of allergic dermatitis, this disease can develop into a disease such as eczema.
Reasons for the appearance of rough, dry spots of different colors on the skin of infants
The condition of the skin is a reflection of the health of any person, including a baby. Therefore, if you find rough spots on a child’s body, he should be immediately shown to a specialist. He will identify the cause of the problem and prescribe adequate treatment.
Rough spots on a child's face always worry parents
Causes of rough spots
Dry spots on a child's skin can appear for a number of reasons. The most common ones include the following.
Exudative diathesis
The baby's body can react with skin rashes to exudative diathesis. With this disease, the scalp begins to peel off first. Seborrheic scales appear on the crown of the newborn. As the disease progresses, diaper rash appears on the body. The stomach especially suffers. The face begins to turn red, and rough patches form on it.
The causes of the development of the disease are most often an incorrectly selected formula for artificial feeding, too early introduction of complementary foods, or an individual reaction to a certain product.
Important! If the factor that provoked the development of exudative diathesis is not identified in a timely manner, the disease can become chronic.
Allergic diathesis
The appearance of red, rough spots on a child’s body may also be associated with allergic diathesis. Its symptom is roughness on the child's face, body, arms or legs. Most often, the disease is caused by the following factors:
- allergic reaction to a product or external irritant;
- heredity;
- infection;
- taking certain medications by the mother during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
There is no need to treat allergic diathesis - it is enough to simply eliminate the allergen, and the symptoms will subside over time.
Diathesis is a very common childhood diagnosis.
Psoriasis (scaly lichen)
An infant diagnosed with psoriasis is a relative rarity in medicine.
If pathology does develop, it is more likely than in adults to be severe and cause complications.
Most often, flaky, dry spots on a child’s skin appear against the background of reduced immunity due to the disease. This happens after infectious diseases, chickenpox or flu.
Psoriasis rashes can affect any part of the body, be it the leg, arm, elbow, etc. You should definitely seek help from a doctor when the first rash appears.
Moreover, when a baby suffers from psoriasis, additional symptoms are often observed. The child’s health deteriorates and he begins to itch.
Scratching the skin, in turn, leads to injury and the formation of new lesions. This greatly increases the risk of infection.
Important! In advanced cases, psoriasis can spread to the mucous membranes of the mouth or external genitalia.
Contact dermatitis
If a newborn or baby has skin rashes in the first month of life, most often the cause is contact dermatitis. It mainly develops when the diaper rubs against the delicate skin of the butt or tummy area.
It can also appear if the baby is bathed in chlorinated water.
In addition to the above, contact dermatitis can be caused by the following factors: detergents, medications, household chemicals, cosmetic or hygiene products, poisonous plants and some metals.
When exposed to strong external agents, the disease can have four stages:
- Superficial lesion with limited redness of the skin.
- Severe damage with the formation of blisters, the contents of which are white or colorless.
- Destruction of the skin structure with tissue necrosis.
- Damage to all parts of the skin and underlying layers.
For your information. An infant with contact dermatitis becomes capricious, eats poorly, and sleeps restlessly.
Other reasons
The appearance of rough, dry spots on the skin of a baby can be explained by other factors. Symptoms may develop due to insect bites. Sometimes spots appear as a result of miliaria, which is a skin irritation that breaks out when exposed to excessive moisture.
Another cause of dry skin and blemishes can be increased sensitivity to sunlight, also known as photodermatitis. With this disease, the epidermis becomes rough to the touch, itchy rashes appear in exposed areas, and redness is often observed.
Differential diagnosis
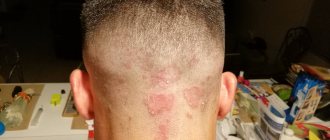
Dry crusts behind a child’s ears and peeling - what to do
If rough spots are detected on the legs and arms of an infant, the child must be shown to a pediatric dermatologist for examination of the skin and differential diagnosis. To determine the disease, the patient will be given directions for general and biochemical blood tests.
If specialists suspect individual intolerance to a particular irritant, an allergen test may be required. A scraping is taken from the affected area for culture. In some cases, an ultrasound of internal organs is performed.
Which doctor should I contact?
Red spots on a child’s body - causes of redness, plaques, irritation
Many parents know that if a child has a toothache, he should be taken to the dentist, and if his child has an earache, he should be taken to an otolaryngologist. Not everyone knows which doctor will help cure rough spots on the skin, since their etymology can be different.
For any rash, the baby should be shown to a dermatologist
You should start with a dermatologist. Based on the results of the diagnosis, he himself will refer the small specialist to another specialist: a rheumatologist, an infectious disease specialist or an allergist-immunologist.
First aid for a child
Why do small red and white pimples appear on a child’s body?
If you discover that the baby’s tummy, arms, legs or chin are “decorated” with rough and dry spots, this is a reason to be vigilant.
The first step is to assess the child’s condition for the presence of additional symptoms.
You should not self-medicate, but before visiting a doctor, you should exclude from the child’s diet all possible allergens and external factors that could contribute to the appearance of spots.
Doctors strongly advise against self-medication
What is prohibited to do
The desire of parents to rid their child of peeling is quite understandable and easily explainable. In their desire to help a child, without having the appropriate knowledge, they can cause harm. So, in no case should you:
- use hormonal creams or ointments;
- pick off any crusts that form;
- independently prescribe medications for allergies and other diseases, especially if the diagnosis is unknown.
Prevention of peeling
It is easier to prevent any disease than to cure it. In order to prevent the appearance of flaky spots, mothers during pregnancy and breastfeeding are strongly recommended to:
- give up any bad habits;
- exclude possible allergens from the diet;
- include daily long walks in your daily routine;
- For artificial feeding, use only high-quality mixtures from leading global manufacturers.
In addition, the following steps will help keep your child safe:
- removing crumbs from the room of all objects that can collect dust;
- minimize the child’s contact with pets;
- carry out wet cleaning on a daily basis;
- monitor the humidity level in the children's room;
- bathe your baby without using soap that dries out the skin;
- refuse synthetic children's clothing;
- use hypoallergenic washing powder for washing children's clothes and linen;
- change baby diapers in a timely manner;
- do not wrap the child.
Attentive attention to the health of the infant will avoid many problems. If the skin does begin to peel and become stained, a timely visit to a specialist will allow you to get rid of the disease with minimal damage and in a short time.
Source: https://kpoxa.info/zdorovie-pitanie/shershavye-pyatna-tele-rebenka.html
Chicken pox
If red spots appear on a child’s belly, what could it be? When answering this question, you should pay attention to such an infectious disease as chicken pox. During this illness, a characteristic rash forms on the baby’s body, presented in the form of reddish bubbles. Initially, such a rash forms on the scalp, after which it spreads throughout the entire body. In this case, only the soles and palms remain untouched. At the first stage of the disease, an acute form is observed. The child's body temperature rises to 39 degrees. Chickenpox can occur in mild, moderate, and severe forms.
A mild form of the disease is characterized by a slight rash and low-grade fever. In its moderate form, chickenpox is accompanied by a significant increase in temperature, headache, as well as nausea and vomiting. The rashes on the skin are profuse and last for almost 1 week. A severe form of chickenpox is characterized by high body temperature, which reaches 39 degrees or more. In parallel with this, severe headaches are felt, vomiting appears, as well as loss of appetite. This rash persists on the child’s body for 9 days.
Rough spots on a child’s body: how to treat dry red or pink rashes on the skin?
Red dry spots on a child on various parts of the body can frighten any parent.
Pediatricians believe that in most cases there is no cause for concern, since flaky areas of skin are often not a sign of pathology and are easily eliminated without consequences for the child’s health.
Despite this, if a newborn baby or older child appears on the thighs, buttocks, face, head, arms or legs, you should immediately take the baby to the doctor.
Diathesis (exudative and allergic) in a child
In newborns and infants, flaky areas of skin on the face, tummy, butt, back, arms and legs often appear due to diathesis. Contrary to popular misconception, this phenomenon does not apply to diseases.
This is nothing less than a constitutional anomaly. In pediatrics, this term refers to the hereditary predisposition of the body to the appearance of certain pathological reactions or diseases.
The table shows the characteristics of the types of this phenomenon.
| Type of diathesis | Causes | Symptoms |
| Exudative |
| First, spots appear on the head in the form of seborrheic scales - gneiss. After this, diaper rash begins to appear on the body, which is very difficult to treat. Then red spots with a rough surface form on the baby’s cheeks. |
| Allergic |
| Flaky reddish areas of skin appear on the child’s face (on the cheeks, above the lip, on the forehead), arms, legs, stomach, back, butt. |
Red spots: skin irritation (dermatitis) and eczema
The cause of this problem in one-year-old babies and older children can also be dermatitis and its more severe form – eczema. In this case, flaky areas of skin may appear on the baby’s forehead, cheeks, above the lip, elbows, knees, feet, and wrists. Detailed characteristics of these types of dermatological diseases are contained in the table.
| Skin lesions | Reasons for appearance | Symptoms |
| Dermatitis | Exogenous:
Endogenous:
| Dry round spots with clear boundaries, which immediately turn red, itchy and painful immediately after their appearance. Most often they occur on the hands, but often affect the soles of the feet if the child walks barefoot. |
| Eczema |
| Dry, reddening rashes have vague boundaries and most often affect the forehead, area above the lip, and cheeks. As the situation worsens, spots that itch and itch begin to spread to the elbows, knees, feet and other areas. |
Lichens of different types
White, pink or red spots with a dry crust on a child's body may be lichen. They are pityriasis, pink, scaly, white. The types of this skin disease differ in the causes of appearance, severity, as well as color, shape and size. Below are detailed descriptions of each type of lichen with photos.
Pityriasis versicolor
The development of this disease is provoked by yeast-like fungi. Factors influencing the appearance of this type of lichen:
- staying in countries with a hot climate (hence another name for the disease - “sun fungus”);
- close, intimate and prolonged contact with an infected person;
- weakened immunity;
- overuse of antibacterial skin care products;
- increased sweating;
- disruption of the endocrine system.
The child develops dry spots on the body, the structure of which resembles bran. As a rule, small spots with clear outlines are localized in the upper part of the body: on the shoulders, neck, elbows, chest, armpits, back and abdomen. They are often dark, reddish-brown in color. The affected areas do not tan, so they look light against the background of tanned healthy skin.
Pityriasis rosea
The causative agent of this infectious-allergic skin disease is currently unknown. Children over 10 years of age are most often susceptible to infection. Favorable conditions for the appearance of pityriasis rosea, which is not a contagious disease, are infections and a decrease in the body's defenses.
The disease begins with the appearance in the child of a so-called maternal plaque - a single nodular formation of a pinkish tint. The apical part of the papule, the diameter of which reaches 2 cm or more, becomes yellow over time. Having acquired a rough surface, it begins to peel off.
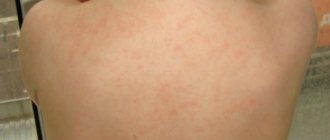
Usually, 2–3 days after the appearance of the first nodule, multiple 0.5–1 cm oval-shaped pink spots appear on the child’s torso, arms and legs. Then barely visible folded scales appear in the center of the spots. This type of lichen does not require specific treatment and goes away on its own within a month.
Scaly (psoriasis)
Young children very rarely get sick with this chronic non-infectious disease, presumably of autoimmune origin. Children over 15 years of age are most susceptible to infection. The disease is characterized by the formation of red, raised spots with a dry surface, which, merging, form large areas of skin elements - psoriatic plaques.
Excessive proliferation of epidermal keratinocytes in them, as well as macrophage and lymphocytic infiltration of the skin lead to thickening of the affected areas of the skin. As a result of this, they begin to rise above the surface of the healthy epidermis and acquire a light, gray or silver tint.
Initially, psoriasis, as a rule, affects those areas of the body that are often subject to friction and compression - the extensor surface of the elbows, knees and buttocks.
There are often cases when the disease affects the nail plates on the feet and hands (psoriatic onychodystrophy).
Pityriasis alba
People at risk for contracting this type of skin disease include:
- people with dark skin color;
- persons suffering from allergies and autoimmune pathologies;
- children under 10 years of age, including newborn babies;
- adolescents in puberty.
The disease is characterized by the appearance of depigmented areas of skin on the lateral surface of the shoulders, arms, thighs, as well as in the area around the eyes, mouth, ears, nose, and anus. Most often, white peeling spots, the size of which reaches 4 cm or more, appear in children in the summer and spring. In most cases, lichen simplex does not require treatment and will go away on its own over time.
Rough sores are a sign of helminthic infestation
Children are among the main risk groups for contracting parasitic infections. Intoxication of a child's body with waste products of parasites, among other symptoms, often manifests itself in the form of damage to the epidermis by elements with a rough surface. In addition to spots on the skin, you can determine that worms have settled in the child’s internal organs by a number of other signs:
- deterioration or complete loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- fatigue;
- weaknesses;
- painful sensations in the navel area.
In advanced forms, the disease in children is accompanied by cough, symptoms of bronchitis and allergies. Parasitic infections most often develop due to failure to comply with basic hygiene rules, consumption of dirty foods, and close contact with domestic or street animals that have not undergone anthelmintic treatment.
Roseola rosea
This infectious disease, the causative agents of which belong to the group of human herpes viruses type 6 and 7, is mainly diagnosed in children under 2 years of age. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. The peak incidence occurs in the spring and early summer season.
After the body temperature normalizes within 24 hours, small pinkish rashes appear on the child’s torso. In this case, the baby does not experience pain. He is still active. In most cases, the rash goes away on its own within 4–7 days.
How to treat and when can’t you do without a doctor?
Treatment in each case is strictly individual and depends on the cause that caused the spots on the child’s skin. To get rid of some rashes, it is enough to adjust your diet, replace personal hygiene products and eliminate the allergenic factor; to eliminate others, long-term use of potent drugs may be necessary.
The well-known children's doctor E. O. Komarovsky, who enjoys well-deserved authority among fellow pediatricians, categorically does not recommend that parents self-medicate if dry spots are detected on the baby's body.
An immediate visit to the doctor is required in cases where, in addition to skin rashes, the following symptoms are present:
- chest pain;
- fainting and delirious state;
- breathing problems;
- increase in body temperature to high levels, which cannot be brought down on your own;
- runny nose;
- signs of anaphylactic shock.
Source: https://www.deti34.ru/simptomy/kozha/shershavoe-pyatno-na-kozhe-u-rebenka.html
Prickly heat
Red spots appeared on the child’s stomach. What else could it be? You should also become more familiar with the disease such as prickly heat. This disease is an irritation of the skin that occurs due to a violation of thermoregulation. The skin of young children, as a rule, is distinguished by its vulnerability. and subtlety. In this case, the ducts in the sweat glands will form before the age of six, so sweating in children is difficult.
General information about the rash
Red spots on a child’s back are elements of any size that affect the mucous membranes or skin under the influence of various kinds of pathological changes in the human body. The rash varies in general appearance, structure and color. Among the initial (primary) types, experts distinguish the following:
- papules (nodules) - swellings whose diameter varies from one millimeter to three centimeters, the tubercles can be felt;
- abscess (pustule) – there is pus inside;
- spots – local changes in the upper skin layer;
- blister - cavity-free pink elements that are characterized by severe itching;
- hemorrhage - dots that appear after hemorrhage under the skin, they also include spots resembling lichen;
- vesicles (their size is more than half a centimeter), containing serous fluid inside.
You need to know that a secondary rash occurs as a complication of the primary one. This includes ulcers, erosion, atrophy of the skin area, abrasions and scars.
Elimination of the disease
If red spots appear on the child’s stomach, photos of which are presented in this article, due to prickly heat, do not worry too much. For treatment, experts recommend taking baths based on medicinal herbs. The most effective are decoctions of string and chamomile. During treatment, rashes should also be sprinkled with baby powder or talcum powder. To avoid heat rash, it is recommended not to overheat your baby. The room temperature should be no more than 22 degrees. In this case, the child should be bathed at least once a day, and diapers should be changed as often as possible.
Preventing skin rashes
Any disease can be prevented. In order not to encounter such diseases, you need to be more careful and follow simple steps:
- Constantly monitor what food your child eats and what components it consists of.
- Constantly ventilate the room where the baby spends more time.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Maintain constant monitoring with a pediatrician.
- Choose the right baby care products.
- If a rash appears, it is urgent to limit the child’s contact with animals and external irritants so that the disease does not develop.
- Daily walks.
- You need to wash and wash your toys at least once a week.
The main thing to remember is that timely consultation with a doctor can prevent a more serious stage of the disease. After all, any pimple does not just appear and in this case you should not trust traditional medicine and the advice of friends. It is allowed to use medications that the baby has already used, but you cannot treat redness with ointments yourself. After all, only a specialist doctor can accurately determine the cause of the disease.
In most cases, in order to determine a specific disease, you will need to visit more than one doctor and undergo many tests. In the case of an advanced stage, it would be better to go to the hospital and be constantly monitored, since the patient may suddenly develop a fever or vomit.
Rubella
If red spots on a child's stomach itch, this may be a sign of rubella. This viral disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. The incubation period of the pathology lasts from 16 to 18 days. After this, an increase in the posterior cervical and occipital lymph nodes is noted. The rash is presented in the form of red-pink spots, which are localized on the skin at the end of the incubation period. The rash can appear on all areas of the skin and last for 3 days. The baby's body temperature is no more than 37.5 degrees.
Other causes of a rash on the stomach of a child
The most common reasons for the appearance of red spots on a child’s stomach with photos and descriptions were described above. However, there are other diseases that can provoke a similar reaction in the child’s body. These diseases include the following:
Scarlet fever
This infectious disease is caused by hemolytic streptococcus. Since newborn babies have innate immunity to this pathogen, children whose age ranges from 2 to 10 years are susceptible to the disease. The symptoms of scarlet fever resemble those of a sore throat. However, in parallel with this, a pinpoint rash forms on the body. The disease spreads by airborne droplets. During the incubation period, which lasts from 2 to 10 days, the baby’s body temperature rises sharply and headaches intensify. General intoxication and malaise are often accompanied by vomiting. A bright red rash covers the main part of the entire body, and red stripes appear in the folds of the skin. The rash persists on the skin for 4 days, after which it changes in color, peels off, and then gradually disappears.
Characteristic symptoms of scarlet fever
This disease is characterized by acute symptoms that precede the disease. The child develops red, rough spots on his back. Before the rash appears, a feeling of nausea and further vomiting may occur, and the temperature may rise. There is also sharp pain and redness of the tonsils, headaches. The skin becomes dry.
Methods of transmission of the disease are direct contact with an infected person or the use of one object. The disease appears 6-10 days after infection. This pathology is bacterial, it is expressed by the following symptoms:
- small red rash on the child’s back;
- crimson color of the tongue;
- weakness.
The causative agent is hemolytic streptococcus. First, the rashes are located in the neck and armpits, after which they move to the back. When you touch the skin, it feels like fine sandpaper.
What do red watery spots on a child’s back mean?
Roseola nursery
Infantile roseola is an infection that affects children under 2 years of age. The symptoms of this disease are similar to those of ARVI, rubella, and allergies, which makes diagnosis difficult. The main causative agent of childhood roseola is considered to be herpes types 7 and 6. Infection occurs by airborne droplets. Most often, the disease appears in autumn and spring.
The main symptoms of roseola infantile are high body temperature, which reaches 40 degrees and lasts for several days. In this case, the baby’s cervical lymph nodes may increase in size, experience general weakness, and decrease appetite. On the 4th day after infection, as a rule, the temperature subsides and pink spots form on the skin.
Pityriasis rosea
The causes of this disease have not yet been studied. Quite often, this disease develops after infectious diseases or due to hypothermia. Initially, a so-called maternal plaque of pink or red color forms on the skin. After 2 days, the resulting spot begins to peel off a little, after which the rash spreads to other parts of the body. Newly formed plaques are smaller in size than the main one. Pityriasis rosea is localized on the abdomen, shoulders, and can sometimes also appear on the scalp.