Mechanism of disease development
Urticaria is an allergic disease that occurs in childhood and adolescence. It is characterized by the appearance of small blisters on the skin. The rash quickly spreads throughout the body, itches severely and irritates the patient.
The development of allergic urticaria in children occurs as a result of the ingestion of an allergen - a substance that irritates the immune system. Due to the individual functioning of the body, it refuses to take a certain substance.
In response to its entry into the body, an allergic reaction develops. A large amount of histamine is released into the blood, the permeability of blood vessels increases, fluid from the plasma enters the tissues and edema forms. Due to an increase in the concentration of histamine, prostaglandins, acetylcholine and immunoglobulin E in the blood, the patient experiences itching and the general condition may worsen.
The disease itself is not dangerous, but against the background of urticaria in children under one year of age, complications may arise or anaphylactic shock may develop.
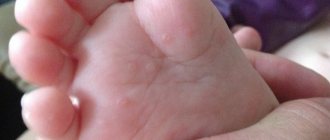
Symptoms of urticaria on the hands
The following symptoms indicate hives:
- rash;
- skin itching;
- general malaise;
- rise in temperature;
- burning (occurs rarely and with concomitant angioedema);
- skin soreness (does not always occur);
- redness and swelling of the skin around the blisters;
- headache;
- skin maceration;
- scratching;
- pain in muscles and joints.
With concomitant Quincke's edema, severe swelling of the lips, tongue, eyelids and cheeks, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, whistling and wheezing appear. If, along with blisters, depression of consciousness, a sharp drop in blood pressure, abdominal pain, fainting, and a feeling of lack of air are observed, then anaphylactic shock must be ruled out.
Small red rash
The main sign of urticaria is the presence of a red or pink urticaria on the hands or forearms. Not only the upper extremities can be affected, but also the torso, face, neck and legs. Urticaria rashes disappear without a trace within 24 hours. No areas of pigmentation remain.
Peeling
Peeling is a rare symptom of hives. It can occur if an infection occurs and dermatitis develops against the background of severe itching.
Redness
The skin around the rash becomes red. The reason is vasodilation. Skin hyperemia may be the first symptom of an allergy.
Blisters
Blisters are bubbles filled with fluid. They are round in shape, rise above the skin and resemble the rash that appears when stung by nettles. Blisters range in size from 2-3 mm to 10-15 cm (with giant urticaria). They have clear boundaries and sometimes merge with each other. Their distinctive feature is their temporary disappearance when the skin is pressed or stretched. The severity of urticaria is judged by the number and speed of the appearance of blisters.
Cracks
Not typical for urticaria. Cracks appear due to scratching and dry skin.
Ulcers
The appearance of ulcers on the skin is possible when tissue suppurates as a result of a bacterial infection.
Features in children
In young children (up to 2-3 years old), the acute form of the disease is diagnosed predominantly. In children under one year of age, this pathology often causes hospitalization. Urticaria in a child is often combined with atopic dermatitis.
Features of the rash in children:
- instant appearance;
- disappearance within the first 2 hours (sometimes lasts up to 2 days);
- formation of large bubbles;
- irregular shape of skin swelling.
Causes
Any substance can provoke acute urticaria in children. Most often, an allergic reaction develops due to food, household chemicals, medications or insect bites.
Causes of urticaria in children:
- food products - seafood, honey, nuts, chocolate, red berries and fruits, citrus fruits, mushrooms, eggs, products with flavors, flavor enhancers and thickeners;
- household allergens - detergents, dust, wool, pollen;
- medications – vitamins, antibiotics, dietary supplements, analgesics;
- insect bites - bees, mosquitoes, flies, hornets;
- other reasons are thermal factors, sun.
In addition to the causes that directly cause allergies, there are predisposing factors:
- pathologies of the endocrine glands (thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- weakened immune system;
- excessive sterility.
All these factors together increase the risk of developing allergic reactions in childhood. But the main cause of urticaria remains altered reactivity of the body.
Causes of allergic rashes on the palms
The response of the child’s immune system in the form of histamine release can be provoked by the following irritants:
- Food. A child may react to one product or several. Doctors divide products according to the degree of allergenicity. The highest levels are found in vegetables and fruits of red or orange color, cow's milk, eggs, nuts, seafood, and chocolate. In addition, cross-allergy is possible, when intolerance to one of the products causes intolerance to others. Allergenic foods can cause allergies on the palms and soles of a child.
- Pet hair (animal hair usually contains their saliva, which contains protein, which acts as an allergen for the child).
- Chemicals in everyday life.
- Insect bites.
- Cold air. An allergic reaction to cold, which can manifest itself as a rash on children's palms and feet, is now being diagnosed more and more often.
- House dust.
Symptoms
It is important for every parent to know exactly how urticaria looks and manifests itself in young children. Allergic urticaria can occur at any age, but is usually diagnosed in children under 12–15 years of age.
The main manifestations of urticaria:
- Blisters . They appear on the skin of the face and body and look like small, red-pink rashes, similar to insect bites or irritation from nettles. Blisters appear first on the face and neck, but can appear anywhere - on the scalp, on the palms and soles, and on mucous membranes.
- Rash . The characteristic symptom of urticaria, which appears quickly, can coalesce and form large spots.
- Itching . Appears immediately with blisters and can be quite severe. Not a single form of the disease is complete without itching.
- Edema . An acute, pronounced reaction is characterized by swelling of the mucous membranes and mild swelling of the subcutaneous fat.
Causes of rash on the palms and feet of a child
The child's body is very susceptible, so a rash on the palms and soles of the feet may indicate the manifestation of certain diseases.
The reason is:
- allergic, infectious diseases;
- parasitic infestations;
- problems with blood vessels, blood;
- failure to comply with hygiene standards.
Rashes associated with infection are always accompanied by fever, cough, rhinitis, and sore throat.
Infectious diseases
The rash is not always harmless; infectious diseases are often accompanied by it.
This group includes the following diseases:
- Chicken pox.
- Rubella.
- Scarlet fever.
- Measles.
- Fungus.
- Enterovirus infection.
- Meningococcemia.
Each disease is characterized by its own type of rash, which covers not only individual areas, but the entire body.
Allergy
Allergic rashes in children are not a rare occurrence. This is how the child’s body reacts to some environmental factors.
An allergic rash occurs due to:
- food products. Sweets, chocolate, citrus fruits, some seafood. During breastfeeding, mothers need to follow the correct diet so that the baby does not accidentally fall asleep;
- animal hair. Even if a child was born in a family where four-legged pets live, this will not help protect him from developing allergies in the future. In some cases, this happens; a disruption occurs in the body, seemingly from its usual habitat;
- chemical substances. A reaction may occur to washing powder, dishwashing detergent, toys, new things with toxic dyes;
- pollen during spring flowering;
- insect bite.
Usually the allergic rash begins to itch, which causes anxiety to the child.
Rashes due to parasites
Infection with skin parasites also causes a rash on the child’s body, palms, and feet. The most common disease that gives such a reaction to the body is scabies. It appears between the fingers and toes, and the heels on the outside.
When scratching, small bubbles burst, forming a tightening crust, the child becomes restless and capricious. An advanced form of scabies can, of course, be cured, but after scratching, spots remain for some time.
Other reasons
A stressful situation and nervous tension cause rashes on the palms and body of a child.
It would seem that children have such deep experiences, but this does not require global reasons; stress causes stress in a child:
- Change of kindergarten, school.
- Moving to a new place of residence.
- Lack of mutual understanding with classmates.
Rashes on the palms can also warn of the onset of a skin disease. But only a doctor’s examination and diagnostic testing can provide accurate data.
Forms
Hives on a child’s face, as well as on other parts of the body, can occur a few minutes after the allergen enters the body or several hours after contact with it. Depending on the time of onset of symptoms, the presence of relapses and the cause of the allergic reaction, the disease is classified into several types.
With the flow
Along the way, urticaria is divided into two forms:
- Spicy . The reaction occurs immediately upon contact with the allergen and lasts for several days or hours.
- Chronic . A rash in the form of hives develops gradually because allergens accumulate in the body and a reaction occurs upon repeated contact with this substance. Periods of exacerbation last longer, symptoms do not stop immediately, and relapses often occur.
According to clinical form
The disease is classified into the following types:
- Spontaneous . Occurs when an allergen enters the bloodstream through the respiratory tract, mucous membranes, and digestive tract.
- Contact . The reaction appears at the site of contact with the allergen, for example, on a child’s feet.
- Physical . The reason for its development is the impact of physical factors (cold, heat, sunlight).
Causes of the disease
The cause of the development of acute urticaria on the palms and fingers in adults and children is repeated contact with the allergen after preliminary sensitization.
Provoking factors include:
- autoimmune disorders;
- physical factors (weather changes, exposure to cold, insolation);
- infectious diseases;
- a history of other allergic diseases (Quincke's edema, asthma, rhinitis, conjunctivitis);
- hormonal imbalance;
- excessive physical activity;
- the presence of concomitant somatic diseases (serum sickness, cryoglobulinemia, helminthiasis, sinusitis, inflammation of the tonsils, helicobacteriosis, lymphocytic leukemia, thyroid pathology and systemic diseases);
- contact with other people's pets;
- insect, arachnid and snake bites;
- stress.
Hives-like rashes are caused by the following allergens:
- Animal poisons. Most often, allergies develop after being bitten by spiders, mosquitoes, bees and wasps. In this case, the rash may disappear only the next day.
- Latex. Gloves and clothing are made from this material.
- Household cleaners and detergents (washing powders, window and dishwashing detergents).
- Sun rays.
- Water (in extremely rare cases).
- Food (citrus fruits, nuts, honey, eggs, strawberries, seafood, chocolate).
- Medicines, including immunobiological drugs (NSAIDs, antibiotics, serums, vaccines).
- Plants, especially pollen.
- Dust.
- Animal fur.
- Particles of dead insects.
- Waste products of insects and mites.
- Mold.
- Low temperature.
Most often, urticaria appears due to direct (skin) contact with an allergen or its ingestion (food, airborne, injection).
Immune variant of the development of urticaria
As in the case of Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock, allergies most often develop through a type 1 immune mechanism.
The following changes occur in the human body:
- IgE production increases. This is a type of antibody that is released upon first contact with an irritant. Immunoglobulins attach to cells (basophils, mast cells) and accumulate in the body (mainly in the skin). This process is called sensitization.
- Mediators (histamine, serotonin) are produced. This happens upon repeated contact with the antigen. It may take years from the period of sensitization to the production of mediators. Histamine is released by mast cells. This substance causes redness, rash, dilation and increased permeability of blood vessels, itching.
- Tissue swelling develops.
Urticaria on the hands occurs as an immune response
With type 1 reaction, urticaria occurs quickly within a few minutes (up to half an hour). This reaction is called immediate. Blisters appear in areas of damage to the papillary layer of skin. This is preceded by edema, which occurs against the background of increased vascular permeability and dilation of capillaries. Sometimes the disease can occur as a type 2 or 3 allergic reaction.
Non-immune variant of the development of urticaria
The non-immune mechanism differs from the immune mechanism in that biologically active substances are produced directly (without a series of immune reactions). Some substances act on mast cells, which leads to the release of histamine. This is how the chronic idiopathic form of urticaria occurs.
Which doctor should I contact for urticaria in children?
If you suspect urticaria, you should contact your pediatrician to rule out other dermatological or infectious diseases. Your doctor may give you a referral to an allergist. After making a diagnosis, you may need to consult an endocrinologist, immunologist or nutritionist.
Diagnostics
The disease is diagnosed by clinical picture and history. To confirm the diagnosis and identify a specific allergen, a detailed examination is carried out:
- blood test (detailed and biochemical);
- Analysis of urine;
- prick tests to determine the connection with a specific allergen;
- determination of immunoglobulin E concentration;
- fecal analysis for helminthiasis;
- cold/heat test.
If urticaria occurs regularly on a child’s hands or body, then additional examinations are carried out:
- chest x-ray;
- study of the functions of the thyroid gland and liver;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- examination of the paranasal sinuses.
Treatment
Each doctor will treat urticaria in children differently. The famous pediatrician Komarovsky does not recommend treating urticaria in children unless there is severe itching and swelling. Other doctors recommend complex therapy, which includes diet, medication and skin care.
Medication
- Antihistamines . The main method of treating urticaria. In the acute phase, these drugs are administered intramuscularly or by inhalation, and if the symptoms of urticaria do not bother the child much, the drugs are prescribed in tablet form. First- and second-generation medications include Suprastin, Tavegil, Fenkarol, Loratadine, Diphenhydramine. They have a sedative and hypnotic effect, but should not be taken for more than 7-10 days. Of the new generation drugs, children are prescribed Zyrtec, Claritin, Telfast, Athorax. They are almost free of side effects.
- Hormonal agents . For severe forms of allergies or developing edema, corticosteroids (Prednisolone or Dexamethasone intramuscularly) are prescribed.
- Enterosorbents . They help reduce the absorption of toxins from the intestines and accelerate their removal from the body. For children use Enterosgel, Polysorb, Smecta.
Folk
You can alleviate the child’s condition with rubdowns, baths or compresses:
- Baths with chamomile, string, calendula . Five st. l. raw materials are poured with 1 liter of boiling water, infused and poured into 10 liters of warm water.
- Baths with oatmeal . Five st. l. oatmeal is stirred in 1 liter of cool water and added to a bath of warm water.
- Compresses or rubdowns with herbs . One tbsp. l. chamomile or calendula is poured into 1 glass of boiling water, left for 1-2 hours and used to wipe the skin or prepare compresses.
It is important to remember that the use of traditional medicine recipes can lead to a worsening of the allergic reaction, so a preliminary consultation with a doctor is required.
Diet
Avoidance of food allergens is the most important condition for treatment. If urticaria occurs in a baby, you should stop introducing new complementary foods. When breastfeeding, the mother should follow a diet or use a hypoallergenic formula.
Basic principles of the diet:
- eliminate all possible allergens from the diet;
- follow a strict diet for 1–3 days with a minimum amount of food in the diet, and for the next 10–14 days the diet is expanded by introducing 1–2 foods per day;
- eat porridge with water (buckwheat, oatmeal, rice), fermented milk products without additives, boiled or stewed vegetables (potatoes, zucchini, carrots), yeast-free bread or crackers, lean soups with lean meat.
Skin care
If the skin of a child with hives is not taken care of, the blisters begin to become wet, the skin cracks, and secondary tissue infection may occur.
It is especially important to care for the epidermis if urticaria is diagnosed in newborns and children in the first year of life:
- Keep your skin clean . It is recommended to dry the skin with air baths. In infants, it is necessary to prevent diaper rash, especially if the blisters appear in natural folds.
- Reduce itching . Children are allowed to use creams and ointments such as Advantan, Fenistil, Elokom.
Rash on palms - causes
Some possible causes of palm rashes include:
Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a common condition that causes dry, sensitive skin. It usually affects young children, but can also occur in adults. Symptoms include:
- itching
- dry skin that may crack
- red patches on light skin and gray or purple patches on dark skin
Some forms of the disease are more common on the palms, such as dyshidrotic eczema. This type of eczema can cause small blisters on the arms, fingers, and palms.
Treatment for eczema depends on the severity of the condition. There are many moisturizers available for mild to moderate cases of the disease. In severe cases, corticosteroids and antihistamines may be required.
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a skin condition that develops when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. Many different substances can cause contact dermatitis, including:
- nickel
- latex
- poison ivy
When the skin comes into contact with something, the body perceives it as dangerous and this can lead to a rash. This rash causes the following symptoms:
- blisters
- itching
- pain
The skin may also be dry and, in severe cases, cracked. Because hands come into contact with many substances every day, they are a common place where contact dermatitis can develop.
The main treatment is to identify and avoid triggers for the condition. A doctor may do a test to determine what substance is causing the reaction. Some people may benefit from moisturizers or corticosteroids.
Hives
Hives are raised, red welts. They cause itching and can appear anywhere on the body, including the palms of the hands. An allergic reaction to certain substances causes this condition. This could be food, medicine or pollen. However, they can also occur in response to infection or physical irritants such as heat or sun exposure. Most cases of hives are acute and resolve when the trigger causing the reaction is no longer exposed. Antihistamines can reduce swelling and allergy symptoms. However, some people experience chronic hives.
Disease of the hands, feet and mouth (enteroviral vesicular stomatitis)
The virus causes enteroviral vesicular stomatitis. It most often occurs in children under 5 years of age, but can also occur in adults. Symptoms include:
- fever
- a sore throat
- a rash on the arms and legs consisting of painful blisters
- headache
- mouth ulcers
- loss of appetite
This disease is sometimes confused with aphthous fever (epizootic stomatitis). However, it is found only in livestock and is not found in humans.
Usually hand, foot and mouth diseases are not serious illnesses and go away without treatment in 7-10 days. At the same time, pain medications can relieve symptoms. However, this disease is contagious and spreads easily. Hand hygiene and avoiding close contact with other people can prevent the spread of the virus.
Fungal infection
Ringworm is a type of fungal infection that affects the hands. Ringworm is contagious, so touching other areas of the body affected by ringworm can lead to infection on the palms of your hands. Symptoms include:
- a small rash on the arms that gradually becomes larger
- itching
- peeling skin
Ringworm can be treated with creams. Your dermatologist may recommend a topical antifungal agent. If the infection persists or is severe, your doctor may prescribe systemic drug treatment.
Avoid touching other parts of the body and avoid contact with other people, as this can spread the infection.
Palmoplantar psoriasis
Palmoplantar (palm-plantar) psoriasis is an inflammatory disease that is accompanied by the appearance of red, scaly patches on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. This is an autoimmune condition that occurs when new cells grow too quickly. Symptoms of psoriasis include:
- red, scaly patches of skin
- itching
- pain
- cracked skin that may bleed
Psoriasis can also affect the fingernails and toenails and may include pustules.
There is no cure for psoriasis, but there are treatments that can relieve symptoms:
- moisturizing steroid creams
- ultraviolet light therapy
- drugs to suppress the immune system, such as cyclosporine
Complications if left untreated
Urticaria is a disease that requires mandatory treatment and prevention. If you do not pay attention to the manifestations of allergies, the process may become chronic or complications may arise.
Why is the development of urticaria dangerous in children?
- Anaphylactic shock. The most dangerous complication that threatens the patient’s life. Frequent allergic reactions in the body lead to the accumulation of allergens, and when the critical level increases, an acute allergic reaction or swelling of the larynx may develop.
- Autoimmune diseases. They can be caused by increased activity of the immune system. Such diseases include glomerulonephritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and pathologies of the pancreas and intestines also occur.
- Development of joint pathology.
- Abdominal syndrome.
How does an allergy manifest on the palms?
Allergies develop on the palms of children in the same way as other skin lesions due to allergies. If, when an allergen penetrates the body, an allergy appears on the palms of a child, it may be accompanied by certain symptoms:
- Rash on palms; the skin of the palms is very itchy and burning. Small bubbles may form and coalesce into larger formations. If treatment is not started, the rash on the palms becomes one large lesion, crusts form, and a crack may appear on the palm.
- Swelling of the skin on the palms, hyperemia.
- Blisters that resemble burns.
- Temperature increase.
Cases where allergic manifestations occur only on the palms are now frequently diagnosed. Signs of allergies on the palms of children can manifest themselves violently, or they can be insignificant.
They usually occur soon after contact with the allergen. Even with minor symptoms, consultation with a specialist is necessary. If the manifestations of allergies on the palms are not treated, the disease will become chronic.
Prevention
Preventive measures reduce the risk of developing urticaria several times. Their implementation is mandatory if regular allergic reactions occur on the back and other parts of the child’s body.
To avoid the negative consequences of urticaria in children and its development in general, it is strongly recommended:
- ventilate the room 2-3 times and do wet cleaning daily;
- monitor the humidity in the room and prevent dry air (normally, the humidity should be at least 50–60%), you can use special humidifiers;
- remove carpets, rugs, rugs, soft toys, pillows and other items that accumulate dust from the premises;
- refuse pillows and blankets with natural down;
- minimize or completely abandon household chemicals, do not wash the child’s clothes with washing powder and rinse aid, do not use glass cleaners, polishes and other products that are sprayed into the air;
- follow a diet and introduce new foods into the diet with caution;
- Do not plant flowering plants at home.
The child's body is characterized by increased sensitivity to external stimuli. Therefore, urticaria in infants and older children is very common. Whether this disease will become the cause of the development of pathologies in older age depends only on the parents and their actions to instill in their child the correct food and hygiene habits.
Author: Dana Shaimerdenova, doctor, especially for Dermatologiya.pro