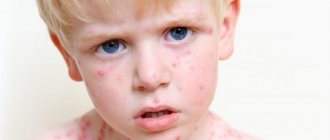
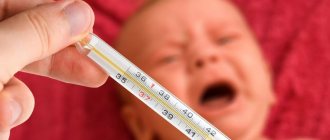
Young children are susceptible to various infectious or bacterial diseases. Often, with such diseases, the child begins to cough, has a runny nose and fever.
Fever when coughing causes many problems for both the youngest patient and his parents. Therefore, the main task of adults is to begin timely and adequate treatment.
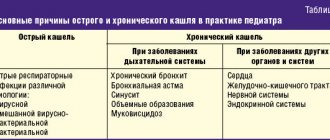
Cough is a characteristic symptom of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract - trachea, larynx and pharynx.
A very dangerous condition when the child’s body temperature rises to critical levels, and in addition vomiting occurs. In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Types of children's cough
When mucus accumulates in the child’s respiratory tract, a foreign body appears, or harmful microorganisms appear, a cough begins. This is a defensive reaction that occurs reflexively. If there is no sputum, the cough is considered unproductive and is called dry. The parents' job is to help him become wet. When the sputum begins to disappear, it means that the child is recovering.
A dry cough, like a wet cough, can be of a different nature:
- Don't stop, neither day nor night. It is then considered permanent;
- Attacks occur at certain times of the day, for example, in the morning after sleep. In this case, they talk about periodic cough. It is also called episodic or mild, and is divided into daytime and nighttime.
Coughs are classified according to duration:
- Chronic, or protracted, bothers the baby for more than 21 days;
- Acute pain resolves within 3 weeks. Usually, it takes 10-14 days to get rid of an unpleasant symptom.
Important! The danger is a barking cough. If measures are not taken in time, it can lead to laryngeal edema or false croup.
Why does a cough appear and the temperature rise?
A child vomits bile with or without fever - how to help with nausea
Fever and severe dry cough in a child occur for several reasons:
- Viral diseases accompanied by a runny nose. After mucous discharge, the baby begins to have a sore throat, a sore throat, and as a result a dry cough;
- Flu. The disease begins with a sharp increase in temperature, values can reach up to 40 degrees. Weakness develops and headache occurs. This is followed by a cough;
- Laryngitis. A distinctive feature is a hoarse voice. The temperature stays around 38 degrees;
- Whooping cough. An infectious disease accompanied by a lingering cough. Medicines have no effect on it, it goes away on its own, but after a long time. It manifests itself in attacks that exhaust the child and can provoke vomiting;
- Pharyngitis. The virus acts on the mucous membrane of the throat, causing inflammation. The temperature rises, but only slightly, usually stopping at 37.5;
- Measles. A barking cough appears and a red rash is noticeable on the body. This is a dangerous disease and requires immediate hospitalization;
- Bronchitis. It can be suspected when the baby does not sleep well at night and has shortness of breath. The presence of fever is a dangerous sign; inflammation can progress and lead to pneumonia. There is no point in delaying treatment; it should be monitored by a doctor.
Parents will not be able to immediately determine what caused a child with a fever to have a severe cough. Self-prescribed treatment will, at best, be ineffective. Only a pediatrician can make a diagnosis after examining the baby, listening to his breathing and seeing his throat.
Medical examination
Urgent call of a specialist
If a child has a temperature of 38 - how to treat
You should call a doctor if you experience the following symptoms:
- The child wheezes and whistles when coughing;
- The baby is overcome by attacks that are difficult to cope with, he is suffocating;
- With a wet cough, the sputum has a green tint;
- The baby's skin turns blue, primarily the nasolabial triangle;
- Body temperature exceeds 38 degrees and lasts for three days;
- The cough lasts for 3 weeks, and chest pain appears.
Recommendations for eliminating symptoms
Before the doctor arrives or visits him, you need to help the child improve his health. For example, a temperature that has jumped the threshold of 39 degrees can be dangerous; it is necessary to bring it down without waiting for a specialist.
Is it necessary to lower the temperature to 38°C?
Cough to the point of vomiting in a child - what to do if a baby is vomiting
It is recommended to give medications that relieve fever when the body temperature is above 38.5. If the child is suffering and at lower values there is no need to wait. It is necessary to evaluate the baby’s well-being, his behavior, and complaints.
A cough in an infant with a temperature of 38 degrees requires immediate action. The smaller the baby, the faster the inflammation develops.
Note! If the child is under 3 months old, then the temperature must be brought down to within 38. You cannot wait if the baby has heart disease. Even a low-grade fever is dangerous for him.
What to do if the temperature rises
When the body temperature rises and antipyretics do not work, you need to call an ambulance. To help your baby, you can wipe him with a towel moistened with water. It should be one degree cooler than the child's body temperature.
We must remember! Antipyretics can be given at intervals of 8 hours. If necessary, if you need to give the medicine earlier, drugs with different active ingredients are alternated.
Child's temperature
How to relieve a coughing attack
Moist air will help get rid of a coughing attack. You need to take the child into the bathroom, turn on the warm water and close the door. A nebulizer, which can be filled with saline solution, can handle this task. The liquid vapor will settle on the mucous membrane of the throat, and the cough will subside. While manipulations are being carried out, it is necessary to call an ambulance. This is especially necessary if the child who wakes up from seizures is not yet a year old.
Warm drink
A warm drink will relieve sore throat and make cough productive. It will not be able to cure, eliminating the unpleasant symptom, but it will alleviate the manifestation. It is not necessary to give your child water; you can offer milk, fruit juice, or tea. Depends on what the baby has already tried and what he prefers.
Important! After two years, children can add a little soda or mineral water to their milk.
Auxiliary procedures
If a child coughs, he needs moist air. You need to make sure that his room is comfortable and not stuffy:
- ventilate the room;
- carry out wet cleaning.
It is recommended to instill saline solutions into the nose. This can be done both during illness and for preventive purposes.
During a coughing attack, you should not leave your child alone. He should feel that his parents are nearby and ready to help. Anxiety will worsen the cough and worsen the baby’s well-being.
What not to do
If a child has a severe dry cough and fever, you cannot treat yourself. Moreover, you should not take antibiotics without a prescription. They fight bacteria, but are useless against viruses. Only a pediatrician will tell you, when he makes a diagnosis, how to treat a child’s cough with fever.
Children under two years of age are not recommended to be given mucolytic agents that promote sputum removal. Babies are not able to cope with large amounts of it, and the cough may get worse.
Note! To bring down the temperature, do not wipe your baby with vinegar and other alcohol solutions. Only water can be used.
Treatment options
Often, an increase in body temperature indicates that the small body is actively fighting an infection. But if the temperature is too high, or it rises quickly and does not go down, then this is a threat to the health, and sometimes even to the life of the baby. The main danger begins with the appearance of seizures - this suggests that treatment must be started immediately.
An infectious disease, expressed by high fever and cough, must be treated with the use of pharmacological drugs. The main thing that parents must remember is maintaining bed rest and using traditional medicine methods: gargling with herbs, decoctions, warm tea with lemon, honey or raspberries. But, nevertheless, the main treatment is medications, which are prescribed under the strict supervision of a pediatrician.
Taking medications
Even when parents are sure that their baby has caught a common ARVI, they should not go to the pharmacy and buy any cough medicine, as many parents often do.
When choosing pharmacological drugs, you need to take into account the age of the children, the nature of the cough and what safety profile the medicine has. For a small baby, the safety of the drugs used is very important. And an older child does not need extra toxins. If infants or children under 6 years of age are sick, the choice of medications is very limited, since many treatment methods and the medications themselves are contraindicated for children. Rubbing, inhalation, and medications in tablet form are also considered unsafe for treating children. Syrup is considered the optimal dosage form for children. The baby will not refuse the next dose of medicine, and an older child will not be cunning and spit it out as soon as the parents turn away. Yes, and it is easier to dose a medicine produced in liquid form.
It is necessary to treat fever when coughing in a comprehensive manner:
- Mucolytics are prescribed - these are drugs designed to thin sputum. Often, as soon as the baby’s cough turns into a wet one, his temperature drops. Mucolytics are prescribed by your doctor if your cough is caused by a cold or flu.
- Expectorants are also prescribed - they have a thinning effect and remove mucus.
- The pediatrician may also prescribe antipyretic drugs, especially if the body temperature has increased significantly. Such remedies bring down the temperature, relieve headaches and discomfort in the joints.
All these drugs are aimed at getting rid of cough and, accordingly, fever. Many parents do not find a place for themselves, begin to get lost and can come up with the worst possible scenario for themselves as soon as the baby develops a cough with a fever. In such a situation, confused mothers or fathers will not help the child in any way, so you need to pull yourself together and begin to act in order to bring real benefit.
When are antibiotics needed?
The doctor prescribes antibiotics for the treatment of cough in rare cases. Such drugs are taken when conventional therapeutic treatment has not brought the desired effect, the temperature lasts for a long time, several days, or even a week. It is the pediatrician who determines how appropriate it is to take antibiotic drugs based on the reasons for the manifestation of symptomatic signs and the condition of the baby. To prescribe a specific type of antibiotic, it is necessary to do a special analysis that will show which infection or bacterium is causing this condition.
The pediatrician prescribes such drugs only based on certain factors:
- results of research conducted;
- poor condition of the baby.
It is worth remembering that each antibiotic has its own spectrum of action, and not every type of such agent is able to fight all types of bacteria or infections.
Komarovsky's opinion
If a child has a cough and fever, then you need to find out the cause of this condition. Komarovsky is confident that a child can cope with the virus himself with the help of his parents. He urges not to get carried away with antipyretics and give the immune system a chance to work. Naturally, if the levels reach critical values, you cannot do without medication. You shouldn’t wrap your child up, hoist his legs, or put mustard plasters on him. At temperatures such actions are prohibited. Compresses and other folk methods soothe parents more than they have a therapeutic effect.
It is important to take care of your baby’s nutrition, offering him light foods rich in carbohydrates and plenty of fluids. When the child’s well-being does not improve within 3-4 days, you need to call a doctor.
Other reasons
The appearance of a cough and temperature of 38 in a child is caused by diseases that are not directly related to the cold:
- whooping cough;
- adenoiditis;
- intestinal infections;
- rubella;
- measles;
- mononucleosis;
- scarlet fever.
Whooping cough. With pathology, the patient's cough is spastic in nature with prolonged coughing and scanty mucus secretion. The condition is often accompanied by vomiting, lethargy, and complaints of fatigue. Hyperthermia can fluctuate between 37.5-38 degrees. A similar clinical picture develops with parawhooping cough.
Adenoiditis and sinusitis. Diseases at the initial stage are manifested by a dry cough and nasal congestion. A constant viscous runny nose gradually develops, and is often profuse. The child is already coughing up sputum, but complains of difficulty breathing. At night he can sometimes choke and snore. Bacterial damage to the nasopharynx provokes headaches, weakness, and hearing loss. Hyperthermia does not rise above 38.5 degrees.
Rubella, measles. The infectious process is characterized by the appearance of specific rashes on the body, conjunctivitis, and photophobia. However, at the first stage of infection, the only symptoms are a cough and a temperature of 38 in the child. Sometimes they are accompanied by a runny nose and lethargy.
Mononucleosis. A dry, unproductive cough develops and the body temperature rises from 38 to 39 degrees. Coughing may be infrequent, but breathing problems may occur due to severe congestion in the nasal passages. Typical clinical manifestations:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- general malaise;
- constant fatigue;
- enlarged liver and spleen.
Prevention of cough with high fever
To reduce the risk of contracting viral diseases, you need to take care of your immunity. Infants are recommended to breastfeed for at least six months. Children at any age should be dressed appropriately for the weather, provided with healthy food, and include fruits and vegetables in their diet.
Baby eating vegetables
Moisturizing the mucous membranes, daily long walks and the comfort of home will help avoid not only coughing with high fever, but also other diseases. If it is not possible to protect yourself from unpleasant symptoms, the child must be closely monitored. When the fever does not subside, you will need medical help. You should not postpone a visit to the pediatrician if your child is choking or his skin turns blue.
Prevention
As preventive measures, it is recommended to monitor the cleanliness of the room, regularly carry out wet cleaning, and ventilate. Walking outside will help prevent infectious diseases. In difficult epidemiological conditions, avoid large crowds of people, but you still need to walk outside.
From birth, parents should consider ways to strengthen the child’s protective functions. Water procedures and hardening are suitable for this.
Don’t forget about vitamin complexes, but this is only possible after talking with your doctor. The specialist will tell you at what age to introduce this or that product into the diet. It is advisable to give natural vitamins rather than medicated ones.