Causes of fever in children without additional symptoms
Numerous studies have proven that in more than 90% of cases of increased general temperature in children and the absence of other pronounced clinical manifestations, a comprehensive examination of the body is required.
This will allow you to identify the cause of the febrile syndrome and make an accurate diagnosis. Instrumental and laboratory tests are prescribed in inpatient settings.
The first step is to conduct a thorough physical examination and radiological diagnosis (by chest X-ray, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal organs).
About a third of cases of critical fever in a child are caused by an infectious lesion of the body. Diseases of this etiology can occur without other clinical manifestations. For example, such pathologies include meningitis and a common cold like acute respiratory infections.
By using microbiological methods (examination of biological fluid taken from the nasal cavity, oropharynx and other areas), it is possible to identify the type of pathogen (virus, fungus, bacteria, parasites) that caused the increase in temperature. A blood test to check antibody levels is also performed to detect infection.
Influence of external factors
Often, the first thing parents think about when the only symptom appears is a fever, that the child is developing an infectious disease. However, the causes are not always associated with pathological factors.
Teething
Often during the period of teething, the child’s general temperature rises. The reasons for this are the following:
- decreased local immunity;
- weakness of the body due to problems with appetite and sleep;
- not fully formed thermoregulation.
According to many well-known pediatricians, there is no need to take any measures to reduce the elevated temperature. After teething, the symptom will disappear.
Overheating
The process of thermoregulation in newborns ends at approximately 1.5-2 months of life. Until this time, the sweat glands do not function at full capacity, so the child quickly overheats.
Hyperthermia can cause an increase in general temperature, which is considered a physiological phenomenon that does not require specific therapy. To reduce the risk of overheating, you need to dress your child according to the weather and give more fluids to prevent dehydration.
Consequence of vaccination
The administration of vaccines is necessary to prevent various diseases and reduce the intensity of symptoms if they occur in the future. An increase in body temperature is the body’s response to the introduction of the composition. Basically, a normal phenomenon is a temperature in the range of 37-39 degrees.
How to cure a runny nose in a newborn: safe medication and alternative treatment
If it is increased to 40, you should consult a pediatrician. It is possible that vaccination was carried out despite contraindications, for example, in case of a developing infectious disease, including a hidden one.
Psychological reasons
If we consider elevated body temperature in a child from the point of view of psychosomatic reasons, such a symptom may be due to tension in the family, emotional impotence, or, conversely, aggression.
Strong, bitter anger, excess stress are the main causes of the clinical manifestation and the higher the temperature, the stronger the child’s mental disorder.
Prevention
The main cause of high fever in a child is infectious diseases, so it is important to prevent their development. To do this you need:
- Provide your child with a balanced diet.
- Monitor the safety and expiration date of consumed products.
- Spend more time outdoors.
- Avoid large gatherings of people or wear a mask in public places.
- Carry out regular wet cleaning of the premises.
- Wash your hands regularly before eating.
- Strengthen children's immunity in different ways.
- Seek medical help at the first signs of an infectious disease.
Any change in the child’s condition causes concern among parents, including an increase in temperature to 40 °C. This condition is an inadequate response of the body to infection, which is accompanied by overexcitation of the center responsible for temperature regulation. To relieve this symptom, you should not only use antipyretic drugs, but also give the child sedatives.
Pathological conditions and provoking diseases
If external factors, as a source of fever, are excluded, this signals the development of an acute or hidden chronic process. Such diseases can only be identified based on the results of comprehensive diagnostics.
Viral infections
Many pathologies that have a viral etiology can occur without obvious symptoms and only with an increase in general temperature. In such cases, conditions under which it will be easier for the body to overcome the infection are important:
- creating an optimal ambient air temperature in a living room (18-22 degrees above Celsius);
- creating acceptable air humidity in a living room (norm - 40-60%);
- daily ventilation of the room, but only at a time when a sick child is not in it;
- avoiding overfeeding;
- correction of drinking regime.
It is worth noting the fact that bacterial diseases always occur with severe symptoms. However, in some cases, for example, with infection of the urinary system in newborns or young children, pathologies can develop without pronounced symptoms other than fever.
The difference between a viral disease and a bacterial infection is that in the first case the skin becomes bright pink, and in the second it becomes pale.
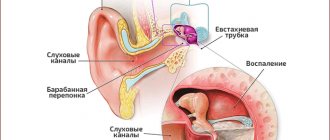
An increase in general temperature without other clinical manifestations is a characteristic symptom of ear diseases. In a latent course, such pathologies occur in the first 2-3 days, after which they are supplemented by pronounced symptoms (pain on the affected side, decreased hearing acuity, etc.).
Viral infections are divided into 3 types:
- respiratory: influenza A and B, coronavirus, metapneumovirus, parainfluenza, adenovirus, rhinovirus;
- digestive system infections: norovirus, adenovirus types 40 and 41, rotavirus, astrovirus.
The first (respiratory infections) are more often transmitted by airborne droplets and general hypothermia, the second (digestive system infections) develop, as a rule, after dirty hands get into the mouth, or consume contaminated food or water.
Infectious childhood diseases
Common childhood diseases of infectious etiology:
- measles;
- rubella;
- chicken pox.
An infectious disease that occurs in children under 2 years of age and is accompanied only by a febrile syndrome without other pronounced symptoms - roseola.
The initial clinical manifestation is a sharp, significant increase in general temperature, which is present without falling for up to 3-5 days. Cough, runny nose, and other signs of pathology are not observed. After this time, red rashes form on the skin, which are similar to the symptoms of measles.
Favorite places for rashes to appear are the face, chest, and stomach. A few hours after the formation of the first plaques, the rash spreads to the entire body and is present for 4-7 days. General malaise, lack of appetite, and sleep disturbance are not observed. In some patients, enlargement of the mandibular lymph nodes occurs.
Signs of pharyngitis in a child and how to treat it correctly
After the first rash appears, the temperature drops and does not rise again. The plaques also disappear, leaving no trace on the skin.
Oncological processes
The general temperature without other clearly expressed symptoms can rise sharply with the development of an oncological process in any area of the body. We are talking about both a malignant and a benign process. Common diseases of this etiology in children are leukemia, lymphocytic leukemia, lymphoma, sarcoma.
Other diseases
Not all patients, but still there are cases of fever as the only initial symptom in the following diseases:
- for tuberculosis;
- with brucellosis;
- with leptospirosis;
- for salmonellosis;
- with hepatitis;
- with intra-abdominal abscess;
- with infective endocarditis;
- for juvenile idiopathic arthritis;
- with vasculitis;
- with systemic lupus erythematosus.
If the febrile syndrome is present for 2 weeks or more, appearing daily, and the results of laboratory tests (culture, etc.) do not show signs characteristic of specific diseases, a clinical picture of unknown origin is indicated.
Possible reasons for undistorted laboratory test results include cancer processes, localized and generalized infections, and connective tissue diseases. Also, provoking factors include diabetes insipidus, complicated by dehydration, intestinal inflammation, and impaired thermoregulation.
How to bring down a temperature of 40 in a child
If a child’s temperature rises sharply and such cases are not isolated, and there are no other warning symptoms, you should not self-medicate. We can talk about serious diseases that require specific therapy. In addition, improper treatment causes negative consequences, and in some cases, death.
The only thing that can be done at home to reduce the elevated temperature is wiping the child’s torso with a damp (room temperature) towel. It is applied to the forehead, wiped over the folds of the body and changed as it cools.
The doctor prescribes antipyretic drugs containing paracetamol and ibuprofen. For newborns, there are products in the form of suppositories and syrup. Older children are given tablets. Any drug is taken no more than once every 8 hours.
Probable Causes
Recommendations on websites for parents usually begin with a list of measures that need to be taken when the temperature jumps to 40 ° C, but the first thing you need to understand is the impossibility of treating such a condition at home without special medical knowledge.
Advice on how to bring down a very high temperature, at which irreversible changes in a child’s body can occur, are not recommendations for eliminating the disease, but just a means to hold out until the ambulance or family doctor arrives. Although calling an ambulance in such a situation is preferable.
Important!
A temperature of 40 °C in a child can be caused by causes that pose a serious danger and the likelihood of death.
Despite reassuring statements that the development of such an indicator can also be caused by harmless reasons, such as overheating, teething and staying in a room with stale air, you should not particularly hope for this. The most likely assumptions are dangerous infectious diseases.
Dr. Komarovsky has repeatedly given recommendations to parents on how to bring down a high temperature in a child, using proven means - rubbing, cool air and maintaining the necessary humidity in the room, bed rest and drinking plenty of fluids.
However, when starting such treatment, you need to make sure that the causes of the fever are not caused by infection or pathology, for which such measures are not enough. This applies to exceeding the 40 °C mark, accompanied by pronounced symptoms, and to a jump beyond the dangerous mark without visible manifestations.
A temperature of 40 °C, in addition to overheating and severe stress, can cause the following dangerous conditions in a child:
- bronchitis, pneumonia of newborns, stomatitis, allergic reaction;
- infections – staphylococcus, meningococcus, scarlet fever, measles, rubella;
- poisoning by toxins, chemicals or plant poisons, medications, foodborne illnesses;
- diseases requiring immediate surgical intervention, such as acute appendicitis.
Note!
In a child under one year old, according to statistics, almost always the cause of a rise in temperature to 40 degrees is caused by the presence of a pathogenic agent in the body - bacteria, a virus, coinfection, microorganisms, mycotic infection.
Teething, which is considered one of the relatively harmless causes of hyperthermia, and even with such a high rise, is considered by traditional medicine to be a dubious version of what is happening in the body with an unformed immune system.
Baby care
At home, measures should be taken to alleviate the general condition of the sick child and eliminate the elevated temperature. As soon as a febrile syndrome is detected, the baby should be changed into light clothing (for example, cotton) and put to bed. It is recommended to ventilate the living space daily. This way pathogens are eliminated faster.
As sweating occurs, the child's clothes are changed to dry ones. If the child wears a diaper, it must be removed, which will prevent increased sweat production and overheating. To replenish the fluid in the body that comes out with sweat, the child is given more fluids. This is not only ordinary water, but also fruit drink, compote, and weak tea.
You should not load your body with food if you have no appetite. As soon as the child wants to eat, he will certainly ask. If there is a prolonged lack of interest in food (to prevent dehydration), you can give light food, for example, broth, puree, porridge.
Cough syrup for newborns: review of the best drugs
How to help your baby?
A child with a high temperature must be provided with plenty of fluids to help avoid dehydration. You can give not only drinking water, but also compotes, teas or decoctions of medicinal herbs; infants should be frequently applied to the breast.
The child’s nutrition also plays an important role at high temperatures, since in this state he loses his appetite and refuses his usual food. You should feed him easily digestible food, excluding fatty, fried and sweet foods for a while.
Depending on the child’s condition and his well-being, he should be wrapped in warm clothes or, on the contrary, some clothes should be removed and covered with a thin blanket. A child with a temperature of 40 °C should be put to bed; ideally, it is better for him to get some sleep before the doctor or ambulance arrives. The child’s room must be constantly ventilated
What children should not take
It is strictly forbidden to give children of preschool and primary school age medications intended for adults. Some parents allow treatment with such drugs, but in a reduced dosage, but this is an incorrect judgment. Medicines are designed for an adult, mature body and pose a great threat to children.
It is not recommended to wipe the body with pure vinegar, alcoholic beverages or natural alcohol. The chemical composition of such drugs increases fever and worsens the condition, causing headaches and other unpleasant symptoms.
Before contacting a doctor, it is prohibited to treat at home with antibiotics, antivirals, diuretics and diaphoretics.
When to go to the doctor
Young children, including infants, cannot say what is bothering them. Therefore, parents must take certain actions to identify warning signs:
- pay attention to the neck, back of the head, submandibular lymph nodes, armpits and groin, where swelling characteristic of inflammation of the lymph nodes may be present, as well as other symptoms characteristic of infectious diseases (hyperemia, etc.);
- examine the skin of the body for rashes;
- look into the throat, which may be red;
- look at the cheeks (is there any redness), pay attention to how the child eats (is there an appetite), is he energetic.
What symptoms should alert you and be a reason to see a doctor:
- fever that occurs in a child under 3 years of age;
- elevated temperature that persists and does not subside after taking an antipyretic drug;
- severe chills, convulsions, increased muscle tone;
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting, epigastric pain, diarrhea;
It is also worth visiting a doctor if there are symptoms of exacerbation characteristic of a chronic process in the lungs, heart, kidneys.
Method of reducing high temperature (medicine and folk remedy)
A temperature of 40 °C requires immediate reduction, otherwise it can cause convulsions, delirium and even hallucinations. Often such a high temperature manifests itself in serious chronic diseases.
In such a situation, it is necessary to call a doctor or an ambulance, and also try to bring down the temperature with the help of antipyretic drugs. The youngest children can be given Nurofen or Panadol syrup. If they cause a gag reflex in a child, then you can use a safe and effective remedy - rectal suppositories Tsefekon or Paracetamol.
For older children, you can use antipyretic drugs in tablet form, such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen, after reading the instructions for use in advance.
If you don’t have medications on hand, you can bring down the temperature in other ways. Rubbing, which is carried out with water or other aqueous solutions, is considered an effective remedy. You can dilute table vinegar 3-6% with warm water in a 1:1 ratio and wipe the child’s body with it, then wait until the skin dries and cover with a blanket without wrapping it. The effect of such rubbing does not last long, so you can supplement it with gauze compresses from the same solution.
Sauerkraut compresses, which should be applied to the groin area, the inside of the elbows and the groin area, are also considered an effective method for bringing down high temperatures.
IMPORTANT: all these methods can only be used in cases where the child does not have seizures and his condition is relatively stable.
Prevention of infectious diseases
There are 2 ways to reduce the risk of developing infectious pathologies that are accompanied by febrile syndrome:
- by introducing into the body ready-made immune serum, globulins, and other components that help increase immune defense;
- by stimulating the production of immune bodies in the body by vaccination.
Many children develop post-vaccination complications after receiving a vaccine. This can be either a feature of the baby’s body or non-compliance with the rules that are followed before vaccination:
- before introducing the composition, it is necessary to exclude infectious diseases (characteristic symptoms - rash on the skin, runny nose, fever, cough, etc.);
- 2 days before vaccination, they begin to take an antihistamine (this is especially true for those children who have a history of allergies);
- It is important to adhere to the vaccination schedule and the period between the administration of vaccines.
If the occurrence of febrile syndrome cannot be avoided, self-medication is not recommended. Only a doctor can find the cause of fever without other symptoms and prescribe effective treatment for the primary process.