Home › From 1 to 3x › Health
The hygiene of your baby’s ears should be given no less attention than other organs and parts of the body. Under normal conditions, wax is released from the ear gradually and in small quantities. It protects the hearing organ from microorganisms and contaminants, and must be removed in a timely manner, taking all precautions.
Should mom worry if the intensity, character, and appearance of earwax secreted from the ear changes? When do these changes become a reason to visit a doctor?
Why does a child have a lot of dark-colored wax in his ears: causes and solutions to the problem
Sulfur is constantly present in a child's ears.
Normally there should be a small amount. When a baby has a lot of sulfur, you need to figure out why this is happening. It is possible that the cause is not related to the disease and is easily eliminated. In other cases, you will have to undergo treatment. ENT doctors do not advise trying to clear wax from a child’s ear on their own – the risk of injury is too great.
Earwax protects the ear canal from infections, but a large amount of it is dark in color - a reason to consult an ENT specialist
Preventive measures
Prevention involves proper care of your baby’s ears:
- Clean your ear openings no more than once a week;
- do not use cotton swabs, they can only clean the auricle;
- use special devices to remove wax from your ears;
- Every six months, visit the ENT specialist, the doctor will prevent trouble from occurring and, if necessary, remove the resulting blockage.
Wax formations in children's ears can be eliminated in several ways; choose the appropriate one. The best option is to follow preventive measures. Regularly monitor the condition of your child’s ears; any abnormalities are a reason to visit a doctor.
Why is there wax in the ears?
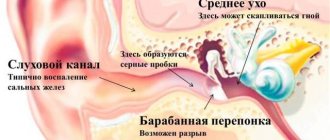
Ear discharge, or wax, consists of gland secretions, skin particles, sweat and sebum. Their function is to protect the ear canal from dust and dirt, they clean and disinfect the outer ear. Wax prevents water from entering the middle ear. Germs and contaminants enter the ear canal and are expelled back through ear secretions.
Changes in consistency, color, and amount of sulfur depend on the health of the baby. In its normal state, sulfur is dark brown in color and odorless. It comes out of the ears on its own and accumulates at the entrance to the ear canal.
Classification
Depending on the “age”, consistency and color, wax plugs in the ears are classified as follows:
- paste-like.
It appeared not long ago and has a soft consistency. The mass is easily removed, often the cork is yellow; - plasticine.
Doctors call it a slightly advanced stage, the sulfur acquires a brownish tint, and it is much more difficult to remove such a formation than a paste-like plug; - dry.
Formed as a result of drying of sulfur, the color of the cork is closer to black. Removing the formation is quite difficult; - epidermal.
The most advanced stage, it consists of dead skin particles, and the discharge of pus is often observed.
Reasons for producing large amounts of earwax
When excessive amounts of earwax are produced, the disorder is called hypersecretion. How can you tell if sulfur production is excessive? The child develops a feeling of constant moisture in the ear, and sulfur stains are noticeable on the bed linen and hat.
Why does a child produce a lot of sulfur:
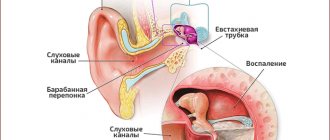
- otitis media, inflammation of the middle ear – often occurs in children under 4 years of age;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- otomycosis, fungal infections;
- the appearance of sulfur plugs;
- hormonal changes in the body during adolescence;
- dermatitis, eczema, allergies in a chronic form, while reddish spots are observed on the auricle and in the ear canal;
- excess cholesterol - this element is part of sulfur and can affect its amount;
- frequent wearing of hearing aids, headphones and other foreign objects in the ears - the nerve endings of the glands become irritated and begin to secrete a large amount of secretion;
- improper ear care, excessive desire for hygiene and constant cleaning of the ears from wax;
- psycho-emotional stress in a child, stress and heavy loads;
- long stay in a dusty, dirty room;
- damage to the ear canal;
- increased secretion in infants from birth.
Unpleasant odor from the ear
For some people, earwax normally has a specific smell. This may be due to metabolic characteristics and hormonal changes. During adolescence or when menopause begins, the smell may intensify. Sometimes sulfur begins to smell when it stagnates in the canal, if for some reason its secretion is impaired. In this case, it is worth cleaning your ears from wax using special preparations.
You should consult a doctor if:
- Earwax smells fishy. This often indicates a staph infection.
- A putrid odor emanates from the ear and from the discharge. It is a clear sign of suppuration.
Sulfur plays an important role in the human body. Its normal separation helps clean the ear canal, protects against inflammation and allergies. This is especially important in childhood. After all, a child is more susceptible to otitis media than an adult, and endures them more severely.
Source: uhonos.ru
Concomitant symptoms of ear diseases accompanied by excessive secretion of wax
Symptoms that should alert parents:
- the appearance of itching, burning, color change;
- greenish sulfur mixed with pus flows from the ear - this sign is characteristic of otitis media;
- sulfur discharge has an unpleasant putrid or rotten odor - this indicates infection with staphylococcus;
- an increase in body temperature and general symptoms of intoxication indicate the development of an inflammatory process in the ears;
- pain or feeling of a foreign object in the ear;
- swelling of the mucous membrane and the feeling of fluid flowing inside the ears indicate allergic otitis media;
- dry sulfur is also characteristic of allergies;
- too dark or black-brown color of sulfur occurs with fungal diseases;
- stuffy ears and hearing loss;
- pain in the ear and temple;
- dizziness and nausea;
- blood from the nose;
- obsessive cough.
How to recognize pathology
Earwax is quite problematic to diagnose at home. Even if a lot of mass has accumulated, it may not give itself away. The child feels discomfort only when the ear canal is completely blocked or hearing loss occurs. Often, unpleasant sensations appear after bathing; the water causes the plug to swell, and the ability to perceive external sounds is lost. The following symptoms of wax plugs in the ears accompany the situation:
- noise in the ear;
- nausea (in rare cases);
- feeling of bursting congestion;
- dizziness, headache in the temples.
Some young patients complain that they hear echoes of their conversations in their ears. Pathology can negatively affect the functioning of the nervous system, heart, and the entire body as a whole. Hearing loss is not the most dangerous complication of untimely removal of the plug from the baby’s ear. After a thorough study of the consequences of sulfur formation, the question of its removal is more than relevant.
Features of treatment depending on the cause of the symptom
Treatment for excessive wax production depends on what condition your doctor diagnoses and its cause. He will prescribe rinsing of the ear canal, medications, or refer you to other specialized specialists (allergist, dermatologist, endocrinologist, etc.).
Self-medication with folk remedies is not recommended. In young children, cleaning the ear canal on your own can easily damage the eardrum - the consequences can be very serious.
Removing wax plug
Often, when there is excessive wax production, parents use cotton swabs to clean their ears, but this is strictly forbidden. This can easily damage the external auditory canal. When using sticks, the opposite process occurs - sulfur is not removed, but, on the contrary, is pushed deeper and leads to the appearance of even more discharge.
Cleansing takes place in several stages:
- if the cork is too dense, softening is necessary with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, petroleum jelly or glycerin;
- often, after softening, the plug comes out on its own; if this does not happen, rinsing is required;
- after washing, a 3% solution of boric acid is instilled into the ear; for a while, the ear canal must be closed with a cotton swab.
Another way to remove wax plug is to use special drops or solutions (A-Cerumen), which are sold in pharmacies. Modern clinics have new generation devices that carefully and painlessly clean a child’s ear.
Treatment of the disease
For otitis media in children, ear drops (Otipax, Otirelax, Albucid) are used and rinsing with antiseptic agents (hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, Miramistin) is carried out. Antibiotics (Flemoxin Solutab) are prescribed based on the child’s condition and only in the presence of a bacterial infection. Each specific case of otitis requires a thorough diagnosis and examination by a pediatric otolaryngologist.
The high temperature (over 38°C) that accompanies ear inflammation must be reduced. In children, Paracetamol, Nurofen, and Ibuprofen are used for this purpose. These drugs will also reduce pain, which is known to be quite intense in ear diseases.
If during examination a foreign body is found in the ear, it should be pulled out. A pediatric otolaryngologist has all the necessary equipment for such cases.
Fungal infections of the ears are treated with antifungal drugs approved for use in childhood. Fluconazole, Itraconazole, and Ketoconazole are often used.
If an allergic reaction or eczema is detected, a pediatric allergist will treat you. He will prescribe antihistamines (Fenistil, Suprastin), vasoconstrictor drops (Otrivin) and indicate the need to eliminate allergens and follow a special diet. Often the allergens are pet hair, dust mites, food, etc.
Workshop
- For a healthy child, it is enough to regularly wash his ears in the morning, washing away the wax that naturally comes out. It is recommended to purposefully clean your ears of wax no more than once a week.
- Cotton swabs can only be used to clean the auricle, without penetrating deep into the ear canal. If necessary, use flagella from a sterile bandage - homemade turundas. You can apply a couple of drops of baby oil to them and remove the sulfur with rotational movements.
- After bathing, it is necessary to dry the ear canal and wipe the ears dry so that the remaining water does not cause inflammation.
Parents often notice that large quantities of wax accumulate in their child’s ears, which looks unsightly and contributes to the further formation of plugs. To get rid of it, parents need to know the nature of its origin, the reasons for its appearance and methods of cleaning the ears at home.
Black, brown, light or red wax in the ears
Not everyone knows that earwax performs the most important protective functions. This component protects the ear canal from external factors and irritants, such as the penetration of foreign particles or small insects. It is worth noting that the color of sulfur, as well as its consistency, may vary and there are no standards, but some changes may all indicate the presence of health problems. For example, dark or black wax in the ears can appear as a result of certain disorders; the most dangerous manifestation of wax in the ears is blood; often such formation indicates perforation of the eardrum.
What is earwax used for?
If the process of work of the sulfur glands proceeds without pathological changes, then the produced component has a yellow color and a soft consistency. The component should be contained in the human ear canal in small quantities, regardless of the gender and age of the patient. This need is due to the fact that earwax protects and lubricates the walls of the ear canal and has a positive effect on the functioning of the hearing organs.
Attention! If the work of the sebaceous glands proceeds without complications, sulfur is contained in the ear canal and its supply is constantly renewed. Its elimination occurs naturally.
The list of the most well-known functions of the composition includes the following characteristics:
- Cleansing the ear canal. Sulfur ensures the removal of all pathogenic microparticles of dirt and dust that have penetrated the ear canal.
- Protective. Helps prevent water from accidentally entering the inner ear. Provides destruction of fungi, viruses and bacteria.
- Lubricating. Protects the ear canal from drying out, increases the elasticity of the epithelium.
Based on this information, it is worth summing up: sulfur in normal quantities should be present in the human ear canal. One should not lose sight of the fact that the production of sulfur of a non-standard shade is a cause for concern.
Causes
The cerumen glands located in the ear continuously produce a viscous secretion called sulfur. It is worth noting that the composition has only an external resemblance to the chemical element and is not classified as its analogue. The average monthly volume of production of the compound for a healthy person is 5 mg, while a deficiency of the substance is no less dangerous for the human organ than its excess.
Among the reasons for the decrease and intensification of production processes, the following factors are distinguished:
- the presence of chronic pathological processes in the hearing organs;
- manifestation of diseases in acute form;
- congenital abnormal structure of the auditory cavity;
- ear injuries.
Dark sulfur can form in individuals whose professional activities involve direct contact with dust and other small particles. In this case, the formation is not dangerous. Patients working at metallurgical enterprises or mining production need to be examined by an otolaryngologist once every 6 months; if there is a plug in the ear, they are washed.
Black sulfur
There are a sufficient number of reasons why there is dark wax in the ears:
- fungal infection of the hearing organs;
- mechanical damage to the hearing organs;
- constant contact with dust and dirt.
The least dangerous cause and the most common is contact with dust. If the patient comes into frequent contact with such particles, the color of the secretion may change.
Attention! When small insects enter the canal, sulfur may form with blood. In this case, the component will also have a dark tint.
Brown sulfur
The presence of brown sulfur, a viscous consistency, in the human ear canal is an indicator of normality. Often sulfur of this color appears in children under the age of 5 years. It is worth noting that its production during this period may be somewhat enhanced.
However, brown sulfur can signal the manifestation of serious diseases associated with impaired patency of blood vessels. It is necessary to pay attention to the manifestation of such a change if blood is present in the secretion. The risk of developing a severe, hereditary disease called Randu-Osler syndrome cannot be ruled out.
Red sulfur
Red sulfur can often frighten people because its appearance is similar to dried blood. If such a color change occurs, you should seek emergency medical attention. This is due to the fact that there is a high probability of perforation of the eardrum.
Liquid sulfur
A change in the usual consistency of sulfur may indicate the development of dangerous pathological processes, such as:
Attention! Liquid sulfur is often produced in patients suffering from hypercholesterolemia. A sudden change in the usual consistency may indicate the development of serious disorders in the human body.
Deviations from the norm
In principle, wax in a child’s ear performs a very important and positive function—protective. It is thanks to it that the eardrum is reliably protected from all kinds of harmful influences from the outside. However, in large quantities and with certain features in the baby’s condition, sulfur can become an alarm signal for parents:
- if earlier wax rarely appeared in the child’s ears, but at some point its production increased several times, this may indicate intoxication of the small organism: in this way it will remove pathological, harmful substances;
- dry wax in a child’s ears most often becomes a symptom of various skin diseases that affect the epidermis of the ear canal - this could be psoriasis, neurodermatitis, some allergic reactions;
- if liquid wax is detected in a child’s ears, it is one of the first harbingers of any inflammation: for example, in this case it is necessary to show the baby to the doctor to begin timely and correct treatment, so as not to lead to high temperatures;
- sometimes black wax appears in the child’s ears, and then parents need to observe especially carefully for some time: usually this is a one-time phenomenon due to the fact that dirt has gotten into the baby’s ear and is now coming out of it in this way; however, if this occurs for several (2-3) days, you should consult a doctor to rule out a purulent inflammatory process;
- the usual dark brown wax in a child’s ears is an indicator of the norm: this is the color of discharge from the ear canal in healthy people, so in this case there is no need to worry about your child.
Most often, dark wax in a child’s ears (but not black) is a kind of indicator of cleanliness, while many mistakenly consider it an indicator of neglect. If you are only confused by the aesthetic factor of this phenomenon, it is enough to clean your baby’s ears just once a week to keep them clean and well-groomed.
What does an excessive amount of sulfur in a child indicate?
Excessive wax formation in a child's ear canal is often a cause for concern for parents. Such a disorder can cause many problems: the child becomes less active because he feels constant discomfort, there is a decrease in appetite, and general apathy can be observed. Such changes manifest themselves in the case of the formation of sulfur plugs, which should definitely be removed as soon as possible, because they interfere with the flow of natural processes.
The reason for the increased activity of secretion from the glands is often the parents’ failure to comply with hygiene rules. That is, in cases where the child’s ear cleaning procedure is carried out too often or in violation of basic rules. Constant, active release of sulfur is a cause for concern; parents should show the child to a specialist.
Sulfur deficiency
The absence of earwax in the cavity is no less dangerous; such a violation can cause many problems with the hearing organs. In the absence of secretion, the middle and inner ear are more susceptible to the influence of pathogenic microorganisms. Often against this background, otitis media progresses.
The list of main reasons for the manifestation of such a violation includes:
- previous inflammatory process of the hearing organs with its subsequent chronicization;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene rules, that is, extremely scrupulous, deep cleaning of the ear canal;
- otosclerosis;
- the presence of tumors blocking the excretory function.
Physiotherapy techniques are often used to restore the natural functions of the glands.
Diagnostics
If any disturbing changes occur, the patient should contact an otolaryngologist. The specialist will be able to identify the presumptive cause of the development of the pathology during the initial examination. To clarify the diagnosis, a comprehensive examination is carried out, after which the optimal treatment regimen is prescribed.
Diagnostics involves the following manipulations:
- examination of the hearing organs using an otoscope;
- Ultrasound;
- CT;
- radiography.
Laboratory techniques are often used, based on the study of the patient’s blood and urine samples. Such actions can reduce the likelihood of hidden inflammation.
If any disturbing changes occur, you should seek help from a doctor; acting on your own is strictly prohibited. After accurately determining the causes of changes in the color and consistency of earwax, the doctor will determine the method of treatment.
For patients experiencing black wax, ear rinsing is indicated. If an inflammatory process of fungal etiology is detected, drug treatment is carried out. In particular, physiotherapy techniques are used to normalize secretion processes. The risk of perforation of the eardrum cannot be ruled out, especially if pain is an accompanying symptom. Any actions in this case are potentially dangerous.
Prevention
Frequent use of headphones can cause excessive amounts of wax
To maintain hearing health, you must follow these recommendations:
- unquestioning provision of personal hygiene rules;
- refusal to wear headphones;
- minimizing the risk of fluid entering the auditory cavity;
- timely completion of preventive examinations;
- wearing hats in the cold season.
The described rules are simple, but they are often a factor in ensuring effective prevention of inflammation.