After the birth of a child, inexperienced parents often worry about everything. For example, why does he sleep so much, cry so much (or little)? Why doesn’t it react to the hair dryer working in the next room? Why are his eyes constantly moving apart? The last two questions will definitely not arise if parents know when their newborn baby begins to see and hear.
Formation of auditory function
You may be surprised, but babies begin to hear in the womb . The hearing organs are formed early - at the 5th week of pregnancy, the rudiments of future ears, or more precisely, the inner ear, are formed. At 7 weeks, the middle ear is formed, and then the auricle. The fetus's ears become hard only shortly before birth.
Important for the ability to hear, the inner ear completes its formation at about 19 weeks. And even after birth, the auricle continues to remain quite soft, the ear canal is narrow, and this will correct itself only by the first year of life.
Children begin to hear the first sounds in their mother's belly after 14 weeks . But while these sounds are more reminiscent of the hearing of a reptile, the fetus picks up the vibrations that accompany the sound waves. As the inner ear completes its formation and the labyrinth hardens, the ability to hear better appears. This happens after the 20th week; by the 26th week of pregnancy, the baby in the stomach hears almost like us, but adjusted for the fact that it is still in an aquatic environment.
He hears his mother’s heart beating and blood flowing through her vessels, how her intestines work. He hears her voice and quickly gets used to it. Sounds from outside begin to interest the baby only in the last weeks of pregnancy. The child hears the music that sounds in the mother’s headphones, but only if the headphones are placed directly on the stomach. If they are on the mother’s ears, the child cannot hear the sounds.
The baby is born hearing. If a newborn’s vision is very imperfect, and the baby perceives only blurry, indistinct spots, then everything is fine with his hearing.
Of course, provided that during the process of the formation and development of hearing organs in the prenatal period of development, no errors or problems arose that could affect the state of hearing.
Fetal hearing: the fetus develops by listening to music
You've probably heard about the “Mozart effect”? This is an incentive to play classical music for your child even before birth. Thanks to this, the baby will have a higher IQ and will study better in the future.
Scientists (led by Alfred Thomas) prove that stimulation by music affects the development of the fetal nervous system.
A child's brain learns to accept and process sounds. It is best stimulated by classical music, which affects the proper functioning of the brain waves and heart of the fetus. Children love the works of Vivaldi, Bach, Mozart, Schumann and Gregorian chants. Listening to this music, he moves calmly.
And when he hears high-pitched and low-frequency sounds that are unpleasant to him, he may even turn his back on the sound wave. For example, the music of Beethoven and Brahms causes anxiety in a child (maybe this is too monumental and dramatic for him?).
However, before you develop your baby with music, check out the findings of scientists from Columbia University. Developmental psychologist William Feather, who works there , warns pregnant women about playing music in close proximity to the fetus, that is, by putting headphones on their stomach, for example.
This can disrupt the unborn baby's sleep and, as a result, disrupt its growth and development, he said. He explains that the child does not need such “artificial” acoustic stimulation, the baby should accept sounds naturally. In addition, it is enough to play music for your child for 5-10 minutes twice a day. The same recordings should be listened to after the birth of the child. When you turn them on, the baby will calm down, as if by magic. Familiar music will give him a feeling of security. Soon you will be able to find out for yourself.
Source of the article: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5a880f8b9b403cdd1c766b2e/chast-iii-sluh-u-ploda-kogda-malysh-nachinaet-slyshat-chto-slyshit-rebenok-v-utrobe-materi-i -kakie-zvuki-liubit-5ab53fdc77d0e620019bc042
Screening after birth
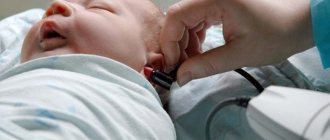
In the first days of life (usually after the second day) in the maternity hospital, all newborns undergo a special test - testing their hearing abilities or audio screening. A special device is used to record the response of hair cells to sound stimuli. The second screening examination is recommended to be carried out at the age of 1 month, 3 months, or six months.
It is difficult to say how reliable such a study is. If it provided the most accurate data, it would be possible to diagnose hearing pathologies within a year.
In the meantime, most cases of minor sensorineural hearing loss and unilateral hearing loss or deafness (if one ear cannot hear) are detected much later. That is, a child who has successfully passed audio screening may well turn out to be hard of hearing.
In the maternity hospital they use the delayed otoacoustic emission method . A portable device with a small, thin, flexible probe is called an audiometer. One part of the probe is placed in the baby's ear. The device sends sounds into the ear through a probe. Hair cells in the inner ear detect them and amplify them if the child hears them. If not, then the hair cells do not receive the signal, there is no impulse. To obtain more accurate results, it is considered optimal if the baby is fed and sleeping.
In the extract from the maternity hospital, if you look closely, you can find the following designations: D (+) = S (+). This means that the child was successfully screened for both the right and left ears. He hears.
If instead of pluses there is a minus, the screening showed the absence of a reaction of hair cells, and therefore the child will definitely be prescribed an additional examination.
Screening of premature babies has its own nuances. They undergo an acoustic examination not on the second day, given the immaturity of all organs and systems, including the hearing organs, but on any day after 2-4 weeks of life.
At risk for possible pathologies are children born to deaf or hard of hearing parents, as well as children born from a pregnancy during which the woman suffered from infectious viral diseases, especially if this happened in the early stages.
Hardware examinations
Screening allows you to accurately determine the impairment of a newly born child’s ability to hear while still in the maternity hospital. Based on the results of the procedure, the doctor can determine where changes have occurred in the child’s body that interfere with the perception of sound.
A correctly conducted examination and the professionalism of the doctor make it possible to accurately determine in which area of the auditory department the changes have occurred, and to build an effective and efficient treatment regimen.
The first screening examination is carried out before the child is discharged from the hospital during the first week of life. This examination is standard and is included in the newborn examination program.
Two different methods are used to examine children:
- study of the reaction of the auditory trunk of the central nervous system (according to the international terminology AVR);
- acoustic emission (OAE).
The test used to check the hearing of a newborn is selected based on the methodology used in the medical institution, the availability of equipment and the level of professional training of the doctor. Both methods do not injure the child and are accurate, but differ in the technology used. In some cases, the newborn may need to have both tests.
How to check at home?
All parents of newborns, one way or another, try to independently understand how the baby sees and hears. At home, a method such as observing the child’s reaction to sounds will help . The behavioral method is only approximate and inaccurate, because if some deviations are detected, it cannot show how significant the hearing loss is and what caused it. But this is not required from a home inspection.
Parents can check their hearing themselves in order to consult a doctor if they receive questionable or unsatisfactory results. There is no need to wait for the child to grow up . For normal mental development and speech development, it is important to hear, and therefore hearing correction is possible in infancy: children are fitted with hearing aids (ear correctors), and operations are performed to restore the auricle if there are defects of the outer ear.
There are many ways to help a child, but help will be more useful if it is provided as early as possible.
If the baby is already a month old, you can try using the behavioral method. It is based on the baby's specific reactions to sounds. It is important that the child is at rest, dry and well-fed .
First, make different sounds from the right ear, and then from the left. Start by clapping your hands from a distance of about half a meter. Then check how your baby perceives quieter sounds, for example, the sound of a rattle (choose a toy with an initially quiet sound). High frequencies can be checked using semolina, which the mother can pour into an empty metal jar. Shake such a jar close to the ear - the baby can only catch the high-frequency sound of the cereal at close range.
How to understand that a child perceives a particular sound:
- he becomes animated by the sound with synchronized waves of his arms and legs;
- he freezes and tries to discover the source of the strange sound;
- the baby opens his eyes wide and changes his facial expression;
- The baby's breathing frequency and depth changes.
Home hearing tests are never performed on children who are sick, have colic, or are teething , or if the baby is hungry or has not gotten enough sleep. Any discomfort that the baby feels increases the likelihood of an incorrect behavioral response to sounds.
In the first month of life, children almost do not distinguish between low frequencies; for them, the high frequency range is more familiar. If tests are carried out on children aged 3 months and older, then such an important sign as turning the head towards the sound source is added to the list of reactions.
A hearing test technique based on playing different sounds by frequency is called the Kalmykova method . For such a test, you will need three plastic containers, which are proposed to be filled by a third with semolina, buckwheat, and peas . These will be high, mid and low frequencies. To check, you will have to involve your dad or grandmother as assistants. While one distracts the child’s attention with a bright toy, an unusual object, the second, half a meter from the right ear, and then from the left ear shakes a can. They start with semolina (that is, with high-frequency sounds), then they take buckwheat, and lastly, peas. Between changing cans, take a break for a couple of minutes.
The test is considered passed successfully if the child, even without being distracted from the toy, reacts (even briefly) to the sound of cereals in jars . He may freeze for a second, turn his head and look at the jar, begin to look for the source of the sound with his eyes, and change his facial expression. If there is no reaction at all, you should show the child to an ENT specialist and an audiologist.
Inner ear examination (UAE)
To check how the hearing aid itself reacts to sound, the otoacoustic emission method is used, which is determined using a special diagnostic device.
To obtain the correct result, the child must sleep. A device consisting of a speaker and a microphone is placed in the baby's ear. The sound is transmitted through the device to the brain, and another sound is generated in parallel, which is not transmitted along the nerve. This effect is called otoacoustic emissions.
The test computer program allows you to determine which sounds the child’s hearing aid responded to, the quality and quantity of these responses.
According to the test results, the child must respond to the intensity of sound, which makes it possible to distinguish quiet speech. Screening is carried out over 10 minutes.
Possible problems
Hearing problems in newborns and infants can vary. The reason for the lack of hearing in severe cases lies in anomalies of the auditory nerve or auditory center of the brain, or may be a consequence of mechanical damage - the mother cleaned the child’s ears with ear sticks and damaged the membrane.
In the second case, sometimes it is enough to clean the ear canals, apply drops, and everything goes away. But more often in the case of hearing loss, medications are ineffective, especially if the hearing loss is congenital. The forecasts, alas, are disappointing. The disease cannot be cured, but you can significantly improve the child’s quality of life, give him a chance to develop normally, learn to speak, and adapt to society. Audiologists and hearing prosthetists will help with this.
Properly selected hearing aids and cochlear implantation surgery can give a child the opportunity to hear. Reviews about such methods are good, because they give hearing-impaired children a real chance for a normal and fulfilling life.
A specialist talks about early diagnosis of hearing impairment in the video below.
- Newborn
- Reflexes
- APGAR scale
- When he begins to hear and see
- Care
- Diapers
- Swaddling
medical reviewer, psychosomatics specialist, mother of 4 children
How to determine whether newborn babies hear: expert advice
Hello, dear readers of my blog! Irina Ivanova is with you, and today, as, indeed, always, we have a very interesting topic for discussion. Let's talk about whether newborn babies hear. I thought about this after a friend of mine, who recently became a mother, confidently asserted that these tiny boys and girls don’t hear anything.
Otherwise, why in the children's ward of the maternity hospital, which she looked into, were only the babies fast asleep when their neighbors began to cry in anticipation of feeding? After all, according to her, if they had hearing, everyone would wake up from the noise. I began to collect information, leafed through medical journals, talked with a neonatologist and pediatrician, and I want to tell you everything that I found out myself.
Does he hear even before birth?
Yes, that’s right, the baby begins to perceive sound-frequency vibrations even during intrauterine development. This occurs between 20 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. It is possible that the fetus acquires auditory function even earlier, but it was during this period that researchers were able to establish a connection between changes in its pulse and movements and sound vibrations from the outside.
We must not forget that all sounds reach the child weakened by the mother’s abdominal wall and the amniotic fluid of the uterus. That is, he hears the noise of her heartbeat and loud sounds from outside, the intensity of which is reduced by about 30-70 decibels. This is the baby's first hearing experience with which he is born.
Kalmykova method
A more complex technique was developed by doctor Kalmykova and involves the use of objects that create sounds of varying strength. For the manufacture of analyzers, identical plastic jars are used, one third filled in each house with semolina, buckwheat and peas.
2 people work with the baby - one plays with the baby, showing him a beautiful, brightly colored toy, the second shakes a can of cereal over the child’s ear at a distance of 10-15 centimeters. At each stage of verification, different banks are used. First use a container with semolina, then with buckwheat, and lastly with peas. Take a one-minute break between tests. In each period of development, the baby reacts to different intensity of sound - up to 6 months it is 70 decibels.
A normal child will be interested in a toy, but at the same time will react to the sound of a can of buckwheat and peas; if the reaction does not appear, this should alert the parents.
If a child is diagnosed with a hearing defect, this is not a reason to fall into despair. Modern methods of treatment and prosthetics allow such a child to be a full-fledged member of society.
Does the newborn like all sounds?
Some readers may say: “What are you talking about? How can a newborn like or dislike something? And, in general, we still need to prove whether children who have just been born see and hear anything!”
Meanwhile, researchers have identified some patterns in the perception of sounds that appeared from the first hours of a child’s life:
- Children enjoy sounds with low frequencies (below 500 hertz), they cause a pronounced reaction in the form of unconditioned reflexes - the baby calms down and stops sucking movements. This is why babies like male and low female voices.
- Newborns become restless and their breathing and heart rates change in response to high-frequency sounds (above 1000 hertz) they hear.
- Both types of reactions are more pronounced in response to speech-like sounds.
- Loud sounds that occur suddenly cause a reflexive start and crying.
Adaptation to the external sound environment occurs during the first month. This innate quality is aimed at improving hearing. By the end of the first month, the baby already knows how to identify the mother’s voice from the sound mass, even distorted by filters or recorded on audio media.