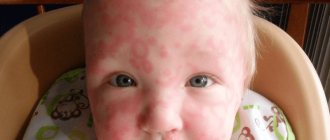
Allergic conjunctivitis in a child is a disease that occurs with the development of an inflammatory process in the conjunctiva of the eye. It develops when allergens of any nature penetrate into the body. Accompanied by swelling, hyperemia, lacrimation, itching, photophobia. The pathology is treated by two specialized specialists - an allergist and an ophthalmologist. The treatment plan includes avoiding contact with the allergen, using antihistamines and immunotherapy.
The human body, especially a child, is hypersensitive to various types of allergens. This is due to the fact that preschool children have not yet developed protective mechanisms that inhibit the reaction to allergen irritants. More often, the reaction manifests itself on the mucous membranes, inflaming them. The mucous membrane covers many organs of our body, including the sclera and the inside of the eyelids. Therefore, along with other pathologies - hay fever, dermatological reactions, asthmatic manifestations, the conjunctiva becomes inflamed, forming the disease conjunctivitis.
Allergic conjunctivitis is a common inflammatory disease of the conjunctiva of the eyes. The disease is usually seasonal. Some children may experience allergic conjunctivitis all year round.
Manifestations of allergic conjunctivitis
Among children, the largest percentage of the disease occurs in patients aged two to four years. As a rule, in schoolchildren, allergies cause conjunctivitis in only five percent of episodes.
The disease is sometimes combined with other allergy symptoms - runny nose, atopy, asthma. When allergic conjunctivitis is combined with a runny nose, the disease is called allergic rhinoconjunctivitis.
Children who are prone to allergies are predisposed to allergic conjunctivitis. If a child has atopy or bronchial asthma, then he also has a predisposition to allergic conjunctivitis.
Allergies are inherited. If parents had allergies in childhood, there is a high probability that the child will inherit the disease.
Cause of the disease
Conjunctivitis caused by allergies is seasonal or chronic. Seasonal allergic conjunctivitis is usually caused by pollen and is called hay fever. Chronic allergic reactions are more often associated with other sources of allergens.
The cause of allergies is the reaction of the child’s immune system to specific environmental factors. The types of allergens are very diverse. It is customary to divide them into types. The most common ones are presented in the table.
Table: Common allergens
| Allergens | Examples |
| Dust | Dust mites |
| Pollen | Wind-pollinated plants, deciduous trees, grasses, weeds (wormwood, nettle) |
| Fungi | Outdoor mushrooms (grow in the soil, spread on rotten plants) and domestic |
| Animals | Epithelium, fur, drool, animal urine, bird feather |
| Food products | Eggs, peanuts, dairy products, soybeans, hazelnuts, fish, crayfish, wheat |
| Medicines | Biologically based drugs (antibiotics, chicken embryo vaccines, contrast agent for X-ray examinations, anesthetics) |
Sometimes allergic conjunctivitis can indicate a dangerous condition of the body - Quincke's edema. This condition requires immediate medical intervention, because it often causes death.
Classification of types and forms
Directly depending on the factors that determine the variants of the disease, the following types are classified:
- acute form;
- subacute form;
- chronic form.
Modern studies of allergies have proven that in young children, genetic predisposition in combination with social and household factors contribute to the disease. In older children, sensitization to the influence of allergens comes into play.
As for the classification of forms, it is derived absolutely depending on what kind of allergen the reaction provoked.
Table: Forms and provoking factors
| Form | Factors and description |
| Hay conjunctivitis | It is also called seasonal, and is expressed as complex rhinoconjunctivitis. Known as hay fever. The peak of manifestation is at the time of flowering of certain elements of the flora. |
| Spring conjunctivitis | Catarrh has another name, occurs more often in boys, and appears in the spring months. This form occurs due to the abundance of sunlight, can easily become chronic, and is divided into three varieties: - conjunctival; - mixed; - limbal. |
| Drug-induced conjunctivitis | As the name of the pathology implies, it occurs after taking or externally using certain medications. |
| Phlyctenular conjunctivitis | Affects infants and children under three years of age. It is called keratoconjunctivitis because it manifests itself as redness and dryness of the conjunctiva in a tearless form and is of allergic-tuberculosis origin. |
| Papillary conjunctivitis | It is called giant or hyperpapillary, and occurs due to the invasion of a foreign body into the eye area and contact of the membrane with it. |
| Allergic-infectious conjunctivitis | The cause of the outbreak of this disease is an increase in sensitivity to exotoxins in the body that release bacterial-viral material. With this form, the pathogen itself is not directly in the conjunctiva. |
Classification
In medical practice, there are several classifications of allergic conjunctivitis. According to the nature of its occurrence, the pathological process can be year-round, periodic and contact .
In the first case, the appearance of symptoms of the disease can appear regardless of the time of year, in the second, outbreaks of the disease are observed mainly in the spring or winter.
The contact form develops immediately after a child is exposed to a certain allergen.
Children's allergic conjunctivitis is divided into the following types:
- Hay fever or hay form (develops seasonally, is caused by pollen of certain plants, in most cases is accompanied by rhinitis or urticaria).
- Hyperpapillary type (provoking factors are foreign bodies in the eyes).
- Dosage form (the main cause of pathology is a negative reaction of the child’s body to certain medications, most often in the form of eye drops).
- Spring catarrh (boys of preschool and primary school age are most susceptible to pathology; the disease manifests itself mainly in the spring).
- Tuberculosis-allergic type (the disease is provoked by waste products of Mycobacterium tuberculosis).
- Infectious-allergic form (pathology occurs under the influence of a specific reaction of the child’s body to infectious allergens).
Read about the symptoms and treatment of gonoblenorrhea in newborns here.
Symptoms of the disease
After interacting with the source of the allergen, the body’s response develops in a few minutes or hours, sometimes longer - up to two days. Histamine is released, which provokes allergic manifestations on the conjunctiva of the eyes.
Inflammation in the conjunctiva can develop in a matter of minutes, or maybe only a few days after the onset of the reaction. The process can start acutely or slowly, gradually or with exacerbations, but both eyes are always affected at once.
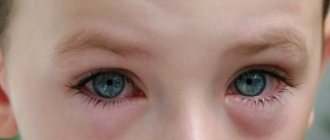
The initial symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis in children are as follows:
- eye swelling, eyelid hyperemia;
- the outflow of tears is increased;
- attacks of photophobia;
- itching of the eye sockets.
It is because of the constant itching that the child rubs his eyelids, provoking an even greater burning sensation and increasing swelling.
With conjunctivitis caused by allergies, there is no purulent discharge. If the transparency of the exudate is impaired, either it is a bacterial purulent conjunctivitis that does not contain an allergic nature, or the child has introduced an infection into the eyes by constant rubbing.
After passing the initial stage, the main stage begins, and the symptoms change:
- there is a pain, a feeling of “sand”;
- the mucous membrane dries out, the exudate dries up;
- when the eyeballs move, sharp pain occurs;
- a veil periodically appears before the eyes;
- due to growing edema, visual acuity decreases, sometimes significantly.
With allergic conjunctivitis, not all of the listed signs of the disease may be present. One or two symptoms are enough to suspect a child has an allergy.
Since conjunctivitis is characterized by intense itching, the child tends to scratch his eyes. This can serve as a favorable condition for the spread of bacterial infection. Therefore, the sooner you see a doctor, the better. Don't stop your child from scratching his eyes. This can negatively affect his psycho-emotional state.
Allergy sufferers feel worst in dry heat. In such weather it is better to refrain from long walks. When it's cool and humid outside, allergy symptoms become less severe.
Additional symptoms may be added to the main symptoms, depending on what caused the disease:
- The seasonal type of conjunctivitis begins with a sudden acute process and proceeds quite violently, supplemented by allergy symptoms of other organs, as well as urticaria, bronchial asthma, rhinitis, Quincke's edema, dermatitis and digestive disorders.
- Spring catarrhal type is almost always complicated by erosions and ulcers. The cornea may be affected.
- The papillary type is also called large-papillary, since this disease is characterized by the covering of the conjunctiva with papillae with a diameter of about one millimeter (this is a lot for the scale of the eye). Has several sources of origin. It can develop either due to contact of the mucous membrane with external irritants or foreign bodies directly located in the eye. These include lenses, prostheses, as well as postoperative sutures.
- The phlyctenular type causes concomitant lesions of the cornea and the appearance of small nodules on it, called phlyctenula. They, unlike papillae, can appear and disappear spontaneously. Sometimes the formations ulcerate, leaving scars. Manifests itself as a hypersensitivity reaction to the presence of bacterial antigens in the body. Usually these are staphylococci, but there may be chlamydia, tuberculosis and other agents. With this form, pathological lacrimation is observed, accompanied by photophobia, as well as severe blephorospasm, in which the orbicularis oculi muscle contracts uncontrollably.
- In the medicinal form, the course also has an acute, sudden form and does not subside until the effect on the body of the drug that caused the allergic process ends. It manifests itself with inflammation of the conjunctiva, occurs after drops or ointments used for the eyes. The active substance and preservatives they contain cause a reaction in children with a predisposition to it. The most “dangerous” drugs from this point of view are anesthetic ointments and antibacterial drops.
- The infectious-allergic type is almost always chronic. It has a slow reaction and is not even immediately noticeable. His symptoms are weak and scanty.
How does allergic conjunctivitis occur in infants?
The disease can begin in the first days of life and is often observed in newborns, but it occurs even more often in infants. There are often cases when a baby’s eyes become sour and wet. They stick together after sleep, and a dirty whitish crust forms and dries on the outside. If the eyelids do not swell and the conjunctiva does not turn pink, then this is not conjunctivitis. It is enough to rinse your eyes with boiled water several times for the signs to disappear.
From birth, not all organs of the baby are functioning, including the ducts of the lacrimal glands cannot cope with the removal of tear fluid. These ducts are attached to the nasal cavity and their patency is often reduced. After two months, it rises to normal, and the eyes cease to have a pathological appearance.
Characteristic symptoms:
- Redness of the conjunctiva along with the eyelids.
- Swelling of the eyelids and around the eye.
- Tearing.
- Cutting in the eye sockets.
- Itchy eyelids.
- Refusal of food.
- Discharge from the organs of vision, ranging in color from off-white to yellow.
- Daytime agitation, crying for no reason
- Child's restlessness and poor sleep.
The difference between allergic conjunctivitis and other types of disease
Conjunctivitis has three types: allergic, viral, bacterial. The symptoms are similar. The causative agents of the disease are different. In order to choose the right treatment tactics for the disease, it is important to distinguish allergic conjunctivitis from other forms of conjunctivitis.
Comparative table of conjunctive symptoms:
| Symptom | Allergic | Bacterial | Viral |
| Purulent discharge | — | + | — |
| Tearing | + | + | + |
| Photophobia | + | + | + |
| Both eyes are always inflamed | + | — | + |
| Edema | + | + | + |
| Temperature increase | — | — | + |
| Enlargement of nearby lymph nodes | — | — | + |
| Itching | + | — | — |
Allergic conjunctivitis differs from other forms of this disease in the absence of purulent discharge and elevated temperature, the presence of itching and the spread of inflammation to both eyes.
This conjunctivitis can be rapid or chronic. This depends on the source of the allergen and the frequency of contact with it.
Prediction and negative consequences of pathology
Allergic conjunctivitis in children is one of those pathologies whose prognosis, if promptly sought qualified medical help, is favorable. The effectiveness of treating the disease with proper elimination of the allergen and the provision of specific immunotherapy is guaranteed to be 95%. The likelihood of relapse of the pathology is also minimized.
Delayed diagnosis of conjunctivitis in children leads to the rapid spread of the inflammatory process not only to the cornea, but also to other eye tissues. This pathological condition leads to the development of various negative consequences as a result of exposure to attached bacteria. This leads to additional infection of the organs of vision.
Possible complications of allergic conjunctivitis in children:
- Retinal detachment
- Keratitis
- Sharpening an image
- Complete blindness
- Ulcerative keratitis
- Scar formation on the conjunctiva
- Perforation of the mucous membrane of the eyes
- Conjunctival atrophy
As a rule, the disease has a chronic form of allergy, which leaves a predisposition to this pathology even in the presence of mild symptoms.
If the slightest signs of pathology appear, you should immediately take the child to the doctor. Attentive attention to health will help avoid the development of complications and obtain a positive prognosis for allergic conjunctivitis in children.
Diagnostics
In order to determine the nature of inflammation in the child’s eyes, it is necessary to contact a pediatric ophthalmologist and, if necessary, an allergist. The doctor’s task is to track the connection between conjunctivitis and the allergen. He prescribes an analysis of the eye fluid and a scraping from the mucous membrane of the eye. In allergic conjunctivitis, an increased level of eosinophils is detected in the test material, and immunoglobulin IgE is detected in the blood.
To determine the source of the allergy, the doctor may prescribe allergy tests for the child. An elimination allergy test involves eliminating contact with the allergen during the period of severe symptoms of the disease. An allergy exposure test is the introduction of an allergen into the body after the symptoms of the disease have subsided. Children over four years old are given skin allergy tests, which include a prick test and an analysis called a prick test.
Experts observe the reaction of the human body and use it to determine sensitivity to a specific allergen.
Then the eye secretion is taken for examination. After examining it under a microscope, the presence of eosinophils is confirmed if there are more than 10%.
If a systemic allergy occurs, for which changes in the conjunctiva are a symptom, complementary basic studies can be done. Feces are collected for worm eggs and an enterobiasis scraping is performed.
It is important to differentiate allergic conjunctivitis from its other types. It differs from bacterial in the characteristics of discharge (absence of pus), and from viral in the presence of swelling and itching.
Allergen tests
Causes
Contact with an allergen is a natural factor influencing the occurrence of any allergic reaction.
Let's look at what main factors can provoke allergic conjunctivitis of the eyes in children:
- pathogenic microorganism toxins;
- response to animal fur;
- allergy to flowering plants;
- solutions necessary for contact lenses;
- cosmetics;
- medications;
- irritation of the eye mucosa by a foreign object;
- response to certain products, for example, chocolate, household chemicals;
- reaction to smoke, particularly cigarette smoke.
If we consider the year-round form of conjunctivitis, the disease can occur due to:
- pet hair;
- bird feathers;
- household chemicals;
- dust containing microscopic dust mites;
- spores of microorganisms actively developing in a room with high humidity.
The seasonal type is provoked by the following factors:
- Poplar fluff;
- pollen from plants that bloom.
Treatment
To prescribe treatment, you must contact a pediatric ophthalmologist and an allergist-immunologist. The doctor will examine the conjunctiva of the eye for the presence of edema and mucosal hyperplasia, prescribe the necessary tests and prescribe medications in accordance with the child’s age.
The treatment of the disease is approached comprehensively. This increases the level of effectiveness of therapy.
- The most important thing to do in case of an allergy is to eliminate contact with the source of the allergen.
- For an allergy sufferer, the cleanliness of the surrounding area is of great importance. Daily wet cleaning is a necessary measure, especially during an exacerbation period.
- Prescribing antihistamines. Among the wide variety of products, you need to choose the one that is suitable for the child’s age. If the child is small, it is better to give preference to drops (Zyrtec). The tablets have a bitter taste and must be crushed to a powder.
- Apply cool, sterile compresses to the eyes. Effectively relieves swelling.
- Using special moisturizing drops (Levocabastine, Azelastine, Olopatadine) - they relieve irritation, remove dryness, are an over-the-counter drug and have no contraindications;
- Instillation of vasoconstrictor drops into the eyes. Such drops relieve redness and swelling well.
- Anti-inflammatory agents for the eyes.
- Applying hormonal ointment (Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone) to the eyes in severe cases of the disease. Corticosteroids should be used carefully, as prescribed by a doctor. Hormonal medications have contraindications. With prolonged use, they often cause keratitis.
- Allergic immunotherapy – a small dose of an allergen is introduced into the body, after which the body adapts to it and develops allergen resistance. The allergen is taken in the form of tablets, drops, or injections.
- Proper nutrition and clean air are the key to health. If it is not possible to frequently ventilate the room, purchase an air washer, if possible. This technique not only humidifies the air, but also cleans it of allergens.
- During the period of exacerbation, the child must adhere to a hypoallergenic diet that excludes highly allergenic foods from the diet. These include: eggs, bee products, some types of nuts, soybeans, red fish.
- It is important to identify allergic conjunctivitis at an early stage, before a bacterial infection is added to the disease, which can cause bacterial keratitis and decreased vision.
If left untreated, inflammation can spread to the cornea of the eye, which can negatively affect vision.
Table: Medicines for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis
| Group of drugs | Drugs |
| Anti-allergenic drops | “Histimet”, “Spersalerg”, “Opatanol”, “Allergodil”, “Lecrolin” |
| Antihistamine drops | "Krom-Allerg", "High-Krom", "Cromohexal", "Ketatifen", "Alokomid" |
| Antihistamines for oral administration | "Loratadine", "Erius", "Zyrtec", "Eden", "Cetrin", "Telfast" |
| Topical corticosteroids | "Dexamethasone", "Medrisone", "Hydrocortisone" |
| Drops from drying out | "Vizin", "Vidisik", "Systane", "Oftogel" |
| Drops for corneal restoration | "Emoxipin", "Oftan Katahrom" |
| Drops against inflammation | "Indocollir", "Diclofenac" |
| Immune drugs | "Histaglobulin", "Cyclosporin" |
Absolutely all drugs are prescribed only by a doctor, who must strictly adhere to the dosage prescribed for the patient’s age. Most of these medications have a strict age limit; they are not prescribed to infants or even to patients under four years of age.
Folk remedies
Some of the recommended remedies provoke even greater allergies, which are difficult to relieve. If you want to help your child using traditional methods, it is better to choose the “harmless” one - tea leaves. It should be fresh and cool. Cotton pads are dipped into the tea leaves and lotions are made.
You can apply discs soaked in chamomile infusion to your eyes. It is also permissible to use thyme and dill (seeds) among medicinal herbs.
If a young patient has a tendency to this pathology, regular monitoring of his condition by an allergist is necessary, and he also needs to have antiallergic drops at home.
Symptoms of the disease should never be missed or ignored. Timely diagnosis of allergic conjunctivitis and a scheme for providing medical care will make it possible to quickly eliminate the disease, preventing it from developing into a serious visual pathology.
Methods of treating a child: medications and traditional medicine
Modern medicine offers several ways to treat allergic conjunctivitis in children. The choice of therapeutic course and selection of medications directly depends on the degree of development of the disease, its etiology and the age of the patient. The effectiveness of treatment directly depends on the implementation of mandatory elimination measures, which consist in eliminating contact with the provoking allergen.
The pathogenetic basis for the treatment of this pathology is the use of antihistamine drugs in the form of tablets and eye drops. Among them, experts identify the following drugs:
- Eye drops: Allergodil, Cromohexal, Opatonol, Optikrom, High-Krom. Quickly relieve the symptoms of conjunctivitis and relieve inflammation in the eyes.
- Tablet medications: Zodak, Zirtec, Fenistil, Telfast, Loratadine, Suprastin, Claritin, Cetrin. Prescribed for acute and moderate forms of the disease. They are characterized by a minimal number of side effects and are easily tolerated by young patients.
- Hormonal drugs with the active substance hydrocortisone or dexamethasone. Can be in the form of eye drops or ointments. Prescribed in short courses when allergic conjunctivitis is severe.
- Moisturizing ophthalmic drops: Pure tear, Visine. Used for increased dryness and irritation.
- Taking into account the etiology of the pathology, antibacterial eye drops, drugs with a membrane-stabilizing effect, and specific immunotherapy drugs can be prescribed.
Also, traditional medicine is considered effective in the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis in children. They will quickly and effectively help reduce the symptoms of the disease. Naturopaths distinguish the following methods of alternative therapy:
- Rinsing the eyes with phyto decoctions, tea, antiseptic tinctures.
- Compresses made from herbal decoctions, tinctures and infusions, vegetable or potato juice.
- Aromatherapy with essential oils and pine sawdust.
- Instillation of the juices of certain plants or bee products into the eyes.
Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis in children should be carried out exclusively as prescribed by a doctor. Self-therapy in this case is strictly prohibited. If treated incorrectly, there is a high probability of a deterioration in the child’s health and an increased risk of developing serious complications.
Prevention
If human contact with the allergen is excluded, the prognosis for allergic conjunctivitis is favorable. Preventive measures depend on the type of allergy - seasonal or chronic.
Allergy prevention
If your child experiences seasonal allergies every year, it is important to prepare for flowering plants in advance. Perhaps the doctor will prescribe a course of antihistamines as a preventative measure, or prescribe a preventive course of desensitizing therapy. In dry heat, it is better for allergy sufferers to stay at home. Such weather aggravates the course of the disease.
If a child’s allergies are chronic, it is necessary to do allergy tests and identify the causative agent of the allergy. For example, if it becomes known that conjunctivitis is caused by animal hair and dust, you will have to wet clean the house daily. Dust mites cannot tolerate high humidity or cold temperatures.
If your child's allergies are caused by household chemicals, make sure that the child's clothes are rinsed well after washing. Wash off cleaning agents and detergents thoroughly with water. Store household chemicals in a closed cabinet. If the allergy is caused by indoor fungi, you should get rid of them and ventilate the room as often as possible.