A common problem in childhood is a runny nose. Its constant occurrence is due to the structural features of the nasal passages in young children. Then the parents are faced with the question of how to help their child, what children’s drops to give for a runny nose. It is important that they are effective and safe.
How does a runny nose appear?
The nasal passages in children are wide and short. This helps the settling of microorganisms on the mucous membrane and the frequent development of a runny nose.
A runny nose is not an independent disease, but a symptom that most often accompanies acute respiratory diseases.
It develops gradually—several stages of its formation can be traced:
- Short initial stage, lasting up to eight hours. During it, there is a burning and itching sensation in the nose, often sneezing.
- The next stage is called catarrhal. Its duration is 3-4 days. During this process, the nasal mucosa swells and edema forms. Breathing through the nasal passages becomes difficult and copious, light-colored discharge is formed.
- The last stage does not always appear. A runny nose can end at the catarrhal stage, or it can go into the stage of bacterial discharge. It appears as a result of the addition of microbial flora. The nature of the discharge changes - it becomes thick and green-yellow in color. Crusts form in the nose.
Condition of the sinuses with a runny nose
How to treat a runny nose
To treat a runny nose in a child, drugs with different effects are used. First of all, their choice depends on the cause of the disease - allergies, viruses, bacteria.
There are different medications allowed for each age. All medications have indications and contraindications - this is also taken into account when choosing treatment.
What groups of nasal drops are prescribed to treat the disease in young children:
- seawater-based cleaning agents;
- agents with a vasoconstrictor effect;
- drops containing an antibiotic;
- antiallergic drugs;
- children's drops for runny nose with a thinning effect.
Each type of drops should be used for the corresponding symptoms.
How to treat a runny nose in a 5 year old child | How to treat a runny nose in a 5 year old child
At the age of 5 years, the child is in the senior group of kindergarten. Developing together with their peers, children strengthen their immunity, because everything contributes to this: healthy eating, physical exercise, constant walks in the fresh air, etc. However, a runny nose in children is not something supernatural and rare.
How to treat a runny nose in a child aged 5 years?
As soon as one person appears in the group with the initial stage of a runny nose, all the children immediately catch a similar illness. The majority, those with stronger immunity, do not get sick further, but some with a runny nose can suffer for a long time.
In order to quickly cure a runny nose, and so that it does not cause any complications, you should definitely consult a doctor. It is he who will determine the reason why the baby has a runny nose, identify a virus or infection, or simply conclude that the child has some kind of allergy. Depending on the underlying cause, appropriate treatment can be prescribed. However, there are 3 main methods that can be used to cure a runny nose in a 5-year-old child.
The main methods of treating rhinitis in children 5 years old
1. Dripping with a runny nose in a child. There is now a huge selection of nasal drops in pharmacies. These include vasoconstrictors, moisturizers, antiviral, homeopathic and other medications. Only by identifying the cause can you determine which drops are needed in a particular case. You need to drip correctly and very carefully. Side effects are not immediately noticeable, so you need to monitor your child’s reaction to the medications. Also relevant are folk remedies for treating a runny nose. The only thing is that the proportions must be strictly observed so that the child does not have burns or any other damage to the mucous membrane.
2. Washing. This procedure can be done in a hospital; it goes by the well-known name “cuckoo”. However, children 5 years old often have fears of the hospital and doctors in particular. Therefore, many parents prefer to wash their child’s nose at home. This can be done with herbal decoctions, infusions, saline solutions, etc.
3. Inhalations. In addition to cleansing the respiratory tract, due to the warm air that enters the nasopharynx, the runny nose thins out (especially if we are talking about an advanced form of the runny nose), under the influence of the necessary additives, unnecessary mucus comes out of the nose.
4. Warming up will help you heal. If there is no temperature, you can warm up the sinuses. This is done with warm bags of salt or herbs. Sometimes a warm egg is applied to the sinuses. It all depends on the reason for which the child has a runny nose.
How to treat a persistent runny nose in a child aged 5 years?
Rhinitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity. A constant runny nose causes a lot of inconvenience to those who were unable to avoid infection, so it is not surprising that people suffering from a runny nose make every effort to finally get rid of all its symptoms. However, no matter how strong the desire to treat acute rhinitis, the causes of its occurrence are the first thing that should be determined by the doctor. After all, it is precisely what factors led to the appearance of rhinitis that determine how its treatment will be carried out.
When a child’s runny nose becomes an annoying problem, parents, one way or another, have to pay special attention to it. In autumn and winter, this disease is not uncommon even for adults, not to mention children. Rhinitis can be either an independent disease caused by hypothermia or an unhealthy climate, or a symptom of other diseases - respiratory infections or influenza.
A frivolous attitude of parents towards this disease can cause a constant runny nose caused by chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasal passages and sinuses.
1. First of all, in treating a persistent runny nose, you should pay attention to thorough cleansing of the nasal passages: to do this, you need to rinse the baby’s nose from time to time or ask him to blow his nose. In addition, it is necessary to ensure constant hydration of the nasal cavity. As a humidifier for a persistent runny nose, ordinary mineral water, saline solution or sea water are perfect. Oil solutions of vitamins A and E effectively relieve irritation of the mucous membrane and moisturize it.
2. From time to time it is necessary to instill children's vasoconstrictor drops into the child's nose. However, they should be handled with care. In particular, before resorting to their use, parents should carefully study the accompanying instructions. Such remedies in the treatment of persistent runny nose in children 5 years old can be addictive, so it is not recommended to use them for more than five days. However, if you organize treatment correctly, this will not be necessary.
3. After instillation of the vasoconstrictor, medicinal drops or ointment should be used. At the same time, you should not select the medicine yourself: it should be prescribed by a doctor. Only on the recommendation of a doctor should you use antibacterial drops when treating a persistent runny nose - if pus appears in the nasal discharge.
In order to be treated effectively, you need to take care of the position that the child takes while lying in bed. The head of the bed should be raised—for example, with a large pillow—so that the patient's upper torso is higher than the legs. In this case, the outflow of mucus will occur much faster and more freely. In general, with the right approach to treatment, the development of persistent rhinitis will never threaten your child.
AstroMeridian.ru
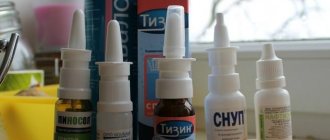
Drops and sprays for rinsing the nose
Used to treat difficulty in nasal breathing in the presence of light, copious discharge. It is used as a prophylactic agent during epidemics of viral infections and flowering of trees.
- "Aqualor". Cold spray for children containing sea salt. There are several spray options with different salt concentrations - physiological and hypertonic solutions. There are also variations in jet pressure - soft shower, normal jet and strong jet. The spray is used for nasal congestion and strong discharge.
- "Aquamaris". Also contains sea salt in different concentrations. Available in two dosage forms - a runny nose spray for children and nasal drops. Can be used to treat difficulty breathing and runny nose.
These are the most famous drugs. There are others, the composition and action of which are similar - “Physiomer”, “Linaqua”.
Approved for use by children from birth - in the form of drops; spray can be used from three months.
Spray for runny nose "Aqualor" is used for strong overlays
There are no contraindications to the use of these sprays for a child; they can be used for quite a long time without an addictive effect.
Inhalations
Pediatric specialists recommend treating a runny nose in children aged 2 to 5 years using inhalations. This method has no side effects, since the dosage of drugs entering the body of a small patient is minimal. Inhalations are used for both therapeutic and prophylactic purposes; they help moisturize the mucous membranes and are characterized by the presence of anti-inflammatory and disinfectant properties. Inhalation is best done using nebulizers. Medicines for physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed by the child’s attending physician!
In order for inhalations to give a quick and favorable result, when carrying out this manipulation you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- An hour before inhalation, feed your child light food.
- Before the procedure and for an hour after its completion, refrain from using antiseptic solutions and expectorant medications.
- After inhalation, it is important that the child is warm and does not go outside for 2-3 hours.
Vasoconstrictor drops and sprays
When a runny nose enters the second stage and swelling of the mucous membrane begins to develop, the use of good vasoconstrictors is required. Their effect is based on spasm of the blood vessels of the nasal mucosa, as a result of which swelling decreases.
- "Nazivin." This medicine is produced in the form of drops and spray. Prescribed for the treatment of severe difficulty in nasal breathing and watery discharge. There are three age dosages of drops - from birth to one year; from one to six years; for children over six years old.
- "Nazol." A drug with a similar effect. For children it is available in the form of drops. There are two age dosages - for children under one year and for children after one year. Can be used for congestion and excessive nasal discharge.
In addition to these vasoconstrictors, there are others with a similar effect - “Xymelin”, “Otrivin”.
Can be used to treat children from birth. Contraindications are atrophic rhinitis and glaucoma, as well as individual intolerance to the drug.
Drops and sprays with a vasoconstrictor effect should not be prescribed to children for more than three days. Otherwise, addiction to the medicine and dry mucous membranes develop.
Antibacterial agents
Drops with this effect are prescribed in the third stage of a runny nose, when microbial flora joins.
- "Polydex". This drug is multicomponent, contains two antibiotics - a vasoconstrictor component and a corticosteroid. The drug is active against many microorganisms that cause purulent runny nose. Used for acute and chronic rhinitis, sinusitis.
- "Isofra". Contains one antibiotic. Available in the form of drops. Indicated for acute inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity.
- “Miramistin. An antiseptic solution widely used to treat inflammatory processes, including in the nasal cavity. Miramistin is used in children from birth.
"Polydex" is used for acute and chronic rhinitis, sinusitis
The drugs are prescribed to children from the age of two. Contraindications are individual intolerance to the components of the drug, glaucoma.
A cheaper Russian-made antimicrobial drug is Albucid for runny nose in children. Its other name is based on the active substance - “Sodium Sulfacyl”. Has a wide spectrum of antibacterial action. It is similar to Miramistin. Used in children from birth. The only contraindication is individual intolerance to the drug.
Dioxidin is an antimicrobial drug that can be used in children only after consulting a specialist. Dioxidin solution is instilled into the nose for purulent rhinitis.
How to treat a runny nose in a 6 year old child | How to treat a runny nose in a 6 year old child
This age of primary school age is characterized by the fact that the child has already learned about the world as much as required. Now the main activity of a 6-year-old child is play. It is important for him to spend a lot of time outside, with his friends, in any weather. Therefore, it is not surprising that children have a runny nose.
6 years is the age when illnesses, one after another, seem to line up and test the state of your child’s immunity. Today we will find out how to manage the disease, even if the baby does not want to be treated and drip his nose.
How to treat a runny nose in a child aged 6 years?
At 6 years old, the body is very sensitive to external stimuli. Even if a child is overcome by an illness, his body struggles, the temperature rises, the desire to eat disappears, because all the energy goes towards self-medication. At the same time, it is undesirable to treat a runny nose on the first day of its appearance. This is due to the fact that a runny nose can go away on its own, depending on the reason that caused it.
How to treat if the baby does not want to drip his nose? Now many parents complain that the child does not want to drip through the nose. It is difficult for him to breathe, his head begins to hurt, his sense of smell decreases, however, the baby refuses such a procedure. What is the reason? Parents need to think about what could cause such a reaction to the drops in their child. On the one hand, children know how to listen to their bodies, and if the baby says “no need,” then, more often than not, it really shouldn’t be done. On the other hand, the child must be treated, because an untreated runny nose can become chronic and then accompany the child throughout his life.
Parents, supporters of traditional medicine, once upon a time could put onion juice on the baby’s nose. But if you do not adhere to the proportions correctly, there is a risk that the mucous membrane will be damaged, and this is not the most pleasant feeling. Remember, perhaps this practice took place in your family. The child has simply developed a fear of nose dripping, because he is sure in advance that it will hurt.
Often children do not want to drip their nose because they do not like the droplets getting into their throat. Naturally, this means that the nose was not dripped correctly in the first place. After all, you need to drip so that the medicine gets into the maxillary sinuses.
Before starting treatment for a runny nose in a 6-year-old child, you should definitely consult a doctor. At the same time, try to listen to your child. Yes, he is very small for you and does not understand anything in this life. But his worldview is much more developed than you can imagine. Therefore, your baby can tell you how to treat a runny nose, and what treatment will be most effective. It's enough to just ask him about it.
How to treat a runny nose with folk remedies in a child aged 6 years?
Treatment of a runny nose in children occurs in several ways. It can be:
- Vasoconstrictor nasal drops
- Rinsing the nasal cavity
- Inhalation
- Acupressure.
We provide some recipes below: /p>
1. An extremely effective remedy for quickly getting rid of a runny nose in children is steam inhalation based on decoctions of plantain, coltsfoot, eucalyptus, pine buds, anise or peach oil.
2. The following recipe is used quite often. The onion is chopped, sautéed in a clean, dry frying pan until it gives juice, then it is transferred to a clean saucer and poured with vegetable oil. After waiting 12 hours, take the oil into a pipette and drop it into the nasal passages.
3. For nasal instillation in children with a runny nose, you can use beetroot, carrot juice, aloe and Kalanchoe juice. You can also prepare special garlic drops: to do this, finely chop a few cloves of garlic, pour warm olive oil over them and leave for about 7 hours in a warm place.
4. An excellent remedy is paraffin heating. A small piece of gauze folded in two or three layers is moistened with paraffin heated in a water bath. The gauze pad is wrapped in cellophane and applied to the nose for 10-15 minutes.
5. You can warm up your nose when children have a runny nose in other ways. The most common of these is warming the sinuses with boiled eggs wrapped in handkerchiefs. If desired, you can heat a little salt, rice or buckwheat in a frying pan, pour it into a cloth bag and apply it to the maxillary sinuses.
6. Onion juice fights the runny nose well. Grate the onion on a fine grater or squeeze out the juice.
If your child has a common runny nose, it is better not to overuse nasal drops in the form of Galazolin, Naphthyzin, which narrow the blood vessels in the nose. In addition, their use should be agreed with the treating pediatrician.
AstroMeridian.ru
Antiallergic drugs
Sometimes a child has a runny nose due to an allergic reaction of the body to plant pollen, animal hair, or house dust. In this case, the use of drops with an antiallergic effect is required.
- "Vibrocil." The product contains antihistamine and vasoconstrictor components. It is used for persistent rhinitis, mainly of an allergic nature. Approved for use by children from birth.
- "Tizin Alergy" is a nasal spray containing an antiallergic component. Used for seasonal allergic rhinitis. Can be used in children from six years of age.
Contraindications to treatment with Vibrocil are allergies to the components of the drug and glaucoma. Contraindications for Tizin Alergy are age less than six years, allergy to the drug, and glaucoma.
"Vibrocil" is used for persistent rhinitis, mainly of an allergic nature.
Drops with a thinning effect
Nasal discharge is sometimes thick, making nasal breathing difficult, and crusts form on the mucous membrane. In such a case, it is necessary to use drugs that can dilute and remove thick secretions from the nose.
"Rinofluimucil". A spray containing acetylcysteine, a substance that thins thick mucus. Indicated for rhinitis accompanied by thick discharge, as well as sinusitis.
The drug can be used in children from three years of age. Contraindicated in case of high allergies, glaucoma, thyrotoxicosis.
Homeopathic medicines
Homeopathic remedies can also be used to treat a runny nose. Homeopathy therapy is individual, it does not give a 100% effect.
Homeopathy remedies that can be used in a child:
- "Corizalia" (tablets).
- "Edas-160" - nasal drops containing thuja extract.
The drugs are approved for use in children from birth, provided that there is no individual intolerance.
How to treat a cold in a child?
Most women consider themselves specialists in three areas: medicine, cooking and raising children, so write on the topic: “How to treat a cold in a child?” - a thankless task. And yet, I will try to discuss a topic about which kilometers of text have already been written.
In medical terms, a cold in children is called an acute respiratory viral disease (abbreviated as ARVI). I highlighted the word “viral” intentionally, since it is key in the further narrative.
Signs of a cold in children are as follows: a sudden, most often asymptomatic rise in body temperature, after which liquid, clear discharge from the nose appears (in Russian - runny nose). If the discharge turns yellow or green, then this is a symptom of a bacterial infection in the nasopharynx. The cough is dry at first, but becomes wet over time. You may experience a sore throat, sore throat, and sneezing.
How to properly treat a child with a cold?
Every mother, sitting over the bed of a sick baby, asks the question: “What should I give my child if he has a cold?” I outline the rules that are taught to any medical student in pediatrics classes:
- Fighting fever - paracetamol in an age-appropriate dose.
- Drinking plenty of fluids can help prevent dehydration caused by fever.
- For a dry cough - antitussives (contraindicated in children under 2 years of age), for a wet cough - expectorants (bromhexine, ambroxol, ACC, etc. see review of all cough expectorants).
- After the temperature has returned to normal, physiotherapeutic methods can be used: foot steaming, soda inhalations, etc.
How not to treat ARVI in children
World statistics say the following
90% of respiratory infections (upper respiratory tract infections) in children are viral in nature. It is a viral one, which antibiotics do not work on. Unfortunately, most mothers consider antibiotics to be medicines for fever and start feeding them to the child for any cold.
There are no safe medications; taking antibacterial agents causes allergies, intestinal dysbiosis, suppresses the immune system and creates antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
Pediatricians, of course, know about the dangers of antibiotics for ARVI, but it is difficult to distinguish a cold from pneumonia, and even at the patient’s home, using only hands, eyes and a phonendoscope, especially with insufficient experience.
For most pediatricians, it’s easier to prescribe an antibiotic to a child on the first day and, as they say, “don’t worry”: the harm from them at the beginning is not very noticeable, if there was pneumonia, it will go away, and if it doesn’t go away, there is an excuse, I prescribed the correct treatment, Yes, and mom is calm.
To summarize: antibiotics for colds are not used for children under 12 years of age for the first 5 days. If you have weak nerves, then every cough or runny nose should be accompanied by a visit to the clinic and additional tests: blood test, x-ray of the lungs, examination by an ENT doctor, urine test, etc.
Increase in body temperature
Adults and children over 6 years of age should manage a fever if it exceeds 390C. This temperature is no longer considered physiological and can harm the body. In young children (under 6 years of age), antipyretics should be used at a temperature of 38.60C, due to the threat of convulsive syndrome. And also in children with convulsive readiness or previously recorded febrile convulsions, the temperature drops from 37.5-38C.
Temperature is an important part of the body's fight against infection. During fever, the vital activity of cold pathogens is inhibited, and the body’s defenses are also mobilized. Therefore, excessive fight against fever only delays recovery. In addition, absolutely all antipyretics can cause allergies, stomach ulcers or severe kidney damage, including kidney failure.
In addition to tablets, there are physical methods of cooling. Of course, in adults they are not very effective, but in a child they can lower the temperature by a whole degree (see how to lower the temperature without medications):
- If the child is red - with red hyperthermia, when the child is pink, you should not wrap up the sick baby, but, on the contrary, undress him down to his panties and leave him to cool in the air. Cruel but effective.
- If the child is pale - white hyperthermia, he should be wrapped in a light blanket and given warm liquid to drink.
- Rub the baby with vodka (not suitable for young children, especially under 1 year), it is better to rub it locally - the arms, legs. The evaporating alcohol will quickly cool the skin. You should not use alcohol solutions of a higher concentration than vodka. This can damage children's skin, and the child can also get drunk, as some of the alcohol will definitely be absorbed.
- Cold on the main vessels. In normal language it sounds like this: take a plastic bottle, pour cold water into it and apply it to the armpits or groin areas. The water will cool the large blood vessels passing through there.
- You should not put a hat on a child indoors, especially if he is sick. This is what old-school grandmothers like to do. The head is the main source of heat loss in the body; up to 80% of the heat is removed through it, so during fever, the head must be cooled in every possible way.
During fever, the evaporation of fluid from the skin increases significantly. Therefore, the child must be given plenty of water to avoid life-threatening dehydration. Any liquid will do: compotes, fruit drinks, tea, juices and just clean water.
The story of how domestic pediatrics turns healthy children into sick ones
Characters:
- Mom is an average Russian mother who thinks she knows EVERYTHING about colds.
- The baby is a normal, healthy five-year-old toddler who regularly attends kindergarten.
- Pediatrician - recently completed his studies and was assigned to an average Russian clinic, full of knowledge on how to properly treat a cold.
So. The baby returns from kindergarten lethargic, snotty, coughing and with a temperature of 38.50C. The next morning, Mom calls the clinic and calls a doctor to her home.
The Pediatrician comes, examines the child and makes a diagnosis: ARVI. He was taught that at this age, 90% of respiratory infections are viral, and therefore are treated as described at the beginning of this article. He prescribes paracetamol, plenty of fluids, and ascorbic acid, and leaves with a calm soul.
But the disease does not go away, the temperature remains around 390C, the child cries, refuses to eat, snots and coughs. Mom knows for sure that ascorbic acid is not a medicine at all, and paracetamol only brings down the temperature. She calls the clinic and swears at everyone and everything there, saying what kind of ignorant doctor you sent me.
In order not to “tease the geese,” the manager comes to see the Kid. pediatric department or deputy chief physician and prescribe an antibiotic. The motivation is clear. Firstly, so that Mom doesn’t interfere with work with hysterical calls. Secondly, if pneumonia does develop and an antibiotic is not prescribed, Mom will immediately sue. In general, we treat “not the right way,” but “the calmest way.”
As a result, a cold that could go away in 7 days lasts for 3 weeks. During the fight against the disease, children's immunity was greatly weakened. The baby is taken to kindergarten, where someone will inevitably sneeze at him and the cold will return.
After a week of going to preschool, Baby again has a fever, runny nose and cough. Mom makes house calls again. The pediatrician was called “on the carpet” last time and explained “how to work with patients.” He comes to the Kid and prescribes an antibiotic from the first day. Everyone is happy: Mom - that the treatment is correct from her point of view, the Pediatrician - he will not be deprived of his bonus again, the management of the clinic - there will be no showdown with another complaint.
And again, the illness that could have gone away in a week lasts for a month. What kind of children's immunity can withstand this? Again kindergarten, again a cold and again a month of “treatment”. This is how our heroes turned a healthy toddler into one who was often and long-term ill (an official term, by the way). I hope you understand where frequent colds in children come from?
Some of the most popular questions from parents
Is it possible to bathe a child with a cold?
This question goes back 200 years, when there was no hot water in houses, and children were washed in a trough in the hallway or in a bathhouse, where they could get even more sick. In the 21st century, it is possible and necessary to bathe a child with a cold, but it is worth remembering that a hot bath at an elevated body temperature is strictly contraindicated. It is enough to limit yourself to a warm shower.
How can you understand that a child has recovered?
3 days of normal temperature can be considered positive dynamics. Also considered a good sign is the transformation of a dry cough into a wet one (provided that the discharge has not turned from transparent to yellow or green). But if a recovering child’s temperature rises again, then a bacterial infection can be assumed.
Herbal remedies
To facilitate nasal breathing and relieve congestion in a child, herbal preparations are used.
- Ointment "Pinosol". It contains pine, eucalyptus and menthol oils. Prescribed for persistent rhinitis in children.
- Kalanchoe - the juice of this plant is often used in folk medicine. Kalanchoe juice is used to treat difficulty in nasal breathing in children from two years of age. It is instilled into the nose, starting with a few drops, because Kalanchoe juice causes an allergic reaction or a burn to the mucous membrane.
The choice of drug for a runny nose depends on the cause of its occurrence. The age and allergic predisposition of the baby should also be taken into account when choosing a treatment.
Drug treatment
How to treat rhinitis in a two-year-old child? If a child has a stuffy nose, a pediatrician may recommend drug therapy using vasoconstrictor drops. However, vasoconstrictor drugs should be used only if the child has severe difficulty in nasal breathing. You can use the drops for no more than a week, since this kind of medicine is addictive and is characterized by the presence of certain side effects.
If a two-year-old child has severe nasal congestion, the following nasal medications may be recommended:
- Galazolin.
- Tizin.
- Naphthyzin.
What to do in case of viral and bacterial rhinitis in a child aged 2 years and older? The drug Euphorbium compositum, produced in the form of a spray, gives a good effect. It should be injected into each nostril of the baby 2-3 times throughout the day. This remedy can be used for prophylactic purposes to prevent colds in the autumn-winter period. Treatment with Euphobrium compositum is contraindicated in children suffering from individual intolerance and hypersensitivity to iodine preparations.
For heavy nasal discharge of mucous consistency, on the recommendation of a specialist, you can use Isofra nasal spray, which includes framycetin sulfate. This drug is characterized by a high degree of effectiveness in the fight against runny nose of bacterial etiology. It is recommended to inject the medicine into the child’s nasal passages 2-3 times a day. Isofra spray will quickly relieve your baby’s condition when he has a runny nose at night.