Nowadays, with regard to introducing a new type of food to children, they adhere to the trend of delayed complementary feeding, i.e. no earlier than 5-6 months of age. You can try feeding artificial ones a little earlier - on the fourth day.
First of all, this is due to the fact that the digestive system of children is still immature, there are not enough enzymes, and there are few glandular juices. In addition, early complementary feeding can affect the amount of mother's milk. The less the baby nurses, the less milk is produced. Therefore, ideally, a baby should eat only mother’s milk for up to six months. Formulas for artificial babies also contain the maximum amount of nutrients and vitamins; their composition is quite close to breast milk.
To determine the time, doctors advise not to focus on age, but to approach this individually.
Signs of maturity to start feeding include:
- When trying to introduce complementary foods, he does not push out the spoon and food with his tongue, and swallows food well.
- If a pacifier or other object gets into the mouth, it makes unconscious chewing movements.
What can you feed:
- at 2 months
- at 3
- when and how to introduce complementary foods correctly
- at 4
- at 5
- at 6
- at 7
- at 8
- at 9
- at 10
What can you feed a 2 month old baby?
Answer: nothing. Whether it is an artificial baby or a baby, both are still too small to accept a new type of food. Formula-fed babies need to be supplemented with water. A baby who suckles on demand needs water only in case of dehydration: with diarrhea, fever or in the heat.
Taking medicinal teas and Plantex does not apply to complementary feeding.
At 4 months?
You can introduce porridge if the child is not gaining weight well or has unstable loose stools . If there are no such prerequisites, then it is better to wait, since formula and breast milk sufficiently cover calorie consumption.
At this age, artificial babies can already be offered vegetable puree . Start with non-colored vegetables: zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli. After assimilation of these products, they move on to purees made from pumpkin, apple, plum and carrot.
Potatoes, despite their hypoallergenicity , are not recommended for use for up to a year. Starchy foods are hard on a baby's stomach.
If you are going to make puree yourself, then steam the vegetables/fruits without adding salt/sugar.
Around this time, you need to add a little vegetable oil to the puree.
Milk porridge for babies
Vegetable purees are usually introduced into a baby’s diet first. No earlier than 3 weeks after this, you can start feeding your baby cereal. Sometimes pediatricians advise starting with cereals rather than vegetables. This is usually recommended for children who have trouble gaining weight and have problems with stool (it is loose and unstable). In any case, the question of when to introduce milk porridge into the infant’s menu is decided individually, preferably after the recommendations of the supervising doctor.
You should always start feeding cereals with gluten-free cereals cooked in water. Buckwheat, rice and corn porridge are well digestible and do not cause allergies. Buckwheat is rich in iron, magnesium, phosphorus and B vitamins. Rice is not as healthy, but is easier to digest. Corn has a pleasant taste and neutralizes fermentation processes. The cereal must be ground - porridge for a baby is more like puree. Of course, they don’t put salt and sugar in it. But you can add a little breast milk to the porridge. You need to start complementary feeding with ½–1 teaspoon, gradually increasing the portion.
If your baby accepts cereal well, you can start introducing gluten-containing grains. First oatmeal, then wheat and barley cereals, and lastly semolina (after 11–12 months). Semolina porridge is considered the most useless - it contains few vitamins and microelements, often causes allergies and contributes to excess weight. If the baby is not gaining weight well, it is quite acceptable and even necessary.
Gluten porridges are harder to digest than buckwheat, rice and corn and can cause allergies. Therefore, they should always be given gradually, with a break of 1–2 weeks, to see the child’s body’s reaction to the product. For the same reason, you can switch to multi-ingredient cereals only after you have introduced each cereal separately into your baby’s diet. To get an overall picture, it is useful to keep a food diary for your baby. It is not worth excluding grains with gluten without an objective reason - they contribute to the proper growth and full development of the child, strengthen his immunity, cleanse the body and remove toxins.
You should use cow's milk to prepare porridge no earlier than 1 year, when the baby has tried all the grains. Remember that milk porridge for your baby should still be cooked in water, only adding a little milk at the end of cooking. After a year, you can gradually switch to all-milk porridges. Only at this age can you begin to introduce millet, pearl barley and barley porridge into your child’s diet. They contain coarse fiber, the baby’s intestines need to “grow” to the ability to digest it. By the age of 1 year, you can already add pureed boiled vegetables and fruits, butter to porridge, and also reduce the degree of grinding of cereals - a child at this age usually already has enough teeth and can chew solid food.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
4.67 3
Nutrition
38040
0
When and how to introduce complementary foods correctly
The introduction of any new product/dish begins at a time when the baby is completely healthy, in a good mood, and does not have stress in the form of moving, moving into a crib, or the appearance of new people for him.
How to enter correctly? The baby wakes up and is given a bottle or breast. For the second feeding, give half a teaspoon of zucchini puree and then feed with milk or formula. During the day, the baby’s condition is assessed. If there are no allergies, loose stools, gas, and the child does not cry, pressing his legs to his stomach, then everything is fine. We can continue. The next day, at the second feeding, a whole teaspoon is given. Every day the amount of puree is increased by one spoon, bringing the amount to 7. An assessment of the condition should be carried out every day and for each new product. Only monocomponent purees should be administered. Combinations of, for example, zucchini and pumpkin can only be offered after both products pass the test separately.
A week is given to introduce one type of puree. If there are problems with stool or allergies, then a two-week break is taken. Then we begin to administer it again, a teaspoon per day.
Breastfed babies usually have enough milk at 4 months. If they are underweight, then porridge is offered to them for the first complementary feeding.
Which porridge is the healthiest?
Many parents are concerned about this issue.
As already mentioned, in all porridges the majority are carbohydrates, in particular starch (from 48 to 74%). They differ from each other in the content of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and microelements.
The approximate nutrient content of 100 g of different cereals can be found in the table
| Gluten free | Contain gluten | ||||||||||
| Grech | rice | Kukur | Millet | Oatmeal | Wheat | Barley | |||||
| Groats | Clap | Tseln | Semolina | Pearl | Yachnev | ||||||
| squirrels | G | 12,5 | 7 | 8,3 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 10,3 | 9,1 | 10 |
| fats | G | 3,3 | 1,3 | 3 | 6,1 | 6,1 | 6,2 | 1,6 | 1 | 1,1 | 1,3 |
| coal | G | 56 | 73,4 | 71 | 65,5 | 57,9 | 58 | 67,5 | 73,3 | 66,9 | 71,7 |
| starch | G | 50,7 | 70,7 | 69,9 | 54,7 | 48,8 | 48,9 | 54 | 67,5 | 65,7 | 65,2 |
| feces | 308 | 305 | 328 | 344 | 303 | 305 | 301 | 328 | 315 | 324 | |
| cell | G | 1,3 | 0,4 | 1,2 | 2,8 | 2,8 | 1,3 | 2,7 | 0,2 | 1,4 | 1,5 |
| potassium | mg | 380 | 100 | 147 | 362 | 362 | 330 | 325 | 130 | 172 | 205 |
| soda | mg | 3 | 12 | 4 | 35 | 37 | 20 | 8 | 3 | 9 | 15 |
| calcium | mg | 20,7 | 8 | 20 | 64 | 64 | 52 | 62 | 20 | 38 | 80 |
| phosphate | mg | 334 | 320 | 109 | 349 | 349 | 328 | 276 | 85 | 323 | 343 |
| glands | mg | 8,3 | 1,2 | 2,7 | 3,9 | 3,9 | 3,6 | 5,2 | 0,95 | 1,6 | 1,8 |
| magnesium | mg | 200 | 50 | 36 | 116 | 115 | 129 | 114 | 18 | 40 | 50 |
| iodine | mcg | 3,3 | 1,4 | — | 4,5 | 5,5 | 5,2 | 11 | — | — | — |
| marg | mg | 1,56 | 1,25 | 0,4 | 5,05 | 5,2 | 5 | 3,7 | 0,44 | 1,322 | 0,76 |
| kobal | mcg | 3,1 | 1 | 4,5 | 6,7 | 8 | 7,6 | 5,4 | 0,03 | — | 2,1 |
| copper | mg | 0,64 | 5,2 | 0,21 | 0,5 | 0,6 | 0,54 | 0,53 | 0,07 | 0,42 | 0,37 |
| zinc | mg | 2,05 | 1,4 | 0,5 | 2,7 | 2,8 | 2,4 | 2,8 | 0,6 | 0,7 | 1,09 |
| VitA | mg | 0,01 | 0,08 | 0,03 | 0,5 | — | — | 0,02 | — | 0,013 | — |
| Vit E | mg | 6,7 | 0,1 | 0,7 | 0,02 | 3,4 | 3,2 | 6,5 | 2,55 | 1,1 | |
| VitV1 | mg | 0,4 | 0,04 | 0,13 | 0,1 | 0,49 | 0,45 | 0,37 | 0,14 | 0,12 | 0,27 |
| VitV2 | mg | 0,2 | 0,4 | 0,07 | 0,9 | 0,11 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,07 | 0,06 | 0,08 |
| Folk-ta | mcg | 32 | 19 | 19 | 40 | 29 | 24 | 46 | 23 | 29 | 32 |
| RR | mg | 4,2 | 7,8 | 2,1 | 9,4 | 1,1 | 1 | 4,94 | 1 | 2 | 2,74 |
Gluten and gluten-free
First of all, all cereals are divided according to their gluten protein content.
Cereals containing gluten what porridge to give to a child
Oatmeal, wheat groats, semolina, pearl barley and barley groats.
Not only are they the cause of celiac disease in people who cannot digest gluten, but they are also more likely than other grains to cause food allergies.
But for healthy people (and children) with normal gluten tolerance, they are no less useful than cereals from the other group.
Gluten free cereals
Buckwheat, rice, corn and millet.
These grains can be eaten by those suffering from celiac disease. These are the most low-allergenic cereals. They are extremely rarely the cause of food allergies.
By protein content
The healthiest proteins are found in buckwheat and oatmeal. Each of these cereals contains 8 essential amino acids. But because The content of some amino acids, in particular lysine, is low; these proteins are digested worse than in animals.
Rice proteins follow, then barley and wheat.
In last place in terms of nutritional value are millet and corn proteins.
By fat content
Oatmeal and millet are the champions here. They contain 6.2 g of fat per 100 g of cereal, and are healthy vegetable fats containing polyunsaturated fatty acids. These cereals have a very beneficial effect on the nervous system.
Content of easily digestible carbohydrates
Oatmeal, buckwheat, and millet porridge contain the least carbohydrates.
And the most carbohydrates are in semolina and rice.
According to the content of vitamins and microelements
Here is the healthiest buckwheat.
Buckwheat contains rutin, which strengthens blood vessels. It is the champion among cereals in terms of iron content, but do not forget that iron is less absorbed from plant foods. In general, it contains more vitamins and microelements than other cereals.
Buckwheat is followed by oatmeal, whole wheat porridge and millet porridge.
It turns out the following rating of cereals
The most useful buckwheat
- It does not contain gluten.
- It contains the most valuable protein.
- Most vitamins and minerals.
- It is low in carbohydrates and starch, and even less in oatmeal.
- It has the lowest glycemic index among cereals and contains the substance chiroinositol, which can be useful for the absorption of carbohydrates, including in diabetes.
Oatmeal What kind of porridge should I give my child?
It is considered the second most useful after buckwheat.
Her virtues
- It has a more delicate, enveloping consistency than buckwheat, so it can be used in the nutrition of patients with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Oatmeal contains many healthy fats.
- It contains the least amount of carbohydrates and starch.
- It's easy to prepare.
- Oatmeal contains quite a lot of vitamins and microelements and quite healthy protein, although it is inferior in all these properties to buckwheat.
It has only one drawback - it contains gluten.
Buckwheat and oatmeal are considered the healthiest for children. Nutritionists recommend including each of them in the child’s menu 2-3 times a week, while other cereals 1-2 times a week.
Whole wheat porridge
- In terms of nutritional value, protein is inferior to oatmeal, buckwheat and rice.
- Contains many vitamins and microelements.
- It contains quite a lot of fiber.
But
- There is gluten.
- There is phytin, which can interfere with the absorption of minerals.
- Contains more carbohydrates and starch than oatmeal and buckwheat.
Corn porridge
- Low-allergenic porridge, does not contain gluten.
- Contains quite a lot of fiber and does not contribute to constipation.
- Corn porridge is the lowest in calories.
- It is easily digested and does not cause increased gas formation.
But
- Corn protein has low nutritional value.
- It contains a lot of starch and has a high glycemic index.
- Low calcium and phosphorus.
- It takes a long time to cook, and most of the vitamins are lost.
Millet porridge
- Does not contain gluten, is a low-allergenic porridge.
- Together with oatmeal, it leads among porridges in terms of the content of healthy, vegetable fats, which is beneficial for the development of the brain and nervous system.
- Despite its high calorie content, it has a low glycemic index. Does not promote weight gain.
- Contains many vitamins and microelements, the champion among cereals in terms of vitamin B6 content (2 times more than in buckwheat and 4 times more than in oatmeal), a lot of phosphorus, magnesium.
- Contains quite a lot of fiber.
But what kind of porridge should I give my child?
- Millet protein has low nutritional value.
- Millet is poorly digested, so it is recommended from 1.5 years.
- It takes a long time to prepare, millet gluten has a slightly bitter taste, so it is recommended to pre-soak the millet before cooking.
Semolina and rice porridge
- They contain approximately 73% carbohydrates and approximately 70% starch. They have a high glycemic index. These cereals are not recommended for people with diabetes and overweight people.
- They contain little fiber, so they are not recommended for constipation.
- Rice is low in protein. But it contains all the essential amino acids, so its nutritional value is close to that of oatmeal and buckwheat proteins. Semolina has more protein than rice. But its nutritional value and digestibility are lower.
- They contain less minerals and vitamins than other cereals. In terms of their nutritional value, they approximately correspond to premium wheat flour. There is no benefit from using them other than weight gain. Therefore, these two porridges are not recommended for daily consumption by healthy children, as well as those with rickets and anemia.
But they are mechanically and chemically gentle food. Therefore, they are useful for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including diarrhea.
Read more about semolina porridge here.
Barley and barley porridge
Pearl barley is a less processed grain than barley. Barley contains less fiber.
- Barley protein has low nutritional value.
- These cereals are difficult to digest, so they are not recommended for children under 2 years of age.
- Contains a lot of carbohydrates and starch.
But what kind of porridge should I give my child?
- They have a lot of fiber
- Contains the essential amino acid lysine, which promotes wound healing,
- They have a low glycemic index,
- They contain quite a lot of vitamins and microelements.
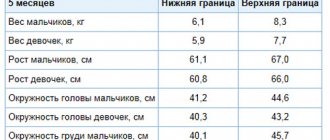
What can I feed at 5 months?
At this time, you can already try giving new food to the baby. It is absolutely normal if the artificial person has not tried anything new before this time.
The choice of the first course depends on: weight gain, the nature of the stool, the presence of allergies and underlying diseases. Only a doctor can give specific nutritional advice.
Now let's talk about cereals. The time when our mothers and grandmothers fed us semolina has sunk into oblivion. Nowadays it is not recommended due to its high gluten content. You should start getting acquainted with gluten-free porridges: corn, rice and buckwheat.
Important : do not cook them in milk.
You should also start with a teaspoon, increasing the portion every day. Be sure to monitor the baby’s well-being.
Then you can offer porridge made from oatmeal, millet, and barley.
Complementary feeding at six months
At this time, most kids have already mastered the first one, in the form of porridge or vegetable and fruit purees. Therefore, at this stage, you can introduce new products: porridge, if vegetables are mastered, and vice versa. At 6 months, children begin to be interested in adult food. To get acquainted with the taste and texture of such food, you can give a little bit of soup or cutlets, in general, what the whole family eats. This is called pedagogical or introductory feeding.
Benefits and harms
Not everyone knows that semolina and wheat cereals are made from the same grain. The only difference between them is the quality of grinding.
With such similarity, wheat cereal is still considered healthier than semolina. It is processed in a more gentle way and retains more vitamins.
Benefits of wheat porridge for a baby:
- It improves intestinal function due to its increased fiber content.
- Serves as a natural adsorbent, accelerates the removal of toxins from the body in case of food poisoning.
- Stimulates normal functioning of the immune system.
- Provides the body with the necessary amount of nutrients and B vitamins.
Wheat, like oatmeal, contains a potentially dangerous component - gluten. The child's digestive tract has difficulty processing this protein, which can lead to bloating and allergic reactions of varying severity. If you have celiac disease, this cereal is strictly prohibited.
Wheat also contains phytic acid. If consumed regularly, it can cause a deficiency of calcium and zinc in the body, which negatively affects the condition of the baby’s bone and nervous systems.
It is also necessary to take into account that wheat porridge contains a lot of starch and carbohydrates. If a child gains weight too quickly, it can make the situation worse.