ADSM is a vaccination against infectious diphtheria (caused by Loeffler's bacillus) and bacterial tetanus (caused by gram-positive tetanus bacillus), and the Infanrix vaccine is an imported analogue of ADSM. There is also Priorix for intramuscular injections and Pentaxim. All of the above vaccines are intended to immunize humans against a number of infectious diseases.
After the injection, weakened toxins enter the human body, which are not able to provoke the development of the disease. The body produces antibodies that form the body's immunity to diphtheria infection and tetanus bacillus.
Brief characteristics of the ADSM vaccine
Vaccination is the introduction of weakened particles of a pathogen into the human body. Its task is to develop a permanent or temporary ability to resist the disease.
Initial vaccination should occur in the first days after birth, then it is carried out according to a special calendar.
The most dangerous diseases for children are tuberculosis, diphtheria, whooping cough and tetanus; they are fatal in most cases. If vaccination against tuberculosis is carried out once, immediately after birth, then to protect against other diseases you need to get DTP vaccination 4 times in order to develop resistance to them for several years.
Over the age of 5 years, the whooping cough virus is relatively easy to transmit, but diphtheria and tetanus are still deadly. You can protect a person from them with the ADSM vaccination (the correct name is ADS-m). The abbreviation stands for: adsorbed diphtheria-tetanus vaccine in small doses.
All ADS-m preparations contain 5 units of tetanus and diphtheria bacillus toxoids, but in an amount half as much as in DTP. In addition, the composition contains additives registered by the manufacturer: preservatives, aluminum hydroxide, formaldehyde and others. A dosage of 0.5 ml activates the immunity already developed by previous vaccinations.
Differences between ADS-m and DTP:
- absence of pertussis toxoids;
- reduced concentration of active substances.
In addition to the bivalent vaccine, there are monovalent vaccines AD (against diphtheria bacillus) and AS (anti-tetanus injection).
General information about vaccines, their composition and action
Since 1940, Russia has carried out universal immunization of the population.
There is an approved National Vaccination Calendar, which all medical institutions adhere to. When a child is just born, he is given the first vaccinations against hepatitis B and tuberculosis. Doctors consider the vaccine against three very dangerous, even fatal, diseases to be the main one for developing children’s immunity:
- diphtheria - an acute infectious disease that affects the upper respiratory tract;
- whooping cough, leading to pneumonia, convulsions and respiratory arrest;
- tetanus - a soil infection accompanied by seizures and problems with the nervous system.
Statistics show the seriousness of these diseases. Thus, before universal vaccination, the mortality rate from tetanus was 90%, and from diphtheria - 25%.
DTP is the name of the vaccine drug produced in Russia, but for convenience, this is what all vaccines against these diseases are called. Foreign vaccines differ from Russian ones in many characteristics.
The imported ones do not contain formalin and merthiolate, since these substances are prohibited in the USA and the European Union. They also lack the acellular anti-pertussis component, which is why they are better tolerated by children of any age.
Many foreign vaccines are produced in combination against polio, hepatitis B and other diseases. However, they are not included in the child’s health insurance, and such vaccinations will have to be paid for.
At the clinic, by default, the baby will be given the Russian vaccine for free. It is inexpensive, compared to Pentaxim and Infanrix, and not very modern. It contains dead pertussis germs, diphtheria and tetanus toxoid.
Toxoids are widely used in the production of vaccines. They are produced by pathogens, but after heat treatment they become harmless. At the same time, toxoids retain antigenic activity, that is, they form immunity in the child.
Merthiolate (thiomersal), an organometallic compound of mercury, is used as a preservative, antiseptic, and also to protect against fungus. This is a dangerous substance, very toxic, carcinogenic, causes allergies, and is a mutagen.
The dose of merthiolate contained in the domestic vaccine is not dangerous for a small child. However, in the body of a newborn, the level of mercury compounds after immunization decreases only after a month. It is this compound that often causes parents to refuse vaccination with Russian drugs.
DPT is used only up to the age of 4 years. When choosing which vaccine to vaccinate your baby with, you should remember that the domestic vaccine has been approved by WHO.
There is a French vaccine similar to DPT. Unlike the domestic one, it also protects the baby from polio and hemophilus influenzae infection. Pentaxim additionally contains inactivated polio virus, and the whooping cough virus in its composition is split and its shell is removed.
In addition, unlike DPT and the polio vaccine, Pentaxim is better tolerated. It reduces the risk of developing vaccine-associated polio, that is, caused specifically by vaccination. This is also evidenced by multiple reviews of parents about the vaccine on the Internet.
In addition to the French vaccine Pentaxim, there is another drug on the Russian pharmacy market - the Belgian analogue of Infanrix. It is intended for vaccination against whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus. Includes components similar to the French vaccine.
The drug Infanrix Hexa additionally contains a vaccine against hepatitis B, Haemophilus influenzae and polio. It additionally contains neomycin and polymyxin. The vaccine is contraindicated if you are sensitive to antibiotics. Parents' subjective assessment of this drug is also very high.
ADSM vaccine and its analogues
To protect against tetanus and diphtheria, you can choose one of the existing drugs:
- Russian ADSM;
- foreign: Imovaks D. T. Adult or D. T. Vaks;
- monovalent AD or AS vaccines.
Foreign analogues have a higher degree of purification and extremely rarely cause any reactions upon administration. Their disadvantages: the need for independent acquisition and high cost.
Vaccination with the Russian ADS-m vaccine is done in any clinic absolutely free of charge, the risk of complications is minimal and is associated only with non-compliance with the recommendations.
Which one to choose?
The ADSM vaccine is bivalent, that is, it produces antibodies to 2 pathogens at once. Such saturation raises concerns about excessive stress on the body, which are completely unfounded.
Pediatricians and therapists in most cases recommend polyvalent vaccination against tetanus and diphtheria, arguing as follows:
- less stress on the body;
- minimal risk of side effects;
- the ability to combine with other vaccinations.
It has been proven that the administration of polyvalent vaccines is safer than monopreparations. The former go through several stages of purification, and their components are selected in such a way as to exclude a reaction for each other.
Today, ADS-m vaccines are produced in disposable syringes and ampoules with several doses of the drug. The former do not contain preservatives, are easier to tolerate, and therefore are preferable for children.
D.T. Wax
Another imported vaccine from France, designed to protect against dangerous infections.
Release form and composition
The drug is a suspension. One dose contains:
- purified diphtheria toxoid – at least 30 IU;
- purified tetanus toxoid – at least 40 IU;
- aluminum hydroxide;
- thiomersal as a preservative.
You can purchase the drug at:
- ampoules containing one dose (pack of 20 ampoules);
- single dose syringe;
- bottles of 10 or 20 doses, packed in boxes of 10 pieces.
pharmachologic effect
The action of the drug is aimed at building immunity against diphtheria and tetanus, which develops after the second injection and lasts for five years.
Restrictions on use
Stop using D.T. Vax is worth it if the patient:
- fever;
- exacerbation of a chronic illness;
- acute infection;
- allergy to the components of the product;
- Strong reactions were observed upon initial administration.
If the reactions were severe, it will be recommended to exclude diphtheria toxoid or reduce its dose.
Side effects
Negative consequences are observed very rarely. However, they may manifest themselves as the following symptoms:
- slight hyperthermia (passes in two days);
- compaction at the injection site (dissolves within a day or two).
More pronounced reactions are usually provoked by the diphtheria component, so if an allergy occurs, its dose should be reduced.
Vaccination dates
Health care providers can offer several options for protecting you from tetanus and diphtheria. The choice of drug depends on the health status and age of the patient:
- ADS. The vaccine differs from DTP only in the absence of pertussis toxoids. It is given to children of the first year of life with severe allergic reactions or high fever that occurred after the administration of DTP. If this drug is also poorly tolerated by the baby, he is given ADS-m or given a medical exemption.
- R1 ADS-m. The first revaccination, according to the vaccination schedule, is carried out at 1.5 years of age (if the child was vaccinated with this particular drug). The medical records of children and adults who were administered DTP will not contain such a record.
- R2 ADS-m. Second revaccination. The vaccine is given to children aged 4 or 6 years.
- R3 ADS-m. The third revaccination is carried out 10 years after the previous one (14 or 16 years, respectively). Subsequently, the vaccine is administered every 10 years, without restrictions on the patient’s age.
What is ADSM vaccination
The ADSM vaccine is given to children aged 6-7 years and older to protect against diphtheria and tetanus pathogens. It has become an excellent replacement for multicomponent multiple injections. Even at an older age, people are vaccinated against diphtheria and tetanus using a similar type of drug. Revaccination is carried out according to the vaccination calendar, which is monitored by the local physician.
However, the question arises as to what the drug for administering the ADSM vaccination is. The vaccine consists of toxins that form diphtheria and tetanus pathogens. They are processed in a special way, after which they lose their toxicity, but retain the ability to develop immunity. Thus, they are not capable of causing harm to the body, but they trigger the body’s protective properties.
The name of the vaccine is deciphered as follows:
A - adsorbed; D - diphtheria; C - tetanus; M - small doses of the diphtheria component.
In addition to the fact that thanks to this vaccine, the child no longer needs to be injected several times, it is also well tolerated by children. Let us remind you that up to 6 years of age, a child is given DTP, which protects against diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough.
Refusal of vaccination
Vaccination, especially in childhood, causes a lot of controversy. Many parents believe that the administration of toxoids weakens the immune system and causes serious complications in the child.
Arguments in favor of a vaccine
To understand whether to vaccinate against tetanus and diphtheria, it is necessary to evaluate the health risks of these diseases.
Tetanus affects the human nervous system and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- a sharp increase in temperature;
- uncontrolled contraction, severe spasm of muscle fibers;
- weakness;
- convulsions;
- difficulty breathing.
Tetanus is dangerous because of a spasm that causes respiratory arrest and paralysis. Today, every fourth case ends in death, even with the use of modern therapy.
The causative agent of the disease is resistant to high temperatures and multiplies quickly. Infection occurs when a person’s skin and muscles are damaged; the risk of infection is very high.
Diphtheria is an infectious disease that affects the human respiratory system. Accompanied by:
- sore throat;
- high temperature;
- swelling of the mucous membrane of the larynx (the so-called croup);
- the appearance of plaque and films, gradually affecting neighboring tissues.
The death of patients occurs from suffocation caused by swelling of the throat. In case of recovery, complications are possible: paralysis, pathologies of the heart and nervous system.
The causative agent of diphtheria is transmitted by airborne droplets and contact, so the risk of infection is very high, as is the case with tetanus.
The human body is not able to develop stable immunity to these diseases even after recovery, so the only way to protect is timely vaccination. Refusing it can result in death or serious problems in the body even with minor abrasions or meeting with a healthy (vaccinated) carrier of the diphtheria bacillus.
Arguments against
Many consider the disadvantage of the ADS-m vaccine to be complications and poor tolerability, especially in childhood. For this reason, adults refuse vaccination, exposing themselves and their children to mortal risk.
Indications and contraindications
ADS-m is included in the compulsory vaccination calendar. It is recommended to do it:
- children upon reaching 6 (sometimes 4) years of age;
- teenagers 14-16 years old;
- adults after 24-26 years every 10 years.
In some cases, for example during a disease outbreak, vaccination is carried out unscheduled.
Contraindications:
- acute and chronic pathologies not in remission;
- 3-4 weeks after illness;
- elevated temperature;
- pregnancy;
- strong reaction to a similar vaccine;
- allergy to one of the components of the drug;
- severe immunodeficiency.
Before vaccination, an examination by a pediatrician or therapist is required; a blood test is taken to identify hidden pathologies. If contraindications are found, the doctor gives a medical exemption from vaccination.
Difference between DTP and ADSM
Many children experience severe complications from the inclusion of the pertussis component in the vaccine. For such children, an analogue of DPT - ADSM - is used as a vaccination. Moreover, upon reaching 7 years of age, the risk of a child getting whooping cough is greatly reduced and in case of danger, the protective mechanisms of previous vaccines will be sufficient.
It is this fact that after a child reaches the age of seven, the risk of getting whooping cough is significantly reduced and gives the right to exclude the anti-whooping cough component from the vaccination calendar, which allows the use of this type of vaccination drug for vaccinating adults.
There really is a difference between these two vaccines. In DTP and ADSM, viral components are distributed differently. The first contains 30 units of diphtheria and 10 units of tetanus and pertussis, and the second contains 5 units of each. After the injection is given, the doctor notes the date of its implementation and the consequences in the child’s medical record.
Children who do not tolerate the pertussis component of the DTP vaccine well are vaccinated with the ADSM vaccine. The timing of vaccination is regulated by the calendar of preventive vaccinations. If a child has had whooping cough, then no one will risk vaccinating him with an anti-whooping cough component, and in the future he will be vaccinated with the ADSM vaccine.
At 6-7 years old, the child is given the R2 ADSM vaccine, where R2 means that this is the second revaccination according to the scheduled vaccination schedule. Then the next revaccination is carried out at 14-16 years of age and is designated as R3 ADSM. After a person reaches 23-26 years of age, he is vaccinated again and continues to do so every 10 years. There is no upper threshold indicating the end of the vaccination period. This is due to the fact that in older people the immune system is too weakened and it is very difficult for them to endure infectious diseases. Therefore, older people, like children, need systematic revaccination.
Features and scheme of vaccination
The schedule for administration of ADS-m toxoid depends on the response to DTP. If the child has tolerated the drug containing the whooping cough component well, vaccination is carried out as follows:
- R2 - 4-6 years;
- R3 - 14-16 years old.
If a child does not tolerate the DTP and ADS vaccine well, and he does not have a medical outlet, the ADS-m vaccination is carried out according to the following scheme:
- first - 3 months;
- second - 4.5 months;
- third - 6 months;
- fourth - 1 year and 6 months.
Revaccination of R2 and R3 is carried out according to the standard scheme.
Any vaccination is very stressful for children. To reduce the load on the nervous system, several vaccines can be administered at once, always in different parts of the body. The only exception is the BCG vaccine; it is administered strictly separately from others.
The drug ADS-m stimulates the production of antibodies to tetanus and diphtheria when released into the blood.
The drug cannot be administered intravenously; the immune system will quickly destroy the pathogen and will not allow the development of antibodies.
The vaccine must be injected into the muscle: shoulder, thigh, or under the shoulder blade (if the patient has a large layer of subcutaneous tissue). Grafting into the buttock can cause injury to the sciatic nerve and is therefore not practiced.
Preparatory measures
How well the ADS-m vaccination will be tolerated depends on many factors. First of all, you need to understand whether there are any contraindications. Necessary actions:
- examination of the medical record to identify previous reactions;
- visual examination by a therapist or pediatrician;
- general blood analysis.
The vaccine is given only to an absolutely healthy person, preferably on an empty stomach. It is recommended to go to the toilet before administering the drug.
For 2-3 days, it is necessary to exclude allergenic foods from the diet and take antihistamines. On the day of vaccination, it is advisable to drink a lot and eat light food in small quantities.
Name of imported analogue of DTP vaccine without pertussis component
There are no imported analogs of DTP that do not contain whooping cough components in our country. But the Pentaxim vaccine produced in France contains the acellular component of whooping cough.
Vaccine Pentaxim
Therefore, it, being cell-free, does not cause such a strong reaction in the body as a similar component included in DTP.
In addition to the three diseases against which DTP is vaccinated, Pentaxim also protects against polio and Haemophilus influenzae (a hemophilic infection responsible for meningitis, pneumonia, etc.).
Reaction, side effects and possible complications
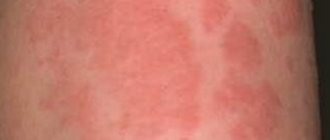
Vaccination with ADS-m is rarely accompanied by side effects; natural reactions usually occur:
- Hyperthermia (37 to 39 °C). If the temperature is above 38.5 °C, you need to take antipyretics (drugs based on paracetamol or ibuprofen).
- Headache. The symptom is easily eliminated with painkillers.
- Moodiness, lethargy and drowsiness.
- Indigestion, diarrhea. If loose stools bother you more than 3 times a day, you should take medications to normalize them (Smecta, Subtil).
- Pain, redness, swelling at the injection site. Unpleasant sensations are relieved with painkillers and antihistamines.
It is worth noting that all these signs are a reaction to the introduction of the vaccine. They can be expressed in mild, moderate and severe degrees (depending on the characteristics of the body and state of health). In any case, they disappear on their own after a few days.
If symptoms persist for more than 5 days or only appear after this time, you should consult a doctor.
Complications occur extremely rarely:
- Severe allergic reactions, for example, angioedema (Quincke's edema), anaphylactic shock, often urticaria. They appear almost immediately after the vaccine is administered and can be stopped by medical workers.
- Encephalitis.
- Meningitis.
- State of shock.
- Inflammation of the injection site due to infection.
Some reactions develop quickly, so it is important to remain under medical supervision for at least half an hour.
Main causes of complications:
- administering a vaccine without prior examination;
- no identified contraindications;
- violation by the patient of the doctor's instructions.
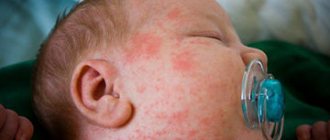
Consequences of vaccinations in a child
ADSM is more easily tolerated by most people than DTP, but, nevertheless, this vaccine can cause severe allergic reactions if it is started only in adulthood.
If all the doctor’s recommendations are correctly followed, the child should not experience any side effects. On the contrary, immunity must be developed against the pathogens of tetanus and diphtheria.
Normal body reaction
The usual reaction of the body in response to vaccination can be considered:
- slight (up to 37 degrees) rise in body temperature;
- lethargy, fatigue and reluctance to perform any actions (for 2-3 days);
- partial or complete loss of appetite;
- drowsiness;
- nausea (in rare cases, vomiting);
- stiffness in the movements of the limb into which the injection was performed;
- thickening of the skin around the injection site;
- mild swelling of the limb;
- slowness;
- redness of the skin in the injection area.
All of the above symptoms should not raise suspicions about an incorrect reaction of the body.
Possible complications after vaccination
ADSM is considered a gentle vaccine, and reactions to its components are extremely rare, even in children with asthma or dermatitis.
In cases where the vaccine administration technique was violated or when the drug was used without consultation with a specialist, the following complications may occur:
- serum sickness;
- diseases resulting from disorders of the nervous system (encephalopathy, polyneuritis, post-vaccination encephalitis);
- poor sensation in the legs;
- convulsions;
- severe nausea and vomiting;
- headache accompanied by dizziness;
- increased body temperature (above 38 degrees);
- joint pain and swelling;
- keloid disease (abnormal growth of scar tissue);
- secondary immunodeficiency;
- anaphylactic shock;
- the appearance of infection.
Features of behavior after vaccination
To ensure that the administration of the ADS-m vaccine is not accompanied by undesirable reactions, certain recommendations must be followed:
- do not eat (1 day before and 3 days after) foods that provoke allergies: citrus fruits, chocolate, unknown dishes;
- observe the drinking regime - drink 2 or more liters of clean warm water;
- do not rub or comb the vaccination site;
- do not drink alcoholic beverages (3 days before vaccination and a week after).
Vaccination weakens the human body, so after it it is recommended to avoid public places and contact with sick people.
Imported analogues of the drug
Many mothers prefer to refuse domestic drugs provided by the clinic. They always have the opportunity to purchase an imported analogue of the vaccine from Germany, America, and Austria.
The most famous analogues of ADSM are:
- monovalent tetanus (tetanus) vaccine;
- Imovax DT Adjudt;
- monovalent vaccine against diphtheria (AD).
Vaccines are in the form of a suspension. The cost of such drugs is approximately 300 rubles. You can order them online or in pharmacies. To administer this injection, you can go to a clinic or medical center. Such imported vaccines are considered less allergenic, but you should not forget about individual intolerance to the components.
Results and clarification of possible questions
On the territory of the Russian Federation, vaccination with the domestic ADS-m vaccine is done in any clinic (you must present identification documents and a medical insurance policy). Anyone can be vaccinated with foreign drugs. However, to do this you will have to go to a private clinic or purchase the vaccine yourself at a pharmacy.
The cost of vaccination with domestic vaccines is 300-500 rubles, foreign - from 1500 rubles.
Attention! The vaccine must be transported in the refrigerator, since toxoids die at room temperature.
The knowledge of adults regarding any vaccinations, including DPT-m, is limited, despite the widespread practice of vaccination. Quite often questions arise that even some pediatricians cannot give a clear answer to:
Should I take my child for a walk after vaccination?
Being outdoors is very beneficial for children, and vaccination is not a reason to stay at home if the child is feeling well and the weather is good outside. The walk should take place in uncrowded places and be calm. If the baby is uncomfortable or has a fever, it is better to stay in bed and ventilate the room well.
On the day of vaccination, the child woke up with a slight runny nose, what should I do?
If there are any, even minor, manifestations of ARVI, vaccination is not carried out due to the high risk of complications. Some pediatricians may argue that a slight discharge of snot is not at all scary. However, parents who value their child’s health should refrain from vaccination for approximately 3 weeks after complete recovery.
Have you been vaccinated, when can you give your child a bath?
During vaccination, water procedures are allowed; it is only prohibited to rub the injection site with a washcloth. Dirt and natural secretions that fall on an open wound are much more dangerous.
Is massage possible after vaccination?
Intramuscular injection of toxoids causes pain and muscle weakness, so you should not massage after vaccination. If a child is undergoing treatment, it is better to do the procedure before vaccination or take a temporary exemption from a pediatrician.
What guarantees does the ADS-m vaccination provide?
Vaccination does not protect 100% against tetanus and diphtheria, but if the disease occurs, it is much milder than in unvaccinated people.
By the beginning of the 21st century, humanity had almost forgotten about many infectious diseases that were considered fatal. This achievement was made possible, among other things, thanks to the invention of vaccines. However, pathogens such as diphtheria and tetanus still live in the environment and are fatal when infected. The only way to avoid this is to get vaccinated with ADS-m on time.
Contraindications for injection
ADS-M is a serious medical drug. The instructions clearly state situations when it is prohibited to give an injection. Contraindications for unvaccinated adult patients include:
- severe diseases associated with immunodeficiency;
- allergic reaction to vaccine components;
- negative reaction to the previous injection.
In addition, there are restrictions on injection. It is necessary to postpone the procedure in women during pregnancy and lactation. If the patient has suffered from acute infectious infections, then a medical exemption is given for two weeks.
Why are polyvalent vaccines more relevant than monovalent ones?
Polyvalent drugs contain several components, which reduces the number of injections that the child will receive. There are separate diphtheria and tetanus vaccines, but they are used primarily to immunize people who have not been vaccinated before.
Despite the fact that immunization against diphtheria and tetanus always causes an increase in temperature and the development of a local reaction, it is necessary to vaccinate the child against these infections. Understanding the difference between DTP and ADS-m, as well as proper preparation for vaccination and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations, virtually eliminate the risk of complications.
Source