Vaccination Prenevar: what is the possible reaction of the body in a child
Often, with infectious diseases, complications develop.
Such undesirable changes are especially often observed in children whose immune systems have not yet strengthened. Therefore, in order to prevent the development of these diseases, vaccination is carried out. To develop a protective barrier to pneumococcus, an appropriate drug is administered. At the same time, parents are immediately interested in what the reaction to the Prevenar vaccine might be.
The body's reaction to this vaccine in children varies.
Reaction to Prevenar vaccine in a child - main side effects
According to research, 80% of all infectious diseases in children are pneumococcal.
Most often they affect children under five years of age; this same age group suffers pathologies more severely. To prevent the occurrence of such infections, a special vaccine was developed - Prevenar. The reaction to the vaccine often worries parents and they are afraid to get it, expecting negative consequences for the child’s health.
A normal reaction to the Prevenar vaccine in a child
The Prevenar vaccine is produced in the USA. It contains 7 or 13 common strains of pneumococcus. Approved for use in children starting from two months and two years of age, respectively. Included in the Russian national calendar in 2014.
A slight increase in body temperature, local reactions on the skin and behavioral disturbances in the child are an absolutely normal response of the body to immunization.
What side effects and complications may occur after vaccination?
According to the manufacturer's assurances (which is also confirmed by reviews from parents), the Prevenar vaccination is tolerated quite easily. Side effects and reactions occur rarely and go away on their own within 1-2 days.
Are common
Common violations include:
- short-term increase in body temperature (usually no higher than 38 degrees);
- lethargy, weakness, drowsiness;
- irritability;
- sleep disturbance;
- loss of appetite;
- vomiting, diarrhea;
- hypersensitivity reaction from the immune system;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- slight weakness of the limb in which the injection was given;
- convulsions.
In extremely rare cases, more severe complications may develop: anaphylactic reactions, Quincke's edema, bronchospasm.
According to studies, such a response from the body occurs in 1 case out of 10,000.
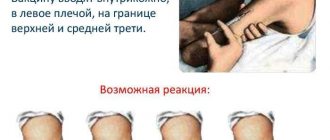
Local
Local reactions include those that occur on the skin in the injection area.
Prevenar may cause:
- redness;
- compaction;
- swelling;
- soreness;
- urticaria (an allergic rash may be local or spread to large areas of the body);
- edema.
There is no need to lubricate the injection site or carry out other manipulations with it - the phenomena described above go away on their own without any health consequences.
How to minimize the risk of unwanted consequences
A competent approach to child immunization can significantly reduce the risk of any negative reactions.
What it should include:
- For 5-7 days before and after vaccination, you must avoid visiting public places (shops, shopping centers, cinemas, etc.). The same applies to schools and kindergartens. Here, a child can easily catch a viral infection, which will prevent the immune system from responding adequately to vaccination.
- For half an hour after administration of the drug, it is recommended to remain under medical supervision, since the most severe reactions occur during this period.
- If a child is vaccinated at a free clinic, you should not wait your turn in a stuffy and crowded corridor full of infections - it is better to do it on the street.
Pneumococcus can cause dozens of different diseases, including such dangerous ones as bronchitis, pneumonia, meningitis and others. The risk of suffering from post-vaccination complications is hundreds of times lower than the chance of suffering severe consequences from such pathologies.
Doctors' advice
Let's look at what doctors recommend to all parents who are afraid to vaccinate their children:
- You should not give children any medications or homeopathic preparations for the purpose of “facilitating the tolerance of vaccinations.” Such funds simply do not exist. But adequate hardening, proper nutrition and sports, present in the lives of children, perfectly strengthen the immune system, which allows vaccination to be tolerated as painlessly as possible.
- In children with allergies, it is permissible to use antihistamines, but only on the recommendation of a doctor.
- Famous pediatrician E.O. Komarovsky believes that before vaccination, it is better to give the baby clean water to drink to eliminate the risk of dehydration. Another recommendation from the doctor beloved by many: do not give children new foods 2-3 days before immunization, and the day before - feed them only easily digestible foods.
- A couple of days before vaccination, it is better to take urine and blood tests to rule out hidden infectious processes.
Such simple measures will allow you to reschedule vaccination as easily as possible.
The Prevenar vaccine is a modern and safe vaccine with proven effectiveness. It is easily tolerated. Most mothers note only mild local reactions on the skin and a slight increase in body temperature in children.
Source: https://vactsina.com/privivki-i-ukolyi/prevenar-reaktsiya-na-privivku.html
Purpose of use of Prenevar
Pneumococcal infection provokes the development of a number of diseases, including:
- angina;
- otitis media of a bacterial nature;
- meningitis;
- pneumococcal pneumonia.
Prevenar 13 is a medicine that contains a weakened infectious agent.
Vaccination using it is designed to create a protective barrier. The body produces an antigen and the risk of developing dangerous infectious diseases is significantly reduced. The possibility of the disease cannot be completely excluded, but it is mild and does not cause complications.
The effect of the drug on the body
The drug contains more than 90% of serotypes of pneumococcal infection, which provokes the development of antibiotic-resistant pneumonia and acute otitis media. Each of these serotypes is a destroyed bacterial enzyme.
When the vaccine penetrates the body, the immune response is activated and the synthesis of antibodies begins. These are special proteins that form an antibody-antigen complex and neutralize the negative effects of the antibody.
In addition, during the period of fighting microbes, immune memory is formed.
If pathogenic bacteria of this variety penetrate again, the child’s body has already prepared “weapons” to fight it. Therefore, with repeated infection, the disease is mild or ends before it begins.
Possible reactions to vaccination
The instructions for the drug indicate that after vaccination a general and local reaction may occur:
- the injection site turns red and a lump appears on it;
- swelling;
- soreness;
- sleep disturbance;
- hyperthermia;
- irritability.
A reaction to the vaccine is often noted from the gastrointestinal tract:
- lack of appetite;
- gagging;
- diarrhea;
- nausea.
The following side effects of the drug are also possible:
- convulsions;
- manifestations of hypersensitivity;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
According to the manufacturer, severe reactions occur if special instructions are neglected.
The drug is not administered if there are a number of contraindications:
- acute respiratory diseases;
- disturbances in the process of blood clotting;
- HIV.
Diarrhea after Prevenar vaccination
Often, with infectious diseases, complications develop. Such undesirable changes are especially often observed in children whose immune systems have not yet strengthened. Therefore, in order to prevent the development of these diseases, vaccination is carried out.
To develop a protective barrier to pneumococcus, an appropriate drug is administered. At the same time, parents are immediately interested in what the reaction to the Prevenar vaccine might be.
The body's reaction to this vaccine in children varies.
Purpose of use of Prenevar
Pneumococcal infection provokes the development of a number of diseases, including:
- angina;
- otitis media of a bacterial nature;
- meningitis;
- pneumococcal pneumonia.
Prevenar 13 is a medicine that contains a weakened infectious agent.
Vaccination using it is designed to create a protective barrier. The body produces an antigen and the risk of developing dangerous infectious diseases is significantly reduced. The possibility of the disease cannot be completely excluded, but it is mild and does not cause complications.
Is there a reaction to the Prevenar vaccine?
Reactions in children to this vaccine are quite rare. Like other drugs, this one can also lead to unwanted changes.
Often, immunization against protococcal infection is carried out simultaneously with other vaccinations. Therefore, it is impossible to reliably determine which vaccine caused the side effects.
The effect of the drug on the body
The drug contains more than 90% of serotypes of pneumococcal infection, which provokes the development of antibiotic-resistant pneumonia and acute otitis media. Each of these serotypes is a destroyed bacterial enzyme.
When the vaccine penetrates the body, the immune response is activated and the synthesis of antibodies begins. These are special proteins that form an antibody-antigen complex and neutralize the negative effects of the antibody.
In addition, during the period of fighting microbes, immune memory is formed.
If pathogenic bacteria of this variety penetrate again, the child’s body has already prepared “weapons” to fight it. Therefore, with repeated infection, the disease is mild or ends before it begins.
Possible reactions to vaccination
The instructions for the drug indicate that after vaccination a general and local reaction may occur:
- the injection site turns red and a lump appears on it;
- swelling;
- soreness;
- sleep disturbance;
- hyperthermia;
- irritability.
A reaction to the vaccine is often noted from the gastrointestinal tract:
- lack of appetite;
- gagging;
- diarrhea;
- nausea.
The following side effects of the drug are also possible:
- convulsions;
- manifestations of hypersensitivity;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
According to the manufacturer, severe reactions occur if special instructions are neglected.
The drug is not administered if there are a number of contraindications:
- acute respiratory diseases;
- disturbances in the process of blood clotting;
- HIV.
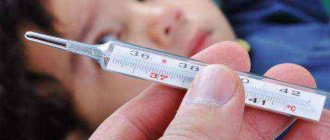
Increased body temperature
It is not uncommon to develop a fever after immunization. The baby becomes lethargic and capricious.
Such changes are observed in every third child who has been vaccinated. As a rule, the readings on the thermometer do not exceed 38 degrees Celsius. Sometimes a more significant increase in temperature is possible.
You can help children cope with the consequences of vaccinations with the help of antipyretics.
To bring down the temperature, the child is given Paracetamol, Ibuprofen or Nurofen. If medications are ineffective and hyperthermia is observed for more than three days, you need to seek help from a medical facility.
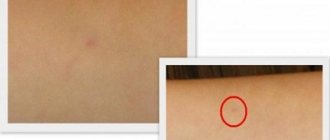
Redness and hardening of the injection site
The most common side effect from the injection of the drug is redness of the injection site. A lump may appear in this area.
Such problems arise for a number of reasons:
- An inflammatory process is observed, provoked by the body's immune response and active synthesis of antibodies.
- The use of low-quality vaccine that was stored or transported without compliance with the standards.
- Incorrect injection. When serum gets into the subcutaneous fat, the risk of compaction increases significantly. This is due to the fact that the drug is absorbed much more slowly.
Source: https://tepcontrol.ru/diareya-posle-privivki-prevenar/
Increased body temperature
It is not uncommon to develop a fever after immunization. The baby becomes lethargic and capricious.
Such changes are observed in every third child who has been vaccinated. As a rule, the readings on the thermometer do not exceed 38 degrees Celsius. Sometimes a more significant increase in temperature is possible.
You can help children cope with the consequences of vaccinations with the help of antipyretics.
To bring down the temperature, the child is given Paracetamol, Ibuprofen or Nurofen. If medications are ineffective and hyperthermia is observed for more than three days, you need to seek help from a medical facility.
Redness and hardening of the injection site
The most common side effect from the injection of the drug is redness of the injection site. A lump may appear in this area.
Such problems arise for a number of reasons:
- An inflammatory process is observed, provoked by the body's immune response and active synthesis of antibodies.
- The use of low-quality vaccine that was stored or transported without compliance with the standards.
- Incorrect injection. When serum gets into the subcutaneous fat, the risk of compaction increases significantly. This is due to the fact that the drug is absorbed much more slowly.
There is no need to try to eliminate the redness and the resulting lump on your own. Pharmacists have not yet developed a drug that can safely and effectively cope with local reactions to the vaccine.
It is strongly recommended not to treat the affected area with iodine, brilliant green or any other antiseptic agents . Compresses are also contraindicated. It is unacceptable to stick a patch to the injection site.
The only acceptable option for relieving the condition is cold. It is applied to the seal for a short time. Thanks to such actions, unpleasant sensations become less pronounced.
As a rule, a local reaction appears on the first day after the vaccine is administered.
Symptoms persist for up to one and a half weeks. The diameter of the speck does not exceed seven centimeters. If it continues to increase or does not disappear for a long time, you should consult your doctor.
Prevenar vaccination: what it is used for, side effects and vaccination schedule
Every year, a significant number of children around the world suffer from such dangerous diseases as pneumonia, otitis media, tonsillitis, bronchitis, sepsis and others. In most cases, these diseases are caused by pneumococci.
Pharmacists offer a huge number of drugs to treat diseases caused by these microorganisms, but there are cases when treatment is delayed and requires a lot of effort from the child. The situation is aggravated by the fact that mass use of antibacterial drugs is now widespread, even where there is no need for it.
Because of this, the bacterial environment has already adapted to antibiotics, as a result of which even the most powerful drugs are ineffective. Therefore, the best way to prevent this problem is timely vaccination. So, what is the Prevenar vaccine and why is it needed?
- Who is being vaccinated?
- Is it mandatory?
- Limitations and adverse reactions
In what cases is it necessary to get vaccinated?
Pneumonia is one of the most serious respiratory diseases that affects both adults and children. Most often it is caused by pneumococci. The problem is that for young children, sometimes the illness does not end in the best way. Therefore, vaccinations against pneumococci are of great importance in the prevention of such a dangerous disease.
The most popular drug that can protect against pneumococci is the Prevenar vaccine. This is the only drug against pneumonia that is intended primarily for children from 2 months to 5 years.
The vaccine affects the body in such a way that it develops immunity against pneumococci, due to which the cells remember the bacterium and react more quickly to it when they encounter it. The use of the drug promotes the body's production of antibodies to the main serotypes of Prevenar in children immediately after the first course of vaccination.
There are two types of vaccinations – Prevenar 7 and Prevenar 13.
The difference between them is the number of strains contained in the drug. Now there is a tendency towards a final transition only to Prevenar 13. The feasibility of this decision has not been fully studied.
Who is being vaccinated?
Prevenar vaccination cannot be prescribed to anyone who wants it. According to the instructions, Prevenar is administered only to children of the following categories:
- age category from 2 months to 5 years, if they get sick often,
- prematurely born,
- allergy sufferers,
- HIV carriers,
- with chronic diseases of the respiratory system, liver, heart,
- with diabetes.
Typically, adults and children over 5 years of age are not vaccinated, since these categories of the population will not develop the desired immune response. Clinical trials on the use of the vaccine by expectant and nursing mothers have not been conducted; accordingly, they also cannot be classified as those who need to be vaccinated.
But sometimes vaccinations for adults are necessary. This applies to the following population groups:
- people over 65 years of age, since they are at risk of developing streptococcal pneumonia with complications due to the fact that their immunity is weakened and cannot quickly respond to infections,
- people suffering from diabetes, chronic lung diseases, heart disease, liver cirrhosis, neurological diseases,
- everyone who has immunodeficiency states of various etiologies.
All of the above categories of the population are at risk of infection with pneumococci with severe complications.
Is it mandatory?
Is Prevenar vaccination necessary for the above population categories? It is worth remembering that this vaccination is a reliable method of protection that helps a weakened body fight infection. Vaccination with Prevenar is recommended, but not required.
Not so long ago, the Russian preventive vaccination calendar did not contain information about Prevenar. The situation changed in January 2014, when the drug for pneumococcal infection was added to this list.
Its implementation is paid for. Vaccinations are carried out free of charge with a similar drug “Pneumo 23”, which was produced in France.
According to the vaccine instructions, there are several schedules for administering Prevenar. What do they depend on? The following factors are relevant:
- Age category of a person.
- The need for vaccination.
- Indications for vaccination.
Preparation and implementation of vaccination
The first step to preparation can be considered obtaining information about the action and composition of the drug. The Prevenar vaccine is produced in the United States of America. The vaccine contains:
- protein,
- pneumococcal structures,
- aluminum phosphate,
- polysaccharides of serotypes, etc.
Proper preparation for the procedure will help avoid negative consequences and strengthen the resistance of the immune system. Before the procedure, you need to visit some doctors and get tested.
The first person you should definitely visit is the pediatrician. He should know about all the parents’ doubts and changes in the child’s health. Additionally, a neurologist, orthopedist or surgeon is visited. If there is a tendency to allergic diseases, the doctor prescribes the use of antihistamines before and after the procedure.
Before vaccination, it is recommended to carry out the following tests:
- a general blood test, which will indicate the presence of inflammatory processes, allergies, metabolic disorders in the body,
- analysis for the presence of antibodies. If antibodies are present, vaccination is not given.
- immunogram. She will provide complete information about the child’s immunity.
Before vaccination, it is recommended not to visit public places. Walking is not prohibited, but care must be taken to ensure that the child does not overheat or become hypothermic. Two weeks before the procedure, if we are talking about a baby, it is not recommended to start complementary feeding or introduce a new product into the diet, as this may provoke an allergic reaction.
Important! It is necessary to monitor the child's health. If he has signs of an incipient disease, vaccination should be postponed.
Symptoms indicating the presence of the disease are:
- disturbing dream,
- lack of appetite,
- causeless whims (in a child) and loss of mood in an adult,
- indigestion.
A couple of days before vaccination, a decrease in the load on the digestive system is indicated. For adults and children over one year of age, it is recommended to reduce the volume and calorie content of meals. You should also not eat an hour before vaccination. It is necessary to measure the baby's temperature and ensure that he does not overheat.
Before vaccination, you need to calmly talk with your child about the procedure and tell him why it is needed. It is strictly forbidden to scare a child with injections. It is advisable to take your baby’s favorite toys or books to the clinic.
Vaccination schedule:
- A child aged two to six months is given three doses of Prevenar every month. Revaccination is carried out annually,
- after seven months, two doses are administered every month or two. Revaccination should be done when the baby is over one year old,
- from one to two years, two doses are administered after two months of two doses, the interval between which should not be less than two months. No need to do it again
- Children from two to five years old receive a one-time injection of Prevenar.
After vaccination, it is necessary to properly care for the injection site. You can wet the wound, but treating it with iodine, brilliant green, peroxide and other antiseptic drugs is strictly prohibited. Also, do not apply a patch or compress.
Many parents are concerned about the question: is it possible to go for a walk after the Prevenar vaccination given on this day? Yes, it is allowed and even recommended to go for a walk if the weather permits. However, the child’s stay in particularly crowded places should be limited.
Limitations and adverse reactions
It is necessary to take into account that Prevenar is a prescription vaccine, so only the doctor decides whether to vaccinate or not. Such an appointment can only be made by a pediatrician.
The use of Prevenar is contraindicated in the following cases:
- child's age up to 2 months or over 5 years,
- severe sensitivity to the previous vaccine administration,
- acute stages of infectious diseases.
If after shaking the vaccine there is a sediment in the form of flakes, the vaccine cannot be used.
Children generally react calmly to vaccination, although negative consequences do occur.
Adverse reactions at the injection site may manifest as:
- redness,
- swelling,
- pain,
- itching,
- dermatitis,
- hives,
- irritability, tearfulness,
- drowsiness or insomnia.
Among the negative reactions, a fever of up to 38 degrees is possible, and the temperature after Prevenar vaccination persists for two days or more. From the gastrointestinal tract the following are possible:
- vomit,
- nausea,
- stool disorders,
- lack of appetite.
The injection can also cause weakness and headache. More dangerous complications may include:
- anaphylactic shock,
- Quincke's edema,
- bronchospasm,
- dyspnea,
- seizures
Prevenar can be given at the same time as other vaccines.
A mandatory condition for vaccination is monitoring the child’s health for half an hour. This is necessary to avoid unwanted reactions of the body. If side effects do not go away within 24 hours, you should urgently seek medical help.
Warning against the fears of parents, it is worth saying that, despite the presence of a significant number of side effects, the Prevenar vaccination is an effective means of preventing many diseases of a bacterial nature, as well as their serious complications.
Loading…
Source: https://prof-medstail.ru/bolezni-legkih/dostoinstva-i-nedostatki-privivki-prevenar
How long does the reaction last?
Typically, the reaction lasts within 48-72 hours. There is no need to be afraid of side effects during this period.
The symptoms that appear indicate that the body is actively working and producing antibodies, thanks to which the small child will be protected from infection.
The following changes should raise concerns:
- pronounced hyperthermia;
- the injection site turned very red, a lump appeared on it, exceeding 7 centimeters in diameter;
- the condition began to worsen a day after the vaccine was administered;
- loss of consciousness is observed;
- severe form of allergic reaction.
Such symptoms are a reason to immediately contact a pediatrician.
Not to be confused with a normal reaction: side effects and complications of Prevenar vaccination
In order to avoid infection and spread of serious and dangerous diseases, a special program for immunization of the population has been created. But not everyone agrees to get vaccinated due to possible adverse reactions.
Therefore, it is important to know about complications after vaccination with Prevenar, which has been included in the national vaccination schedule as a recommendation since 2014.
What are they vaccinated against?
Prevenar is a polysaccharide pneumococcal adsorbed vaccine. The manufacturer is Pfizer. Vaccination promotes the development of an immune response to pneumococcal bacteria, which cause such severe pathologies as pneumonia, meningitis, otitis media, sepsis and others.
The likelihood of contracting the infection is the same in both adults and children. For newborns, these diseases are especially dangerous and often lead to death.
Composition of the vaccine in a dosage of 0.5 ml:
- pneumococcal conjugates;
- polysaccharides of serotypes 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, 23F;
- carrier protein;
- aluminum phosphate;
- water for injections;
- sodium chloride.
The main components mean variants of pneumococcus, against which the vaccine is intended.
Auxiliary components are fillers and stabilizers. Thanks to vaccination, antibodies are produced against pathogenic microorganisms. In clinics, this drug can be administered for a fee, since this vaccination is only a recommendation.
Not so long ago in Russia, in the national calendar of preventive vaccinations, there was no information about such vaccines. Only since January 2014, the drug against pneumococci has been added to this list.
The clinic administers an analogue of Prevenar, the French vaccine Pneumo 23, free of charge.
Can a child get sick after vaccination?
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of this vaccination. This medical advance saves the lives of children under 5 years of age. If a child has been vaccinated against pneumococcus, parents do not have to worry, since the baby’s body is protected from infections.
Research shows that thanks to vaccination, the likelihood of developing lobar pneumonia, meningitis and other pathologies caused by pneumococci is reduced by 6 times.
Also, vaccinated children are less likely to suffer from bronchitis, influenza, ARVI, sore throat, etc. In the event of infection with pneumococcal infection, the disease is much easier to tolerate and does not end in death. Treatment time is also reduced, without the need to use expensive drugs for therapy.
A child's normal reaction to a vaccine
Prevenar is a modern drug that produces antibodies to all 13 serotypes of the group. During the first week after the injection, you may experience slight discomfort and pain in the injection area.
Such reactions are rare, but are considered normal. If three days after vaccination there are no problems, you don’t have to worry.
After administration of the drug, it is worth limiting water procedures, only short showers are acceptable.
Side effects of the Prevenar vaccine
In general, the drug is well tolerated and with proper preparation for vaccination, adverse reactions occur extremely rarely. Only 1% experience an increase in temperature, and 5% have a local reaction.
Increased body temperature
After administration of the drug, an increase in body temperature is possible. However, this is not considered a pathological condition, it is just a signal that the body is fighting an infection.
The value on the thermometer can be from 37.5 to 39 °C . It can last for a day, then returns to normal. The temperature should not last more than 2-3 days, in which case you should consult a doctor.
Redness and thickening
After vaccination with Prevenar, redness or hardening may occur at the injection site. This phenomenon occurs more often in older children. This reaction should go away within 2-3 days.
Rash
Manifestations in the form of a rash may appear near the site where the vaccine was given. If the child does not suffer from allergies, the rash should go away after a few days.
Otherwise, it is better to visit a specialist to clarify the situation. The local reaction occurs as a response to introduced pathogens, and the more of them, the stronger the manifestation of the body’s struggle. This is a normal reaction and does not require additional treatment.
It is not recommended to rub or wet the rashes.
Cough and snot
After vaccination, exacerbation of chronic diseases accompanied by cough and runny nose is possible. Often the drug is administered simultaneously with another vaccine, which causes similar symptoms. It is observed quite rarely.
Other side effects and consequences of vaccination
Other side effects include general condition disorders and allergic reactions.
Among the consequences of vaccination are:
- swollen lymph nodes;
- the child may be capricious, cry, drowsy and irritable for some time after vaccination;
- lack of appetite, vomiting, nausea;
- convulsions and temporary cessation of breathing (apnea);
- Quincke's edema, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock.
To avoid negative reactions, it is necessary to study contraindications and make sure that the child is healthy.
Contraindications
Contraindications for vaccination are temporary or permanent.
Vaccination is not done in the following cases:
- intolerance to components;
- for respiratory diseases;
- at elevated body temperature;
- in the stage of exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- children under 2 months.
If the child has had a blood transfusion, vaccination should be postponed for 3-4 months.
What to do to avoid complications after Prevenar vaccination?
In order to avoid unwanted reactions, parents must follow simple rules.
Among the mandatory ones it is worth highlighting:
- Before vaccination, show the child to a pediatrician for examination, this is necessary to determine possible contraindications;
- It is forbidden to bathe the child for 24 hours after administering the drug; the injection site should also not be wet;
- Walking is acceptable if weather conditions permit. They should be performed in a place with the least crowd of people to avoid infection;
- It is not recommended to introduce new foods that can cause allergies into the child’s diet;
- Nursing mothers should also not consume new foods during this period;
- If the temperature is higher, the child should be given an antipyretic.
Before administering the drug, the child does not need any preliminary preparation. Still, some pediatricians advise taking a blood test to make sure there are no inflammatory processes.
Children prone to allergies are recommended to take antihistamines before and after vaccination.
on this topic
Dr. Komarovsky about possible complications in the post-vaccination period:
Many parents still wonder whether their child should get the pneumococcal vaccine. After all, until recently it was not included in the list of mandatory ones.
New antibacterial drugs are appearing less and less frequently, and microorganisms are becoming resistant to them every day. Perhaps, after many years, the pneumococcal vaccine will be the only one in the fight against infections.
Source: https://vactsina.com/inektsionnyie-preparatyi/oslozhneniya-posle-prevenar.html
Possible reaction of the body to revaccination
To achieve a lasting result, revaccination is carried out some time after the first vaccination. The reaction to the second vaccination varies.
Often, in cases where pronounced side effects were observed during the first administration of the vaccine, there were no such changes after revaccination. It is also possible that the body's reaction will be brighter.
The most common symptoms that appear are:
- pain and swelling in the injection area;
- hyperthermia observed for a short period;
- loss of appetite;
- insomnia or increased sleepiness;
- excessive irritability and excitability.
In fact, with revaccination, exactly the same negative effects may appear as with the first administration of the medication.
What other side effects may occur?
In rare cases, the following consequences of immunization have been observed:
- chills;
- hives;
- dyspnea;
- pain syndrome localized in the joint area;
- redness of the skin due to enlarged capillaries (erythema);
- apathy;
- cessation of breathing for a short period (noted when there are problems in the functioning of the respiratory system);
- itching in the area where the drug was administered;
- flushed face;
- headache;
- increased fatigue.
Such symptoms occur rarely and are often caused by non-compliance with the rules of preparing for immunization and performing the procedure in the presence of contraindications. In the vast majority of cases, no unpleasant changes are observed during vaccination. Children tolerate the Prevenar vaccine well.
Can a child get sick after vaccination?
Prevenar is a modern drug that produces antibodies to all 13 serotypes of the group. During the first week after the injection, you may experience slight discomfort and pain in the injection area.
Such reactions are rare, but are considered normal. If three days after vaccination there are no problems, you don’t have to worry.
After administration of the drug, it is worth limiting water procedures, only short showers are acceptable.
Common causes of indigestion
Diarrhea in a child who has received another vaccination is often a normal reaction. Each vaccination is stressful for a small organism. Side effects almost always occur, they just may differ depending on the type and composition of the drug.
Much depends on the level of reaction of each individual organism. Everything is individual. If everything goes smoothly for a baby in one family after vaccination and there are no problems, this does not guarantee the same easy transfer of the same vaccine for another baby.
There is a greater likelihood of diarrhea with fever after vaccination in the following cases:
- before vaccination, the baby had digestive problems;
- the vaccination was given on a full stomach;
- diarrhea did not develop due to vaccination, but due to consumed food that was spoiled.
Diarrhea can often be stopped with the help of folk remedies or with the help of drugs intended for these purposes. If such treatment does not help, symptoms include vomiting and diarrhea, nausea and fever, it may be better to consult a specialist as soon as possible.
It is necessary to urgently call an emergency medical team if the following symptoms appear:
In such cases, you cannot do without an experienced doctor, and in order to preserve life and health, it is important to get immediate help.
Depending on which vaccine was introduced into the body of a child or an adult, the reaction is different. Let's look at the main symptoms that occur during vaccination.
Can a child get diarrhea from vaccinations?
Most people understand that diarrhea itself is not a disease, but a symptom of another internal condition. Digestive disorders can develop in response to a change in diet, food poisoning, or even a vaccine. It is necessary to understand why diarrhea occurs after vaccination, whether assistance is needed, and whether such diarrhea is dangerous.
Common causes of indigestion
Diarrhea in a child who has received another vaccination is often a normal reaction. Each vaccination is stressful for a small organism. Side effects almost always occur, they just may differ depending on the type and composition of the drug.
Much depends on the level of reaction of each individual organism. Everything is individual. If everything goes smoothly for a baby in one family after vaccination and there are no problems, this does not guarantee the same easy transfer of the same vaccine for another baby.
There is a greater likelihood of diarrhea with fever after vaccination in the following cases:
- before vaccination, the baby had digestive problems;
- the vaccination was given on a full stomach;
- diarrhea did not develop due to vaccination, but due to consumed food that was spoiled.
Diarrhea can often be stopped with the help of folk remedies or with the help of drugs intended for these purposes. If such treatment does not help, symptoms include vomiting and diarrhea, nausea and fever, it may be better to consult a specialist as soon as possible.
It is necessary to urgently call an emergency medical team if the following symptoms appear:
We recommend: Causes of yellow diarrhea in a child and methods of treatment
In such cases, you cannot do without an experienced doctor, and in order to preserve life and health, it is important to get immediate help.
Depending on which vaccine was introduced into the body of a child or an adult, the reaction is different. Let's look at the main symptoms that occur during vaccination.
Vaccination against polio
The polio vaccine can cause diarrhea. The vaccine consists of a certain amount of live bacteria. Although there is a synthetic analogue with non-viable microorganisms, the effectiveness of such grafting is low. Therefore, a live version of the drug is used.
When the vaccine enters the patient’s body, microorganisms begin to actively reproduce. An increase in the number of pathogenic bacteria in the microflora of the digestive tract causes a malfunction, and intestinal disorder begins. This is a common and common occurrence.
Vaccination against hepatitis
When a person receives a vaccine that protects their health from hepatitis, side effects may occur. Usually they do not develop immediately, but over the next two days after the procedure.
The symptoms are as follows:
- diarrhea;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- temperature.
It is important to create the most comfortable conditions for the patient, provide him with plenty of fluids and adequate nutrition. Symptoms continue for another two days. After this, all signs of the pathological condition disappear on their own.
Mantoux grafting
Mantoux is not exactly a vaccination, but only an external reaction to the presence of the substance tuberculin in the human body. However, the penetration of foreign substances into the body causes a temporary decrease in immune defense and leads to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Local reactions include the appearance of a slight swelling and the appearance of a reddened area. Common symptoms in children often include diarrhea and low-grade fever. Possible loss of appetite and, in rare cases, vomiting.
If negative symptoms appear once, a doctor’s intervention is not necessary. Everything goes away on its own. For protection, it is better to cover the vaccine injection site with a band-aid so that the baby does not scratch it and infection is not introduced there.
We recommend: What to do if a child has green diarrhea?
Medical attention is necessary if you have the following symptoms:
- the temperature lasts a long time and does not go astray;
- an abscess appeared at the injection site;
- the child refuses to eat and drink;
- convulsions begin.
If you do not provide emergency assistance at such a moment, death occurs.
DTP vaccination
After DPT vaccination, most children experience unfavorable symptoms. This vaccine can provoke the most reactive manifestations.
The vaccine itself does not always cause a pathological reaction. Negative symptoms develop against the background of a sharp decrease in immunity. This allows other opportunistic microorganisms to actively multiply, which causes diarrhea, nausea and vomiting in many cases.
Most often, negative symptoms disappear within two days. If warning signs do not go away, consultation with a specialist is required.
Vaccinations against measles, mumps and rubella
All three diseases have a viral etiology and are very quickly transmitted from sick people to healthy people. If a person is not vaccinated, it is very easy to become infected. Diseases are difficult to tolerate and can cause serious complications.
After vaccination against measles, mumps and rubella, the following unpleasant manifestations are possible:
- diarrhea;
- skin rash;
- severe vomiting;
- local reaction in the form of compaction at the injection site;
- heat.
When such vaccinations are given to boys, slight swelling and swelling of the testicles is possible. The vaccine is commonly called the “MRV vaccine” - measles, rubella, mumps (mumps).
Flu shot
Vaccination during the flu epidemic helped many protect their health from a dangerous viral disease and the consequences that are associated with it. After administration of the drug, nausea, diarrhea and fever begin. This is due to the fact that restructuring processes are launched in the body.
If the temperature rises during the period after receiving a flu shot, it should be brought down to prevent the development of seizures.
General recommendations
If, shortly after receiving a vaccine against a disease, adverse symptoms appear, they are most often associated with the drug that entered the body. At the same time, it cannot be ruled out that other factors influenced the person, for example, banal poisoning or diseases of the digestive system.
Vaccination is carried out according to the schedule established by the Ministry of Health. All manipulations should be carried out only after examination by a doctor and his permission. Vaccines are not administered if a person is sick or has any ailments.
It is important to choose the right medications. They differ in quality, and if you have the opportunity to choose, it is important to give preference to trusted manufacturers. For example, to vaccinate newborns (against diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus and some other pathologies), the French composition Pentaxim is used. The English vaccine Prevenar, used against pneumococcal infections, has a good reputation.
To protect yourself from possible negative symptoms, it is important to prepare in advance for vaccination. If vaccinations are carried out in a hospital, you need to spend as little time as possible in the clinic so as not to become infected from other visitors and not to mistake the onset of illness for an adverse reaction to the vaccine.
Source: https://OPonos.ru/deti/ponos-posle-privivki
Vaccination against polio
The polio vaccine can cause diarrhea. The vaccine consists of a certain amount of live bacteria. Although there is a synthetic analogue with non-viable microorganisms, the effectiveness of such grafting is low. Therefore, a live version of the drug is used.
When the vaccine enters the patient’s body, microorganisms begin to actively reproduce. An increase in the number of pathogenic bacteria in the microflora of the digestive tract causes a malfunction, and intestinal disorder begins. This is a common and common occurrence.
Mantoux grafting
Mantoux is not exactly a vaccination, but only an external reaction to the presence of the substance tuberculin in the human body. However, the penetration of foreign substances into the body causes a temporary decrease in immune defense and leads to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Local reactions include the appearance of a slight swelling and the appearance of a reddened area. Common symptoms in children often include diarrhea and low-grade fever. Possible loss of appetite and, in rare cases, vomiting.
If negative symptoms appear once, a doctor’s intervention is not necessary. Everything goes away on its own. For protection, it is better to cover the vaccine injection site with a band-aid so that the baby does not scratch it and infection is not introduced there.
Medical attention is necessary if you have the following symptoms:
- the temperature lasts a long time and does not go astray;
- an abscess appeared at the injection site;
- the child refuses to eat and drink;
- convulsions begin.
If you do not provide emergency assistance at such a moment, death occurs.
Can children have a runny nose after vaccination?
Parents believe that vaccination will only harm the child and do so with caution, since rumors are now widespread that after the injection there is a high probability of adverse consequences.
Vaccination as a process is safe, the main thing is that the vaccination itself is in order. But today we are interested in how sensitive a child is to vaccination and how the reaction to various vaccinations manifests itself. Runny nose in a child
Vaccination Information
At this point, scientists have adopted a lot of vaccines, with the help of which they are able to fight various severe infections and viruses in many countries of the planet.
The vaccine helps the body develop immunity to pathogenic bacteria; after the injection, the process of forming antibodies begins and the person becomes immune.
The only disadvantage of this form of immunity formation is that it is impossible to prepare the body to protect against several diseases at once with one injection.
Based on this, in order to develop immunity to each disease, you have to inject yourself separately - you need to be vaccinated every time, against each disease separately.
At the same time, you need to understand that despite diseases that are dangerous and fatal to humans, vaccination is carried out only against some of the ordinary diseases that are often encountered in everyday life. For example, if a child lives in a temperate climate zone, then in principle it makes no sense to be vaccinated against some tropical fever.
The other side of the coin is that some people argue that there is no point in getting vaccinated against smallpox, although there are reservoirs containing anthrax and black smallpox on Russian territory. Although the disease is not widespread even within the country.
However, it is worth taking care of your own safety. The fact is that the spores of these diseases live quietly even in unfavorable conditions for about a hundred years and you never know where they will take you in life.
Epidemiologists consider the risk of spreading this disease to be high.
Vaccination
Injection calendar
The healthcare system assumes that by the age of 14, a child’s body should become immune to common diseases. Vaccination is carried out in educational institutions so that every child acquires immunity.
Naturally, the Infanrix vaccine cannot be given if you have a runny nose or other illness, but nothing will prevent you from being cured and after a runny nose, the child goes to the hospital at his place of residence, where he will be given the appropriate injection.
In civilized countries there is a certain order of injections, which are performed according to the following schedule:
- On the first birthday, an injection is given that will trigger the appearance of immunity against rubella, measles and mumps. This is already the fourth injection, however, vaccinations up to a year have nuances and this is a topic for a separate discussion;
- At one and a half years old, a second DTP injection is given, which is aimed against tetanus, diphtheria, and whooping cough. Doing DTP for a runny nose and other symptoms is prohibited;
- Polio drops are prescribed at one year and seven months; use is also prohibited for a runny nose;
- The next vaccination is at 6 years old, against measles, rubella and mumps;
- At this age an injection is given for tetanus and a few months later for tuberculosis;
- And lastly, in adolescence, as early as 14 years old, vaccination against tetanus and diphtheria is given.
Vaccination calendar
Patients are vaccinated against hepatitis separately. Every child who has reached one year of age is vaccinated. The flu vaccine is given in the same order. Until the age of 18, it is also mandatory to take injections against rubella, since this disease makes girls unable to conceive.
Is it possible to have a runny nose after vaccination?
As we already know, vaccination can successfully develop immunity to many infections in children. However, every vaccine has side effects, and one of them is a runny nose.
However, even before vaccinating, the doctor should take into account the contraindications and characteristics of each child’s body.
Often, children develop a runny nose after DTP the next day, this indicates that the vaccination was performed incorrectly.
Parents are concerned about the issue of side effects; they doubt whether it is worth getting the DTP vaccine if they have a runny nose.
At the same time, doctors have actually recorded a huge number of cases where snot after vaccination is not the only negative aspect; sometimes a cough also appears after DTP vaccination.
Parents come to hospitals with their children and try to understand what the doctors did wrong. However, referring to the research of doctors, it is worth saying that it is not the vaccine itself that causes snot after DTP vaccination.
You need to understand that there is always the possibility of an infection in the child’s body even before the vaccination is given, it just did not manifest itself until the opportune moment. In this case, vaccination for a runny nose acts as a catalyst that provokes the development of the disease.
Therefore, you cannot vaccinate if you have a runny nose, but it is better to take tests and be examined by a doctor first.
And it is better to vaccinate with Pentaxim for a runny nose immediately after tests and check-ups, since it may turn out that during the time that passed from the examination to the injection, the child fell ill.
Runny nose after vaccinations
There is a certain set of diseases for which vaccinations are mandatory. Otherwise, if a child meets them without immunity, he may not survive this meeting. These are the diseases:
Measles
The first on the list, polio, is a dangerous disease, and parents try to protect themselves from it using available means. Therefore, it is not advisable to do polio when you have a runny nose, but it is necessary. This vaccine, like others, can provoke certain complications, but a runny nose and cough after polio vaccination are less common than with the same DPT vaccine.
Moreover, in other cases, when people are vaccinated against measles, rubella or mumps, tests must be carried out twice, just as they are also vaccinated twice - at 1 year and at 6 years, before the child has to go to school.
It is also prohibited to get the MMR vaccine if you have a runny nose, but you need to have time to get cured and vaccinated before going to school, because these diseases spread well among children. It has been noted that, if a runny nose occurs after this type of vaccination, it does not occur immediately, but after two or three weeks.
As a rule, parents do not notice the connection between the vaccine and complications after such a period and are treated as usual.
Snot after vaccination against measles, rubella and mumps does not appear immediately because the vaccine contains real infections of each of these diseases, they are simply weakened to the required degree.
After 10-15 days have passed, the bacteria develop and, having reached their peak, provoke the body into an immune reaction.
This reaction to DTP vaccination and polio appears faster or slower, depending on the individual characteristics of the child’s body.
It is worth noting that not everyone develops a runny nose and cough after a flu shot, and children tolerate the vaccination normally, strengthening their body. A runny nose and side effects occur in a small percentage of children, but this can be managed. It is more difficult to treat a disease to which immunity is developed through vaccination.
When is the best time to get vaccinated?
It is important to understand that cough and vaccination do not always go together; complications simply arise as a result of the irresponsibility of both doctors and the patient’s parents. You must always remember about negative indications, and if they exist, then doing any vaccinations is prohibited.
The best solution would be to go to the doctor some time before getting the injection and get tested, which is required. And only when you see the results, consult your doctor about whether it is worth revaccinating DPT for a runny nose, and then get down to business.
It must be clearly understood that a child’s body, weakened by severe illnesses, will not be able to adequately tolerate the vaccine and the consequences are unlikely to be pleasant. The only exception is considered to be mantu, since this injection is not accompanied by the introduction of a vaccine into the body and the reaction can be successfully monitored even during illness. Doctors recommend injecting this reaction even if you have refused typical vaccines.
Parents need to understand that vaccination is the introduction of a strain of infection into the body, which over time provokes the body to develop immunity. Therefore, even a flu shot with a runny nose provokes complications under certain conditions, which no doctor can predict.
Therefore, vaccination for a runny nose in an infant , preschool child or even a teenager is excluded, since it will be more difficult to cure the consequences than the disease for which the person is vaccinated.
Both cough and fever are considered mandatory prohibitions - these are negative factors that will make an ordinary vaccination a mistake.
Source: https://nasmorkoff.ru/runny-nose/mozhet-li-u-detej-byt-nasmork-posle-privivki/
DTP vaccination
After DPT vaccination, most children experience unfavorable symptoms. This vaccine can provoke the most reactive manifestations.
The vaccine itself does not always cause a pathological reaction. Negative symptoms develop against the background of a sharp decrease in immunity. This allows other opportunistic microorganisms to actively multiply, which causes diarrhea, nausea and vomiting in many cases.
Most often, negative symptoms disappear within two days. If warning signs do not go away, consultation with a specialist is required.
Vaccinations against measles, mumps and rubella
All three diseases have a viral etiology and are very quickly transmitted from sick people to healthy people. If a person is not vaccinated, it is very easy to become infected. Diseases are difficult to tolerate and can cause serious complications.
After vaccination against measles, mumps and rubella, the following unpleasant manifestations are possible:
- diarrhea;
- skin rash;
- severe vomiting;
- local reaction in the form of compaction at the injection site;
- heat.
When such vaccinations are given to boys, slight swelling and swelling of the testicles is possible. The vaccine is commonly called the “MRV vaccine” - measles, rubella, mumps (mumps).