Children's health is vulnerable at any age. Parents regularly take various measures to protect their children’s bodies. One of these is vaccination. Most mothers and fathers are wary of vaccinations against various diseases.
One of the most controversial is DPT. This is an adsorbed pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus vaccine. It consists of a large number of killed pertussis microbes and purified diphtheria and tetanus toxoids.
Pediatricians always warn parents that after the administration of this drug they need to closely monitor the baby’s condition. This is necessary in order not to miss the moment when emergency medical care may be required. So what is the child’s behavior after DPT?
What behavior of a child after vaccination is considered normal?
According to the vaccination calendar, the DTP vaccine is administered to the child exactly four times.
It is administered for the first time at three months. After this, you need to monitor the baby’s condition. If no complications arise and the child feels well, then two more vaccinations need to be given. They are allowed only if there are no contraindications. They should be done with a time interval of forty-five days. But the last DPT vaccination, which is called revaccination, must be done at one and a half years.
As for the vaccine itself, three drugs are introduced into the child’s body at once. They all unite to perform a common task - creating a strong immune system that will resist dangerous diseases.
The most aggressive of these three vaccines is pertussis. The whole point is that traces of pertussis toxin and lipopolysaccharide are often found in it. This vaccination is one of the most dangerous, as there is a threat to the child’s life.
It must be remembered that the child’s behavior after vaccination may be different. After the vaccine is administered, his condition should be monitored. Often, due to some reasons, the reaction to it can be severe.
DPT vaccine
According to statistics, approximately 95% of all toxic reactions to drug administration occur in the first twenty-four hours. To be fair, it should be noted that this is a rather painful reaction to the vaccine, which is extremely rare.
When it comes to your own child, even one case in a million is already a lot. After the procedure, the baby's body temperature may rise. Most likely, the pediatrician will warn the mother about this symptom.
The temperature rises within a few hours after the vaccine enters the child’s body. This body reaction is considered absolutely normal and acceptable. Of course, we are talking about those cases when the temperature is not higher than 37.5 degrees Celsius.
If its level rises to 38, then you need to give the baby an antipyretic drug. Before administering the vaccine, you need to ask your pediatrician what to do if your temperature rises.
He will recommend the most suitable drug in this situation. It must be remembered that the DTP vaccine can cause a temperature rise of up to 39 degrees Celsius.
That is why you need to carefully monitor the child’s condition. If your body temperature continues to rise after taking an antipyretic, you should immediately call an ambulance. In this case, we are talking about the appearance of complications during the administration of the vaccine. This is very serious and there is no need to delay contacting a doctor.
Please note that an increase in body temperature can also be accompanied by sleep disturbances and lethargy of the baby. If these symptoms persist for several days after vaccination, this is normal. It is acceptable for symptoms to persist for three days, but no more than that . If symptoms do not disappear, you should urgently visit a pediatrician.
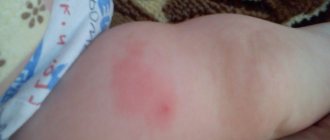
The vaccine often causes lumps to appear at the injection site. Under no circumstances should you rub this area. You need to monitor your child so that he does not do this.
You should also not heat the injection site. This compaction can persist for one month. Normally, it goes away on its own. It also does not pose any danger to the child’s life.
In this case, you need to monitor the child’s feelings. If touching the injection site causes pain or discomfort, then you need to visit a specialist.
Don't put off visiting the doctor. Especially in cases where the compaction volumes become larger and exceed the size of a small pea.
After administration of the DTP drug, a cough often appears. Despite the fact that one of the components of the vaccine is pertussis germs, coughing after administration of the drug is not the norm. If you notice this symptom, you should immediately consult a doctor.
During this period, the protective functions of the child’s body cannot cope with the administered vaccine. This makes it easier for other infections to enter the baby’s body. A severe course and even the occurrence of dangerous complications become more likely.
Adverse reactions
DTP vaccines are the most reactogenic, “heavy” childhood vaccines.
On average, adverse reactions occur in a third of vaccinated people, and not with every vaccine. The peak frequency of reactions is observed, as a rule, on the third and fourth injections of the vaccine, which coincides with the peak rates of immunity development. In a sense, the occurrence of adverse reactions to vaccination is natural, as a “by-product” of the process of developing immunity. The fact is that during an immune reaction, special mediator substances, internal immunostimulants of the body, enter the bloodstream, which, among other things, have properties that provoke inflammatory processes. On the other hand, when creating vaccines, every opportunity is used to minimize, albeit natural, but still unpleasant side effects, which is achieved by minimizing the content of ballast substances and a special balance between the quantity and quality of antigens.
In general, the presence of mild adverse reactions is a favorable sign, indirectly indicating the correct formation of the child’s immune system and the effectiveness of the immunity being formed. On the other hand, as a result of efforts to minimize the risk of adverse reactions, their absence should not be taken as an alarm signal or interpreted as a defect in the immune system.
Reactions at the site of vaccine administration (in general, observed in 15-25% of vaccinated people, without taking into account the preparation of the child for vaccination):
- redness (1-2%) and swelling (1-2%) caused by immune inflammation at the injection site and the action of the adjuvant (see above).
- pain at the injection site (probability about 15%, manifested by the fact that when moving the child “protects” the leg and cries) is also a consequence of the inflammatory reaction.
General reactions (on average observed in 20% of vaccinated people, excluding the preparation of the child for vaccination):
- increase in body temperature (up to 30%),
- others (anxiety or vice versa, lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea, appetite disturbances).
As a rule, all adverse reactions to DPT vaccines develop no later than 24 hours after vaccination and last no more than 24 hours. Reactions that occur later and last longer cannot be caused by the vaccine and in such cases another cause should be sought. As a rule, these are teething, acute respiratory infections, and intestinal infections. In some cases, the cause of a late rise in temperature may be serious diseases, such as otitis media and meningitis, so do not rush to conclude that such a reaction is related to the vaccine and consult your doctor in order to exclude serious diseases.
To avoid confusion between adverse reactions to vaccination and food allergies, at least one day before and one day after vaccination, new complementary foods should not be introduced or the mother’s diet should not be changed if she is breastfeeding.
In addition to normal ones, severe adverse reactions may occur, the frequency of which must be recorded and monitored by regulatory organizations in order to prevent low-quality batches of vaccines from entering practice. If certain values are exceeded (to exclude cases of individual reactions of individual children), specific series of vaccines may be withdrawn from circulation or recalled by the manufacturer.
Severe adverse reactions include:
- Prolonged unusual crying, when a few hours after vaccination the child begins to cry loudly, and the crying is more like a squeal. The cause of this reaction is pain at the injection site and, presumably, a headache. The frequency of such a reaction is 1 in 200 vaccinations.
- Increased body temperature (measured in the axillary region) over 39°C.
- Significant swelling at the site of vaccine administration, covering an area greater than 8 cm in diameter.
Such reactions can (and should) be avoided through the prophylactic administration of antipyretics (in preparation for vaccination), which have, among other things, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
The effect of the vaccine on the children's nervous system
Often after vaccination, a baby develops high-pitched scream syndrome. This complication is diagnosed in children under six months of age.
The main symptom of such an undesirable condition is obvious: the child screams at high pitches, and this continues for quite a long time.
This is due to complex and painful processes that occur in the brain.
In this case, visiting a specialist is mandatory.
What should you do if your child is capricious after the DPT vaccination and cries a lot all day?
After vaccination, the child's mood may change. He becomes irritable, constantly capricious, and cries. As a rule, babies cry and cry immediately after the vaccine in question is administered.
Usually they calm down immediately after contact with their mother, but often the crying drags on for several long hours. This may occur in one case in a thousand children. During such a hysteria, the child takes frequent and deep breaths. Because of this, brain hypoxia may develop. This becomes the main cause of unbearable headaches.
Parents should be alerted to the child's incessant crying. Especially if it lasts for three or more hours. In this state, the baby’s body quickly evaporates moisture, which can lead to dehydration. In this situation, it is necessary to do everything possible to ensure that the child calms down as soon as possible.
To stop the baby from crying, you need to give him warm water. Babies may cry little by little, but very often. This is a common reaction following complications and a painful lump at the injection site.
As a rule, tears appear in the child’s eyes every time he feels severe pain in the lump. This is a completely understandable reaction, with the help of which the baby shows others his condition.
If the crying does not stop for a second, then this is considered a serious cause for concern.
hepatitis B vaccination and the horrors of tonight
I probably should have. no one warned
serious story, but the doctor said that the vaccine does not give a reaction. Is it worth doing it at all?
there is so much hepatitis around now
but we haven’t done any more vaccinations yet, medical advice
or an ambulance if you have a fever
How did you calm your daughter down after the vaccination?
Small ! What a pity! Good health to you!
It seems to me that it’s dangerous to give a free vaccine at all. It is unknown what consequences there will be later. I bought a barrier reef for now and I smear my nose with Viferon so that the viruses cling to it. But I can’t decide to get vaccinated, even if it kills me.
Mom won't miss
Our pregnancy calendar reveals to you the features of all stages of pregnancy - an extremely important, exciting and new period of your life. . We will tell you what will happen to your future baby and you in each of the forty weeks
We will tell you what will happen to your future baby and you in each of the forty weeks.
If the child is lethargic and turns his head after vaccination
After vaccination, the child often appears lethargic. This is a normal reaction to the vaccine and will go away on its own.
The baby can turn his head, which is also one of the body’s reactions to the administration of the drug in question. All alarming symptoms should disappear after five days.
If this does not happen, then you need to visit a pediatrician. You also need to ensure that there are no complications after the vaccine is administered.
They are often severe and completely unpredictable.
Child after vaccination Frequently asked questions
The principle of developing immunity to infections after vaccination
Vaccinations for children after one year - calendar
1.
12 months
– vaccinations against measles, rubella and mumps. The fourth vaccination is against hepatitis B, if it is carried out according to the scheme 0 - 1 - 2 - 12 (the first vaccine in the maternity hospital, the second at 1 month, the third at 2 months, the fourth at 12 months).
2.
1.5 years
– repeated administration of the DPT vaccine (against whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus) and repeated vaccinations against polio and Haemophilus influenzae.
3.
20 months
– third polio vaccine.
4.
6 years
- second vaccination against measles, rubella and mumps.
5.
6–7 years
– repeated vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus (DT).
7.
14 years old
- third vaccination against diphtheria, tetanus, polio and tuberculosis.
How to behave immediately after the injection?
Child's behavior after vaccination
In addition, vaccination is a little stressful for most children who do not like injections. Therefore, the child’s behavior may change after the procedure. The most common behavioral reactions observed in children are:
- the child is capricious;
- prolonged crying or screaming;
- anxiety;
- lack of sleep;
- refusal of food.
The child is capricious.
This is a completely natural reaction in response to illness and stress from the injection. In addition, if a child experiences mild unpleasant symptoms, he does not understand what is happening, where it is coming from - so he is capricious.
Temperature increase
Skin rash
Diarrhea after vaccination
1.
The vaccine contains microbes that can affect the intestinal mucosa. If before the injection the child had any digestive problems (for example, bloating, colic or constipation), then the intestines are weakened, and the vaccine may well cause diarrhea.
2.
The parents fed the child too much, against his wishes, or with foods that caused indigestion.
Child's cough after vaccination
Runny nose after vaccination
Is it possible to bathe a child after vaccination?
How to bathe?
A lump or lump in a child after vaccination
The child is limping
The child fell ill after vaccination
2.
Severe allergies and suffocation after diphtheria vaccination. The child was vaccinated due to diathesis; in addition, direct relatives (mother and grandmother) are allergic. In this regard, the instructions give instructions to vaccinate six months after the disappearance of signs of diathesis on the skin. As a result, in this situation, untimely vaccination led to increased allergic inflammation.
Rubella in children after vaccination
Is a child contagious after vaccination?
- pregnant women;
- patients with neoplasms;
- people who have suffered a serious illness and are in a period of rehabilitation;
- patients after major surgery;
- patients with HIV/AIDS.
What to give a child after vaccination - how to help him?
Possible complications of vaccination
According to research, the development of complications after vaccinations is due to the following factors:
1.
Storing vaccines in inappropriate conditions (freezing, heating, etc.).
2.
Incorrect administration of the drug (intramuscular administration of vaccines, which should only be subcutaneous).
3.
Failure to comply with vaccination rules (active failure to clarify contraindications).
4.
Individual characteristics (severe allergies when the vaccine is administered for the second and third time).
5.
The presence of an infectious process against which the vaccine was administered.
Author: Nasedkina A.K.
Specialist in research of biomedical problems.
Video on the topic
Dr. Komarovsky about what to do after vaccination:
For every mother, the health of her own child is the most important thing in the world. Therefore, whether to vaccinate or not is up to each parent. He needs to remember that the introduction of vaccines is necessary so that the baby’s body learns to cope with serious infectious diseases.
If four or five days after the injection the child’s condition does not improve, an urgent visit to the pediatrician’s office is necessary. If your temperature rises and antipyretics do not work, you should urgently call an ambulance. Otherwise, there is a threat to the child's life.