Why do spots appear on the tongue of a baby or teenager?
White, pink or other plaque or spots on a child’s tongue should be a reason for an urgent visit to pediatric dentistry. Such signs may indicate:
- about the onset of the development of dangerous childhood diseases, when the success of treatment directly depends on the timeliness of diagnosis;
- about general problems in the baby’s body, which will require correction of metabolic processes and concomitant treatment;
- about a banal allergy to food, synthetic clothing or toys, in which it is enough to take care of strengthening the immune system and removing the allergen.
All the reasons why spots may appear on a child’s tongue are divided into three groups:
- hygienic – insufficient or improper oral care;
- somatic – diseases of infectious/non-infectious nature;
- external – burns, mechanical damage.
Types of rashes vary in structure, color and location. In infants, young children, middle age and adolescents, the following shades and shapes of spots are common: white, yellow, red, dark, bald, complex in shape.
To understand why the tongue becomes spotted, you need to take a closer look at the plaque covering it. Usually it precedes spots that form as a result of a violation of its structure or after the plaque “peels off.” The film on the tongue of an infant or older child can be of the following shades:
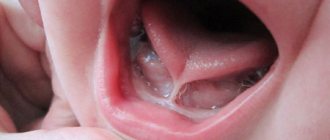
- Thrush Thin white coating. Often observed in newborns and children in the first year of life. Appears in the morning, structurally it is a thin, transparent film of whitish color. It is enough to remove the deposits with a damp gauze swab so that they no longer appear during the day. This plaque is an allergic reaction of the baby to an artificial formula or to products that make up the mother’s diet (during breastfeeding).
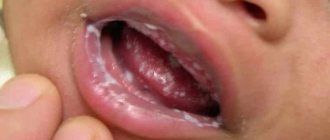
- Curdled white coating. A dense film of rich white color with hidden ulcers, foul-smelling and difficult to remove - a symptom of thrush (candidiasis) or stomatitis. In infants with such diseases, instead of a solid plaque, white spots of very impressive size often form.
- Yellow plaque. Formed when there is a malfunction of the child’s liver, kidneys or bile ducts.
- Fungal infection of the tongue Gray coating. The initial sign of dangerous childhood diseases - scarlet fever and diphtheria. Sometimes this appearance of the taste organ indicates severe dehydration. In both cases, you need to start treating the root cause of the symptom as soon as possible, since such diseases are dangerous not only for the health, but also for the life of the baby.
- Plaque in the form of green spots. The manifestation indicates a fungal infection in the oral cavity of a small patient. Usually the rash spreads to the palate, cheeks, and mucous membranes of the lips.
- Brown deposits. The result of a malfunction of the digestive system, accompanied by stagnation of bile in the bile ducts. In infants, the symptom often signals dehydration; in older children, it indicates a deficiency or malabsorption of B vitamins. In addition, if brown spots appear on the baby’s tongue, an allergy to herbs can be suspected, even if the nursing mother takes them.
- Black deposits. They are a consequence of taking certain antibiotics, overdose or the body’s rejection of the drug. Sometimes the reasons for the appearance of black plaque lie in intestinal disorders: colitis, enteritis and gastritis.
Causes of white spots on a child's tongue
The appearance of white spots on a child’s tongue is difficult to miss: they clearly stand out against the background of pink soft tissues.
The main reasons for their appearance may be:
- Thrush . The main culprits of its occurrence are yeast-like fungi (candida), which are found in the body of every person. With strong immunity, they are inactive, but as soon as it begins to decline, they immediately develop rapidly. That is why infants and infants are especially susceptible to thrush, since their body (and immunity in particular) is just beginning to adapt to new environmental conditions. Symptoms of this disease manifest themselves in the form of a white, cheesy coating that first forms on the tongue, gradually spreading throughout the entire oral cavity (including the inner surface of the cheeks).
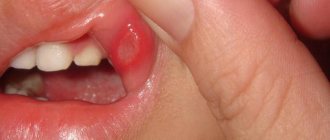
- Stomatitis. This is an inflammation of the oral mucosa, in which whitish spots form on it, which can cause both discomfort and severe pain.
- Leukoplakia. The root cause of this disease is microtrauma of the mucous membrane (cuts, bites, burns), which are accompanied by infection. In this case, white spots form precisely on the damaged areas and if left untreated, the tissues can become keratinized.
On the tip
Spots on the tip of the tongue often indicate problems in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. In this case, along with visiting a pediatrician, you should consult a cardiologist.
On the root
White spots at the root of the tongue indicate dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract:
- colon (spots at the base of the tongue);
- duodenum (spots on the middle part of the tongue);
- dysbacteriosis or gastritis (the whole tongue is whitish).
The appearance of spots on the root of the tongue is a reason to consult a gastroenterologist as soon as possible. This will identify a probable disease and prevent complications of the condition in the future.
Side
If white spots are localized on the side (or sides) of the tongue, you need to look for the cause in the liver and gallbladder.
In addition, similar symptoms can occur in children with malocclusion and those who wear braces (due to incorrect installation). In such a situation, you should immediately contact your dentist or specialist who installed the braces.
Does the nature of plaque depend on the type of feeding?
There really is a relationship between breastfeeding and plaque on the tongue. Due to poorly developed salivary glands, the baby's mouth does not clean so well after eating. However, the layer on the surface of the uvula after feeding is uniform, slightly transparent, and the papillae are visible on the organ. Such plaque does not need to be treated, nor is it recommended to remove it, since it does not harm the baby, and mechanical cleansing can cause injury to the mucous membrane and the development of infection.
Such plaque is more common not on artificial feeding, but on breastfeeding. In babies who frequently suckle at the breast, plaque may be constantly present; in artificial babies, as a rule, it disappears within half an hour after feeding. The distinctive signs of “safe” plaque and candidiasis are presented in the table.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Caseous plugs in the throat (on the lacunae of the tonsils): causes and treatment
| Plaque after feeding | Plaque caused by Candida fungi (for more details, see the article: instructions for using the Candida oral solution for newborns) |
| Mainly present on the tongue, also on the gums and palate | White spots on the tongue, palate, gums, and on the cheek mucosa |
| Disappears after the baby drinks | It is difficult to clean with a cotton swab, the child is restless |
| The layer evenly covers the tongue | At first it appears as specks or dots, later it evenly covers the mucous membrane |
| Translucent, easy to clean | Dense, mucous membrane covered with bright red color |
Types of stains with explanations
In case of untimely treatment of a particular disease or if the causes of the disorder in a child are unclear, formations in the tongue may have the following character:
- A plaque of uneven structure may indicate the bacterial origin of the disease, the accumulation of food particles under the epithelium and waste products of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Epithelial proliferation often occurs with burns, scratches, cuts and other organ damage. In this case, a bald round spot may first appear, and later a compaction of overgrown tissue forms in its place.
- A bald spot or many spots often occurs when an allergic reaction develops.
- Sometimes various benign or malignant formations are found in the oral cavity.
From the above information it is clear that various formations on the oral mucosa can indicate both harmless conditions and severe pathologies.
In this regard, if alarming symptoms are detected, especially in young infants, you should immediately make an appointment with a specialist.
We suggest you read: How to help a baby with teething
Signs of herpes
Dr. Komarovsky believes that spots on a child’s tongue rarely appear due to herpes. The manifestation of this virus is the lot of adult patients, but if symptoms appear in a newborn, parents need to work on raising his immunity.
Symptoms:
- raised red spots appear on the sides and at the tip of the muscular organ;
- the infection can only affect one side;
- Contrary to popular belief, itching does not always occur.
Dr. Komarovsky does not rule out that viral spots may appear on the tongue of an infant or newborn in the first year of life. But this is only possible in two cases - the baby has already had this disease, or the child’s mother suffered an infection during pregnancy.
Dark spots may appear in a child's mouth after eating food that is colored. Such spots and circles are easily removed after several hygiene procedures. However, there are reasons not related to coloring food, here are some of them:
- As a result of long-term antibiotic therapy, the microflora in the mouth was disrupted: the active growth of foreign fungi and bacteria began. The dots and circles will be almost black in color, blackening will be observed for 2-3 weeks.
- Very rarely, the cause of this symptom is systemic dystrophic disorders, accompanied by the death of areas of the mucosa.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
The famous pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky claims that hygiene takes a special place both in the treatment process and in the prevention of diseases associated with the oral mucosa and tongue.
This is why it is necessary:
- allocate separate dishes, towels, napkins for the baby;
- thoroughly wash and sterilize the baby’s dishes, pacifiers and bottles;
- During treatment, stop kissing on the lips and bathing together.
For artificially fed children, it would be useful to add probiotics to the adapted mixture, which will improve digestive processes and minimize the possibility of thrush and stomatitis.
As for infants, they receive their portion of all nutrients from their mother’s milk. At the same time, it is important that a nursing woman takes a shower (bath) every day and refuses synthetic underwear and clothing, giving preference to natural fabrics.
Another important point in the process of treatment and prevention of oral diseases is the activation and restoration of the bactericidal and protective functions of saliva.
To do this, parents need:
- thoroughly clean the baby’s nose and make sure that his breathing is easy and nothing interferes with him;
- do not allow the mouth to dry out (due to prolonged screaming or crying);
- regularly carry out wet cleaning;
- maintain normal temperature in the room (20-22 degrees).
Since the appearance of white spots on a child’s tongue can have different reasons, to clarify them and make a correct diagnosis, you must immediately consult a doctor. This will allow you to begin treatment as soon as possible and prevent a deterioration in the baby’s general condition. Along with the use of cleaning solutions and medications, maintaining hygiene conditions and maintaining optimal temperature and humidity in the room where the child is located is of great importance.
On the root
The presence of red spots or dots on the underside of the organ can be caused by the following reasons:
- allergy;
- throat infections;
- herpes;
- injuries;
- Kawasaki disease;
- syphilis;
- scarlet fever;
- leukopathy;
- throat cancer and others.
We invite you to read: Yellow coating on the tongue in adults: causes and treatment, what does yellowness on the tongue mean?
To identify the provocateur of spots on the lower part of the tongue and on its root, it is necessary to analyze other manifestations that the child has, for example, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, elevated body temperature. The shape, appearance and size of the spots also matter.
Red dots and spots on the side of the organ are not specific signs of any pathological condition. Such manifestations can be caused by most pathologies, as well as being a consequence of injuries after dental procedures, or be the result of a child accidentally biting his tongue while eating.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with what the doctor’s recommendations say: is it possible to take painkillers after tooth extraction?
What can white spots indicate?
The reasons for these changes can be very different. Scientists all over the world are studying this issue, since the tongue is a multifunctional organ, and any changes in the structure of its tissues may indicate a more serious pathology on the part of other organs and systems.
The appearance of spots on the tongue can be caused by:
- disruption of digestive processes;
- tongue injuries;
- fungal infection;
- allergic reaction;
- infectious disease (for example, scarlet fever, herpes infection);
- malignant and benign neoplasms in the digestive organs;
- venereal disease (for example, syphilis), etc.
As you know from human anatomy lessons, the tongue is an unpaired outgrowth at the bottom of the oral cavity. This organ takes part in the act of chewing, the formation of sounds and speech, the perception of taste and salivation.
A feature of the mucous membrane of this organ is the tight fusion of the lingual fascia and intermuscular connective tissue. Another feature is the absence of a submucosal layer. Thanks to these factors, the mucous membrane remains motionless and is not prone to folding. From the outside, the mucosa is covered by stratified squamous epithelium. This membrane contains glands, taste buds and lymphoid formations.
At the tip, back, root, and edges of the tongue, its surface is rough. The lower surface of the marginal sulcus appears smoother, while its anterior part is thicker, with various nodular elevations of lymphatic follicles. The frenulum of the tongue is formed from the mucous membrane along the midline, and on the sides of it fringed folds are formed that converge forward.
In the posterior part of this organ, this membrane creates three folds (one unpaired - median, and two paired - lateral), directed towards the epiglottis (they were called lingual-epiglottic folds). Each of them borders on the supraglottic recesses.
The upper surface and anterior part of the edges of the tongue from the border sulcus are covered with the papillae of the tongue. On the body of this organ, papillae are formed from the epithelium and mucous plate. There are several types of them: filamentous, mushroom-shaped, groove-shaped, cone-shaped, leaf-shaped. Each of them differs from each other in location, structure, function, quantity.
The appearance of a different color of the tongue can occur due to a particular disease associated with the pathology of one or more organs. But in order to determine where exactly the “failure occurs”, it is important to know the location of the spots. And only after this can one judge the localization of the disease.
A change in the color of the mucous membrane of this organ occurs due to its coating with plaque, and the severity of the pathology often depends on the degree of its severity.
| Tongue coloring | Reasons for its appearance |
| Red | Infectious diseases, high hyperthermia |
| Dark red | Kidney failure, infectious diseases |
| Raspberry (strawberry) | Scarlet fever, B12 – deficiency anemia |
| Very pale | Anorexia, anemia |
| Yellowish | Impaired liver function, excess bile in the gallbladder |
| Blue | Diseases of the cardiovascular system, heart rhythm disturbances |
| Dark purple | Blood clotting disorder, coronary heart disease, chronic heart failure |
| Black | Hypovolemia (with dehydration), severe functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, cholera, long-term antibacterial therapy |
| Green | Stagnation of bile |
| Brown | Kidney diseases |
| Blue | Dysentery, typhoid fever |
The appearance of this symptom may indicate the presence of an infectious or non-infectious process in the baby. Examples of non-infectious diseases are: gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, appendicitis, cholecystitis, B12-deficiency anemia, heart failure, etc. Examples of infectious diseases are scarlet fever, measles, food poisoning, dysentery, typhoid fever, etc.
Most excited mothers immediately begin to panic when they discover a white coating on their baby’s tongue. However, not in all cases such a phenomenon signals a serious illness. So, for example, it can appear in a baby during breastfeeding. In addition, traces of the nutritional mixture often remain on the tongue even during artificial feeding.
This is what a “coated” tongue looks like
. So, what can a “coated” tongue in a baby indicate? This symptom most often indicates the following problems:
- viral stomatitis: often becomes a complication of chickenpox, measles and scarlet fever, as well as infectious diseases,
- dysbacteriosis: the entire surface of the tongue is covered with a dense coating,
- thrush: curdled discharge appears, characteristic lumps can be seen,
- problems with the intestines and stomach,
- manifestation of neuroses,
- lack of vitamins and microelements, anemia, weak immune defense,
- diabetes,
- poor oral hygiene,
- allergies to medications, in particular to some types of antibiotics.
Stomatitis is common in infants.
The tongue may become noticeably white if the child has a sore throat. There is no need to worry, since the symptom will disappear on its own as soon as the baby gets better. In addition, the baby may simply burp, causing food residues to appear in the oral cavity. Another fairly common reason is the rapid eruption of the first teeth.
Other factors for the appearance of whiteheads
- What you eat? A white coating on the tongue remains when consuming dairy and curd products and cheese. Sweets promote the growth of bacteria and fungi, resulting in a white coating. You can easily get rid of such plaque.
- Improper oral care. Not everyone knows that the tongue, just like teeth, needs daily cleaning. The papillae of the tongue accumulate microscopic food debris, resulting in the formation of bacteria and an unpleasant odor. White spots may appear due to certain toothpastes and rinses that are unsuitable for a person.
- Poisoning. In case of poisoning, the mucous membrane may be susceptible to the appearance of erosions and ulcers. I am concerned about the general condition of the body.
- Bad habits. Due to exposure to tobacco products, the mucous membrane is exposed to a number of chemical factors and elevated temperatures. Alcohol abuse dehydrates the body, resulting in a constant feeling of dryness in the mouth. Naturally, the mucous membrane becomes covered with plaque. So don’t be surprised that after a “fun night” your tongue turns white.
Causes of plaque
In normal condition, the surface of the tongue of a healthy child should be pink. The formation of a thin white or grayish coating, through which the papillae and the natural color of the tongue are visible, is also considered normal. This type of plaque usually appears in the morning, is easily removed with a toothbrush and does not have an unpleasant odor.
In summer it thickens slightly, acquires a yellowish tint, and in winter it becomes thin and white. If such a phenomenon occurs in hot weather due to extreme thirst, then to eliminate it it is enough to drink a sufficient amount of water.
In infants, a white coating on the tongue after feeding most likely means milk residues that can be easily removed. Other safe reasons for a white-yellow coating on a child’s tongue include:
- Consumption of certain foods: carrots, persimmons, strong tea and coffee, drinks with orange dyes.
- Taking certain medications: Furazolidone, sore throat lozenges, vitamins, antibiotics.
- Incorrectly selected milk formula.
- Overeating fatty, fried foods.
This plaque has a dense texture, is difficult to remove and is accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the mouth. The reasons for this phenomenon can be very diverse.
Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity
Inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa, which are commonly called stomatitis, are one of the common causes of the tongue covering with a whitish coating with grains. Depending on the type of stomatitis, symptoms may occur:
- round white sores on the oral mucosa;
- burning, pain, dry mouth;
- loss of appetite;
- bad breath;
- increased salivation;
- lethargy, weakness.
Sometimes there may be an increase in body temperature, swelling of the tongue, gums or cheeks. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Fungal diseases and dental caries
There are various microorganisms in the human mouth that do not cause harm. But in the presence of predisposing factors, fungi begin to actively multiply. Children are diagnosed with candidiasis, an oral disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida. A sign of this pathology is a white cheesy coating on the tongue.
Symptoms may occur:
- discomfort, pain during feeding;
- loss of appetite;
- redness of the oral mucosa;
- itching, burning;
- plaque formation in the mouth;
- dry mouth.
A white tongue in a child means an advanced form of caries, which is an infectious focus. Proper oral care can prevent the progression of pathology.
Pathologies of the body's respiratory systems
The white surface of the tongue sometimes indicates the presence of pathological changes in the respiratory system of the body that are viral or bacterial in nature. If the cause is influenza or acute respiratory infections, the following symptoms are observed:
- redness of the throat;
- cough;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness;
- runny nose.
If the tonsils are covered with a white coating, then a sore throat is diagnosed, and a change in the front part of the tongue may indicate bronchitis. As the disease progresses, the plaque becomes foamy, thickens, and acquires a darker color. Tonsillitis is characterized by inflammation of the tonsils and is manifested by whitish covering of the tonsils, pain when swallowing and hyperthermia of the body. With pharyngitis, a dense, bumpy whitish coating, redness and looseness of the throat may be observed.
Infectious diseases
If the white coating on the surface of the tongue is infectious in nature, then it is quite difficult not to notice, since the pathology usually has severe symptoms in the form of high fever and signs of intoxication. This manifestation is characteristic of scarlet fever and diphtheria. With scarlet fever, the tongue becomes covered with a white film with small red spots, symptoms are observed:
- rash on the body;
- lymphadenitis;
- throat hyperemia;
- change in color of the tongue and tonsils to white-yellow;
- severe intoxication.
Other causes of plaque on the tongue
The formation of a white or yellow coating on the surface of a child’s tongue may indicate the presence of pathological conditions:
- allergic reaction;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- metabolic disease;
- pathologies of the kidneys, liver, lungs;
- frequent constipation;
- dehydration of the body;
- helminthic infections;
- food poisoning;
- autoimmune diseases.
The reason is a weakening of the immune system, which can result in colds and infectious diseases. As you can see, the causes of plaque on a child’s tongue can be very diverse. To make an accurate diagnosis, you must contact a medical facility.
Associated symptoms
There are no general clinical signs, since this is a symptom of a nonspecific nature. Symptoms will depend on the underlying cause.
A white spot on the tongue may be caused by stomatitis, which is characterized by the following clinical picture:
- spots on the tongue become covered with a white coating;
- formation of ulcers;
- feeling of discomfort and pain while eating and drinking;
- formation of spots on the gums and oral mucosa;
- increased salivation.
It should be noted that some cardiovascular pathologies can be asymptomatic for a long time and white spots at the end of the tongue will be the only sign of the development of the disease.
With the clinical manifestations described above, you should seek medical help and not self-medicate. Otherwise, serious complications may develop. Only a doctor can determine the exact etiology after an appropriate examination.
Geographical language in children
This interesting term refers to a special type of spots on the mucous membrane of the tongue - red, uneven silhouettes framed at the edges by a white coating, constantly changing and not causing any sensations. The spots take on round, oval and other unexpected shapes. There is no inflammatory process. If a geographic picture is present, a diagnosis of desquamative glossitis is made, but do not be alarmed by this.
Indeed, it was once believed that such symptoms appear together with worm parasites and are associated with hormonal imbalances and digestive disorders. Many authoritative experts on childhood diseases claim that geographic spots on the mucous membrane of the tongue are an independent and absolutely harmless phenomenon that does not require treatment.
- treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic agents;
- taking vitamin complexes;
- the use of drugs that promote natural acceleration of tissue regeneration.
white, yellow and red spots on a child’s tongue may be a symptom of the disease
A variety of spots on a child’s tongue
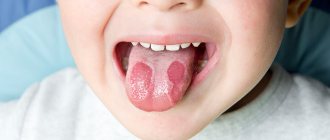
Spots on a baby's tongue can be very diverse: red, white, geographical, yellow, dark and bald.
Red spots on the tongue
Red spots on a child's tongue are, in most cases, painful. When they appear, children eat poorly and are capricious. High hyperthermia may occur. Since they are almost always based on infectious diseases.
The appearance of spots of this color can be due to herpes, glossitis, stomatitis, bacterial dermatosis, allergic reaction, scarlet fever, syphilis, etc.
A red spot on your baby’s tongue can also appear as a result of an allergic reaction; it often appears on the tip. If this type of change occurs, it is recommended to consult not only a pediatrician, but also an allergist.
White spots
Most often, this type of spots appears in infancy. Their occurrence is due to the weakening of the baby’s immunity or infection from the mother (during labor or pregnancy). At this age, they have a second name - thrush (it is characterized by the fact that spots form on the mucous membrane of the tongue, which have different shapes and sizes, and above them there is a plaque that has a cheesy consistency).
In adulthood, such spots can appear in people with a weakened immune system in the form of a secondary infection (during chemotherapy, anorexia, severe anemia, AIDS, etc.).
Geographic spots
Spots appear on the mucous membrane of the tongue that are red in color and framed by a white or yellow coating. They tend to change shape and location. These changes are painless and not dangerous. Most often, their appearance is associated with chronic diseases of the digestive system, allergic diseases, helminthic infestation, hormonal changes, and in some cases with mental disorders.
Yellow spots
They can cover the entire tongue or be located at its tip. Their appearance most often indicates a disease of the digestive system. Often this symptom can be combined with the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the baby’s mouth.
This type of change cannot be treated on its own, and parents should consult a doctor for further examination and prescribing the necessary therapy.
Dark spots
Their appearance may be associated with food (currants, blueberries, blackberries can stain the mucous membrane of the tongue), but there are also more significant reasons for their appearance.
The appearance of black spots on the tongue of a baby may be due to helminthic infestation and bacterial infection treated for a long time with antibacterial drugs. With properly prescribed therapy, they disappear on their own and without a trace.
The appearance of blue spots is most often associated with problems in the cardiovascular system (congenital and acquired heart defects, vascular tumor, etc.).
Bald spots
This type of change in the tongue can be a consequence of injury, glossitis or burn. When examining the baby’s oral cavity, “bald” areas are noticeable, asymmetrical in shape and unevenly pink in color. It should be noted that they do not require special treatment, as they disappear on their own.
Etiology
The appearance of white spots on the tongue of a child or adult may be due to the following etiological factors:
- stomatitis;
- gastroenterological diseases;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes in the body;
- fungal infection;
- HIV;
- dehydration of the body;
- allergic reactions to certain foods or medications;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- consequences of long-term medication use;
- poor oral hygiene.
In children, the formation of white spots on the tongue may be due to improper introduction of complementary foods, inappropriate formula, or an infectious or fungal disease.
It should also be noted that the manifestation of such a symptom is more likely when a person has a weakened immune system.
Symptoms and clinical picture
The disease has pronounced symptoms:
- burning and itching. The tongue itches and there is a tingling sensation. This is especially felt during meals;
- the appearance of unusual patterns in the language that really look like a map. Drawings can be bright or faint;
- bright red spots on the tongue. May be of different sizes. The spots are smooth to the touch;
- the tongue increases slightly in size. Swelling is observed;
- discomfort while speaking. The person feels pain and tingling. He has difficulty pronouncing words;
- weakness. The person becomes lethargic and drowsy.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to wear dental trainers
If the disease is in the later stages, the child's condition will worsen. He will become lethargic, his appetite will disappear, and the burning and tingling sensation of his tongue will intensify.
When should you start worrying?
The following symptoms will be a cause for concern:
- thick, uneven plaque distributed on the inner surface of the cheeks and gums;
- bright spots in the mouth surrounded by whitish or yellowish flakes;
- an inflamed or swollen organ;
- dry mouth appears;
- burning and itching appears;
- papillae increase in size;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
If such symptoms appear, you should consult a pediatrician to determine the cause and receive further recommendations.
The spread of a white or yellowish film over the surface of the tongue may mean:
- over the entire area of the organ – gastrointestinal diseases, gastritis or dysbacteriosis;
- red tip and coated middle - increased stomach acidity;
- a stripe in the middle of the tongue - troubles with the duodenum;
- back part – malfunctions of the large intestine;
- the front and sides are diseases of the respiratory system.
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis after an in-person examination of a small patient.
What does Komarovsky advise?
Well-known pediatrician Evgeny Olegovich Komarovsky recommends following these steps if a problem arises:
Under no circumstances should you ignore the appearance of rashes or plaque on the tongue and let the disease take its course. This can lead to quite serious consequences.
How to get rid of white spots on your baby's tongue
Until a diagnosis is made, no manipulations should be carried out with the white spots on the child’s tongue. Self-medication (including folk remedies) in this case is unacceptable, since it is unknown how the delicate mucous membrane will react to this or that remedy.
In most cases, doctors recommend:
- Treat the affected areas (for stomatitis and thrush) with a soda solution, which allows you to create an alkaline environment in the oral cavity that is harmful to the fungus. For this purpose, one or two teaspoons of soda are dissolved in a glass of warm water. Having thoroughly washed his hands, an adult wraps a sterile bandage (gauze) around his finger, dips it into the solution and slowly, delicately, avoiding strong pressure, wipes the areas with white spots, repeating the procedure about six times a day.
- Lubricate white spots with a solution of methylene blue, a two percent solution of boric acid (for stomatitis).
- Use (if the child’s age allows) special antifungal drugs in the form of a gel, cream, solution, tablets or suspensions.
- Eliminate sour fruits, carbonated drinks, hard, hard, hot and cold foods, pickles, spices, and sweets from the child’s diet.
- If the temperature rises, take antipyretic drugs and drink a sufficient amount of fluid (preferably clean, still water).
To relieve inflammation and soothe the mucous membrane, you can use sea buckthorn oil or herbal decoctions: chamomile, sage, calendula. But this should only be done with the permission of a doctor.
Green plaque
A spotted tongue in a child of early age or after 2, 3, 4 years can be explained by the presence of a fungal infection. In this case, rashes and spots can appear on various parts of the organ, on the tip, side, middle and even on the palate. As a rule, the plaque has a greenish or yellow tint.
The causes of this disease include the following provoking factors:
- Infection of the baby during childbirth.
- Use of antibacterial drugs.
- Frequent regurgitation after feeding.
- Failure to comply with the rules of oral hygiene in infants.
- Insufficient cleaning of pacifiers, dishes or toys that the toddler puts in his mouth.
- Various diseases of the digestive system, most often dysbiosis.
Treatment should be aimed at maintaining oral hygiene and using antifungal agents.
What does Komarovsky say?
Recommendations from pediatrician E.O. Komarovsky - do not panic and monitor the baby’s well-being. If the baby eats with appetite, does not show signs of anxiety, and the plaque is washed off with water, there is no need to wipe the tongue or treat the child with medication.
Another thing is when he cries, cannot suckle due to pain, and the plaque has a thick, cheesy consistency. In this case, it is necessary to examine the pediatrician and follow all his recommendations. If candidiasis is diagnosed, Komarovsky advises not to use a soda solution to treat the tongue and mucous membranes, but to use ready-made pharmaceutical products that are specially designed for this and have a more pleasant taste.
Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist, graduated from Samara State Medical University with a degree in Pediatrics.
If whiteheads hurt
The tongue is an indicator of health. Everyone should remember this. This organ should be examined regularly. At the first problem, you need to contact your dentist.
Its structure is such that it has many small spots, but they are invisible. If white spots on the tongue of an adult or child cause severe irritation, such a symptom cannot be ignored.
This may indicate health problems.
An adult often remembers this organ when it hurts, when discomfort, burning or unpleasant sensations begin, including ulcers and cracks.