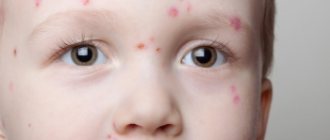
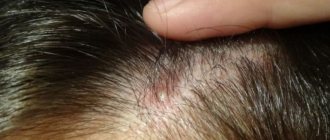
Gneiss represents elements of a scaly rash in atopic and seborrheic dermatitis. If gneiss occurs, you should be wary of the development of such skin diseases. Accompanied by severe itching, dense crusts of a yellowish tint. Appears on the scalp. Most often found in infants. It is important to treat the skin in a timely manner, since the baby himself can remove the scales and injure the epithelium.
Gneiss in children - what is it in medicine, what is its localization?
Gneiss - in medicine, this means the formation of crusts on the scalp.
Each scale is dense and dark yellow in color. Accompanied by severe itching. Such elements appear in a child from the first days of life. Periodically affects the scalp. This process can last up to 3 years of age. It is important to understand that gneiss does not pose any threat to the health and life of the baby. An infant does not experience any discomfort from the presence of such scales. Despite this, pediatricians recommend not to ignore gneiss and consult a doctor. The presence of such crusts indicates a predisposition to allergic reactions. Localization of scales exclusively on the scalp.
How to remove yellow (milky, seborrheic) crusts on a child’s head? Seborrheic dermatitis in children.
What it is?
Dark brown or yellow crusts appear under the hair of most babies. Doctors call this seborrheic dermatitis and consider the condition not dangerous for the baby. There is still debate about the reasons for the development. It is well established that the following factors provoke the appearance of gneiss:
Normally, the condition stabilizes on its own as the baby grows and develops. If gneiss persists for a long time or occurs repeatedly, the possibility of a hidden allergy is suspected.
Causes of the disease in a newborn and young child
Gneiss occurs very often in newborns. Parents begin to worry and do not understand what caused the crusts. Gneiss is not a disease, but a temporary pathology. There is no specific cause for the occurrence of scales. There are predisposing factors that cause this pathology. The main ones include:
- unformed digestive system;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract during pregnancy;
- avitaminosis;
- consumption of a large number of allergens during pregnancy;
- taking medications;
- dysfunction of the sebaceous and sweat glands in the baby.
If the expectant mother does not adhere to a healthy diet, then the child has an increased risk of encountering allergies from the first days of life. Almost always, the health of the unborn baby depends on the mother.
Causes
There is an opinion that the baby's scabs appear due to breastfeeding, and when the mother stops breastfeeding, they disappear. That is why such crusts are called milk crusts. But this is a myth. There is no connection between gneiss and breastfeeding.
Seborrheic crusts are called not because they indicate a disease, but because the forming scales are similar in appearance to those that form with seborrheic dermatitis.
The main cause of gneiss is hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands. In a baby, many organs and systems operate in “tuning” mode. Firstly, the hormonal background fails, which changes somewhat after birth. Secondly, the sweat and sebaceous glands have not yet learned to cope with their tasks, so scales form on the head as a result of excess sebum secretion. There are other factors that can aggravate this condition.
Seborrheic dermatitis, scrofulosis or scrofula - differences
| Name of the disease | Description |
| Seborrheic dermatitis | The causative agent is a pathogenic microorganism that lives on the epithelium of every person. Affects the skin in the area of the sebaceous glands. Most often it appears on the scalp, behind the ears, in the area of the nasolabial triangle. Accompanied by severe inflammation, itching, peeling of the skin |
| Scrofula | Manifestation of tuberculosis on the skin. The body's response to mycobacteria. The immune system recognizes it as an allergen in the primary form of tuberculosis of the lungs and bones. The rash can affect the skin, mucous membranes, and lymph nodes. The infection is very similar to an allergic reaction. The rash may appear in the form of scales or pustules. In addition, the lymph nodes become very inflamed. Very rare nowadays |
| Scrofula | In children, scrofula occurs more often than in adults. Initially, the skin peels off and severe itching occurs. The manifestation is minor, but increases over time. The scrofulous color of crusts is noticeable on the scalp. The disease occurs due to the presence of tuberculosis bacillus, which belongs to tuberculosis microorganisms |
A detailed description of each disease helps to determine the differences between gneiss and them. Basically, skin rashes can occur due to an infection or an allergic reaction. Gneiss is not one of them and does not pose a threat to the health and life of the baby. Its scales affect only the scalp.
Processing gneiss at home
Doctors do not advise parents to peel off the scabs with their fingers or a washcloth. It is so easy to injure delicate baby skin, and open abrasions and cracks can become infected. This procedure is painful and dangerous for the child. Instead, here are some simple tips for caring for skin affected by seborrheic dermatitis:
To process gneiss you will need oil and a comb or brush with rare, soft teeth.
Medicines for the treatment of gneiss (antibiotics and antiallergic) have a strong effect and are prescribed only in cases of infection.
Typically, regular brushing and oil treatment will eliminate the appearance of dermatitis.
The appearance of gneiss in children under 2-3 months is recognized by doctors as a normal variant. As a rule, parents can cope with the problem on their own if they do not injure the child’s delicate skin. In any case, you should consult your pediatrician before starting treatment.
Gneiss with exudative diathesis
Exudative diathesis refers to diseases that appear in newborns or infants. This causes vulnerability of the skin, mucous membranes of the throat, respiratory organs, gastrointestinal tract, and reproductive system. Signs of ECD appear in a pronounced form. The skin begins to itch, diaper rash, eczema, and milk scab occur.
Gneiss in exudative dermatitis is often its harbinger or symptom. Therefore, it is important not to ignore this manifestation and consult a doctor in time.
With this diathesis, the manifestation of gneiss is observed very often.
Brovchenko family. How and with what help to remove seborrheic crust (plaque) on the baby’s head.
Symptoms of milk eschar in infants
Basically, the baby encounters gneiss in the first month of his life. Its main symptom is the formation of scales on the scalp. After removing them with special ointments, red spots remain. If irritation of the dermis occurs, weeping elements remain. Exudate is released from them, after which it dries in the form of a yellow-brown mass. Then new scales form.
The crust itself can be dry and flaky. The baby's hair may stick together and fit tightly to the skin. Such unpleasant manifestations do not cause discomfort or pain in the baby. If parents properly care for the gneiss, it will soon disappear. Otherwise, healing may take up to 5 years.
Is treatment required for seborrheic dermatitis in children?
It is important to understand that damage by gneiss does not affect the life and development of the child. The method for eliminating scales does not require drug treatment. Doctors say that seborrheic dermatitis does not cause discomfort to babies. Therefore, this pathology does not require treatment.
Despite the safety of seborrhea, the disease cannot be ignored. At the first manifestations, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
If parents do not have experience, then it is prohibited to process the scales themselves. Improper care can lead to skin irritation and infection.
Prevention measures
Despite the prevalence of dermatitis, according to the advice of Dr. Komarovsky, it is necessary to take measures to prevent the formation of crusts:
- Avoid overheating the baby. Try to take off hats and bonnets indoors;
- When choosing fabrics for underwear, bed linen, and clothing, give preference to natural, breathable materials, preferably cotton. After washing, rinse baby clothes thoroughly and iron them on both sides;
- Take regular sun and air baths. Leave the baby naked in the sun. The duration of daily procedures is 15 minutes;
- Create a comfortable temperature regime. Recommended temperature 20 degrees. Maintain air humidity within - 70%. You can achieve the desired effect using special humidifiers and conditioners;
- Carefully select hygiene products for baby skin care.
Technique for treating the scalp in infants
Treatment of the scalp with gneiss should be carried out with extreme caution. The processing procedure is carried out using the following means:
- vegetable oil;
- sterile swab;
- napkins;
- medical gloves;
- crest.
It is important to consider that the herbal ingredient must be sterile. The doctor must explain to the mother how the skin on the baby’s head should be treated. Prepared materials must be sterile. Treatment should be carried out on a changing table that has been previously disinfected. If there is no such place, then you can use another place, the main thing is to comply with sanitary standards.
Before treating the skin, a woman should wash her hands with soap and wear medical gloves. The blotting swab should be moistened in vegetable oil. Each movement to remove gneiss should be unforced, soft and smooth. This is very important to observe so as not to lead to skin irritation and infection.
Bandages or gauze bandages are applied to the affected areas, and a cap is put on for 2 hours. Removing the crusts will be easy. Therapy should end with washing your hair. Brushing should be carried out as long as possible to remove scales.
Treatment
Gneiss does not require specific therapy using medications or other means. If there are no complaints of restless sleep, crying or other signs of itching, parents are given general recommendations:
- Correction of mother's nutrition if the child is breastfed. Potential allergens should be excluded from a nursing woman's diet.
- Compliance with thermal conditions. Avoid overly wrapping your baby, especially in summer or in hot rooms.
- Avoid washing too often, especially with shampoos or soaps that dry out the skin. Excessive dryness of the skin provokes activation of the sebaceous glands, which leads to excess sebum.
To normalize metabolic processes in the scalp, it is recommended to periodically remove gneiss flakes. The procedure is usually carried out once a week, and it is strictly forbidden to scrape off sebaceous plaques with your nails or use combs without first softening the crusts.
An hour and a half before bathing, you need to lubricate the affected areas of the skin with oil (special baby oil, burdock oil, castor oil, etc.) and put a cotton cap on the child. When washing, use shampoo or soap twice, and after drying your hair, comb out the scales with a soft natural brush or even a toothbrush. Some of the crusts usually flake off during the washing process, and the remaining ones are easily removed by combing in the direction from the forehead to the back of the head.
Removing crusts without first softening them can cause damage to the baby’s thin skin and infection of microtraumas. Therefore, trying to scrape them off “dry” with nails or combs is unacceptable. When removed correctly, the scales come off easily and without the risk of subsequent inflammation. Along with seborrheic plaques, individual hairs are often combed out, which is normal and does not cause concern to the baby.
Crust removal algorithm
Gneiss removal algorithm:
- Preparation of materials.
- The woman washes her hands with soap and puts on sterile gloves.
- Treat the surface with a disinfectant.
- Free the child from clothes.
- Put dirty clothes in the wash.
- Prepare a cotton swab and treat the affected areas with sterile vegetable oil.
- After completing the procedure, you should buy the child and wash your hair thoroughly.
It may be difficult for mom the first time, but if you repeat such manipulations often, it will be easier to remove the gneiss. The treatment process can last up to 3 years.
Getting rid of lepa
You will need a comb and brush. The comb must have blunt teeth so as not to injure delicate skin. A brush with synthetic bristles is unsuitable; you only need to choose combs with natural, soft bristles.
For children's cosmetics, you will need shampoo or gel-cream suitable for daily washing of the head and body. It is advisable to choose products without a strong odor, bright color, with plant-based detergents that do not contain soap. The list of ingredients (on the product label) should not contain dyes or preservatives, only natural ingredients: herbal extracts, oils and water emulsions.
So, having prepared everything you need, you can begin the procedures for cleaning your head from mold. An hour, or at least 20-30 minutes before bathing, you need to thoroughly lubricate the little one's head with warm baby oil (olive, vegetable, vaseline). To prevent the oil from spreading and getting into the child’s eyes, you need to wear a cap, which additionally acts as a warming compress. Under the influence of oil, the scales soften, as a result, it will be much easier to remove the plaque. Before washing your hair, you can carefully remove exfoliated scales with a cotton swab.
While bathing, a little shampoo foams in your hands and is applied to the baby’s head, after which it is carefully washed off, avoiding foam and water getting into the baby’s eyes and ears. During daily water procedures without using shampoo, areas where crusts have accumulated can be gently rubbed with a sponge, without being particularly zealous.
A few simple rules and daily care of a child’s scalp can do wonders without any medications, the help of which should be sought only on the recommendation of a doctor.