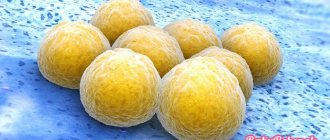
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that, unlike many prokaryotes, has a golden color, which is the causative agent of purulent-pathological processes in the human body.
Children are most susceptible to infection with Staphylococcus aureus, so today we will talk about the causes of diseases resulting from infection, symptoms and consequences of Staphylococcus aureus for children.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Staphylococcus aureus has different symptoms, which depend on the form of infection.
1. Early form of infection : symptoms appear within a few hours after activation of the harmful microorganism. It can be:
- high fever in children;
- diarrhea;
- vomit;
- loss of appetite;
- lethargy.
2. Late stage of infection : signs may appear only 3-5 days after activation of staphylococcus. Among them:
- skin lesions;
- blood poisoning;
- damage to internal organs.
Often, Staphylococcus aureus in a child does not manifest itself at all, being asymptomatic. Therefore, only certain tests can confirm the diagnosis.
Signs and symptoms. How is the analysis performed?
There are many signs of Staphylococcus aureus in newborns and preschool children. These are:
- Ritter's disease (scalded skin syndrome). In this case, a rash or area of inflamed skin with clear boundaries appears on the skin.
- Staphylococcal pneumonia. Pneumonia caused by staphylococcal infection is much more severe than in other cases. There is severe shortness of breath, pronounced intoxication, and chest pain.
- Cellulitis and abscesses. Deep lesions of the subcutaneous tissue followed by purulent melting. With an abscess, the inflammation has the shape of a capsule, which prevents the process from spreading further. Cellulitis is a more serious form, because the purulent inflammatory process further expands throughout the tissues.
- Pyoderma is a lesion of the skin in the area where hair emerges from the surface of the skin. The appearance of an abscess in the area of hair growth, when an abscess forms around the hair (folliculitis), indicates a superficial lesion. With more serious skin lesions, not only inflammation of the hair follicle develops, but also the surrounding tissues (furuncle), as well as inflammation of an entire group of hair follicles (carbuncle).
- A brain abscess or purulent meningitis can develop due to the appearance of carbuncles and boils on the face, because the blood circulation on the face is specific and staphylococcus can get into the brain.
- Osteomyelitis. In 95% of cases, purulent inflammation of the bone marrow occurs due to a staphylococcal infection.
- Sepsis - when a huge number of staphylococcal bacteria are spread by blood throughout the body, where secondary foci of infection subsequently occur, manifesting themselves in internal organs.
- Endocarditis is a heart disease that ends in death in 60% of cases. Occurs as a result of damage by staphylococcus to the inner lining and valves of the heart.
- Toxic shock. A large number of aggressive toxins entering the blood cause fever, an immediate drop in blood pressure, headache, vomiting, abdominal pain, and impaired consciousness. With food toxicosis, the disease manifests itself 2-6 hours after eating.
To identify the causative agent of the disease, you need to take a blood and/or biological fluid from the wounds test for Staphylococcus aureus. After conducting research in laboratories and testing for susceptibility to antibiotics, the doctor prescribes antibiotics that can kill staphylococci.
Tests for staphylococcus
To confirm or refute the diagnosis, the child must be tested for the presence of staphylococcal infection. They are done immediately after childbirth, since this process greatly undermines the baby’s immunity. Therefore, Staphylococcus aureus is often detected in newborns immediately in the maternity hospital.
Provoking factors can also be various infectious diseases suffered by children at an older age and weakening the immune system. Microorganisms can be found in different bacterial cultures:
- Staphylococcus aureus found in feces indicates its presence in the intestines: if symptoms of gastric upset (vomiting and diarrhea) are observed, feces are examined for opportunistic and pathogenic microflora;
- in the throat and nose: if the symptoms are associated with the lungs, bronchi and respiratory tract, bacterial culture is taken with a special probe from the throat and nose - such an infection can cause the development of bronchitis (read: how to treat bronchitis in a child) or pneumonia;
- detection of Staphylococcus aureus already in the blood is a threat of sepsis, which often ends in death.
In bacterial culture, the number of pathogenic microorganisms is counted manually and compared with standards, after which appropriate conclusions are drawn and treatment is prescribed. In different laboratories, the norm of Staphylococcus aureus in children may not be indicated in the same way. Parents can see it on the test result form.
For example, according to the Industry Standard number 91500.11.0004—2003, the norm is the complete absence of Staphylococcus aureus in any childhood and in any bacterial culture. Since this is rare, most scientific institutes develop their own standards, according to which this microorganism in an amount of 10 to the 4th power is a completely normal indicator for children over 1 year old. But Staphylococcus aureus in infants in such quantities will already require treatment.
It’s another matter if it grows:
- if it is indicated that the growth is abundant and massive, then the infection is gaining momentum, the previous therapy was unsuccessful and a new course of treatment is urgently required;
- moderate and meager growth of microorganisms according to the results of the latest tests - such an indicator should not cause alarm, the child’s condition is satisfactory.
In each individual case, the disease in children occurs differently. The same indicators can lead to completely different consequences. For some, the disease passes quickly, for others it can result in serious consequences. This largely depends on the immune system. In any case, everyone needs to undergo therapy.
Which doctor treats staphylococcus in the nose and throat
However, sometimes staphylococcus in the intestines, nasopharynx, skin and other organs causes disease.
How to treat staphylococcus in the throat and nose?
Staphylococcus is considered one of the most common microorganisms with which humans come into contact.
This is a large group of bacteria, most of them opportunistic, that live on the surface of human skin and mucous membranes.
But with a weakened immune system, the presence of open wounds or massive infection, they can cause various purulent diseases - from completely harmless to extremely dangerous.
Features and forms of staphylococcus
This group of microorganisms is ubiquitous. Staphylococci live not only on human skin, but also in the soil, in the air, on surrounding objects, and even on food products. Under a microscope they look like immobile, spherical bacteria. These are anaerobic, opportunistic microorganisms capable of synthesizing color pigments.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ARu6i7bxOWY
Most staph bacteria are purple in color and cluster in grape-like clusters. It is not for nothing that the name “staphylococcus” translated from ancient Greek means “grape grain”. However, bacteria can be painted in other colors - white, yellow, golden.
A person is constantly in contact with staphylococcus, but usually this does not have any consequences for him. However, some types of staphylococcus cause an inflammatory process as soon as they come into contact with the skin.
Staphylococcus contains about 10 different enzymes that have a negative effect on the human body; they can increase blood clotting, causing immune reactions and disrupting metabolism.
In addition to enzymes, adhesins are secreted - proteins responsible for attaching the microorganism to the cell membrane and beta-lactamase - a substance that increases the resistance of the microorganism to penicillin antibiotics (not all staphylococci produce).
Types of staphylococcus
There are many types of staphylococcus (more than 50), but three types are considered the most common - aureus, saprophytic and epidermal.
There are also more dangerous forms, such as hemolytic Staphylococcus, penicillin - and vancomycin-resistant forms of Staphylococcus aureus.
Since this group of microorganisms is the most common, among them the percentage of bacteria that have developed sensitivity to various types of antibiotics is highest.
The greatest risk of infection with staphylococcus is the elderly, whose bodies are weakened by chronic diseases, and children whose immune system has not yet fully formed and sanitary and hygienic skills have not yet been fully developed.
Transmission routes
Staphylococcus is transmitted in all possible ways:
- Airborne (this is how Staphylococcus aureus that lives in the nose or throat is transmitted). The likelihood of infection increases significantly when you are in crowded places during an epidemic of respiratory diseases.
- Contact-household - when contaminated soil or objects come into contact with a wound surface or damaged mucous membrane. You can also become infected within your family if you share personal hygiene items (for example, washcloths, towels) or sleep in the same bed with a carrier of the infection.
- Airborne dust. Both street and house dust contain a huge number of microscopic particles consisting of dead skin cells, animal hair, as well as various microorganisms - fungi, viruses and bacteria. And when we breathe dusty air, pathogenic pathogens enter our body.
- Nutritional (if a large number of pathogens enter food from dirty hands or dishes). Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules often becomes the cause of severe infectious diseases, including those caused by staphylococcus.
- Medical. Infection with staphylococcus is possible during various medical procedures if they are not provided with a sufficient level of sterility. Or, in the case when, during diagnostic procedures related to violation of the integrity of the skin or surgical operations, instruments treated with an antiseptic to which staphylococcus has developed resistance are used.
Infection with staphylococcus is facilitated by a decrease in the body's immune defense.
The reasons for this condition may be:
- banal hypothermia;
- diseases of the ENT organs (tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis);
- diseases of the respiratory system (bronchitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis);
- viral infections (flu, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections);
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus);
- immunosuppressive conditions (HIV);
- bad habits (alcohol, drugs, smoking);
- chronic stress and insomnia;
- physical inactivity;
- unbalanced diet, vitamin deficiencies;
- long-term and unsystematic use of certain medications (antibiotics, vasoconstrictor drops);
- injuries associated with violation of the integrity of the skin;
- unfavorable environment, air pollution, work in hazardous industries.
Symptoms of staph infection
Symptoms of staphylococcus infection, regardless of location, are very similar.
An active inflammatory process develops with the formation of pus, an increase in local and general temperature, headache, and clear signs of general intoxication of the body.
If inflammation develops in a confined space (otitis media, abscess, purulent skin lesions), then an abscess is formed, which gradually increases in size and breaks into neighboring organs or the external environment.
Staphylococcus in children causes much more dangerous consequences, which can quickly lead to death. The younger the child, the more dangerous it is for him to become infected with microorganisms, which quickly turns into sepsis and threatens the baby’s life.
Staphylococcal diseases of the ENT organs
Staphylococcus is the most common causative agent of purulent tonsillitis, purulent otitis media, pharyngitis and rhinitis. Staphylococcus is almost always present in the throat, so talking about infection in many cases makes no sense.
However, bacteria normally do not cause harm; they become dangerous when local immunity is impaired.
Most often this occurs with viral diseases (pharyngitis, rhinitis) or with the spread of infection from neighboring organs (otitis media, tonsillitis).
Source: https://ckiom.ru/gorlo/kakoy-vrach-lechit-stafilokokk-v-nosu-i-gorle/
How to treat Staphylococcus aureus in children
The danger of Staphylococcus aureus for children is that these microorganisms are highly resistant to external influences. That is why neither hydrogen peroxide nor boiling helps get rid of them. The only effective disinfectants against bacteria are brilliant green and chlorophyllipt.
Before starting treatment, you must pass all the required tests (perhaps even more than once to see the growth of bacteria). Only after confirmation of the diagnosis can a course of therapy begin. Here we need to take into account one more important nuance. If Staphylococcus aureus is detected in a child, but he feels great, treatment is not prescribed.
1. Drug treatment:
- immunostimulating drugs;
- vitamins;
- antibacterial drugs;
- hygiene procedures (sterile compresses);
- if necessary, blood transfusion;
- antibiotics are used only if purulent inflammation and high temperature are detected.
2. Treatment with folk remedies:
- decoction of calendula for gargling: pour calendula flowers (1 teaspoon) with boiling water (250 ml), heat in a water bath, leave for an hour and a half, strain;
- a decoction of St. John's wort for oral administration and gargling: pour boiling water (250 ml) over St. John's wort flowers (2 teaspoons), leave for half an hour, strain;
- chamomile decoction for oral administration, nasopharyngeal rinsing, gargling: pour boiling water (250 ml) over chamomile flowers (1 tablespoon), boil over heat for about five minutes, close with a lid and leave for 20 minutes.
All parents need to understand that in order to avoid danger and for a speedy recovery of a sick child, you cannot self-medicate. It is necessary to contact specialists as soon as possible.
source: www.vse-pro-detey.ru
Staphylococcus aureus is an infectious disease caused by bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus. It multiplies in the nasal cavity, mouth or skin. Approximately 25% of people are carriers of the infection, but may never get sick with staphylococcus.
Staphylococcus aureus in children - causes
The causes of Staphylococcus aureus disease are several factors:
- weakened immune system;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- poor nutrition.
When a child often suffers from colds and viral diseases, the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus can join them. It enters the body through the respiratory tract from the carrier of the infection and is transmitted by airborne droplets. Also, a baby can “pick up” the staphylococcus bacteria from dirty toys or through unwashed hands. In this case, the development of the disease begins in the mouth and penetrates the stomach.
Staphylococcus aureus - symptoms
- Skin rashes (acne, blisters, ulcers, skin peeling, etc.).
- Fever (above 38 degrees).
- Vomit.
- Diarrhea (with black spots or blood).
This bacterium can cause diseases such as pneumonia, meningitis, sepsis.
If you identify signs of Staphylococcus aureus in a child, be sure to contact your pediatrician and take the necessary tests to determine the number of staphylococci in the body.
The norm for Staphylococcus aureus in a child is: 10^3, 10^4.
Dysbacteriosis in children and Staphylococcus aureus
If a child's intestinal microflora is disturbed, dysbacteriosis occurs. This means that there is a lack of certain beneficial bacteria in the gut. It can appear after treatment with antibiotics, poor diet, poisoning, or eating unwashed foods.
It happens that against the background of dysbacteriosis, the staphylococcus bacterium joins. The child begins to lose weight and appetite, stool loss is impaired, body temperature rises, vomiting and abdominal pain may occur.
Staphylococcus aureus in children - treatment
Staphylococcus cannot be completely cured, since immunity to it is not developed. It does not respond to treatment with many types of antibiotics. Using laboratory tests, the resistance of bacteria to any antibiotic is determined.
But even if you choose the right antibiotic, treatment with it may not give the desired result. Since staphylococcus can quickly adapt to it.
For effective treatment, it is necessary to normalize the microflora in the intestines and remove the staphylococcus bacteria.
To do this, you will need to do an enema with special anti-infective drugs. Take antibacterial medications internally.
After the stomach is cleansed, it must be repopulated with beneficial bacteria. There are a lot of specialized medications for this; your doctor will recommend them.
It is imperative to boost immunity and restore hormonal levels.
Folk remedies against staphylococcus
Folk remedies will help increase the effectiveness of treatment, but they are necessary in a comprehensive drug course. Before using any of the drugs and folk remedies, be sure to consult with your doctor.
It has been proven that acne caused by staphylococcus can be easily eliminated with the help of brilliant green, so lubricate the affected parts of the skin with brilliant green.
Apricots are excellent for removing intestinal staphylococcus. They should be eaten in the morning on an empty stomach. Give your child at least six apricots daily.
It is also necessary to consume 300g of blackcurrant. in a day.
Excellent fight against staphylococcus:
- Chamomile (it is used to wash the eyes and nasal cavity).
- Calendula (gargle).
- Let your child drink St. John's wort infusion.
- Treat the rash with a swab dipped in the infusion of the string.
source: WomanAdvice.ru
Staphylococcus aureus (aureus) in the throat is completely normal for most people.
When we talk about this bacterium, we must understand that there is a conditional norm for Staphylococcus aureus. And there is a pathological infectious process that occurs under certain conditions.
Until we have obvious symptoms of an infectious process or a significant excess of the norm, treatment should not be started.
What are the consequences and why is it dangerous?
Staphylococcal infection can affect any organ. The consequences of Staphylococcus aureus are unpredictable, because. It is this type of staphylococcus that can cause diseases that in the future, if not treated in time, can become chronic.
According to statistics, already on the third day, 99% of newborn babies have staphylococcus bacteria, both inside the baby’s body and on the surface of the skin . With strong immunity, this bacterium coexists peacefully with other bacteria in the body.
- Most often, staphylococcus affects the nasopharynx, brain, skin, intestines, and lungs .
- Staphylococcus aureus is dangerous because untimely treatment of an advanced disease can lead to death .
- In case of food poisoning and superficial manifestations on the skin, you need to sound the alarm and contact qualified specialists, and not wait until the staphylococcal infection affects the internal organs and takes on a septic form , i.e. - blood poisoning.
To protect your newborn as much as possible from infection with Staphylococcus aureus:
- Support your child's immunity;
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- Keep bottles, pacifiers, spoons, other feeding utensils, toys and household items clean.
The site Colady.ru warns: self-medication can harm your baby’s health! The diagnosis should only be made by a doctor after an examination. Therefore, if you notice symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in a child, be sure to consult a specialist!
Causes of staphylococcus in humans
We live in a world inhabited by thousands of species of microorganisms. Staphylococcus and streptococcus are microbes that are present almost everywhere:
- In our homes;
- on food products;
- on the street;
- on door handles, etc.
We meet them starting from the first days of life. And this is despite the fact that in maternity hospitals increased attention is paid to infection prevention issues.
Staphylococcus aureus “lives” on our skin, on our mucous membranes (including in the throat), and in the digestive tract.
Prevention
It is known that any infection, including staphylococcal infection, is much easier to prevent than to cure. For healthy children with high immunity, staphylococcus poses no danger - the defense mechanisms are able to cope with it on their own. Thus, the main task of prevention is to prevent the impact of negative factors on the child’s body.
Factors that negatively affect immunity include:
low level of personal hygiene;- physical inactivity (lack of activity);
- poor nutrition;
- lack of vitamins in the diet;
- stress;
- unfavorable environmental conditions.
From an early age, a child should be taught to regularly wash his hands with soap (parents should help young children), and he should not be allowed to put toys and other objects that may contain bacteria into his mouth.
Important: in order to strengthen the immune system and reduce the likelihood of developing staphylococcus in children, children need to be taken out for walks in the fresh air more often, and it is better to give preference to outdoor games. It is undesirable to include smoked meats, sausages and, especially, fast food in your diet. It is advisable to limit the consumption of flour and sweets. It is advisable to take your child on country walks more often so that he has the opportunity to breathe unpolluted air.
To strengthen the body's defenses, children of preschool and primary school age are recommended to undergo hardening (regular rubdowns and douches), as well as physical education and sports.
Chumachenko Olga, pediatrician
29, total, today
( 176 votes, average: 4.57 out of 5)
What can you eat if you are poisoned: tips, allowed foods, sample menu
Diseases caused by staphylococcus
Related Posts
Can you get a staph infection?
Undoubtedly, it is possible, like any other bacterial infection.
For example, in childhood we all often suffer from colds and respiratory diseases. Many of them are accompanied by fever and purulent inflammation - sore throat, rhinitis with purulent discharge, sinusitis. In some cases, the cause of the disease is staphylococcus.
When faced with Staphylococcus aureus, a child gets sick with rhinitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, otitis media, etc. Having had a staphylococcal infection once, the child develops anti-staphylococcal immunity. Over the years, the human immune system trains, becoming familiar with new variants of bacteria.
In an adult with good health and a moderately strained immune system, the body coexists peacefully with staphylococcus, suppressing its excessive spread.
However, in some cases, an opportunistic bacterium can trigger an infectious process.
The main reason for the transition of an opportunistic microbe to a staphylococcal infection is weakening of the immune system.
The main factors of weakened immunity:
- Respiratory viral diseases;
- recurrent herpes virus;
- chronic diseases;
- immunodeficiency conditions, including those arising during therapy.
Additional factors of weakened immunity:
- Mobility deficit;
- consumption of toxic substances, the main ones being alcohol and tobacco;
- poorly balanced or deficient nutrition;
- bad ecology;
- excessive emotional and physical stress.
Types of bacteria
There are more than two dozen varieties of staphylococcus. Of these, 14 live on human mucous membranes and skin, only 3 of these species cause disease.
The most common types:
- Staphylococcus aureus (Aureus) is the most common and dangerous bacterium. Bacterial colonies have a yellowish color. It contributes to the emergence of about a hundred different diseases, some of which can become chronic. Settles in any healthy organ.
- Epidermal (Epidermidis) . Habitat: nose, mouth and eyes. Occurs in children born prematurely or who have undergone surgery. More often appears with weakened immunity. Dangerous if present in the blood, causing inflammation of the endocardium or sepsis.
- Saprophyticus staphylococcus is rare in newborns. More often in women, it affects the bladder and kidneys.
- Staphylococcus gastrointestinal tract. Habitat: skin, mucous membranes, feces, breast milk. The disease is accompanied by purulent rashes and becomes more active when the immune system is low.
- Klebsiella. Most often, Klebsiella and staphylococcal infections in infants manifest themselves in the form of dysbacteriosis. These pathogenic enterobacteria are found in a healthy human body and usually do not manifest themselves in any way. If conditions are favorable, microorganisms multiply.
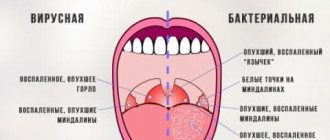
Main symptoms
How does staphylococcus manifest in the throat:
- Pain, burning in the throat;
- soreness;
- abrasion;
- the need to swallow frequently;
- slight coughing (clearing the throat).
Local symptoms of staphylococcus increase over a period of several hours to 2-3 days, after which the infection becomes more severe.
Suppuration Staphylococcus is a classic purulent infection. Bacteria, gaining a foothold on the mucous membrane, secrete specific enzymes that destroy our cells. These microbes feed on cell destruction products. In addition, in this way they move deeper into the tissues. Immune cells try to deactivate the bacteria, resulting in pus. Therefore, the symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus infection in the throat are:
- Boils, pustules;
- inflamed tonsils.
Fever
Since the infection is accompanied by a purulent process, it always manifests itself as fever with high temperature.
General intoxication
Signs of staphylococcus in the throat:
- Weakness;
- nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- dizziness.
Cough
Cough with staphylococcus in the throat is the main symptom of infection.
The microbe often affects the tonsils, causing a sore throat.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to determine the nature of the infection (type of pathogen) at home, therefore, when the first symptoms of a staphylococcal infection appear in a child, it is strongly recommended to immediately seek medical help.
To identify the infectious agent, the doctor first prescribes a series of tests. A laboratory examination of blood, feces, purulent discharge and washings from the skin and mucous membranes is carried out. It is advisable to collect material in the acute phase of the disease, since microorganisms are most active during this period and are easier to detect.
Important: the presence of staphylococci in the blood does not indicate sepsis. If bacterial growth is not observed, then we are talking about the so-called. "transient bacteremia".
At the next stage, the sensitivity of the detected staphylococcus strain to antibacterial drugs is determined. This is necessary to prescribe adequate antibiotic therapy.
Important: during a standard blood test, Staphylococcus aureus is not always immediately detected. Bacteriological culture is considered the most informative laboratory diagnostic method.
Serological blood test
The material for the study is the blood serum of a sick child. The diagnosis is considered confirmed if specific antibodies to the infectious agent are found.
PCR
Polymerase chain reaction is an additional analysis that allows you to identify single molecules of staphylococcal DNA.
Analysis of mother's expressed breast milk
This study is necessary if staphylococci are found in the baby’s stool in quantities exceeding the permissible norms. The analysis allows us to identify the possible source of infection (microorganisms are easily transmitted to the baby from the mother).
A positive result is a good reason for immediately interrupting breastfeeding and transferring the child to artificial milk formula.
Please note: the insignificant presence of bacteria in the baby’s body does not allow us to talk about a staphylococcal infection, especially if the child’s health does not suffer. Treatment in such situations is not required.
Diagnostic methods
Before curing Staphylococcus aureus, it is necessary to examine the microflora of the throat. A smear on the flora from the throat reveals bacteria inhabiting the mucous membrane, and also allows you to create an antibiogram (i.e., determine sensitivity to antibiotics) for each type of bacteria found.
An antibioticogram is extremely important. Our bacteria has developed resistance to some antibiotics. Although antibiotics are known to be ineffective, additional analysis is needed to determine the correct treatment in each case.
In regular clinics operating within the compulsory medical insurance system, such an analysis is done within a few days. In case of an acute infectious process, this is too long. In these cases, when prescribing treatment, doctors have to rely on their theoretical knowledge and experience, assuming the likelihood of a particular pathogen and its sensitivity to a particular antibiotic.
Types of bacteria
There are three main types of staphylococcus:
- epidermal;
- golden;
- saprophytic.
Each of the pathogens can cause any disease or simply be found in the human body. The most unfavorable type is Staphylococcus aureus
, especially if it is detected in a child. However, asymptomatic carriage of this strain is also possible.
This or that pathology depends little on the type of staphylococcus. The entrance gates of infection and the general condition of the body are much more important. The more weakened a person is, the more severe the pathology caused by staphylococcus will occur. However, when a doctor treats a staph infection, he first determines the type of bacteria. The severity of the process and its treatment will depend on the specific etiology. Staphylococcus aureus is the worst to treat.
What is the norm for Staphylococcus aureus?
You can get rid of Staphylococcus aureus in your throat, but not for long. The norm for the constant presence of Staphylococcus aureus in the upper respiratory tract is 10³ CFU/ml, i.e. 1000 bacteria, each of which is capable of multiplying into a separate colony (colony-forming unit - CFU) in 1 ml of medium.
It should be borne in mind that, apart from the symptoms, this indicator is not very informative. That is, if a person has, say, 10 to 4 CFU/ml, and no signs of an inflammatory process are observed, then this value can be considered as not exceeding the normal range.
The exceptions are children, the elderly and people with chronic respiratory diseases. In these cases, an excess of 10³ CFU/ml, which is not accompanied by additional symptoms, requires sanitation of the throat.
Causes of the disease, how is it transmitted?
- Staphylococcus aureus is transmitted both by airborne droplets and through food (contaminated meat, eggs, dairy products, cakes, cream pies) or household items .
- Staphylococcus aureus can also enter a child’s body through microtraumas of the skin or mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
In most cases, infection with Staphylococcus aureus occurs in medical institutions.
An imbalance of intestinal microflora, a weakened immune system, and autoinfections are the main causes of infection with Staphylococcus aureus. Premature babies and children with weakened immune systems are at greatest risk of infection .
During childbirth , through wounds or scratches, as well as through breast milk, the mother can infect the child. If bacteria enter the mother's body through cracks in the nipples, this can lead to purulent mastitis in her.
How and with what to treat staphylococcus?
Many people pose the fundamental question: how to kill staphylococcus in the throat. It is difficult to remove it, and it is not necessary, because after some time it will return, in any case.
The main goal of treating carriage of Staphylococcus aureus or an infectious process in the throat is to increase immune resistance.
Treatment at home
There are 2 possible conditions that require action:
- The concentration of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat is 10 to 4 degrees or 10 to 5 degrees CFU/ml, with no inflammatory symptoms;
- there is purulent inflammation, fever and intoxication.
Immunostimulation
First, we must stimulate the immune system to naturally resist the spread of the microbe. We should not forget that it is a dangerous pathogenic bacterium. If its concentration is greatly exceeded (and 10 to the 5th power is 100 times higher than normal), it means that the immune system is suppressed and needs help.
Immunomodulators are used for this purpose. These are drugs that contain deactivated fragments of various bacteria. Having received such a “breeding ground” of bacterial antigens, the immune system triggers the production of its own interferon and other processes, which together lead to a significant improvement in the immune response.
Immunomodulators are of local and general action. Preparations for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat - topical use. Among them the most famous:
- Imudon;
- IRS-19.
Imudon is a lozenge. Take 8 tablets per day for 7-10 days.
IRS-19 can be sprayed both into the nasal passages and onto the mucous membrane of the throat. Regimen: 1-2 sprays 5 times a day for 7 days or until symptoms of infection disappear.
Antibiotics
If we have a full-blown staphylococcal infection, then we cannot do without antibiotics. Staphylococci may show resistance to some antibiotics. However, the resistance of this bacterium has been exaggerated. She is sensitive to most antibiotics. Among them:
- Azithromycin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Cefriaxon;
- Linezolid;
- Teicoplanin;
- Vancomycin;
- fusidic acid.
Antibiotic sprays:
- Bioparox;
- Miramistin.
You should not overuse antibiotics for staphylococcus in the throat, including topical use: these substances are aggressive to the mucous membranes of the throat and mouth.
How to gargle for Staphylococcus aureus?
To treat Staphylococcus aureus in the throat, phytoantiseptics are used:
- Calendula tincture (alcohol);
- Chlorophyllipt (alcohol solution of eucalyptus leaves).
20 drops of calendula or Chlorophyllipt tincture are diluted in 1/2 cup of water. Gargle three times a day for a week.
Treatment with folk remedies
Classic antimicrobial agents of plant origin:
- St. John's wort herb;
- calendula flowers;
- eucalyptus leaves.
They can be used individually or made into mixes of 2-3 herbs. The herb is brewed with hot water at the rate of 1 tbsp. per glass of water. Gargle three times a day.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat should not be replaced exclusively with folk remedies.
Staphylococcus aureus in a child's throat
Treatment of staphylococcus aureus in a child’s throat involves sanitation. For this use:
- Local antiseptics, for example:
- Lizobakt – 1 tablet, lozenge, three times a day;
- Octenisept - spray into the throat three times a day, or gargle with a solution of the drug diluted in water in a ratio of 1:2.
- Staphylococcal bacteriophage
To treat Staphylococcus aureus in the throat, use bacteriophage in the form of a gargle three times a day.
Immunomodulatory drugs, as a rule, are not prescribed to children.
Dr. Kamarovsky explains to parents what the risk is for their child if staphylococcus is cultured from the mother.
Features of treatment of staphylococcus in the throat during pregnancy
Everyone knows well that no medications are recommended during pregnancy: not only antibiotics, which are clearly contraindicated, but also harmless immunomodulators.
What can be treated:
- Spray locally into the throat antiseptic preparations based on miramistin (for example, Octenisept);
- gargle with staphylococcal bacteriophage;
- dissolve Lizobact tablets.
In general, if staph does not cause problems, then it is better not to do anything about it. Just walk more often, eat well and variedly, don’t worry and get plenty of rest.
Who treats staphylococcus and which doctor - No runny nose
Now there are a small number of antibiotics that help treat diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
Along with this, research conducted by doctors is aimed at discovering a universal method that would help treat all infectious forms and get rid of the bacteria completely. Initially, doctors and scientists studied the structure of the harmful bacterium.
The name Staphylococcus aureus, as it turned out, is not related to the color of the bacterium itself. The areas of destruction appearing around her were painted gold.
These areas were affected by toxic substances released by microbes. In addition, the studies helped to understand how it is possible to carry out treatment.
To begin treatment for a staphylococcal infection, you need to contact a doctor who works with this disease:
- dermatologist if you have pyoderma (folliculitis, furunculosis and other skin diseases);
- dentist – for stomatitis and caries;
- ENT - all infections in the nose, throat, etc.;
- pediatrician, if symptoms of staphylococcal infection are detected in newborns, etc.;
- gynecologist during pregnancy;
- infectious disease specialist and immunologist.
That is, treatment of staphylococcus should be carried out by a certain specialist, depending on the source of inflammation.
Don't know which doctor to see?
We will promptly select the right specialist and clinic for you!
Staphylococcus aureus is a constant companion of a person throughout his entire existence: from birth to death.
According to some data, almost 70% of the population is infected with it. Which doctor should I contact for help?
Since the microbe likes to settle in the nasal and oral cavities, staphylococcus is most often treated by an ENT specialist. Staphylococcal infection often causes diseases such as sinusitis, tonsillitis, rhinitis, purulent tonsillitis, otitis media, etc.
Surgeons do not stop fighting against epidermal staphylococcus, since it is responsible for many different postoperative complications.
Why is it so common, but not everyone develops the disease? The fact is that this bacterium, living on the skin or mucous membrane of a person, normally does not pose a threat. But under certain circumstances, staphylococcus begins to multiply, which leads to inflammatory processes. Our immunity plays an important protective role: if it is strong, we are not afraid of staphylococcus.
The information published on the site does not constitute a recommendation for use and is intended for informational purposes only.
Staphylococcus aureus is a type of spherical gram-positive bacteria from the genus Staphylococcus. According to medical statistics, up to 40% of the human population are carriers of this pathogen. Favorite locations are the nasopharynx, respiratory tract, and skin.
Staphylococcus aureus, like other representatives of this group, are normal inhabitants of our body. But their quantity should not exceed, for example, 102 CFU/ml in the pharynx.
Exceeding normal values indicates that the disease is caused by this particular pathogen. Basic principle of therapy:
- Reducing the amount of pathogen to a safe level.
- Eliminate clinical manifestations of the disease.
- Minimizing the risk of relapse.
It is impossible to get rid of Staphylococcus aureus. But it is quite possible to cure the disease caused by it.
Tell your friends! Share this article with your friends on your favorite social network using social buttons. Thank you!
Follow site updates on social networks!
If a nasopharyngeal infection develops, you can contact a pediatrician, therapist, and in more severe cases, an ENT doctor. In case of repeated episodes of staphylococcal infection or the formation of a carrier state, you need to consult an infectious disease specialist, immunologist, and take a blood sugar test.
However, sometimes staphylococcus in the intestines, nasopharynx, skin and other organs causes disease.
The specialty of the doctor you should contact will depend entirely on the type of disease. If you have doubts about choosing a doctor, you can first go to a therapist, who will diagnose and refer you to the right doctor.
The main specialist in staphylococcal pathologies is an infectious disease specialist. However, it is used in severe cases when difficulties arise with treatment and diagnosis.
- surgeon (all skin pathologies);
- otolaryngologist (nasopharynx, ears, throat);
- ophthalmologist (eye problems);
- dentist (caries and stomatitis);
- dermatologist (the doctor treats skin pathologies that do not require surgical intervention);
- pediatrician (doctor to treat Staphylococcus aureus in children);
- immunologist (if the cause is immune deficiency);
- endocrinologist (is an auxiliary doctor to whom they are referred for consultation if diabetes is suspected).
The basis of treatment for staphylococcus are antibacterial drugs, which should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Each strain of the pathogen has its own characteristics in treatment, therefore, before carrying out therapy, the bacteria are identified.
After this, the doctor treating Staphylococcus aureus, checking the results of the antibiotic sensitivity test, prescribes medications. Pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy is carried out in parallel.
Save the link, or share useful information on social media. networks
Copying site materials is prohibited!
Self-medication can be dangerous to your health. At the first sign of disease, consult a doctor.
LadyVeka.ru Health Diseases and treatment
Staphylococcus aureus, as the causative agent of many infections and diseases, is known to many, unfortunately, firsthand. Staphylococcus aureus can infect an organism with a weak immune system, and turns out to be resistant to antibiotics. But in uncomplicated cases, treatment can also be effective.
Angina. Thank God it's all over
Looks like we have laryngotracheitis again
I apologize for the not entirely correct title. It would be more correct to say “how to treat infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus, including furunculosis (review of drugs)”, but this is too complicated and long.
Source: https://dimelli.ru/kakoy-vrach-lechit-zolotistyy-stafilokokk/
Methods for preventing staphylococcal infection
Improve your immunity:
- Eat a balanced diet;
- don’t forget to move – walk more rather than drive;
- stop smoking - smoking significantly reduces the local immunity of the respiratory tract, helping staphylococcus spread.
Since the transition of a microbe to a pathogenic form occurs in most cases against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, you should pay increased attention to your health during seasonal increases in morbidity. It is recommended to take prophylactic antiviral drugs twice a year: in mid-autumn and in late winter/early spring.
Staphylococcus aureus, a dangerous causative agent of purulent inflammatory processes, manifests itself under certain conditions. A bacterial infection specialist explains how an infection develops.
Types of staphylococci detected in children
There are several types of staphylococci:
- saprophytic;
- epidermal;
- hemolytic;
- golden.
Saprophytic is detected in children relatively rarely. It affects the skin and mucous membranes of the genitourinary system, causing acute inflammation of the urethra and bladder. This infectious agent is considered the least dangerous for a child; With adequate therapy, it can be eliminated in just a few days.
Epidermal can multiply on any areas of the skin and mucous membranes of the ENT organs and eyes. It provokes conjunctivitis, purulent urinary tract infections and postoperative complications. In severe cases, endocarditis and even sepsis cannot be excluded. At risk are weak and premature babies, as well as children who have undergone various operations. It is not dangerous for a child with high immunity; the very fact of the presence of epidermal staphylococcus on the mucous membranes of children is regarded as the norm if the baby’s health is good. Skin lesions are an indication for local therapy.
Hemolytic staphylococcus can cause purulent inflammatory processes in many organs. It affects the skin, organs of the urinary system and endocardium. Against the background of this infection, with reduced immunity and in the absence of treatment, a septic condition may develop.
Staphylococcus aureus is the most pathogenic for humans, as it can cause severe purulent inflammation in almost any tissue and organ. It is characterized by high virulence (pathogenicity) and resistance to drying, boiling, solar ultraviolet radiation and the effects of antiseptics such as hydrogen peroxide and ethanol.
A specific feature of this pathogen is the ability to synthesize the enzyme coagulase. The infectious agent quickly adapts to antibiotics, acquiring resistance (immunity). Particularly dangerous are methicillin-resistant strains that are resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics (cephalosporin and penicillin drugs). The detection of this infectious agent in stool analysis or mucosal washings is the basis for starting complex therapy only if the child’s well-being worsens .