Signs of meningitis are determined by the characteristics of the children's nervous system. The Yusupov Hospital has created the necessary conditions for the treatment of meningitis: isolated wards, dietary nutrition for patients, and the use of modern methods for diagnosing infectious diseases of the central nervous system. Doctors use innovative methods of treating meningitis with the latest drugs registered in the Russian Federation. The clinic accepts patients aged 18+.
How is viral meningitis transmitted?
Most often, viral meningitis occurs due to enterovirus infections. The peak of epidemics of viral meningitis occurs in the warm season. It is caused by polio and mumps viruses. However, the disease can also be caused by other reasons, such as:
- adenoviruses that cause acute respiratory diseases;
- ECHO viruses belonging to the group of enteroviruses;
- cytomegaloviruses, which have a particularly strong effect on the bodies of young children;
- arenaviruses;
- tick-borne encephalitis virus;
- herpes virus.
It is dangerous for a healthy person to be near someone with meningitis, since this disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, it enters the respiratory tract of a person nearby. From the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, the pathogen enters the bloodstream, and then spreads with it throughout the body. Ultimately, meningitis affects the central nervous system and the lining of the brain.
Incubation period
The incubation period is the period of time between the entry of the pathogen into the body and the manifestation of the primary symptoms of the disease. The incubation period for viral meningitis in adults reaches 2 weeks. It will take 2-4 days for the child to develop the first symptoms.
The incubation period for meningitis caused by the ECHO virus can reach 2-10 days. After infection with enteroviruses, symptoms will appear within 1-18 days. Acute aseptic meningitis is characterized by an incubation period of a week to 12 days.
After infection with the tick-borne encephalitis virus or herpes, symptoms will appear only after 2-3 days.
Main symptoms in children
Meningitis is a serious disease that is especially difficult for children. If a completely healthy child can avoid contracting this disease, then the body of some will not be able to resist the virus. The following categories of children are more prone to contracting meningitis:
- Infants with hypoxia or infections;
- premature babies with weak immune systems;
- children under 3 years of age with chronic diseases;
- children with disorders of the nervous system, brain injuries.
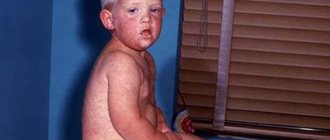
A sick child may have a fever of up to 40 degrees, a severe headache with sudden movements and frequent vomiting. Convulsions and fear of light are also observed. The baby may often tilt his head towards his chest due to severe tension in the neck. Infected infants experience regurgitation and diarrhea.
With viral meningitis in children, in addition to high fever and severe headache, the following is observed:
- Tension in the neck;
- vomit;
- redness in the throat;
- uncontrolled flow of tears;
- the appearance of conjunctivitis.
Viral meningitis requires careful treatment, but the chances of a complete recovery with this type of disease are very high.
The list of symptoms may grow depending on the cause of the disease. Thus, when infected with tick-borne encephalitis, patients are bothered by severe pain in the head with any movement, fear of bright light, constant pain in the eyes and dizziness.
Helpful information
All these symptoms are accompanied by fever and do not go away until the temperature subsides. It usually increases very quickly and lasts for two weeks.
During an illness caused by the mumps virus, severe pain in the abdomen and kidneys may occur. In boys, the testicles may become inflamed, and in girls, the ovaries may become inflamed.
Often the symptoms of viral meningitis are mild, so you should pay special attention to the child’s behavior and movements. Viral meningitis is characterized by upper and lower Brudzinski symptoms. When a child tilts his head, his legs may involuntarily bend, and when one leg is straightened, the other unbends on its own. It may also be difficult to straighten the legs, which is called Kerning's sign.
Causes of meningitis in children
Children tend to:
- generalized cerebral reactions;
- motor automatism and hyperkinesis;
- convulsions and a low threshold for their occurrence;
- increased body temperature;
- peripheral circulatory disorders.
The child's body is unable to localize the source of excitation. Children are predisposed to swelling and edema of the brain, and thermoregulation disorders due to infectious pathology. Meningitis is an acute infectious disease that is characterized by a general infectious and cerebral syndrome due to inflammatory changes that occur mainly in the pia mater.
There are primary and secondary meningitis. The primary purulent process occurs during an acute infectious process caused by meningococcus. Secondary meningitis develops when infectious agents enter the membranes of the brain from another source of infection in the body. The primary source of microorganisms can be in the nasopharynx, bronchi, lungs, ear, bones.
Based on the nature of the inflammatory process and changes in the cerebrospinal fluid, serous and purulent meningitis are distinguished. The disease can have an acute, protracted or chronic course. There are mild, moderate and severe degrees of the disease. Meningitis in children can occur without complications, complications, with a layer of secondary infection or with exacerbation of chronic diseases.
In children, meningitis is most often caused by the following pathogens:
- bacteria (pneumococcus, meningococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, staphylococcus, yersinia),
- viruses (enteroviruses, mumps virus, measles, rubella);
- mushrooms;
- toxoplasma;
- spirochetes (Borrelia, Leptospira);
- rickettsia;
- malarial plasmodium.
The source of the disease is often humans, less often wild and domestic animals. The following mechanisms of infection transmission are distinguished:
- airborne;
- contact;
- fecal-oral;
- transmissible (from tick bites);
- vertical - from mother to child.
The entry points for infection are the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract. When an infectious agent fixes and multiplies at the entrance gate, a local inflammatory process develops. After this, the pathogen penetrates the meninges through a hematogenous route, causing inflammation of a serous or purulent nature. Spread of infection by contact is possible only in the presence of anatomical disorders of the skull bones.
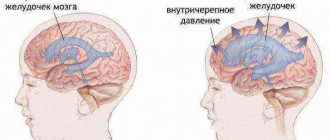
Irritation of the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain by an infectious agent and its waste products leads to excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid with impaired reabsorption. This forms hypertensive liquor syndrome and determines the main clinical signs of the disease.
At the height of the disease, blood supply to brain tissue and oxygen saturation deteriorate, which leads to the development of cerebral edema. With bacterial meningitis with the development of purulent-fibrous inflammation, the movement of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted and external or internal hydrocephalus is formed in children.
Diagnostics
To accurately diagnose meningitis, you need to consult a physician. He will prescribe a list of studies, which may include:
- Lumbar puncture is a method in which a needle is inserted into the cavity between the membranes of the spinal cord to determine the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Direct analysis of cerebrospinal fluid.
- CT scan.
- MRI of the brain.
The main emphasis is on lumbar puncture, since this analysis allows you to accurately determine the cause of the disease and the type of pathogen.
Laboratory diagnosis of meningitis
The diagnosis of meningitis in children is established on the basis of the clinical picture of the disease and the results of studies of biological media:
- bacteriological examination of blood, mucus from the nasopharynx, cerebrospinal fluid on nutrient media, followed by determination of the sensitivity of pathogens to antibiotics;
- microscopy of blood and cerebrospinal fluid;
- express diagnostics – detection of antigen in cerebrospinal fluid and blood and cerebrospinal fluid;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR);
- immunofluorescence analysis - detection of antibodies to specific antigens of the IgM or IgG class.
A comprehensive examination of the child allows you to establish or exclude the diagnosis of meningitis in children.
Treatment of viral meningitis
After the doctor has diagnosed the child, parents must ensure complete rest for the patient. As a rule, children are prescribed painkillers to relieve unpleasant symptoms. To reduce the temperature to normal, it is necessary to take antipyretic tablets, and antiviral drugs are used to combat the pathogen. As an antiviral agent, doctors prescribe acyclovir, which is administered intravenously using droppers.
Helpful information
The child also needs to adhere to strict bed rest. During the entire treatment, the patient should be in a darkened room, since at this time the eyes react painfully to bright light.
It is advisable to provide the child with frequent warm drinks and high-quality nutrition.
After the course of treatment, the patient is assigned sick leave for 3 months. This is enough for complete rehabilitation, during which the psychological support of his family is important to him. During this time, any physical activity is prohibited, and periodic visits to a neurologist are recommended.
Meningitis in infants and children under 3 years of age should be treated under the strict guidance of a specialist. It is advisable to admit the child to the hospital during treatment. With a quick response to symptoms and timely initiation of therapy, it will be possible to get rid of the disease without severe consequences, since viral meningitis is the best treatable.
Effective treatment of meningitis at the Yusupov Hospital
Patients with meningitis who applied to the Yusupov Hospital are urgently hospitalized. After the patient is diagnosed with meningitis, and the symptoms in children under one year of age differ from the signs of the disease in adults, inpatient treatment begins.
The Yusupov Hospital provides comfortable conditions for patients to stay:
- staff provides 24-hour care;
- patients are in comfortable rooms;
- on the territory of the Yusupov Hospital there is wireless Internet and satellite television;
- delicious food;
- respectful and attentive attitude of employees.
The combination of high-quality medicine with an individual approach allows you to effectively treat the inflammatory process and prevent complications. Patients can make appointments with qualified neurologists by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Complications
Almost all people who have had meningitis experience causeless malaise and fatigue for a year after recovery. This is the most harmless consequence of the disease.
Ten percent of meningitis cases are fatal in adults. Mortality from viral meningitis among children reaches 15-20%.
Other complications of the disease include:
- Loss of vision;
- ischemic strokes;
- hearing loss;
- paralysis;
- constant cramps of the limbs;
- hydrocele (fluid accumulation in the brain), etc.
The consequences of meningitis are observed in 20-30% of all people who have had the disease. Since the body of young children is weakened, they may experience more serious complications. In some cases, the child’s nervous system does not fully recover, and various psychological and mental abnormalities develop.
To avoid severe complications after the disease, it is necessary to consult a doctor in time and begin treatment.
Complications of meningitis in children
Children suffering from meningitis develop cerebral edema. It is characterized by impaired consciousness (stunning, stupor), convulsions, unstable focal symptoms manifested by hemiparesis (incomplete paralysis of half the body) and ataxia (disorder of coordination of movements). With increasing cerebral edema, compression of the brain stem occurs and all vital functions are disrupted, dislocation of the brain stem and herniation syndrome develops. Patients experience respiratory and cardiac arrest.
Acute hydrocephalus in children is manifested by the following symptoms:
- tension and bulging of the large fontanel;
- divergence of the sutures of the skull;
- expansion of liquor spaces;
- increase in head circumference.
Young children may develop subdural effusion. Despite adequate antibacterial therapy, the child has a persistent fever for more than three days. His condition worsens, consciousness is depressed, local convulsions and hemiparesis appear. The fontanelle becomes denser and there is no pulsation.
Subsequently, the baby develops drowsiness, vomiting, stiff neck, and congestion in the fundus. The protein content in the cerebrospinal fluid increases sharply.
Ventriculitis syndrome is characterized by bulging and tension of the large fontanelle, headache, dehiscence of the sutures of the skull, dilation of the veins of the fundus, and uncontrollable vomiting. Impairment of consciousness progresses, convulsions occur, and opisthotonus develops. The child takes a convulsive pose with a sharp arching of the back, throwing the head back (an arc pose with support only on the heels and the back of the head, stretching the legs, bending the hands, feet, fingers and arms).
Prevention
Meningococcal infection manifests itself in winter and spring. At this time, vaccinations of students are carried out in kindergartens and schools. Vaccinations are given to children from one year to 8 years inclusive, later vaccination is carried out for students in grades 3-11. Students and adults are vaccinated upon request.
Despite the fact that vaccination almost completely eliminates the possibility of contracting meningitis, care should be taken to ensure proper prevention. To do this you need:
- Visit crowded places less often during an exacerbation of infection.
- In a difficult epidemic situation, always wear a medical mask or respirator.
- Periodically ventilate living and working areas.
- Carry out wet cleaning of your home every day.
It is also important not to forget about proper nutrition, exercise and hardening. A strong and healthy body will always be able to overcome infection.