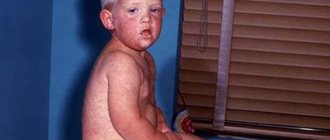
Pneumonia is an acute inflammatory process that occurs in the lungs. The cause of the disease is most often bacteria: pneumococci, staphylococci or streptococci. There are also pneumonia of viral and fungal forms of the disease.
Pneumonia is the most common infectious-inflammatory disease. In the structure of all childhood pulmonary diseases it occurs in 80% of cases.
The right lung consists of three lobes, and the left lung has two. The lobes, in turn, are divided into segments, and these into smaller alveoli. So they become inflamed during pneumonia.
Pneumonia in a child is diagnosed based on the results of x-rays and a blood test for the presence of an inflammatory process.
Why is pneumonia dangerous in children ? Today, despite the significant achievements of modern medicine, pneumonia in children at an early age leads to death in 1.5% of cases.
A little difficulty
The condition is characterized by respiratory discomfort, a feeling of lack of air.
- In infants under 2 months of age, a breath rate greater than 60 breaths per minute is considered high.
- In children from 2 months to a year - above 50 breaths per minute.
- Over 1 year – above 40 breaths per minute.
Difficulty breathing is divided into inspiratory (during inhalation) and expiratory (during exhalation). Basically, there is a combined type, that is, combining both types.
Lack of oxygen in the lungs is very life-threatening!
Treatment of pneumonia in children under three years of age is carried out in a hospital due to the more severe course of the disease and the risk of serious complications. Children over three years of age with a mild course of the disease can be treated at home.
Treatment of difficulty breathing involves eliminating its cause. Antibacterial agents must be used, the choice of which depends on the age of the child and the causative agent of the disease. A broad-spectrum antibiotic is immediately prescribed. In this case, the conditions for the occurrence of the disease, the probable spectrum of the pathogen and the severity of the disease are taken into account.
To facilitate sputum discharge, mucolytic agents are needed. Usually this is enough to restore breathing.
Online test for pneumonia detection
Congenital pneumonia
Due to a number of circumstances (acute and chronic infectious and non-infectious diseases, insufficient obturator function of the mother’s cervix, a long anhydrous interval during childbirth, etc.), some children are born with inflammatory changes in the lungs. Sometimes they develop pneumonia soon after birth. Congenital infection is especially common in premature babies, since one of the main causes of premature birth is infection of the amniotic fluid and the fetus.
The disease is usually severe. Therefore, nursing of sick babies is carried out exclusively in neonatal pathology departments or intensive care units. Despite the fact that neonatal pneumonia is a serious disease, modern medical technologies make it possible to successfully combat this disease. Among them are massive antibacterial therapy, immunotherapy, helium-neon laser irradiation of the projection area of pneumonia foci, etc. After discharge from the hospital, the child must receive medications that normalize the intestinal flora (bifidumbacterin, primodophilus) and multivitamins. In this situation, breastfeeding is also a remedy.
If a child has suffered congenital pneumonia, this does not mean that pneumonia will inevitably haunt him throughout his life. However, the likelihood of frequent respiratory diseases in such children is higher.
To prevent congenital pneumonia, a woman must treat all chronic foci of infection before conception or already during pregnancy. A balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle for the expectant mother are also important.
Symptom of respiratory failure
In case of respiratory failure, the lungs are unable to meet the body's need for oxygen, and the body's compensatory functions are depleted.
The risk of respiratory failure in childhood is very high, since the mobility of children makes it difficult to notice the first manifestations. Up to 5 months, a sign of respiratory failure is cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle (blue discoloration between the lip and nose). It especially manifests itself during sucking.
Important! The appearance of symptoms of respiratory failure requires urgent hospitalization.
There are 4 degrees:
- The first is characterized by the appearance of shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat.
- The second is manifested by bluish skin and convulsions.
- At the third degree, shortness of breath alternates with periods of complete cessation of breathing.
- On the fourth , a hypoxic coma develops, complete cessation of breathing.
Treatment of respiratory failure in children includes the use of bronchodilators , mucolytic drugs, and inhalations .
Specific drugs will be discussed below.
In severe stages, the child is connected to a ventilator, and after spontaneous breathing is restored, intensive oxygen therapy is administered.
Complications and consequences
If the disease is not treated, negative consequences may occur, which manifest themselves in the form of:
- Pleurisy . Characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the respiratory system.
- Pulmonary abscess . Accumulation of pus in the cavities of the lungs.
- Blood poisoning . It entails a very serious condition; for a weakened child’s body, the likelihood of death increases.
- Endocardial damage. The inner lining of the heart suffers. This entails various heart diseases.
- Anemia, blood clotting disorder. The baby may be pale; in case of anemia, nutrients are not absorbed in the required quantities.
- Psychosis . The disease negatively affects the nervous system, leading to psychosis and stress. The baby becomes nervous and irritable.
Dyspnea
Dyspnea is difficulty breathing, accompanied by a feeling of lack of air. In this case, distant wheezing (whistles and noises during inhalation and exhalation) may also be observed. The reason is the accumulation of exudative fluid in the alveoli of the lungs. The appearance of shortness of breath is a reason for urgent hospitalization due to the high risk of pulmonary edema. The child should be in a position with the upper body elevated; infants are placed on their stomach.
Mucolytic and bronchodilator are indicated to relieve symptoms and treat shortness of breath . After the acute period is over, inhalations are used. The drugs will be discussed below.
Prevention of pneumonia in young children
The key to a child’s health is breastfeeding, prevention of rickets, restorative massage and gymnastics, hardening (air baths and rubbing). During epidemics of respiratory infections, it is especially important to limit the baby’s contact with strangers, even with relatives. It is advisable for adults who live in the same apartment with a child to get a flu shot. If the mother becomes ill with a respiratory viral infection, it is necessary to continue breastfeeding, because the baby will receive antiviral antibodies with milk. The only condition for this is the use of a protective mask. Even a mother taking antibiotics is not a contraindication for breastfeeding; the drugs that are safest for the baby are simply selected.
Wheezing
Wheezing is a noise in the chest heard when breathing. Wheezing is a sure sign of inflammation , especially in children. They appear due to uneven air flow in the lungs during an inflammatory process in the tissues of the lungs and adjacent parts of the bronchial tree.
There are several varieties:
- Crepitation . A quiet sound made by the alveoli of the respiratory organ when inhaling. Manifests itself at the initial stage of pneumonia.
- Wet wheezing . They arise due to the accumulation of fluid in the bronchi and lungs due to inflammation.
- Dry wheezing . Appear in the absence of an obstacle in the form of liquid. More often observed with swelling of the bronchial mucosa.
- Pleural friction noise . A scraping sound is characteristic. Occurs as a complication of pneumonia - pleurisy.
The treatment strategy for wheezing depends on its type and stage of the disease. Since they are a manifestation of pneumonia itself, antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for wheezing. Expectorants and inhalations improve the effectiveness of treatment.
Pneumonia with mild symptoms
appear much weaker in them than in older children. only an X-ray examination can detect the disease in young children . It must be prescribed in any suspicious cases - young children are very susceptible to this disease.
Suffice it to say that schoolchildren suffer from pneumonia much less often. If in children under 1 year of age pneumonia occurs in 15-20 cases per 1 thousand patients, then at school age this figure drops to 7 .
In the absence of cough and fever, but difficulty breathing, sweating, and signs of general intoxication, a medical examination should usually show the presence of wheezing in the lungs.
Treatments
In the treatment of difficulty breathing and respiratory failure, bronchodilators play a major role. These are medications that relieve bronchial spasm and restore breathing. They come in short- and long-acting forms, and are available in the form of sprays, syrups and solutions for inhalation.
Children are usually prescribed inhalations with bronchodilators, which are carried out using nebulizers. Inhalation medications approved for use in childhood include substances such as salbutamol, fenoterol, ipratropium bromide, budesonide.
These drugs are used to eliminate bronchospasm and are prescribed by a doctor strictly according to indications!
In the presence of wheezing (wet) and shortness of breath, mucolytic agents are used. They liquefy mucus and remove it from the lungs. This group includes medications based on ambroxol, acetylcysteine, and bromhexine. All of them have certain contraindications and side effects.
Expert opinion
Lyudmila Sokolova
Pediatrician, doctor of the highest category
Ask a Question
All drugs, dosages and treatment regimens are determined by the doctor. Self-use is prohibited.
Risk group
Most often, pneumonia affects young children, less often schoolchildren. In adults, chronic forms of the disease are observed.
Why are babies 1-2 years of age at risk? To answer this question, it is enough to pay attention to the development of the child’s respiratory system:
- the respiratory system is not yet fully formed and has narrower ducts;
- reduced level of gas exchange as a result of underdevelopment of lung tissue;
- blood vessels in the mucosa are located almost on its surface, which leads to vulnerability and swelling of the latter;
- immaturity of the cilia complicates the separation of sputum and its removal from the body;
- at an early age, children are characterized by abdominal breathing, that is, all breathing is through the stomach;
- weakly developed immunity.
Often, predisposition to the disease is influenced by the environment, passive smoking and lack of child care.
Double pneumonia in a child aged 2-3 years is rarely contagious. More often, this is a consequence of untreated infectious diseases. Due to the nature of the respiratory system, the lungs are poorly ventilated, thereby creating ideal conditions for the development of bacteria. If action is not taken in time, pneumonia can be fatal.
Reference materials (download)
| # | File | file size |
| 1 | Pneumonia in children. Clinical recommendations. | 180 KB |
| 2 | Guidelines for using the spirometry method | 669 KB |
| 3 | Clinical pharmacology of drugs for the treatment of respiratory diseases | 4 MB |
| 4 | Laboratory standards (blood, biochemical, feces, respiratory function, etc.) | 218 KB |
| 5 | Use of expectorants | 32 KB |
| 6 | Nebulizer therapy. Kozlovsky.2014 | 4 MB |