With hydrocephalus, a lot of excess fluid accumulates in the head. If a person is healthy, then in his skull there is also fluid (cerebrospinal fluid), which is formed in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the brain. Moving in the brain between the ventricles, the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord, it carries nutrients to all brain cells.
Another function of cerebrospinal fluid is to cleanse the brain of metabolic products. Hydrocephalus develops due to the fact that the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted, and it begins to accumulate in the skull. The patient's intracranial pressure gradually increases. The majority of cases of this disease are among infants, as they have a specific brain structure.
Types of hydrocephalus
In cases where there is an obstacle on the path of the cerebrospinal fluid from the lateral ventricles to the exit from the fourth ventricle and the cerebrospinal fluid cannot freely enter the subarachnoid space, hydrocephalus is called non-communicating (closed, occlusive). In other cases, hydrocephalus is called communicating (open). Hydrocephalus can be primary (as the underlying disease) and secondary, i.e., a complication of other diseases (tumors, malformations of the central nervous system (CNS) and cerebral vessels, etc.). There are many classifications of hydrocephalus, but these are the main ones and are used most often.
Features of the disease in newborns
This disease
Not only newborns are susceptible, but also older children and even adults. As noted above, this disease disrupts the circulation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Typically, cerebrospinal fluid washes the cavities of the brain and its outer membranes, performing protective functions. The brain seems to “float” in this liquid.
In case of disturbances caused by various circumstances, the circulation of this fluid and its natural absorption are difficult.
Therefore, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the ventricles and subarachnoid space of the brain, causing disruption of its functioning and enlargement of the head. Intracranial pressure increases. Brain swelling may occur. Liquor looks like water, hence the name hydrocele.
Features of this disease in a newborn include the following:
- Deformation of the child's skull, excessive head growth.
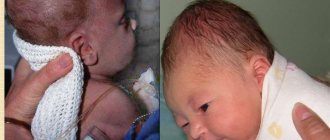
Due to the fact that the bones of a newborn’s skull are soft and have not fully fused, when fluid accumulates in the brain, the head circumference increases sharply. Especially the frontal part. The fontanelles protrude and enlarge, the scalp becomes thinner, the subcutaneous veins swell, the eyes seem to sink, the forehead droops, and the shape of the skull is deformed. Such features are in the photo.
- It can be either congenital or acquired as a result of birth trauma.
Congenital hydrocephalus can be caused by certain infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy. For example, toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus. Hemorrhage during pregnancy, genetic pathology, malformations of the brain and spinal cord.
- It is important to diagnose the disease in a newborn in a timely manner. To do this, the doctor prescribes a set of examinations, including NSG of the brain.
In infancy, up to 1 year, neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) can help with this.
Manifestations of hydrocephalus
Impaired circulation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid leads to its excessive accumulation and increased intracranial pressure. This manifests itself differently in children under 2 years of age and in older children.
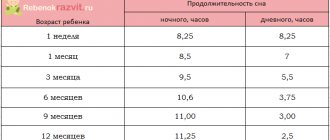
The main symptom of the development of hydrocele in children under 2 years of age is accelerated growth of head circumference. The sutures of the skull in babies have not yet healed, and the size of the head increases because the bones of the skull are pushed apart from the inside by the growing brain. In the same way, a balloon increases in volume when we inflate it. There is a graph for head circumference growth. It must be measured every one to two months; this is done by the local pediatrician during preventive examinations. If the baby’s head grows faster than normal, this is an alarming symptom; it most often indicates the development of hydrocephalus, when accelerated head growth occurs due to an excess of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain. This is often the first symptom of the disease. In addition to accelerated head growth in children, an enlarged and bulging large fontanelle can be detected, which should close by approximately 1 year, but with hydrocephalus it can be open until 2 or even 3 years. The bones of the skull become thinner, the forehead becomes disproportionately enlarged and protruding. A venous network appears on the forehead and face. In more advanced cases, the eyes may droop downwards (Graefe's symptom). The tone of the leg muscles increases. Convulsive seizures may occur.
The child begins to lag behind in the rate of psychomotor development. He doesn't hold his head in time, doesn't sit, doesn't get up, doesn't play. A sick child is lethargic, apathetic, and at times unmotivatedly whiny. The baby may be experiencing a headache: he may clutch his head.
Most symptoms of increased intracranial pressure can only be recognized by an experienced pediatrician, neurologist or neurosurgeon, but parents can measure the rate of head growth themselves and check it using special charts. In any case, the accelerated growth of the child’s head circumference, as well as an incomprehensible lag in the pace of its development, should serve as a reason for a serious examination of the baby by a neurologist or neurosurgeon to rule out hydrocephalus.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in infants
Manifestations of external hydrocephalus
If a newborn has such a disease, this can be understood by visible signs:
- Large head sizes. A head with a circumference of 33.0 to 37.5 cm is considered normal;
- "Sunset" symptom. There is a noticeable displacement of the eyeballs under the lower eyelid;
- The fontanel protrudes above the surface of the head. This gives the impression of a convex tubercle. Normally, the fontanel does not protrude above the surface of the head;
- The venous network is clearly visible. Its manifestations are noticeable on the temples, and in some cases, on the child’s forehead;
- The frontal lobe of the head is noticeably protruding;
- The scalp is too thin. In medicine, this phenomenon is called “marble skin”.
When parents see some of these symptoms in their children, they begin to panic. This disease appears in the baby due to infection in the mother's womb. In some cases, the disease is inherited.
Internal hydrocephalus and its symptoms
It is impossible to draw a conclusion based on the presence of such a disease. This will require consultation with specialists.
The following symptoms are characteristic of internal dropsy:
- The baby sleeps constantly. Sometimes it takes a lot of effort to wake up a baby;
- The child is capricious and refuses to eat;
- Cases of regurgitation are higher than normal;
- There are cramps in the limbs, the chin shakes;
- Vision is impaired. The eyeballs may move in a chaotic manner.
Unfortunately, with age, the size of the head will become increasingly larger. In this case, it is necessary to regularly measure your head circumference once a month. Normally, circumference growth per month is no more than three centimeters. You should also monitor the ratio of the size of the child’s chest and head. Another serious complication of the disease is the baby’s developmental delay. The baby is passive, recovers quickly, and may be obese.
The following signs may also indicate the presence of hydrocephalus:
- at three months the child cannot hold his head up on his own;
- does not roll over onto its side;
- does not respond to toys;
- does not show motor activity.
Signs of a mixed type of disease
With mixed hydrocephalus, a mixture of different signs is also observed. Some of the kids have a protruding forehead and indifference to others, others refuse to eat and have symptoms of “setting sun.” No specialist can give an exact answer to the question about the difference in symptoms.
As mentioned earlier, such a disease can become acquired. Therefore, parents need to do everything to prevent their child from having head injuries.
Signs that indicate dropsy of the brain can be completely different. But as soon as parents notice at least one of them, it is necessary to immediately take the child to the doctors, there is no delay. Doctors will prescribe many different examinations to clarify the diagnosis.
This may be a tomography, ultrasound of the brain, consultation with an ophthalmologist, fluoroscopy of the skull
Causes of hydrocephalus in children
The causes of hydrocephalus are very diverse and largely depend on the age of the child.
- Hydrocephalus in the fetus. Modern types of prenatal diagnostics (for example, ultrasound examination) can detect hydrocephalus in an unborn baby. In most cases, it is caused by various malformations of the central nervous system (CNS). In 20%, dropsy is associated with intrauterine infections (cytomegaly, herpes, toxoplasmosis). When planning a pregnancy, parents should undergo testing for these infections, which often occur hidden, and treat them. This will avoid many problems with the baby's health. In rare cases, hydrocephalus is caused by genetic disorders.
- Hydrocephalus of newborns. Most often (up to 80%) dropsy in newborns is caused by malformations of the brain and spinal cord and the consequences of intrauterine infections. In approximately 20%, hydrocephalus is a consequence of birth trauma, especially in premature infants, which is accompanied by intracerebral or intraventricular hemorrhage and associated meningitis (inflammation of the meninges), which leads to impaired absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. It is extremely rare at this age that tumors and vascular malformations of the brain are detected, which can also cause the development of dropsy.
- Hydrocephalus in babies and older children (1-2 years and older). There are many reasons for the development of hydrocephalus in such children. These include tumors of the brain and spinal cord; consequences of meningitis, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), various infectious diseases (for example, tuberculosis); malformations of the brain and cerebral vessels; consequences of hemorrhages; consequences of traumatic brain injury; genetic disorders. Sometimes the cause of hydrocephalus cannot be determined.
What are the signs of illness in a child?
To begin with, you should pay attention to the emotional state of the child; alarm bells may include signs such as continuous crying and constant restlessness, difficulties with feeding, and problems with head and neck mobility.
Congenital hydrocephalus can be immediately identified by obvious external parameters. The most important feature is head circumference. Relative to established development standards, the size of an infant’s skull should increase by an average of 1 cm per month.
According to this norm, the rest of the baby’s physical parameters must be strictly proportional. These include weight, height and chest circumference.
As a result of the examination, the attending physician decides whether there are any abnormalities and what additional tests and measurements need to be performed.
If the pediatrician sees that the child’s skull has a hydrocephalic shape, which is characterized by a disproportionately large size of the head relative to the body, then he will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Other symptoms of hydrocephalus in newborns include:
- Excessively high intracranial pressure
- Problems with the fusion of the fontanel - remains open for three years or rounded surfaces form in its place
- Problems with the eyeballs - their displacement, strabismus or constant active vibrations
- Nausea and vomiting
- Periodic seizures
- Deterioration of sleep
- Hearing and vision loss
The above signs may apply not only to younger but also older children.
However, over time, headaches, involuntary urination, memory loss, and low level of motor coordination may develop. In the last stages of the disease, a general slowdown in development is observed.
How is the diagnosis made?
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus is based on the clinical picture, examination of the fundus, as well as additional research methods, such as neurosonography (NSG), ultrasound examination of the brain (in infants under 2 years), computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain brain The primary diagnosis can be made by a neonatologist, pediatrician, neurologist or neurosurgeon.
If any brain pathology is detected, a CT or MRI is necessary. Without them, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis, identify the cause of hydrocephalus, and even more so carry out treatment. This equipment is expensive and is still not installed in all hospitals. In this case, parents should insist on having a CT or MRI scan performed at other centers or perform them themselves on a commercial basis. It should be borne in mind that a clinic that undertakes the treatment of children with hydrocephalus is required to have this equipment. Otherwise, we can recommend that parents choose another, more equipped hospital, at least in another city.
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus in newborns
If hydrocephalus began its development in the womb, then doctors must determine this diagnosis using ultrasound. Nowadays, such examination is necessary for all pregnant women. To confirm the diagnosis, blood is taken from the umbilical cord (cordocentesis) or from amniotic fluid (amniocentesis).
Pediatricians and specialists examine the newborn immediately after birth. But it is not always possible to draw a conclusion about this type of disease during this period of a child’s life. Unfortunately, if there are no external manifestations, then the child cannot yet explain what is bothering him.
There are often cases when, without fully understanding the cause of the baby’s illness, he is prescribed the wrong course of therapy, and this threatens to worsen the problem. Time is lost, the disease is progressing.
An experienced neonatologist may notice a problem during the first examination of the baby. If this does not happen, then the only hope lies with the pediatrician, who sees him quite often in the first months of the baby’s life and may notice undesirable symptoms. If a personal doctor notices a problem, the child is referred for a consultation with a neurologist.
With the development of medicine, it became possible to conduct various high-precision studies. First of all, we are talking about neurosonography. The examination is carried out using ultrasound through the child's fontanel. For the baby, this procedure does not pose any danger and goes away very quickly (within 5-10 minutes).
Nowadays, at the age of two months, all children without exception undergo such an examination. Thanks to this method, it is possible to detect the presence of various pathologies in time. And this contributes to an earlier start of therapy and obtaining the desired effect.
If the picture is not entirely clear, doctors may recommend further procedures. These can be various examinations and consultations:
- More accurate information about the baby’s condition can be obtained by performing MRI and CT scans. During this examination, the baby is given general anesthesia;
- consultation with an ophthalmologist. A doctor examines the fundus of a small patient;
- during craniography, the size of the head and the presence of suture divergence are studied;
- A common type of diagnosis today is lumbar puncture. Cerebrospinal fluid samples help determine the presence of infection and the pressure that cerebrospinal fluid puts on the brain;
- conducting magnetic resonance angiography and electroencephalography. These are additional ways to examine patients.
Based on the results obtained after carrying out all the above diagnostic methods, doctors determine the diagnosis and the necessary course of treatment for the baby. Important! You don’t need to think long before agreeing to have your child examined. This is exactly the situation when delay is like death.
You can find out how to reduce a child’s temperature in our article. Read about the signs of bronchitis in children here.
Read about antibiotics for children here
Treatment of hydrocephalus
It is not easy for parents to decide whether to undergo surgery. However, a prolonged increase in intracranial pressure causes a delay in psychomotor development, which cannot always be compensated after unreasonably delayed surgical intervention. It should also be noted that the excessively large head of a child suffering from dropsy, even after the operation, will no longer return to its previous size - it will only be possible to stop its further growth. Literally, it will be difficult for the child to carry it on his shoulders, in addition, it will cause many cosmetic problems in the future. Parents of children with hydrocephalus should be aware that even if the neurologist does not refer them to a neurosurgeon, they should take the initiative and organize this consultation themselves.
The purpose of the operation is to divert cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain to other cavities of the body. The most common operation is ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS). Through a system of silicone catheters, cerebrospinal fluid from the lateral ventricle of the brain flows into the abdominal cavity, where it is absorbed between the intestinal loops. The amount of flowing liquor is regulated by a special valve. Catheters are placed under the skin and are not visible from the outside. More than 200 thousand such operations are performed annually in the world. Bypass systems have saved millions of children's lives.
Less commonly, the cerebrospinal fluid is diverted into the right atrium (ventriculoatrial shunt), into the cistern magna (Torkildsen operation), or the spinal canal at the lumbar level is connected by a catheter to the abdominal cavity (lumbo-peritoneal shunt).
With the development of modern endoscopic technology (an endoscope is inserted into the cavities of the human body through small incisions, allowing them to be examined and manipulated), it has become possible to treat patients without installing a shunt system. Using an endoscope, a bypass path for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is created deep in the brain. This is a very effective operation (called endoscopic ventriculostomy), which avoids the implantation of a foreign body, such as a shunt system, and thereby prevents many complications. Unfortunately, this operation can only help a limited number of patients (about 10% of the total number of patients) with some forms of occlusive hydrocephalus. In other cases, it is necessary to install a shunt system, since there will be no improvement from endoscopic surgery.
Treatment
Treatment of hydrocele in newborns is carried out on the basis of diagnostic studies by a neonatologist, neurologist, or neurosurgeon. Doctors use two treatment tactics: medication and radical (surgical).
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is aimed at reducing intracranial pressure by reducing the production of cerebrospinal fluid and speeding its removal from the brain. For open, non-progressive hydrocephalus, Diacarb is prescribed. The medicine removes potassium from the body, blocks some enzymes, and increases urination. Take it on an empty stomach in an adult dosage.
There are two types of diuretics that accelerate the elimination of excess fluid:
- Osmotic , increasing plasma osmolarity. Under their influence, water from the brain moves into the vessels and is excreted naturally. These are Glycerin, Dulcite, Sorbitol, Mannitol.
- Saline , removing fluid, blocking sodium absorption (Furosemide).
Treatment of hydrocephalus is carried out under the strict supervision of doctors. They can also prescribe Encephabol, Aminalon, Bravinton, Calcium hopanthenate, which eliminate intracranial hypertension.
If medications do not help reduce intracranial pressure and eliminate other signs of hydrocele in newborns, doctors resort to radical measures.
Surgical treatment
Surgery stops the progression of dropsy and saves the brain. Modern doctors often use endoscopic techniques to avoid bypass surgery. A small endoscope is inserted deep into the brain. It creates a bypass channel for the exit of cerebrospinal fluid. This operation is called endoscopic ventriculostomy.
But in most cases, doctors use a shunt system that drains fluid into the right atrium. Successful surgery stops the progression of hydrocele, and many children can return to normal life.