In neonatology, this pathological condition is called: “increased neuro-reflex excitability” or is defined as “hyperexcitability syndrome” by a neonatologist or diagnosed by a pediatric neurologist immediately after the first consultation.
But many parents may notice that “something is wrong” with the baby - the child sleeps poorly, constantly shudders (and not only from frightening sounds, but also at rest), there is tremor of the chin and arms, sluggish sucking, frequent regurgitation. arching of the baby and many other signs.
Many specialists in Europe and the USA consider this syndrome to be a borderline condition that does not require therapy, and our pediatric neurologists prescribe treatment for children.
Who is right and how to behave in this situation?
After all, many parents take the same position - everything will go away by itself and “there is no point in stuffing the child with various chemicals immediately after birth...”.
In this article I want to understand this situation from the point of view of a practicing pediatrician.
Reasons or why this happens
First of all, you need to understand that neuro-reflex excitability is a normal, healthy reaction of the body to stimuli. Conditionally pathological is increased excitability.
I use the term conditionally pathological due to the fact that the baby’s nervous system finally “matures” after it is born. And even if your child exhibits symptoms of increased neuro-reflex excitability, it is quite possible that as the nervous system matures, these manifestations will disappear on their own, without additional treatment.
Please note that only a doctor can decide whether treatment is necessary or whether it is useless.
And so, back to the reasons. If by the end of the first half of the year the child still has symptoms of increased excitability, there is reason to talk about damage to the central nervous system (CNS). It is in her defeat that the essence of the problem lies. The central nervous system can be affected both during fetal development and during childbirth and in the postnatal period.
The mechanism is simple - connections between the cerebral cortex and its deeper parts responsible for the perception of the outside world are disrupted.
What is the danger of hyperexcitability syndrome?
It is important to remember that in the absence of timely treatment, hyperexcitability syndrome may develop:
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder;
- neuroses;
- weather dependence;
- anxiety disorders;
- minimal brain dysfunction;
- delayed speech development and/or mental development;
- epilepsy or other serious organic changes in the nervous system that are masked by hyperexcitability syndrome.
Therefore, children with various manifestations of hyperexcitability syndrome should be constantly monitored by a pediatric neurologist and fully follow all the doctor’s recommendations. This will significantly reduce the risk of complications.
pediatrician Sazonova Olga Ivanovna
Save
Article read: 1,284
What leads to damage to the central nervous system
- prematurity
- chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia
- hypoxic-ischemic brain damage during childbirth
- intrauterine infections, especially viral (usually herpesvirus)
- incompatibility of fetal and maternal blood (Rh conflict)
- traumatic, infectious, toxic brain lesions in the intra- and postnatal period
- medical error during childbirth (birth trauma)
You can click on the selections and get acquainted with the details.
Signs and symptoms of increased neuro-reflex excitability
- First of all, you cannot help but pay attention to the sleep disturbance of an infant. Shallow, restless sleep, with long hours of wakefulness and desperate crying.
I met parents who tried to “raise” their baby, not paying attention to his crying. Iron nerves! I don't think such upbringing is beneficial. A healthy child spends the first months of life more asleep than awake. If the baby cannot sleep and cries, then there are reasons for this and these are not whims.
- Frequent and unmotivated crying is also one of the symptoms of increased excitability
- Reaction to external stimuli. An unexpected sound, rapid movements or the movement of large objects in the child’s field of vision lead to flinching, excitement, and it looks like fear. The child shudders, arms outstretched, freezes for a moment, then increased chaotic motor activity follows and ends with crying again
Our daughter had this symptom especially pronounced. We could calmly react to a passing plane, because the sound, although loud, grew gradually. But from some ringing sounds in words, not necessarily spoken loudly, she not only shuddered, but shuddered. For example, these were the sounds of the letters Z, S, D
- Increased spontaneous motor activity. Spontaneous movements are physiological movements produced unconsciously
- Unconditioned reflexes are excessively animated, and tendon reflexes are also increased. You can read about reflexes in an article specifically dedicated to them.
- Tremor - trembling of the limbs and chin, blueness of the nasolabial triangle during crying
Symptoms of hyperexcitability
Manifestations typical for the syndrome begin to appear at the very beginning of the baby’s life. The main clinical symptoms include severe neuropsychic excitability, somatovegetative disorders, and exhaustion.
In children who suffer from hyperexcitability, the following symptoms can be noted:
- Increased and spontaneous motor activity;
- Sleep disturbances (wakefulness is significantly longer, the child has difficulty falling asleep, his sleep is intermittent, and he often starts in his sleep).
Despite receiving proper care and nutrition, children tend to behave restlessly and cry very often for no apparent reason. When a baby screams, he may experience some vegetative reactions, namely:
- The skin turns red or becomes marbled;
- Acrocyanosis, tachycardia, tachypnea, and increased sweating are present.
Such children tend to latch poorly, are interrupted during feeding, and have a tendency to regurgitate heavily, as well as gastrointestinal disorders (constipation alternating with diarrhea). Poor weight gain.
There are also such typical signs indicating hyperexcitability in newborns:
- The presence of variable muscle tone;
- There is tremor of the hands and chin;
- There is a revival of congenital unconditioned reflexes (spontaneous Moro reflex);
- Characteristic features include foot clonus and horizontal nystagmus.
In children with a similar pathology, one can observe rapid motor, emotional and sensory reactions to various external stimuli, which fade away as quickly as they appear. Thus, increased mental exhaustion manifests itself.
In premature babies, the disease is a reflection of the threshold of convulsive readiness; in these children, convulsions begin very easily (due to hyperthermia, exposure to strong irritants, and the like).
With a favorable course of the pathology, the severity of its symptoms in most cases decreases in the period from 4 to 6 months, and by the year it disappears completely.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
In the case of an unfavorable course over time, one can note the presence of a slight lag in speech and psychomotor development, pronounced activity, encopresis, enuresis, nervous tics, stuttering, anxiety disorders, parasomnia, and epilepsy. The second option requires special treatment.
What examinations need to be done
To find out the extent of damage to the central nervous system and correctly prescribe treatment, additional examinations will be recommended. It is quite possible that among them will be:
- Neurosonography
This is an ultrasound examination of the brain, which is performed through the fontanel. The survey is quite informative. Allows you to assess the state of the brain substance, liquor pathways, see developmental defects, and also, with a certain degree of probability, understand the cause of the lesion - hypoxia, hemorrhage or infection. The examination is believed to be absolutely harmless.
- Dopplerography
The examination allows you to assess the condition of the blood vessels supplying blood to the brain and the condition of cerebral blood flow, respectively.
- EEG, electroencephalography
This examination evaluates the state of the bioelectrical activity of the brain, the degree of its maturity, as well as the prerequisites for the convulsive syndrome.
Main signs
Key signs of hyperexcitability in an infant boil down to:
- Poor sleep, and not from time to time, but regularly. He has trouble falling asleep and often wakes up at night from any noise. In the middle of the night it makes sounds similar to screaming or crying.
- Low appetite. Doesn't eat enough and is reluctant to take a breast or bottle. Sucks lazily.
- Clenching your fists.
- A pained expression on his face.
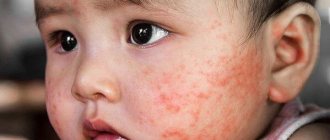
- A child's skin may appear bluish (marble-colored) or red at first glance, as it is pierced by a network of blood vessels located very close to its surface.
- From the outside, the child seems constrained and tense.
Watch your baby: hyperexcitability syndrome in newborns shows itself almost instantly. It will not be difficult for observant parents to notice that something is wrong with their baby and his actions differ from generally accepted standards at this age.
What are the symptoms of hyperexcitability in infants identified by Komarovsky? You can familiarize yourself with the treatment offered by a famous pediatrician and the symptoms of hyperexcitability by watching the video below.
Treatment and rehabilitation measures
The doctor will prescribe medication. I assume that it will be aimed at reducing nervous excitability and correcting intracranial hypertension.
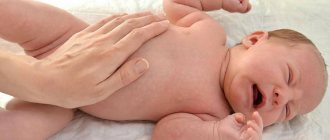
Among the rehabilitation measures, massage is a must. Learn massage yourself, because mother's hands have an additional therapeutic effect. Massage and crying don't mix. The goal is to relax and calm the baby's nervous system, and crying is unlikely to contribute to this.
Therapeutic gymnastic exercises. The main one is rocking in the fetal position. You can do it in your hands, you can do it on a gymnastic ball. In general, oscillatory movements calm and relax, for the first year of our lives we walked exclusively on swings))) Just don’t get confused, the child needs to be rocked, not shaken.
And of course hydrotherapy. I think you understand that bathing is a hygienic procedure. We are talking about swimming in a lot of water, in a large bath. About taking herbal baths, about a light underwater massage in the shower. You can follow the links and find out more about it.
Predictions and consequences
If increased neuro-reflex excitability is caused by elementary immaturity of the nervous system, the prognosis is favorable. The measures recommended and taken by you, the maturation of the brain as it grows, will reduce the problem to nothing.
If the reason is a more serious damage to the central nervous system, the options are not so optimistic, it all depends on the degree of damage. The most serious consequences can be the development of epilepsy and cerebral palsy. But this is not the worst thing, believe me! And you can cope with this and achieve good results.
Perhaps I have exhausted my knowledge about increased neuro-reflex excitability. You and I found out what its causes are, got acquainted with the signs and symptoms, and decided on examinations, treatment and rehabilitation measures. We know that in any case, consultation with a doctor is mandatory.
If I missed anything and have any questions, please write. I will definitely answer.
9 Feb 2014
Syndrome of increased neuro-reflex excitability (hereinafter referred to as HIRS) refers to neurological disorders. Diagnosed in children from birth to one year. The diagnosis can be made by a neurologist based on examination and some studies. Mostly, SNRV is diagnosed in children under 3 months of age.
Often this syndrome is not detected in time, since consultation with a neurologist is not mandatory after the birth of the child. In this article, we will look at the main signs of SIDS and tell you how not to miss timely treatment.
First of all, every mother should understand that a healthy child needs little - food, sleep, comfort. A week after being discharged from the maternity hospital, the newborn’s routine will already be established, and you will see how much he sleeps, how often he eats, how long he stays awake. If a child is full, dry, and does not want to sleep, he should not scream. The cry of a newborn is not a whim, but a signal of discomfort.
Children with SAD sleep little, it is difficult to feed and calm them. They react painfully to any touch and often flinch. Especially for visitors to the site razvitierebenca.ru. These are the first signs that you should pay attention to.
It is necessary to observe the child’s motor activity. If at least one of the clinical symptoms listed below is detected, the baby should be shown to a specialist. Especially for the site razvitierebenca.ru
The syndrome occurs due to damage to the child’s nervous system perinatally. Various factors can contribute to this, such as:
- hypoxic disorders during fetal development;
- complications during childbirth (placental abruption, bleeding, asphyxia, etc.);
- C-section;
- maternal drug addiction;
- multiple births;
- maternal diseases during pregnancy (infections, diabetes).
Characteristics of the disease
According to some estimates, hyperexcitability in infants is diagnosed in more than 40% of children born.
The attitude towards this phenomenon in different countries is ambiguous. Thus, in Europe, hyperexcitability is considered a borderline (temporary) condition that does not require special adjustment, while in the countries of the post-Soviet space it is considered a pathology that requires treatment. Increased nervous excitability in psychology is the human body’s reaction to overwork, a large amount of information and conflicts. The disorder affects 20% of the population and occurs in children, adult men and women. The formation of this disorder is influenced by hereditary predisposition, metabolic pathologies and hormonal imbalances in the body.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytadvertiseru
Depressive states, neuroses, psychopathy and schizophrenia also provoke the development of this disease. Increased nervous excitability occurs in people during withdrawal symptoms (after prolonged use of alcohol) and drug addiction. Also, the reasons for the formation of nervous excitability include the following:
- poor nutrition;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- constant stress;
- individual psychological characteristics (suspiciousness and anxiety);
- caffeine overdose;
- lack of B vitamins;
- past infectious diseases;
- degenerative disorders (Alzheimer's disease).
Clinical symptoms of SNRV:
- sweeping movements of the limbs;
- decreased sucking reflex;
- chin trembling;
- poor sleep;
- throwing the head back;
- tremor of the limbs;
- frequent crying;
- increased tendon reflexes;
- motor restlessness;
- long look at one point.
What is the diagnosis based on?
Upon visual examination by a specialist, the child tenses up and a high-pitched cry appears. There is anxiety, and convulsions are often observed. In response to stimuli (sounds, light, loud voices, touches, changes in body position), muscle motor activity increases.
Muscle tone and spasms appear. Intracranial pressure may be increased. The specialist will check whether the child’s behavior matches his physical development.
Sometimes the child is so excited that it is impossible to calm him down. In this case, it is likely that there are other lesions of the nervous system (movement disorder syndrome, psychomotor development delay syndrome, vegetative-visceral dysfunction, hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, etc.)
If there are insufficient visual signs, an additional study is prescribed - neurosonography. This is an ultrasound scan of the child’s brain, which does not cause radiation exposure to the body. This diagnostic method has no contraindications.
Main clinical manifestations and types
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
There are basic symptoms of a person’s excited state. These include the asymmetric nature of the facial muscles and disturbances in the movement of the eyeballs. Disturbances in spatial orientation are noted.
Such personality characteristics of patients as conflict and increased irritability are observed. Patients get nervous over little things and lash out at loved ones and their subordinates. They are often bothered by nightmares. There is increased tearfulness, melancholy and self-pity.
The person is verbose and performs impulsive actions that indicate psychomotor agitation. The patient complains that he cannot fall asleep for several hours, tosses and turns in bed and wakes up in the middle of the night.
| View | Characteristic |
| Hallucinatory-delusional | There is isolation and tension. The patient experiences fear and anxiety. The clinical picture includes hallucinations and delusions. Because of this, the patient poses a danger to himself and others |
| Depressive | There is a depressive depressed state. The patient is pessimistic about the future |
| Catatonic | Movement disorders are noted. The patient’s speech is slurred, and his behavior is absurd and inappropriate for the social situation. |
| Manic | There is an increased emotional background, sudden mood swings (emotional lability) |
| Psychogenic | Occurs against the background of psychological trauma (death of a loved one, breakup of a relationship, road accident). There is panic and fear. Suicidal attempts and thoughts are observed |
| Epileptic | Occurs in individuals who suffer from epilepsy due to hallucinations. Paroxysms come and go abruptly, without warning |
| Embittered | This condition occurs in a person in relation to the person who is the offender. The patient is tense, screams, insults another. Sometimes hysterical attacks develop |
- constant stress of a pregnant woman;
- early weaning of the child;
- taking medications during pregnancy that were not prescribed by doctors.
In children under 4 years of age and newborns, increased nervous excitability has its own characteristics. There is motor restlessness that occurs when touched or changing position. If a child hears a sharp sound, he begins to shudder. Increased nervous excitability occurs in children if disturbances in the central nervous system (CNS) occur during childbirth or in early infancy.
Newborns have restless and short sleep. They often lie with their eyes open. In infants, the plantar reflex does not work. Regurgitation and slow weight gain are observed.
If treatment is incorrect or absent, consequences may occur. This disorder progresses into ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder). Such children become restless, forgetful and aggressive.
Subsequently, if untreated, they suffer from speech delay, i.e., vocabulary accumulates more slowly than that of healthy peers. The child uses phrases incorrectly. Motor acts suffer.
Diagnosis of this disease in children is carried out by asking the mother about the progress of pregnancy and childbirth. In this way, the child’s development is checked for appropriateness to his age, on the basis of which a diagnosis is made. Depending on the severity and type of violations, the necessary drug treatment is prescribed. In addition to medications, it is recommended to correct the daily routine, attend massage and swimming sessions.
Treatment of SNRV
Prescribed by a neurologist. Does not require hospitalization, includes conservative methods.
- Massage. It is one of the most effective treatment methods. Acupressure, general, relaxing massage may be prescribed. The main effect is aimed at reducing muscle tone and general excitability.
For children, it is better not to use aromatic oils for massage, as they can cause allergies. It is better to get by with baby cream or special baby oil, approved from birth. Massage should be performed only by a specialist, preferably within the walls of a clinic.
- Drugs to improve cerebral circulation. Newborns are usually prescribed drugs in the form of a suspension. Some drugs are available in the form of dragees or tablets - in this case they need to be crushed and mixed with breast milk or water. The dosage is calculated according to the child's weight.
- Setting the mode. Any specialist will confirm that the daily routine is the basis for the normal development of a child. For children with disorders of the central nervous system, adherence to the regimen is necessary for therapeutic purposes. Babies cannot control their rest due to the imperfection of the nervous system. Sleep should be by the hour, walks in the fresh air are required.
- Swimming, gymnastics. Labor-intensive but effective method. Its essence lies in the daily supply of the right impulses to the brain. By performing physical activity, the brain “gets used” to processing more information, and with medications it begins to work faster. Thus, damaged tissues are restored faster.
The benefits of water are invaluable: it relaxes tense muscles and tones weakened ones. Spasms are relieved, metabolism is stimulated, blood circulation improves. Water relieves tension and has a hardening effect, which is especially useful for newborns.
It is better to swim with your child in the pool, according to a specific program for the little ones. A specially trained trainer will help you perform exercises in the water, which you can then repeat at home. The temperature difference method is effective: gymnastics in water of different temperatures gives positive results 2 times faster.
A child cannot perform gymnastics on his own. You will need the help of a massage therapist or pediatric specialist.
- Aromatherapy. Natural oils that neutralize excessive excitability can be prescribed with caution. It could be lavender, geranium, marjoram, mint. For very young children, diluted, non-concentrated oils are used.
The oil must be dosed carefully, 1-2 drops at a time. To do this, it is better to purchase an aroma lamp and place it in the room where the child is. Adding essential oils to baby’s bath water is strictly prohibited - they can cause burns!
- Herbal baths. This could be an herbal mixture or a specific plant. Chamomile, string, mint, lemon balm, hawthorn, and pine are widely used. Children's skin is highly permeable due to the abundance of nerve endings, so the healing properties of plants penetrate into it instantly. The water temperature for newborns should be 36-37 degrees. The course consists of 10-15 procedures.
- Prescribing diuretics. Justified in case of high blood pressure in a child. Additionally, medications with potassium are prescribed.
Any method of treatment must be completed over a course. Therapy usually involves a combination of medications with functional methods. Following all recommendations usually gives visible results. By the age of one year, symptoms of SIDS usually no longer appear.
There is a myth that this neurological syndrome goes away on its own, regardless of treatment. This is wrong. NSAID is a disorder of the nervous system, and ignoring treatment can lead to a number of complications in the future.
The main complications of SNRV include:
- development of vegetative-vascular dystonia in older age;
- frequent headaches;
- attention disorder (deficit) syndrome;
- hyperactivity.
These illnesses have a significant impact on the child’s mental health and can cause problems in kindergarten and school. An undertreated syndrome leaves a mark on the cells of the central nervous system, and its development is inhibited. Due to increased load, the nervous system will no longer cope and will begin to periodically block information.
Children with untreated SIDS become fussy, overly impulsive, and restless. They are bad at knowledge, they are forgetful, capricious and impatient. In the future, ignoring such neurological problems is fraught with the development of epileptic syndrome.
Memo for parents
If you suspect your child has SAD, don't be afraid to seek medical help. Find a qualified specialist who will select an effective course of therapy. Children with SNRV are required to register with a neurologist and undergo a preventive examination every 2 months.
From birth, set a routine for your child. Sleep should be by the hour, according to the child’s age. Daily walks in the fresh air are required, at least 2 hours a day.
Treatment must be completed over a course. 1-2 procedures will not give any therapeutic effect.
It is best to continue breastfeeding as long as possible.
Therapy with folk remedies
Folk remedies are also used. In order to eliminate this disorder, valerian root, motherwort flowers, and plantain are used. Such antidepressants can be purchased in pharmacies without a prescription; they do not cause addiction. It is recommended to prepare alcohol-based tinctures or water-based decoctions from the dried components.
You need to use a remedy made from calendula flowers. To prepare it, mix the plant with oregano and tansy. These ingredients must be poured into a hot glass of boiling water and left for 60 minutes, then strained. Scheme: 100 g for 3 weeks.
A decoction of St. John's wort should be taken 1 tbsp. l. 2-4 times a day (after meals). You can use an alcohol composition with lemon zest. You should also use an infusion of motherwort. To do this, you need to infuse 2 teaspoons of the herb for 6-8 hours and take 20-25 drops 3-4 times a day (half an hour before meals).