Many parents are not sure whether it is possible to do Mantoux if their child has a runny nose. Interestingly, the opinions of pediatricians themselves about whether Mantoux can be done for a cold or runny nose differ. Some experts believe that Mantoux is acceptable for snot. A runny nose without other cold symptoms is not a reason not to give your child Mantoux. Other doctors believe that snot is a sign of an inflammatory process (residual or, on the contrary, beginning), and the immune system cannot cope with the additional load in the form of the Mantoux test. In addition, there is a high risk of a false positive result.
Injection and runny nose
The tuberculin test is an annual diagnostic procedure performed in children and adolescents (from 1 year to 7 years). An allergen (tuberculin) is injected under the skin, and the result (immune response) is assessed three days later. From 7 to 15 - Diaskintest (a different substance, but has the same contraindications for the reaction).
Tuberculin diagnostics is not a vaccination, but a test of immunity. That is, for the procedure to be carried out successfully, the immune system must have the strength to respond to the aggressor (foreign bodies).
Before administering the injection, the health worker must ensure the child’s health and obtain written consent from the parents. That is, if parents doubt whether Mantoux can be done, they have every right to refuse. Despite what the specialist will say. The reason for doubt is often the question of how well the injection and runny nose are combined.
There are four main points of view:
- Mantoux and snot are incompatible. Mantoux should not be taken if you have a runny nose, much less if it is combined with other symptoms (cough, fever).
- If a child has a runny nose without other symptoms, then Mantu can be done for a runny nose.
- You can give an injection even during illness. This will not harm the baby, but may skew the results.
- Ambiguous opinion. It states that each case is unique and requires an individual approach and a private examination. It is impossible to say unequivocally and generally whether Mantoux can be used for a runny nose, cough, cold, or red throat or not. Sometimes a healthy baby may have an erroneous result, but a child with a runny nose may get a perfectly correct and accurate result.
A runny nose can be a symptom of an exacerbating chronic disease. Under this condition, performing the Mantoux test is strictly prohibited for a runny nose. Otherwise, serious complications may occur after vaccination.
If a runny nose is a manifestation of an allergic disease, then complications often arise. This fact requires a clear understanding of the genesis of rhinitis.
Several types are common:
- Allergic. It is forbidden to use the test during an exacerbation; during remission - with caution.
- Colds (viral infection).
- Associated with redness of the larynx and fever. A sign of serious inflammation, the test is prohibited.
The type of discharge also plays a role. Transparent mucus is not a reason to ignore diagnosis. Yellow or green snot is prohibited. In combination with other symptoms - a categorical taboo. That is, the answer to the question whether Mantoux can be done if the child has snot and cough is no.
For safety reasons and to be on the safe side, it is recommended to refrain from vaccinations if you have any type of runny nose. Provided that the procedure is not urgently required (recent contact with infected tuberculosis, suspected infection). Ultimately, only parents decide whether their child can be given Mantu for a runny nose.
Injection and cold
Most pediatricians agree on whether Mantoux can be given to a child if there are signs of a cold and a diagnosed illness. The answer is that diagnostics cannot be done during the period of a cold. But there are controversial points of view regarding the period of medical withdrawal. Some experts say that it is enough to wait two weeks (or even one), while others advise refraining from diagnosis for a month after recovery.
If the doctor independently decides to postpone the diagnosis during the examination of the child, he will issue a medical discharge, the maximum period of which is one to two months from the moment of complete recovery. The length of the delay depends on the severity of the disease. For example, for a cold it is enough to wait 30 days, for pneumonia - 60, after chickenpox - 6 months, after measles - 1.5, a year after mononucleosis.
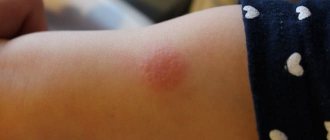
After tuberculin is administered, leukocytes begin to move to the injection site. Visually it looks like swelling. It is called a papule, or in common parlance, a button, the size of which is estimated 2-3 days after the procedure.
Injection and cough
Is it possible to do a Mantoux diagnosis if a child has a cough? This is another question that haunts parents. A cough, like a runny nose, can be a sign of ARVI, rhinitis, bronchitis and other pathologies of the respiratory system, allergies. Even if a child coughs without fever or redness in the throat, this is a sign of temporary problems with the immune system.
The recommendations are the same:
- reschedule the diagnosis based on a written medical report from a pediatrician;
- reschedule the test based on the written refusal of the legal representatives;
- perform a test, understanding the risk of a possible false result or complications.
O.E. Komarovsky notes that it is better to transfer Mantoux when coughing, since there is a high probability of an erroneous result. Moreover, Oleg Evgenievich claims that Mantoux does not pose a danger to the child’s health when coughing and other symptoms of viral infections occur. The specialist also strongly recommends against canceling the diagnosis altogether.
If there is any doubt about whether Mantoux can be done, a preliminary blood test is allowed. This will allow you to identify (refute) an allergy or a low-grade infection in the body.
Some doctors clearly distinguish between a cough and a runny nose. In the sense that a coughing child is strictly forbidden to perform Mantoux. While a runny nose calls into question the possibility of diagnosis, but does not exclude it.
General information on tuberculin diagnostics
Ultimately, responsibility for the outcome of the diagnosis falls on the shoulders of the parents. As well as the final word on whether the procedure will be carried out.
When making a decision, parents should know the reference points in this matter:
- The purpose of diagnosis is to identify tuberculosis in the early stages, prevent the spread of infection, identify risk groups, and identify those in need of repeated administration of the BCG vaccine.
- You cannot get tuberculosis or a cold from tuberculin (dead bacteria of animal and human tuberculosis, polysorbate, phenol, ethyl alcohol, trichloroacetic acid).
- Refusal from Mantoux is the legal right of parents.
- If Mantoux is refused, legal representatives are required to provide alternative diagnostics to their child and provide a written report to the school (kindergarten).
- Mantoux is not carried out during quarantine and for a month after it.
- Mantoux does not serve as a source for making an accurate diagnosis. With its help, you can suspect tuberculosis and prescribe additional diagnostics for confirmation.
- Alternative diagnostic methods include x-rays and blood tests. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent test (ELISA) detects antibodies. Is an accurate method.
- The result of the tuberculin test depends on compliance with the injection technique, caring for the “button”, compliance with contraindications and precautions.
Most false or excessive results are due to poor injection site care. Or mistakes before performing Mantoux (ignoring medical history, taking medications).
To avoid distortion of the results and, as a consequence, visits to a phthisiatrician, preventive chemotherapy, and additional diagnostics, it is not recommended to perform the test during the period of illness and its individual symptoms. It is worth rescheduling the diagnosis until the child has fully recovered.
Some experts clearly distinguish between Mantoux and other injection interventions. Based on the fact that Mantoux is a diagnostic test, not a vaccination. The same doctor can categorically prohibit vaccination after an illness, but allow Mantoux to be performed literally the next day.
>
The question of whether it is possible to do Mantoux when a child has a runny nose is relevant. Already in the maternity hospital, a healthy child begins to be vaccinated with the BCG vaccine, which ensures the formation of active immunity against mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Routine vaccination makes it possible to create a broad immune layer among the population, which significantly reduces the incidence of infectious diseases.
The vaccination calendar involves the planned administration of inactivated or attenuated vaccines against various infectious diseases, which requires strict adherence to the implementation technique and taking into account all contraindications.
What is Mantoux grafting? Why do they do it?
A tuberculin test, or a modified Mantoux test, is carried out to study the degree of immunity that should have been developed in response to the introduction of the causative agent of tuberculosis infection.
Initially, this reaction was called the Pirquet test and was performed using the scarification method (applying drops to the skin). However, several decades later, a doctor of French origin, C. Mantoux, suggested administering tuberculin only intradermally.
Important
Tuberculin is a complex substance made from pathogens or special culture filtrates of acid-fast bacteria (tuberculosis bacilli).
Being an inferior antigen, or hapten, it provokes the development of a delayed-type immunological reaction, which normally manifests itself 24-72 hours after administration. The tuberculin test is difficult to overestimate, since it is a good protector against infection and shows an existing disease. Thus, tuberculin diagnostics (Mantoux vaccination) allows the following:
- To identify primary infection with acid-fast mycobacteria - the causative agents of tuberculosis.
- Confirm an infection already activated in the body that provokes the disease.
- Identify bacteria carriers who do not have any manifestations or complaints.
- Select a contingent of children in need of revaccination.
- Record the number of infected individuals with a post-vaccination infiltrate diameter of more than 6 millimeters within one year.
- Identify infected people with a hyperergic reaction to tuberculin administration.
Body reaction
Three days after the test with two tuberculin units (TU), the Mantoux reaction is assessed, that is, the diameter of the resulting infiltrate or hyperemic area of the skin is measured.
Characteristics of the results:
The diameter of the infiltrate is up to 1 mm inclusive - this indicates a negative reaction. Thus, we can say that the child’s body does not have antibodies against tuberculosis bacilli.
This may be due to an incorrect BCG diagnosis (that is, the pathogen did not enter the body at all) or to immunodeficiency.
Isolated hyperemia or infiltrate from 2 to 4 mm is a questionable nature of the reaction, that is, there are anti-tuberculosis antibodies in the blood, but in low concentration.
The resulting infiltrate of 5 to 16 mm is a positive reaction, which indicates sufficient tension of the immune system. That is, when “meeting” a pathogen, the body is able to give an adequate response.
The size of the infiltrate exceeds 17 mm, the appearance of vesicles, necrosis or regional lymphadenitis is a hyperergic reaction, which most often indicates the active phase of tuberculosis.
The tuberculin test is set when a negative reaction changes to a positive one or when an infiltrate is diagnosed that is 6 mm larger than the previous one. It is a direct indication for consultation with a phthisiatrician.
Technique for performing a modified Mantoux test
After an objective examination of the child, the doctor makes an entry in the outpatient chart that there are no contraindications to the test and sends him to the manipulation room.
Wearing disposable gloves, the nurse processes the ampoule with tuberculin solution with a cotton swab soaked in 96% alcohol.
After this, break off the upper end of the ampoule and draw 0.2 ml of solution into a disposable syringe. The skin on the inside of the left forearm is treated with two sterile cotton wool (with alcohol) and stretched with two fingers.
The syringe is placed almost parallel to the arm and the needle is carefully inserted intradermally (the bevel of the needle should be facing upward). 0.1 ml is injected, which results in the formation of a so-called lemon peel. Is it possible to do Mantu for a child with a runny nose?
Unfortunately, children are often characterized by frequent respiratory diseases of viral origin, which is associated with the immaturity of the body’s immune function and constant contact with children who are in the incubation period of a particular infection.
A similar question is often asked: is Manta administered for a runny nose? In this case, it is necessary to understand the genesis of acute rhinitis.
Most often, rhinitis is one of the symptoms of acute respiratory infections or occurs as an isolated allergic disease. Both of these conditions are accompanied by an inflammatory process in the nasopharynx and the release of biologically active substances such as histamine and serotonin, which are allergy inducers.
Remember
The tuberculin test is not a vaccination; when administered, live or weakened bacteria and viruses are not introduced into the child’s body.
It is just a diagnostic test showing the absence or presence of anti-TB antibodies.
Therefore, performing the “Button” will not complicate the course of the disease in any way, but may affect the result itself, that is, a false-positive or hyperergic response may occur.
This is due to allergization of the body and its inadequate reaction. In order to avoid registering with a TB doctor or undergoing a course of chemotherapy, you should refrain from the procedure until complete recovery.
Is it possible to do Mantoux if a child has snot and cough?
Again, the presence of complaints of a runny nose and the fact that the child is coughing, even at normal body temperature, indicates the persistence of a viral or bacterial infection.
In some cases, it speaks of an allergic condition.
The doctor who examined such a child will not give his permission to perform tuberculin diagnostics, as he does not want to encounter false reactions.
In this case, a temporary medical referral is issued, appropriate therapy and a second consultation are prescribed, and the answer to the question of whether Mantoux can be given for a runny nose and cough suggests itself. Mantoux test for a runny nose in a child: Komarovsky
It has already been said above what will happen if you do Mantoux when you are sick - this can lead to a false reaction, which is often interpreted as an infection and will necessarily be sent to a tuberculosis clinic with all the ensuing consequences.
A fairly well-known pediatrician, Komarovsky, also believes that the tuberculin test simply shows the strength of the immune system, and does not produce specific antibodies in the child’s body.
At the same time, snot is a manifestation of a disease in which certain inflammatory processes occur that can lead to an incorrect assessment of the test.
Is it possible to make Mantu for a cold?
Colds in children are most often caused by viruses or their association with bacteria and trigger a cascade of inflammatory processes in the lymphoid tissue and organs of the respiratory tract.
The main symptoms are fever, rhinorrhea, cough, weakness and sometimes sore throat.
The presence of an acute infection or an exacerbation of a chronic one is an absolute contraindication to a tuberculin test, so the answer is negative.
Is it possible to vaccinate Mantoux at a fever?
An increase in body temperature is an adequate response of the thermoregulatory center to the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms.
It is accompanied by the synthesis of substances such as histamine, bradykinin, leukotrienes, which are also characteristic of allergies.
If a child has a fever of infectious or neurological origin (thermoneurosis, hydrocephalus), then the Mantoux test is not performed until complete recovery or stabilization of the condition.
If tuberculin testing was done for a cold, then you should expect an unreliable result, but at the same time follow all the recommendations of the doctor and nurse (do not wet the “button” for three days, do not apply any ointments or balms to it).
How long after illness can Mantoux be done?
If at the time of examination the doctor identifies contraindications to the procedure, then the tuberculin test is not completely excluded, but simply postponed.
According to official documents, the medical withdrawal period is one to two months from the moment of recovery, which depends on the specifics and severity of the disease.
For example, after suffering from acute respiratory viral infection, you can come for a test within a month, while for pneumonia it is advisable to give two months for recovery.
If the doctor is in doubt about when to test, then it is best to take a detailed blood test, which can help rule out allergic changes and sluggish infection.
Many parents are also interested in the question: is it possible to go for a walk after Mantoux. The performed procedure does not in any way restrict the child from walking, the only thing is that it is advisable to avoid contact with infectious patients and under no circumstances wet the infiltrate during the first 72 hours.
Runny nose after Mantoux
If, after a tuberculin test, any catarrhal manifestations appear, such as a runny nose or cough, this does not mean that the child has contracted tuberculosis or has developed a complication.
Most likely, the procedure was performed during the incubation period of an acute infection or during the season of atopic rhinitis, so there is no need to panic, but it is recommended to begin appropriate treatment.
Contraindications to the Mantoux test
In order to avoid misinterpretation of the results, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the absolute contraindications for tuberculin diagnostics in children:
- Any allergic, bacterial or fungal skin diseases.
- The presence of an acute infection or exacerbation of a chronic pathology. In this case, the reaction is given after a month, taking into account the disappearance of all symptoms and complaints
- Quarantine in organized groups (kindergarten, school classes).
- Any allergic condition and disease.
- Epilepsy.
Alternative methods
In cases where the tuberculin test is not possible for a number of reasons, alternative methods are used to diagnose infection with acid-fast bacteria.
based on the intradermal injection of a recombinant tuberculosis allergen, which provokes the development of an immune reaction, has proven itself well
Tuberculosis can be suspected using a clinical analysis of peripheral blood. Characteristic criteria will be an increase in the percentage of rod- and segmented leukocytes with a simultaneous decrease in the level of monocytes and lymphocytes, ESR also increases.
There is also a Quantiferon test and a detection method using PCR (polymerase chain reaction that determines the DNA of the pathogen).
Video on the topic
What is the Mantoux test? This test is used to determine the reaction to the tuberculosis antigen. This procedure is regularly performed on children starting at one year of age. This is done to prevent disease and the spread of tuberculosis. Is it possible to do Mantu with a runny nose? This issue is described in detail in the article.
For what purpose do doctors administer a tuberculin test?
Mantoux is a test that is necessary to determine the causative agent of tuberculosis. A subcutaneous injection is not considered a vaccination and is used for timely detection of Koch's bacillus.
Tuberculin contains dead bacteria that enter the child’s body. After administration of the drug, a button forms at the injection site, which enlarges in the presence of a pathogen.
The tuberculin test performs several functions:
- Mantoux vaccination serves to identify people who are carriers of Koch's bacillus. The immunological reaction appears only 24-72 hours after administration of the drug.
- Thanks to the procedure, it is possible to confirm the presence of an infection that is in the active phase.
Why are runny nose and cough contraindications?
The Mantoux test has little in common with vaccinations and vaccinations, since it does not serve to create protective functions, but only to identify dangerous tuberculosis bacilli in the body.
In children, especially preschool age, a runny nose with cough can usually be caused by several reasons:
- ARVI and other acute infectious diseases;
- allergic conditions (rhinitis, asthma);
- exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx (sinusitis, chronic rhinitis).
All of the above conditions are a contraindication to the Mantoux test, because against their background the result of the procedure can be false positive.
As Dr. Komarovsky says at his parenting school classes, it is extremely important that the child is healthy and that he does not receive any vaccinations for a month before the test is performed. If he has already suffered an illness, then the required delay must also be at least one month.
In addition, a false result is possible when performing a Mantoux test during the period of active treatment of a runny nose and cough with anti-inflammatory or antihistamine drugs. A skin reaction to injected tuberculin is essentially an allergic response of the body. And if you take medications that suppress allergies or inflammation, the presence of tuberculosis infection in the body may not affect the skin. Then it is possible that the necessary moment for therapeutic anti-tuberculosis actions will be missed.
Healthy children have general reactions to the administration of tuberculin in the form of elevated body temperature, weakness, and loss of appetite. If a child has an acute viral infection, even in a mild form - only with a runny nose and a moderate cough, then the test will aggravate the condition of the child’s body, creating an additional burden on the immune system and provoking an increase in intoxication syndrome.
Also, unpredictable consequences after the test are possible during the period of exacerbation of allergic rhinitis or asthma, since tuberculin contains a large number of allergens and biologically active substances.
A completely opposite picture emerges when a child is bothered by a prolonged cough without a runny nose or previous cold, especially if it is accompanied by weight loss, sweating, and chest pain. In this case, the baby must be examined for pulmonary tuberculosis as quickly as possible. And the Mantoux test serves as one of the main diagnostic steps, in addition to radiography of the ore cell organs and sputum analysis. A positive Mantoux result will indicate activation of Koch bacilli in the body, which will require specific treatment with antibacterial drugs.
How does the Mantoux test affect babies with a runny nose?
Doctors do not have a clear opinion regarding the issue of performing Mantoux for a runny nose. Some experts believe that subcutaneous administration of the drug is not capable of having a noticeable effect on the state of the immune system.
When administered subcutaneously, the reagents are localized in a specific location. Under the influence of tuberculin, a certain reaction occurs in the baby, which makes it possible to identify the fact of carriage. Most parents refuse the procedure if the baby has a runny nose.
The following diseases may be reasons for refusing Mantoux:
- The baby has symptoms of bacterial or viral rhinitis.
- The child suffers from catarrhal or allergic rhinitis in a chronic form.
- The baby began to develop ozena, an unpleasant disease that is accompanied by the discharge of pus. The administration of tuberculin can lead to a deterioration in the child’s condition.
- A severe cough indicates damage to the nasopharynx by dangerous bacteria or viruses. In this condition, the baby needs drug treatment.
Doctors evaluate the state of the child's immune system. After ARVI, the baby should not be given Mantu for a month.
Children suffering from pneumonia require long-term treatment. In this case, the procedure will have to be postponed for at least 2 months. To make a decision, a detailed blood test may be required.
Why do some doctors say that the procedure can be done? What are the pro factors?
So is it possible to do the Mantoux reaction with a runny nose? It is better to postpone the procedure to a time when the child is completely healthy.
A runny nose is one of the symptoms of acute respiratory infections, the causative agent of which is bacteria other than tuberculin, which is injected under the skin to test the immune system. However, any stress on the immune system, which is resisting the disease at the time of the test, will affect the result. It is possible that the result will be incorrect. If there is a runny nose, the injection can affect the child’s immunity, weakening it and worsening its health.
Mantoux is not an accurate method for determining the disease; the addition of factors such as viral infection will make it more difficult to identify the results of a tuberculin test. Considering all this, it is better to wait for recovery and only then carry out the test.
Doctors' opinions on this issue still differ. Some believe that since the Mantoux test is not a vaccination, it cannot have a negative effect on the child’s body, which means that cough and snot are not a contraindication.
What effect does a runny nose have on test results?
Colds complicate the examination process. An increase in the size of a papule does not always indicate the presence of Koch's bacillus. The body of a child with symptoms of a runny nose is forced to fight pathogenic microorganisms.
Recommended video:
When examining a patient, doctors receive a distorted picture, since inflammatory processes cause swelling and redness at the injection site.
Several factors can be identified that influence the reliability of the results obtained.
- The state of the immune system depends on the presence of infectious diseases.
- It is necessary to properly care for the sample site for 3 days.
Is it possible or not to wet Mantu?
On the day of tuberculin injection, you can wash your hands and take a shower, but it is better to avoid bathing and visiting a sauna or steam bath. This precaution is due to the fact that an increase in temperature causes the pores to expand, through which the injected substance can be partially eliminated from the body along with sweat.
Water cannot get through the puncture and distort the results if you do not perform any actions that damage the skin: combing, rubbing the forearm with a washcloth. Only after such manipulations may the injection site turn red and increase in size. After the injection, you will need to monitor the child’s actions during bathing and explain to him the rules that should be followed after the injection.
In some cases, the sample size increases in children after visiting a pool, lake, or sea. Experts recommend not swimming in these places until final results and examination are obtained, as there may be substances that irritate and allergize the skin. Doctors are also of the opinion that after the injection you need to wait one hour until the blood clots and a drop of water gets through the puncture. Most likely, the time required for this process is spent much less, but doctors advise to play it safe.
Komarovsky's advice
Often parents do not know the purpose of the tuberculin test. They perceive this procedure as an inoculation or vaccination. The main task of Mantoux is to timely identify the fact of carriage.
The dose of tuberculin present in the sample is so small that it cannot have a detrimental effect on the child’s immune system. Komarovsky recommends giving up Mantoux if your baby has a severe cough and runny nose.
During the process of reproduction, harmful bacteria release toxins. The child’s immune system is forced to respond to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. To conduct the examination, the consent of the baby's parents is required. Komarovsky does not recommend making Mantu if quarantine has been introduced at school or kindergarten. The reaction to the drug depends not only on the physiological characteristics of the child.
It is necessary to properly care for the injection site. After introducing the reagents under the baby’s skin, tuberculin reacts with the immune system. The procedure allows you to identify antibodies that are produced in the body.
Tuberculin contains neutralized segments of tuberculosis bacteria. Most doctors are convinced that there is no clear connection between the Mantoux test and a runny nose.
The tuberculin test does not pose a danger to the baby, provided that precautions are followed. Mantu should not be given to children who are infected with a bacterial or viral infection. During this period, the body's defenses are under increased stress. The introduction of a tuberculin composition can only complicate the baby’s condition.
Advice! The immunological test can be started only after complete recovery.
Arguments against"
Other doctors are of the opinion that the test should be done only when the child is completely healthy. Since the presence of any viruses in the body can distort the result.
The question of whether it is possible to do the Mantoux test for a runny nose cannot be given a definite answer. The reaction can be positive both in a child with a runny nose and in a healthy one. If the test response is questionable, the doctor may prescribe a repeat test.
Parents' fears that complications may arise after the test are mostly far-fetched. The tuberculin test is introduced into the body in a very small amount, which is not capable of causing harm to the child.
How long after illness can Mantoux be done?
If the baby has suffered from ARVI, you will have to wait for a month. The Mantoux test cannot be performed immediately after an illness. Premature administration of the tuberculin drug will distort the results. Residual symptoms of a runny nose are not an obstacle to the procedure.
Important! Only the attending physician can determine the exact date of the examination. Typically, the duration of recovery after an acute respiratory infection is 1 month.
Is it possible to do Mantu for a runny nose in children?
A runny nose occurs frequently in children. It comes in various origins. It could be a cold, flu, or an allergic reaction to something.
To understand whether it is possible to do Mantu for a runny nose, you first need to determine the nature of rhinitis. If a runny nose is associated with seasonal allergies, then it makes sense to schedule a test for another time of year.
If there is a year-round reaction, even with symptoms such as sniffles, sneezing and coughing, but in the absence of fever, a test can be done.
If the pediatrician diagnoses a child with a runny nose due to an infectious disease, then it is better to postpone the test for tuberculosis.
Why is it better not to do it if you have a runny nose?
Nothing happens, but the test results may be incorrect. The Mantoux test is very important, as it helps to detect the presence of the disease in the early stages. Therefore, the results must be accurate. If there is an infectious disease, runny nose, fever, then in this case the immune system directs all its forces to fight the disease. First, you need to wait for the child to fully recover and only then do the test. Given that such a procedure is carried out once a year, moving the time by two weeks will not be critical.
What points should you pay attention to?
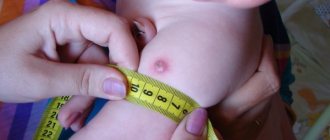
3 days after the procedure, doctors evaluate the Mantoux reaction. Specialists measure the diameter of the infiltrate that forms at the injection site. To identify the presence of the causative agent of tuberculosis, you can use the table.
| Infiltrate size | What diagnosis do doctors make? |
| Up to 1 mm | If the area of hyperemic skin does not exceed 1 mm, then the child is considered healthy |
| From 2 to 4 mm | The diameter of the papule can range from 2 to 4 millimeters; such a reaction may indicate the initial stage of the disease. To make sure there is no infection, doctors write a referral for re-examination. |
| From 5 to 16 mm | The size of the infiltrate, which is 5-16 mm, indicates the presence of Koch's bacillus in the body. The child is a carrier of the tuberculosis pathogen. |
| More than 17 mm | When the active phase of tuberculosis occurs, the diameter of the papule can exceed 17 mm. The patient needs medical attention. |
How it works?
Everyone is accustomed to thinking that Mantoux is a vaccine. But in reality this is a test. That is a skin test. This injection allows you to determine how the body reacts to the tuberculosis pathogen. At birth, the child is vaccinated against tuberculosis, the vaccine is called BCG. The Mantoux test is a way to detect the presence of tuberculosis infection in the body.
A positive reaction to the test means that the body is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but this does not mean that the child is sick. Such children are at risk. Therefore, careful monitoring of their health over several years is necessary.
Is it possible to put mantu on a runny nose?
The mantoux reaction is given to children, and there is a lot of disagreement on this issue on the part of parents, although on this issue everything should be clear - yes, it must be done! But is it possible to give mantu to a child with a runny nose?
This is a completely different question, because the body’s response can be unpredictable and everything will fully depend solely on the state of the body and the strength of the immune system.
What is the point of vaccines?
A vaccine is specially introduced into the body, to which it begins to release special antibodies that produce immunity. Each vaccine is unique and has its own administration regimens, contraindications and routes of administration:
- intradermally;
- orally;
- subcutaneously;
- intramuscularly.
There are several mandatory vaccinations for children, but they should not be given during a runny nose.
For some vaccines, a single dose is sufficient, while for others, multiple vaccinations are required. Almost all vaccinations are strictly prohibited when you have a runny nose.
As for the mantoux test, there is a lot of controversy on this topic, because in essence it is not a vaccine, but a procedure that shows the body’s reaction to tuberculin introduced into it . Experts say that the presence of snot may well be the cause of various side effects, so it is better to cure a child’s runny nose.
Naturally, everything depends on the characteristics of the body and the state of health , so whether to vaccinate with a runny nose or not should be done by a pediatrician after he has carried out a full examination of the child.
What is the procedure?
All children are given mantu. Thanks to this study, it is possible to assess the presence of antibodies against the causative agent of tuberculosis. The idea is to inject a harmless amount of tuberculin under the skin . Then, over the course of 3 days, a reaction is observed.
It is very important not to wet or scratch the sample site during this period. This place cannot be sealed with a plaster and treated with antiseptic drugs so that this does not affect the final result. At the end of the period, a conclusion is made based on the size of the injection site.
Contraindications to the procedure
The mantoux test is not dangerous to the body and health of the child, but only if all precautions are taken by the doctor who will perform this procedure.
To avoid any, even the most minimal, consequences, this procedure is not performed while snot is present . Nasal discharge very often signals that there is a disease and sometimes it can be very serious.
Also , a test is not done if there is a cough , this symptom indicates the presence of inflammation in the body. And if the mantoux test is sometimes done for rhinitis, at the pediatrician’s own risk and with the permission of the parents, then for coughing it is strictly prohibited.
Most parents and doctors are well aware that it is best not to interfere with the functioning of an organism in which there is a pathogen. This is due to the fact that during a runny nose, all the body’s forces are thrown into the fight against the pathogen , and the mantoux test can further weaken the immune system, which can not only aggravate the treatment process, but also cause other complications.
If the body is severely weakened by a runny nose, especially a long one, then it is best to leave the mantu test until the child has fully recovered. Read how to cope with a runny nose if your child is teething.
Should I give my child mantu if he has a runny nose?
Mantoux
This test is an immunological test; it allows you to determine whether the baby’s body is infected with the tuberculosis bacillus. Tuberculin test is a diagnostic method of research, carried out by subcutaneous injection of tuberculin.
The result is assessed after three days. The appearance of the “button” determines a positive or negative reaction to tuberculosis. You need to understand that mantu is not a vaccine. Live bacteria are not introduced into the toddler’s body.
This study allows us to detect the presence of antibodies to Koch's bacillus.
Runny nose