The first year of a child’s life poses a large number of questions to young parents, the solution of which, at times, makes it very difficult for them. Of course, vaccinating a baby is a special issue for many. Despite the fact that the Mantoux test is not a vaccination, but a test that identifies the causative agent of tuberculosis, the controversy still continues. Is it necessary to make Mantoux?
Experts agree on this issue: the Mantoux vaccination (test) should be done if there are contraindications. And we are talking not only about the health of your child, but also about the protection of children with whom your baby comes into contact. According to WHO, about one third of the world's population is infected with the tuberculosis bacterium. The above data is followed by the opinion of the organization: the test is mandatory for countries where the likelihood of the disease is high.
The vast majority of cases occur in India, followed by Indonesia, China, Nigeria, Pakistan and South Africa. But Russia is also at risk. Should I make Mantoux? Does your child need a Mantoux vaccination at this particular time? Whether it is mandatory or not for you is up to you and your pediatrician to decide.
What is BCG and how is the Mantoux test different?
The first immunoprophylaxis against tuberculosis is carried out in the maternity hospital on the 3rd – 5th day after the birth of the baby, although it can be delayed by 1-2 months. It is also worth noting that there are contraindications for administering the BCG vaccine:
- HIV infection;
- Presence of tuberculosis;
- Malignant blood diseases;
- Oncology of malignant and benign nature;
- Immunodeficiency type 1;
- Skin diseases;
- Prematurity;
- Infections received by a child in utero;
- Use of corticosteroid drugs in large volumes.
It is carried out with a special BCG vaccine - Bacillus Calmette-Guerin. Such rods are obtained by artificially cultivating them in the laboratory from cow serum. It represents strains of the tuberculosis bacillus, weakened to such an extent that they are not capable of starting the process of infection in the body, however, acting as an antigen, they cause the development of antibodies. This is how the immune response is triggered - that is, immunity to the causative agent of human tuberculosis is formed.
Although the duration and activity of this vaccine have been little studied, based on the results of studies over the years, one can trace a trend towards a decrease in morbidity in vaccinated children compared to those who were not vaccinated.
Subsequent vaccination - that is, revaccination - is carried out at the 6-7th year of the child’s life. The two above procedures - the introduction of BCG in the first days of life and after 7 years - are vaccination against tuberculosis. The Mantoux test is not a vaccination and does not relate to the development of immunity. She only assesses the state of the child’s body in relation to this infection.
BCG is a vaccination with the development of immunity; the Mantoux test is a diagnostic option, the purpose of which is to determine the sensitivity of your child’s body to tuberculosis.
What is the normal size of a Mantoux papule?
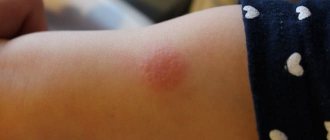
When the child is healthy and his body has not encountered pathogenic bacteria, the papule has a minimal size. In older children, after 7 years, the size of the tumor stops at 5 millimeters. In children, indicators may fluctuate. This is due to the fact that the immune system is just being formed and cannot adequately respond to introduced antigens.
| Age category of the child | Normal reaction rates to Mantoux |
| 1 year | from 5 to 11 millimeters |
| from 2 to 3 years | from 5 to 10 millimeters |
| 4 years | from 5 to 8 millimeters |
| from 5 to 6 years | from 5 to 6 millimeters |
| 7 years and older | no more than 5 millimeters |
From the table it becomes clear that the indicator of 5 mm, subject to a negative immune response, is established upon reaching the age of seven. The mark of 8 millimeters is quite normal for a 4-year-old child, and 10 for a three-year-old child.
In a one-year-old child, the size of the papule can range from 5 to 11. This size may be due to a reaction to a previously administered BCG vaccination.
At the age of 7 years, the reaction should stabilize towards negative or appear as “weakly rapid”.
Indicators may vary slightly, as the body's reaction is often influenced by a variety of factors. Children may have hyperactive immunity or have a previous infectious disease, which will give a false positive indicator. In this case, a more in-depth laboratory study is necessary.
Goals and objectives of the Mantoux test
The purpose of tuberculin diagnostics is to confirm the diagnosis of tuberculosis, if it was identified during the study, or to perform prophylaxis in children if there is no infection in the body.
We recommend reading! Follow the link: Can I eat sweets while being tested for tuberculosis?
The main objectives of the Mantoux test are:
- Identification of children requiring revaccination against tuberculosis;
- Determination among children of carriers of the tuberculosis bacillus, which occurs without any clinical signs of infection, but is capable of releasing mycobacteria into the environment and infecting upon contact;
- Identify children whose infection has lasted for more than a year;
- To identify children with tuberculosis for the first time.
The considered method of tuberculin diagnostics is carried out with a special substance - tuberculin. It consists of extracts and fragments of mycobacteria, that is, tuberculin does not contain either dead or weakened tuberculosis bacilli. The drug is completely safe for the body; it is used on animals and humans to determine sensitivity to the tuberculosis bacillus, and it does not cause infection or any reactions.
As with any diagnosis involving the administration of substances, Mantoux has contraindications:
- Chronic and acute skin diseases;
- Epilepsy;
- Infectious diseases, especially in the acute phase;
- Allergic diseases of any origin;
- Somatic diseases – rheumatism, bronchial asthma, etc.;
- A different vaccination performed on the same day will result in a false positive test.
Important! It is prohibited to administer tuberculin that has expired, or if there were gross violations during the transportation of the drug and its storage.
In addition to the Mantoux test, fluorography of the chest circumference, an x-ray of the chest organs can be performed, a bacteriological examination of the sputum secreted by the patient is performed for the presence of mycobacteria, and a biochemical and general blood test is performed. The listed methods will most likely help diagnose tuberculosis in a patient.
How is the procedure performed?
This technique has been successfully functioning for more than a hundred years. The story begins with the invention of the drug tuberculin by the German scientist Robert Koch in 1890. Years later, Charles Mantoux proposed using this drug intradermally to diagnose tuberculosis, and in 1908 the German doctor Felix Mendel described the tuberculin reaction, which is still used today as a basis for conducting the test.
How is the test conducted today? The first Mantoux vaccination (test) is given to a baby when he is one year old. It does not make sense to carry out this procedure earlier due to the high probability of an inaccurate result, although false positive and false negative results do occur even after the child reaches the required age. The child is injected with tuberculin intradermally (into the arm) and then the local reaction is monitored after three days.
At the time of the test, the child must be absolutely healthy, and all relatives living with him in the same apartment must also be healthy. This caution is necessary, first of all, to avoid possible complications from the administration of the drug. Is it necessary to give a child a Mantoux vaccine every year? It is also possible to transfer the sample if the child has been given any vaccine. In this situation, the procedure is postponed for at least a month - the test can be taken after this period. You also need to know about contraindications to the Mantoux reaction test. Here are some of them:
- individual intolerance to the drug;
- skin diseases such as dermatitis;
- bronchial asthma;
- epilepsy;
- other acute chronic diseases;
- a contraindication is if the child has previously received a blood transfusion, been given hormones, or has undergone a course of immune therapy, or, as stated above, has been vaccinated.
Before administering Mantoux to a child, it is necessary to inform the attending physician about all diseases, and, in case of contraindications, the doctor will help you decide on an alternative diagnostic method. It is also possible that the following adverse reactions may occur after the test: allergies and fever, as well as more serious reactions such as fever or asthma attack. Be sure to consult a doctor if you have these symptoms.
Vaccination calendar against tuberculosis
When is Mantoux made for the first time?
For the first time, this vaccination is performed in a year. It is not advisable to do it earlier - the immune system of a child in the first year of life is imperfect. Experts do not trust the results of such tuberculin diagnostics. From the age of 2, Mantoux is performed annually, and negative results of previous tests are not taken into account.
Age until which Mantoux is made
Depending on the incidence of tuberculosis in the population, tests are performed up to 18 years of age - if the situation is unfavorable. Up to 16 years of age - if the area is considered free from this infection. The test can also be performed in adults.
We recommend reading! Follow the link: Signs and symptoms of tuberculosis in adults, causes of the disease
How many times to do tuberculin diagnostics
As a rule, once a year, except in cases where the child’s place of residence belongs to areas unfavorable for tuberculosis or the child had contact with a patient with an open form of tuberculosis. In addition, there is a need to repeat the test if a positive reaction to the administered tuberculin appears. The maximum number of administrations during the year is 3 times.
If the reaction to the injected tuberculin is positive, or “magnificent”, as doctors say, a few days later the test is performed again. If the answer to the test is again positive, the child needs a consultation with a TB specialist and additional examination methods - laboratory (blood and sputum tests) and instrumental (x-ray diagnostics, tomogram).
What does it mean
If the Mantoux test in a child has a positive reaction, before taking any measures, the fact of prior vaccination or revaccination with BCG should be established. An important component of diagnosis is the period after vaccination, which should be compared with the size of the resulting infiltrate. Parents of a child whose papule looks larger than the declared normal size should not sound the alarm in vain. This means that the antigen contained in the vaccine is still present in the baby’s body. Sometimes its presence causes a similar reaction in the body in children.
We recommend reading:
- Pharmacy remedies for papillomas
- What is Madelung syndrome
- How to get rid of a wen on the forehead
A large papule in a child may be a consequence of an allergy to BCG. 1 - 1.5 years after vaccination, approximately 60% of children have a positive response, only 40% have a doubtful or negative response. The effect of allergies develops after about 1.5-2 months, and reaches its apogee by 1-2 years of age. This phenomenon is caused by the maximum severity after the vaccine effect, which occurs during this period. Children in the first two years of life can be diagnosed with a positive mantoux response, with a papule size of up to 16 mm.
If a child has a positive test result, the pediatrician will refer him for additional consultation with a phthisiatrician. This specialist will conduct a diagnosis to determine all possible factors.
The following will be taken into account:
- recent vaccinations;
- previous infectious diseases;
- allergic reaction to the components of the immunological test.
You can distinguish an enlarged papule after vaccination from one that indicates the presence of infection by pigmentation. The result of the vaccination appears as a pale pink papule without clear edges. After 2 weeks there is no trace left of it. Tuberculous Mantoux has a more intense coloration, clear contours of the formation and leaves brown pigmentation.
Is the Mantoux test required?
Parents often underestimate the importance and accuracy of this tuberculin diagnostic method. According to the rules established in health care institutions, parents who oppose BCG vaccination and the Mantoux test must provide a refusal in writing. At the same time, the pediatrician always warns that Russia is one of the disadvantaged countries in terms of the prevalence and incidence of tuberculosis. However, even being warned about the dangers that tuberculosis infection brings with it, the final word remains with the baby’s parents - to give consent or refuse anti-tuberculosis measures.
How to perform the Mantoux test in children
The test is performed by a specially trained health worker - a nurse in the vaccination room. Before this, parents, or the patient himself, are warned that it is impossible to injure - scratch or try to squeeze out the formed “button”. It is also forbidden to wet Mantoux, although in this case many people confuse it with the Perquet test, in which tuberculin is dripped onto the skin and can actually be washed off with water. The Mantoux test is an intradermal injection of tuberculin with a volume of 0.1 ml, which contains 2 tuberculosis units. The injection syringe has a thin needle and is inserted parallel to the skin, with the cut side up. A small amount of blood may bleed from the resulting papule. There is no need to worry or touch it, it will stop on its own.
Reading the results after the Mantoux test
The assessment is read by a specialist on the 3rd day after the test. Depending on the size of the “button” the result will be positive, negative or doubtful. In addition to the above, experts highlight the following results of the Mantoux test:
- False-positive (occurs in patients uninfected with tuberculosis due to allergies, infections, non-compliance with the interval between vaccinations);
- False negative (when people infected with tuberculosis have a negative reaction to tuberculin);
- Vesiculo-necrotic (occurs with enlargement of the child’s lymph nodes and lymphangitis).
In addition to local reactions to tuberculin administration, general reactions may occur - weakness, headache, fever and enlargement of regional lymph nodes. These conditions are considered by specialists as complications after the Mantoux test. However, they do not have a serious effect on the body. If general reactions of the body to the administration of tuberculin occur, symptomatic therapy is recommended - offer the child painkillers and antipyretics, taking into account the child’s age.
We recommend reading! Follow the link: Symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis in adults, forms of the disease
Is it possible to do?
To understand whether it is possible to make mantu during pregnancy, it is necessary to understand the effect of tuberculin on the body. It is this substance that is injected under the skin for the Mantoux test. Purified tuberculin is not a vaccine or an active substance; it cannot cause infection, does not form immunity and does not cause complications of existing diseases. Therefore, he is also unable to disrupt the natural course of pregnancy.
Another thing is that the test results can sometimes be distorted under the influence of changing hormonal levels in women in an “interesting position.” In rare cases, the administered drug may cause an individual reaction, and this should also be known in advance.
Specifics of the Mantoux test
It is better if parents take care to exclude allergens, both food and household, from their baby’s diet at the time of tuberculin testing. Oranges, chocolate, honey, some nuts, and also limit contact with pets and household chemicals.
A separate issue for parents is the Mantoux test during an acute respiratory viral infection in a child. In cases where a runny nose is a clinical sign of an infection occurring in the body, it is better to postpone the procedure. If parents are sure that there is no disease, a test can be performed. The same can be said about the child’s cough.
During tuberculin diagnostics, you should not change the child’s daily routine. Do not exclude walks in the fresh air and bath procedures. Experts have proven that a simple shower or bath cannot cause any harm to the sample, since water will not penetrate inside the papule.
Important! Swimming in open water should be excluded from water procedures. There is a high risk of infection of the papule, which is why the reaction is read as a false positive.
Tactics of parental behavior in case of a positive Mantoux test
After being informed that the result of an intradermal test in a child is positive, do not panic. First of all, it is worth making sure whether measures to prevent a false positive response have been followed. First of all, to do this, you need to monitor both the technique of performing the test and reading the result. If there were no violations on the part of the medical staff, you should pay attention to the characteristics of your child’s body. A false positive result can occur for a number of reasons, from hereditary to infectious. If all causes of a false-positive reaction are excluded, the doctor must prescribe laboratory and instrumental methods for diagnosing tuberculosis.